Deck 3: Cardiovascular Physiology
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/59
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 3: Cardiovascular Physiology
1
A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery?
A) Decrease to
B) Decrease to
C) Decrease to
D) Decrease to
E) No change
A) Decrease to
B) Decrease to
C) Decrease to
D) Decrease to
E) No change
Decrease to
2
When a person moves from a supine position to a standing position, which of the following compensatory changes occurs?
A) Decreased heart rate
B) Increased contractility
C) Decreased total peripheral resistance (TPR)
D) Decreased cardiac output
E) Increased PR intervals
A) Decreased heart rate
B) Increased contractility
C) Decreased total peripheral resistance (TPR)
D) Decreased cardiac output
E) Increased PR intervals
Increased contractility
3
At which site is systolic blood pressure the highest?
A) Aorta
B) Central vein
C) Pulmonary artery
D) Right atrium
E) Renal artery
F) Renal vein
A) Aorta
B) Central vein
C) Pulmonary artery
D) Right atrium
E) Renal artery
F) Renal vein
Renal artery
4
A person's electrocardiogram (ECG) has no wave, but has a normal QRS complex and a normal wave. Therefore, his pacemaker is located in the
A) sinoatrial (SA) node
B) atrioventricular (AV) node
C) bundle of His
D) Purkinje system
E) ventricular muscle
A) sinoatrial (SA) node
B) atrioventricular (AV) node
C) bundle of His
D) Purkinje system
E) ventricular muscle

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
If the ejection fraction increases, there will be a decrease in
A) cardiac output
B) end-systolic volume
C) heart rate
D) pulse pressure
E) stroke volume
F) systolic pressure
A) cardiac output
B) end-systolic volume
C) heart rate
D) pulse pressure
E) stroke volume
F) systolic pressure

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
An electrocardiogram (ECG) on a person shows ventricular extrasystoles.
-The extrasystolic beat would produce
A) increased pulse pressure because contractility is increased
B) increased pulse pressure because heart rate is increased
C) decreased pulse pressure because ventricular filling time is increased
D) decreased pulse pressure because stroke volume is decreased
E) decreased pulse pressure because the PR interval is increased
-The extrasystolic beat would produce
A) increased pulse pressure because contractility is increased
B) increased pulse pressure because heart rate is increased
C) decreased pulse pressure because ventricular filling time is increased
D) decreased pulse pressure because stroke volume is decreased
E) decreased pulse pressure because the PR interval is increased

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
An electrocardiogram (ECG) on a person shows ventricular extrasystoles.
-After an extrasystole, the next "normal" ventricular contraction produces
A) increased pulse pressure because the contractility of the ventricle is increased
B) increased pulse pressure because total peripheral resistance (TPR) is decreased
C) increased pulse pressure because compliance of the veins is decreased
D) decreased pulse pressure because the contractility of the ventricle is increased
E) decreased pulse pressure because TPR is decreased
-After an extrasystole, the next "normal" ventricular contraction produces
A) increased pulse pressure because the contractility of the ventricle is increased
B) increased pulse pressure because total peripheral resistance (TPR) is decreased
C) increased pulse pressure because compliance of the veins is decreased
D) decreased pulse pressure because the contractility of the ventricle is increased
E) decreased pulse pressure because TPR is decreased

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
An increase in contractility is demonstrated on a Frank-Starling diagram by
A) increased cardiac output for a given enddiastolic volume
B) increased cardiac output for a given endsystolic volume
C) decreased cardiac output for a given end-diastolic volume
D) decreased cardiac output for a given end-systolic volume
A) increased cardiac output for a given enddiastolic volume
B) increased cardiac output for a given endsystolic volume
C) decreased cardiac output for a given end-diastolic volume
D) decreased cardiac output for a given end-systolic volume

