Deck 3: Second-Order Linear Differential Equations
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/119
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 3: Second-Order Linear Differential Equations
1
What is the characteristic equation for the second-order homogeneous differential equation 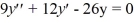 ?
?
A) 9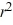 - 14r = 0
- 14r = 0
B) 9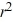 + 12r - 26 = 0
+ 12r - 26 = 0
C) 9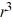 - 14
- 14 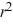 = 0
= 0
D) 9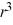 + 12
+ 12 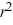 - 26r = 0
- 26r = 0
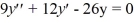 ?
?A) 9
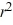 - 14r = 0
- 14r = 0B) 9
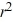 + 12r - 26 = 0
+ 12r - 26 = 0C) 9
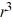 - 14
- 14 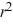 = 0
= 0D) 9
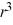 + 12
+ 12 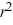 - 26r = 0
- 26r = 09 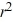 + 12r - 26 = 0
+ 12r - 26 = 0
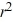 + 12r - 26 = 0
+ 12r - 26 = 0 2
For which of these differential equations is the characteristic equation given by r(10r + 1) = 0?
A)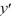 (10
(10 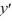 + 1) = 0
+ 1) = 0
B) 10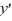 + 1y = 0
+ 1y = 0
C)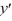 (10
(10 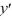 + 1y) = 0
+ 1y) = 0
D) 10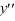 + 1
+ 1 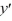 = 0
= 0
E) 10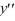 + 1y = 0
+ 1y = 0
A)
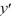 (10
(10 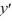 + 1) = 0
+ 1) = 0B) 10
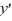 + 1y = 0
+ 1y = 0C)
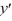 (10
(10 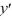 + 1y) = 0
+ 1y) = 0D) 10
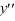 + 1
+ 1 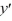 = 0
= 0E) 10
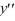 + 1y = 0
+ 1y = 010 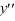 + 1
+ 1 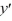 = 0
= 0
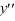 + 1
+ 1 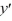 = 0
= 0 3
For which of these differential equations is the characteristic equation given by 6 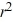 + 7 = 0?
+ 7 = 0?
A) 6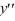 + 7 = 0
+ 7 = 0
B) 6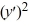 + 7 = 0
+ 7 = 0
C) 6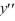 + 7y = 0
+ 7y = 0
D) 6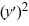 + 7y = 0
+ 7y = 0
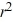 + 7 = 0?
+ 7 = 0?A) 6
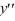 + 7 = 0
+ 7 = 0B) 6
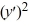 + 7 = 0
+ 7 = 0C) 6
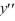 + 7y = 0
+ 7y = 0D) 6
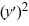 + 7y = 0
+ 7y = 06 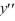 + 7y = 0
+ 7y = 0
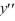 + 7y = 0
+ 7y = 0 4
For which of these differential equations is the characteristic equation given by 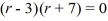 ?
?
A)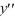 + 4
+ 4 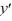 - 21y = 0
- 21y = 0
B) (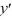 - 3)(
- 3)( 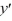 + 7) = 0
+ 7) = 0
C)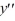 + 4
+ 4 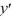 - 21 = 0
- 21 = 0
D)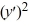 - 4
- 4 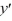 - 21 = 0
- 21 = 0
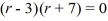 ?
?A)
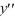 + 4
+ 4 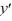 - 21y = 0
- 21y = 0B) (
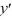 - 3)(
- 3)( 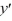 + 7) = 0
+ 7) = 0C)
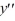 + 4
+ 4 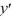 - 21 = 0
- 21 = 0D)
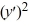 - 4
- 4 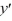 - 21 = 0
- 21 = 0
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Which of the following are solutions to the homogeneous second-order differential equation 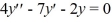 ?
?
Select all that apply.
A)
B) , where is any real constant
C)
D) , where is any real constant
E) , where and are any real constants
F)
G) , where is any real constant
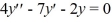 ?
? Select all that apply.
A)
B) , where is any real constant
C)
D) , where is any real constant
E) , where and are any real constants
F)
G) , where is any real constant

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Which of the following are solutions to the homogeneous second-order differential equation 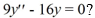 ?
?
Select all that apply.
A) , where is any real constant
B)
C) , where is any real constant
D) , where is any real constant
E)
F)
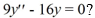 ?
? Select all that apply.