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
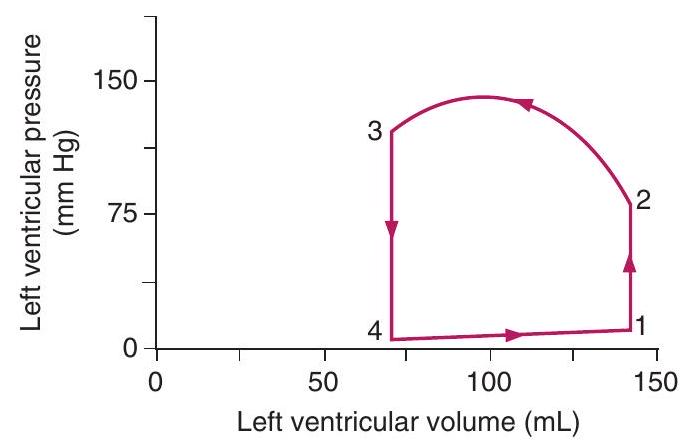
-On the graph showing left ventricular volume and pressure, isovolumetric contraction occurs between points
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10

-The aortic valve closes at point
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11

-The first heart sound corresponds to point
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12

-If the heart rate is 70 beats/min, then the cardiac output of this ventricle is closest to
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
In a capillary, is is , is , and is .
-What is the direction of fluid movement and the net driving force?
A) Absorption;
B) Absorption;
C) Filtration;
D) Filtration;
E) There is no net fluid movement
-What is the direction of fluid movement and the net driving force?
A) Absorption;
B) Absorption;
C) Filtration;
D) Filtration;
E) There is no net fluid movement

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
In a capillary, is is , is , and is .
-If is , what is the rate of water flow across the capillary wall?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
-If is , what is the rate of water flow across the capillary wall?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The tendency for blood flow to be turbulent is increased by
A) increased viscosity
B) increased hematocrit
C) partial occlusion of a blood vessel
D) decreased velocity of blood flow
A) increased viscosity
B) increased hematocrit
C) partial occlusion of a blood vessel
D) decreased velocity of blood flow

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
A 66-year-old man, who has had a sympathectomy, experiences a greaterthan-normal fall in arterial pressure upon standing up. The explanation for this occurrence is
A) an exaggerated response of the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system
B) a suppressed response of the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system
C) an exaggerated response of the baroreceptor mechanism
D) a suppressed response of the baroreceptor mechanism
A) an exaggerated response of the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system
B) a suppressed response of the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system
C) an exaggerated response of the baroreceptor mechanism
D) a suppressed response of the baroreceptor mechanism

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The ventricles are completely depolarized during which isoelectric portion of the electrocardiogram (ECG)?
A) PR interval
B) QRS complex
C) QT interval
D) ST segment
E) wave
A) PR interval
B) QRS complex
C) QT interval
D) ST segment
E) wave

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
In which of the following situations is pulmonary blood flow greater than aortic blood flow?
A) Normal adult
B) Fetus
C) Left-to-right ventricular shunt
D) Right-to-left ventricular shunt
E) Right ventricular failure
F) Administration of a positive inotropic agent
A) Normal adult
B) Fetus
C) Left-to-right ventricular shunt
D) Right-to-left ventricular shunt
E) Right ventricular failure
F) Administration of a positive inotropic agent

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The change indicated by the dashed lines on the cardiac output/venous return curves shows
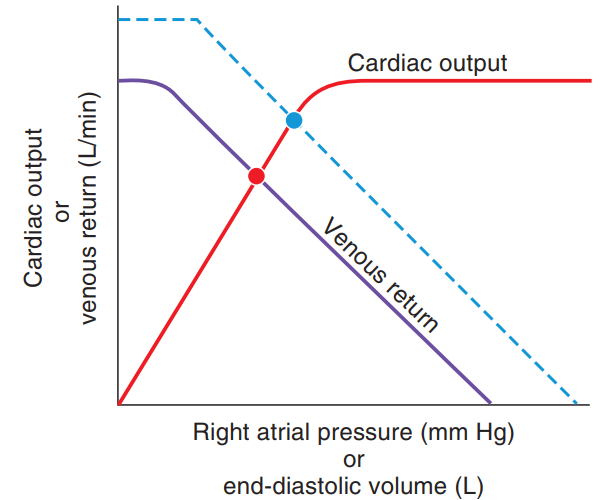 Right atrial pressure or end-diastolic volume (L)
Right atrial pressure or end-diastolic volume (L)
A) decreased cardiac output in the "new" steady state
B) decreased venous return in the "new" steady state
C) increased mean systemic pressure
D) decreased blood volume
E) increased myocardial contractility
 Right atrial pressure or end-diastolic volume (L)
Right atrial pressure or end-diastolic volume (L)A) decreased cardiac output in the "new" steady state
B) decreased venous return in the "new" steady state
C) increased mean systemic pressure
D) decreased blood volume
E) increased myocardial contractility

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
A 30-year-old female patient's electrocardiogram (ECG) shows two waves preceding each QRS complex. The interpretation of this pattern is
A) decreased firing rate of the pacemaker in the sinoatrial (SA) node
B) decreased firing rate of the pacemaker in the atrioventricular (AV) node
C) increased firing rate of the pacemaker in the SA node
D) decreased conduction through the AV node
E) increased conduction through the HisPurkinje system
A) decreased firing rate of the pacemaker in the sinoatrial (SA) node
B) decreased firing rate of the pacemaker in the atrioventricular (AV) node
C) increased firing rate of the pacemaker in the SA node
D) decreased conduction through the AV node
E) increased conduction through the HisPurkinje system

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
An acute decrease in arterial blood pressure elicits which of the following compensatory changes?
A) Decreased firing rate of the carotid sinus nerve
B) Increased parasympathetic outflow to the heart
C) Decreased heart rate
D) Decreased contractility
E) Decreased mean systemic pressure
A) Decreased firing rate of the carotid sinus nerve
B) Increased parasympathetic outflow to the heart
C) Decreased heart rate
D) Decreased contractility
E) Decreased mean systemic pressure

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The tendency for edema to occur will be increased by
A) arteriolar constriction
B) increased venous pressure
C) increased plasma protein concentration
D) muscular activity
A) arteriolar constriction
B) increased venous pressure
C) increased plasma protein concentration
D) muscular activity

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Inspiration "splits" the second heart sound because
A) the aortic valve closes before the pulmonic valve
B) the pulmonic valve closes before the aortic valve
C) the mitral valve closes before the tricuspid valve
D) the tricuspid valve closes before the mitral valve
E) filling of the ventricles has fast and slow components
A) the aortic valve closes before the pulmonic valve
B) the pulmonic valve closes before the aortic valve
C) the mitral valve closes before the tricuspid valve
D) the tricuspid valve closes before the mitral valve
E) filling of the ventricles has fast and slow components

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
During exercise, total peripheral resistance (TPR) decreases because of the effect of
A) the sympathetic nervous system on splanchnic arterioles
B) the parasympathetic nervous system on skeletal muscle arterioles
C) local metabolites on skeletal muscle arterioles
D) local metabolites on cerebral arterioles
E) histamine on skeletal muscle arterioles
A) the sympathetic nervous system on splanchnic arterioles
B) the parasympathetic nervous system on skeletal muscle arterioles
C) local metabolites on skeletal muscle arterioles
D) local metabolites on cerebral arterioles
E) histamine on skeletal muscle arterioles

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
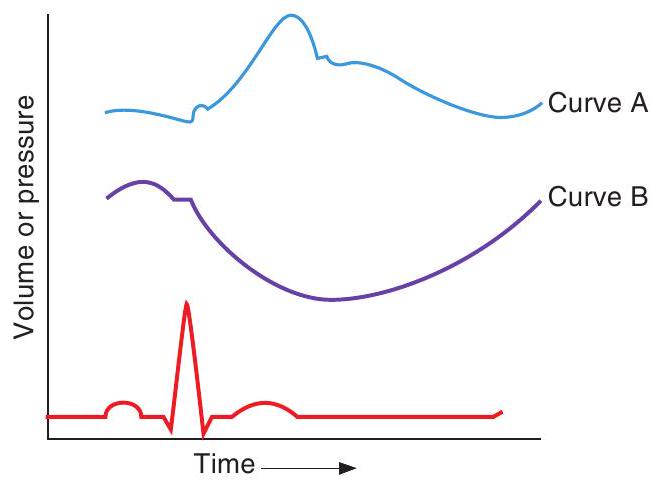
-Curve A in the figure represents
A) aortic pressure
B) ventricular pressure
C) atrial pressure
D) ventricular volume

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26

-Curve in the figure represents
A) left atrial pressure
B) ventricular pressure
C) atrial pressure
D) ventricular volume