A) , where is any real constant
B)
C) , where is any real constant
D) , where is any real constant
E)
F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which of the following is the general solution of the homogeneous second-order differential equation 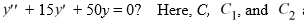 are arbitrary real constants.
are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
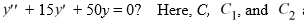 are arbitrary real constants.
are arbitrary real constants.A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Which of the following is the general solution of the homogeneous second-order differential equation 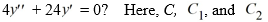 are arbitrary real constants.
are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
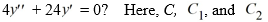 are arbitrary real constants.
are arbitrary real constants.A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
For which of the following values of r is y = C 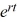 a solution of the second-order homogeneous differential equation 4
a solution of the second-order homogeneous differential equation 4  + y = 0? Select all that apply.
+ y = 0? Select all that apply.
A)
B) -4
C) 0
D)
E) 4
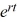 a solution of the second-order homogeneous differential equation 4
a solution of the second-order homogeneous differential equation 4 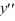 + y = 0? Select all that apply.
+ y = 0? Select all that apply.A)
B) -4
C) 0
D)
E) 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
What is the solution of the initial value problem
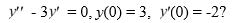
A)
B)
C)
D)
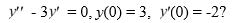
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Consider the second-order homogeneous differential equation 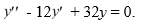
What is the general solution of this differential equation? Here, C, C1 , and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
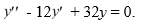
What is the general solution of this differential equation? Here, C, C1 , and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Consider the second-order homogeneous differential equation 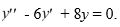
If the differential equation is equipped with the initial conditions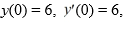
what is the solution of the resulting initial value problem?
A)
B)
C)
D)
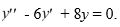
If the differential equation is equipped with the initial conditions
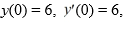
what is the solution of the resulting initial value problem?
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Consider the initial value problem
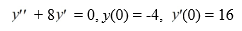
What is the solution of this initial value problem?
A) y = -4 + 2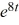
B) y = -4 + 2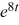
C) y = -2 + 2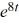
D) y = -2 - 2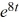
E) y = -4t - 2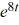 F) y = -2t - 2
F) y = -2t - 2 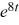
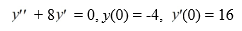
What is the solution of this initial value problem?
A) y = -4 + 2
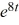
B) y = -4 + 2
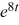
C) y = -2 + 2
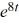
D) y = -2 - 2
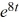
E) y = -4t - 2
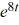 F) y = -2t - 2
F) y = -2t - 2 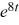

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Consider the initial value problem
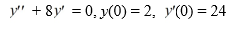
Fill in the blank: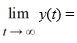 ________
________
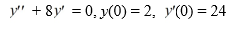
Fill in the blank:
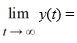 ________
________
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Consider the initial value problem
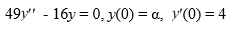
What is the solution of this initial value problem?
A)
B)
C)
D)
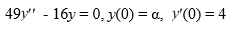
What is the solution of this initial value problem?
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Consider the initial value problem
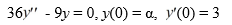
For what value of ? does the solution of this initial value problem tend to zero as t ?
A) - 6
B) -
C) 0
D) 6
E)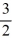
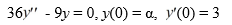
For what value of ? does the solution of this initial value problem tend to zero as t ?
A) - 6
B) -
C) 0
D) 6
E)
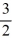

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Consider the initial value problem
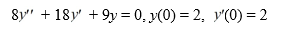
What is the solution of this initial value problem?
A)
B)
C)
D)
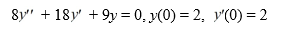
What is the solution of this initial value problem?
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Consider the initial value problem
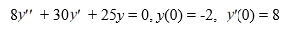
What is the t-coordinate of the local extreme value of y = y(t) on the interval (0, ∞)? Enter your answer as a decimal accurate to three decimal places.