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
An increase in arteriolar resistance, without a change in any other component of the cardiovascular system, will produce
A) a decrease in total peripheral resistance (TPR)
B) an increase in capillary filtration
C) an increase in arterial pressure
D) a decrease in afterload
A) a decrease in total peripheral resistance (TPR)
B) an increase in capillary filtration
C) an increase in arterial pressure
D) a decrease in afterload

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The following measurements were obtained in a male patient:
Central venous pressure:
Heart rate: 70 beats/min
Systemic arterial
Mixed venous
Whole body consumption:
What is this patient's cardiac output?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
Central venous pressure:
Heart rate: 70 beats/min
Systemic arterial
Mixed venous
Whole body consumption:
What is this patient's cardiac output?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Which of the following is the result of an inward current?
A) Upstroke of the action potential in the sinoatrial (SA) node
B) Upstroke of the action potential in Purkinje fibers
C) Plateau of the action potential in ventricular muscle
D) Repolarization of the action potential in ventricular muscle
E) Repolarization of the action potential in the SA node
A) Upstroke of the action potential in the sinoatrial (SA) node
B) Upstroke of the action potential in Purkinje fibers
C) Plateau of the action potential in ventricular muscle
D) Repolarization of the action potential in ventricular muscle
E) Repolarization of the action potential in the SA node

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
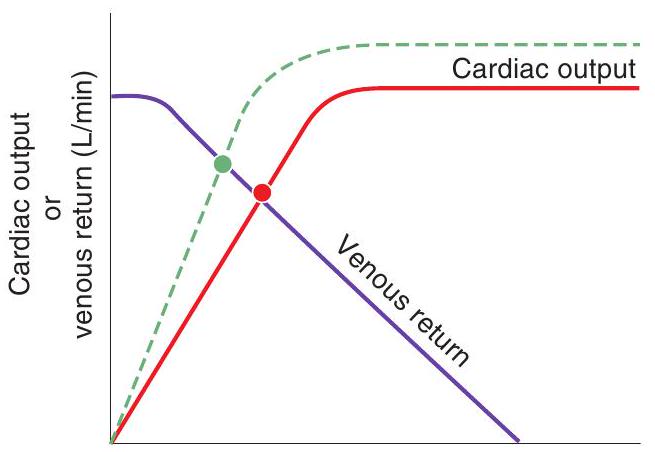 Right atrial pressure
Right atrial pressure -The dashed line in the figure illustrates the effect of
A) increased total peripheral resistance (TPR)
B) increased blood volume
C) increased contractility
D) a negative inotropic agent
E) increased mean systemic pressure

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
 Right atrial pressure
Right atrial pressure -The -axis in the figure could have been labeled
A) end-systolic volume
B) end-diastolic volume
C) pulse pressure
D) mean systemic pressure
E) heart rate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The greatest pressure decrease in the circulation occurs across the arterioles because
A) they have the greatest surface area
B) they have the greatest cross-sectional area
C) the velocity of blood flow through them is the highest
D) the velocity of blood flow through them is the lowest
E) they have the greatest resistance
A) they have the greatest surface area
B) they have the greatest cross-sectional area
C) the velocity of blood flow through them is the highest
D) the velocity of blood flow through them is the lowest
E) they have the greatest resistance

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Pulse pressure is
A) the highest pressure measured in the arteries
B) the lowest pressure measured in the arteries
C) measured only during diastole
D) determined by stroke volume
E) decreased when the capacitance of the arteries decreases
F) the difference between mean arterial pressure and central venous pressure
A) the highest pressure measured in the arteries
B) the lowest pressure measured in the arteries
C) measured only during diastole
D) determined by stroke volume
E) decreased when the capacitance of the arteries decreases
F) the difference between mean arterial pressure and central venous pressure

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
In the sinoatrial (SA) node, phase 4 depolarization (pacemaker potential) is attributable to
A) an increase in conductance
B) an increase in conductance
C) a decrease in conductance
D) a decrease in conductance
E) simultaneous increases in and conductances
A) an increase in conductance
B) an increase in conductance
C) a decrease in conductance
D) a decrease in conductance
E) simultaneous increases in and conductances

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
A healthy 35 -year-old man is running a marathon. During the run, there is a increase in his splanchnic vascular resistance. Which receptor is responsible for the increased resistance?
A) Receptors
B) Receptors
C) Receptors
D) Muscarinic receptors
A) Receptors
B) Receptors
C) Receptors
D) Muscarinic receptors

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
During which phase of the cardiac cycle is aortic pressure highest?
A) Atrial systole
B) Isovolumetric ventricular contraction
C) Rapid ventricular ejection
D) Reduced ventricular ejection
E) Isovolumetric ventricular relaxation
F) Rapid ventricular filling
G) Reduced ventricular filling (diastasis)
A) Atrial systole
B) Isovolumetric ventricular contraction
C) Rapid ventricular ejection
D) Reduced ventricular ejection
E) Isovolumetric ventricular relaxation
F) Rapid ventricular filling
G) Reduced ventricular filling (diastasis)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Myocardial contractility is best correlated with the intracellular concentration of
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Which of the following is an effect of histamine?
A) Decreased capillary filtration
B) Vasodilation of the arterioles
C) Vasodilation of the veins
D) Decreased
E) Interaction with the muscarinic receptors on the blood vessels
A) Decreased capillary filtration
B) Vasodilation of the arterioles
C) Vasodilation of the veins
D) Decreased
E) Interaction with the muscarinic receptors on the blood vessels

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Carbon dioxide regulates blood flow to which one of the following organs?
A) Heart
B) Skin
C) Brain
D) Skeletal muscle at rest
E) Skeletal muscle during exercise
A) Heart
B) Skin
C) Brain
D) Skeletal muscle at rest
E) Skeletal muscle during exercise

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Cardiac output of the right side of the heart is what percentage of the cardiac output of the left side of the heart?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The physiologic function of the relatively slow conduction through the atrioventricular (AV) node is to allow sufficient time for
A) runoff of blood from the aorta to the arteries
B) venous return to the atria
C) filling of the ventricles
D) contraction of the ventricles
E) repolarization of the ventricles
A) runoff of blood from the aorta to the arteries
B) venous return to the atria
C) filling of the ventricles
D) contraction of the ventricles
E) repolarization of the ventricles

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Blood flow to which organ is controlled primarily by the sympathetic nervous system rather than by local metabolites?
A) Skin
B) Heart
C) Brain
D) Skeletal muscle during exercise
A) Skin
B) Heart
C) Brain
D) Skeletal muscle during exercise

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Which of the following parameters is decreased during moderate exercise?
A) Arteriovenous difference
B) Heart rate
C) Cardiac output
D) Pulse pressure
E) Total peripheral resistance (TPR)
A) Arteriovenous difference
B) Heart rate
C) Cardiac output
D) Pulse pressure
E) Total peripheral resistance (TPR)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
A 72-year-old woman, who is being treated with propranolol, finds that she cannot maintain her previous exercise routine. Her physician explains that the drug has reduced her cardiac output. Blockade of which receptor is responsible for the decrease in cardiac output?
A) Receptors
B) Receptors
C) Receptors
D) Muscarinic receptors
E) Nicotinic receptors
A) Receptors
B) Receptors
C) Receptors
D) Muscarinic receptors
E) Nicotinic receptors

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
During which phase of the cardiac cycle is ventricular volume lowest?
A) Atrial systole
B) Isovolumetric ventricular contraction
C) Rapid ventricular ejection
D) Reduced ventricular ejection
E) Isovolumetric ventricular relaxation
F) Rapid ventricular filling
G) Reduced ventricular filling (diastasis)
A) Atrial systole
B) Isovolumetric ventricular contraction
C) Rapid ventricular ejection
D) Reduced ventricular ejection
E) Isovolumetric ventricular relaxation
F) Rapid ventricular filling
G) Reduced ventricular filling (diastasis)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Which of the following changes will cause an increase in myocardial consumption?
A) Decreased aortic pressure
B) Decreased heart rate
C) Decreased contractility
D) Increased size of the heart
E) Increased influx of during the upstroke of the action potential
A) Decreased aortic pressure
B) Decreased heart rate
C) Decreased contractility
D) Increased size of the heart
E) Increased influx of during the upstroke of the action potential

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Which of the following substances crosses capillary walls primarily through water-filled clefts between the endothelial cells?
A)
B)
C)
D) Glucose
A)
B)
C)
D) Glucose

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
A 24-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with severe diarrhea. When she is supine (lying down), her blood pressure is (decreased) and her heart rate is 100 beats/min (increased). When she is moved to a standing position, her heart rate further increases to 120 beats/ min. Which of the following accounts for the further increase in heart rate upon standing?
A) Decreased total peripheral resistance
B) Increased venoconstriction
C) Increased contractility
D) Increased afterload
E) Decreased venous return
A) Decreased total peripheral resistance
B) Increased venoconstriction
C) Increased contractility
D) Increased afterload
E) Decreased venous return

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
A 60-year-old businessman is evaluated by his physician, who determines that his blood pressure is significantly elevated at 185/130 mm Hg. Laboratory tests reveal an increase in plasma renin activity, plasma aldosterone level, and left renal vein renin level. His right renal vein renin level is decreased. What is the most likely cause of the patient's hypertension?
A) Aldosterone-secreting tumor
B) Adrenal adenoma secreting aldosterone and cortisol
C) Pheochromocytoma
D) Left renal artery stenosis
E) Right renal artery stenosis
A) Aldosterone-secreting tumor
B) Adrenal adenoma secreting aldosterone and cortisol
C) Pheochromocytoma
D) Left renal artery stenosis
E) Right renal artery stenosis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50

-During which phase of the ventricular action potential is the membrane potential closest to the equilibrium potential?
A) Phase 0
B) Phase 1
C) Phase 2
D) Phase 3
E) Phase 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51

-During which phase of the ventricular action potential is the conductance to highest?
A) Phase 0
B) Phase 1
C) Phase 2
D) Phase 3
E) Phase 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52

-Which phase of the ventricular action potential coincides with diastole?
A) Phase 0
B) Phase 1
C) Phase 2
D) Phase 3
E) Phase 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Propranolol has which of the following effects?
A) Decreases heart rate
B) Increases left ventricular ejection fraction
C) Increases stroke volume
D) Decreases splanchnic vascular resistance
E) Decreases cutaneous vascular resistance
A) Decreases heart rate
B) Increases left ventricular ejection fraction
C) Increases stroke volume
D) Decreases splanchnic vascular resistance
E) Decreases cutaneous vascular resistance

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Which receptor mediates slowing of the heart?
A) Receptors
B) Receptors
C) Receptors
D) Muscarinic receptors
A) Receptors
B) Receptors
C) Receptors
D) Muscarinic receptors

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Which of the following agents or changes has a negative inotropic effect on the heart?
A) Increased heart rate
B) Sympathetic stimulation
C) Norepinephrine
D) Acetylcholine (ACh)
E) Cardiac glycosides
A) Increased heart rate
B) Sympathetic stimulation
C) Norepinephrine
D) Acetylcholine (ACh)
E) Cardiac glycosides

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
The low-resistance pathways between myocardial cells that allow for the spread of action potentials are the
A) gap junctions
B) T tubules
C) sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
D) intercalated disks
E) mitochondria
A) gap junctions
B) T tubules
C) sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
D) intercalated disks
E) mitochondria

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Which agent is released or secreted after a hemorrhage and causes an increase in renal reabsorption?
A) Aldosterone
B) Angiotensin I
C) Angiotensinogen
D) Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
E) Atrial natriuretic peptide
A) Aldosterone
B) Angiotensin I
C) Angiotensinogen
D) Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
E) Atrial natriuretic peptide

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
During which phase of the cardiac cycle does the mitral valve open?
A) Atrial systole
B) Isovolumetric ventricular contraction
C) Rapid ventricular ejection
D) Reduced ventricular ejection
E) Isovolumetric ventricular relaxation
F) Rapid ventricular filling
G) Reduced ventricular filling (diastasis)
A) Atrial systole
B) Isovolumetric ventricular contraction
C) Rapid ventricular ejection
D) Reduced ventricular ejection
E) Isovolumetric ventricular relaxation
F) Rapid ventricular filling
G) Reduced ventricular filling (diastasis)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
A hospitalized patient has an ejection fraction of 0.4 , a heart rate of 95 beats/min, and a cardiac output of . What is the patient's end-diastolic volume?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