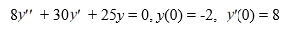
What is the t-coordinate of the local extreme value of y = y(t) on the interval (0, ∞)? Enter your answer as a decimal accurate to three decimal places.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Consider the initial value problem
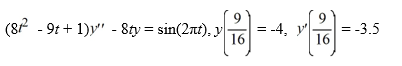
On which of these intervals is this initial value problem certain to have a unique twice differentiable solution? Select all that apply.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
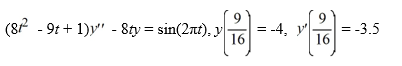
On which of these intervals is this initial value problem certain to have a unique twice differentiable solution? Select all that apply.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Consider the initial value problem
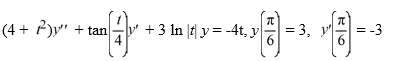
On which of these intervals is this initial value problem certain to have a unique twice differentiable solution? Select all that apply.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
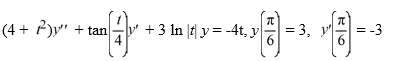
On which of these intervals is this initial value problem certain to have a unique twice differentiable solution? Select all that apply.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Consider the initial value problem
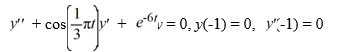
Which of these statements are true? Select all that apply.
A) There exists a nonzero real number r such that y(t) =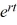 is a solution of the initial value problem.
is a solution of the initial value problem.
B) This initial value problem has only one solution on the interval (-7, 5).
C) The constant function y(t) = -1 is a solution of this initial value problem for all real numbers t.
D) There must exist a function y = ?(t) that satisfies this initial value problem on the interval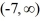 .
.
E) The constant function y(t) = 0 is the unique solution of this initial value problem on the interval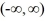 .
.
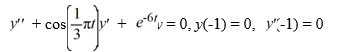
Which of these statements are true? Select all that apply.
A) There exists a nonzero real number r such that y(t) =
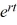 is a solution of the initial value problem.
is a solution of the initial value problem.B) This initial value problem has only one solution on the interval (-7, 5).
C) The constant function y(t) = -1 is a solution of this initial value problem for all real numbers t.
D) There must exist a function y = ?(t) that satisfies this initial value problem on the interval
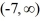 .
.E) The constant function y(t) = 0 is the unique solution of this initial value problem on the interval
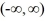 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Suppose that Y1 and Y2 are both solutions of the differential equation 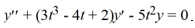 .
.
Which of the following must also be solutions of this differential equation? Select all that apply. Here, C1 , and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
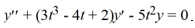 .
. Which of the following must also be solutions of this differential equation? Select all that apply. Here, C1 , and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
If Y1 and Y2 are both solutions of the differential equation 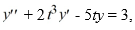 then Y1 - Y2 is also a solution of this equation.
then Y1 - Y2 is also a solution of this equation.
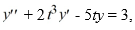 then Y1 - Y2 is also a solution of this equation.
then Y1 - Y2 is also a solution of this equation.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Consider the differential equation 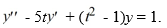
Which of the following statements is true?
A) If 2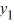 is a solution of this differential equation, then so is
is a solution of this differential equation, then so is 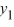 .
.
B) If Y1 and Y2 are both solutions of this differential equation, then Y1 - Y2 cannot be a solution of it.
C) The Principle of Superposition guarantees that if y1 and y2 are both solutions of this differential equation, then C1 y1 + C2 y2 must also be a solution of it, for any choice of real constants and .
D) There exist nonzero real constants C1 and C2 such that C1 y1 - C2 y2 is a solution of this differential equation.
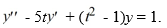
Which of the following statements is true?
A) If 2
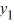 is a solution of this differential equation, then so is
is a solution of this differential equation, then so is 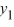 .
.B) If Y1 and Y2 are both solutions of this differential equation, then Y1 - Y2 cannot be a solution of it.
C) The Principle of Superposition guarantees that if y1 and y2 are both solutions of this differential equation, then C1 y1 + C2 y2 must also be a solution of it, for any choice of real constants and .
D) There exist nonzero real constants C1 and C2 such that C1 y1 - C2 y2 is a solution of this differential equation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Compute the Wronskian of the pair of functions 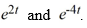
A) -2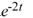
B) -6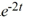
C) -8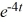
D) -6
E) -8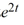
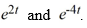
A) -2
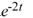
B) -6
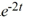
C) -8
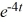
D) -6
E) -8
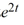

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Compute the Wronskian of the pair of functions sin(5t) and cos(5t).
A) -5
B) -4
C) 1
D) 4
E) 5
A) -5
B) -4
C) 1
D) 4
E) 5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Compute the Wronskian of the pair of functions 2t 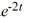 and 4
and 4 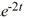 .
.
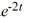 and 4
and 4 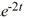 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Consider the pair of functions y1 = ln t and y1 = t ln t.
Compute the Wronskian of this function pair.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
Compute the Wronskian of this function pair.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Consider the pair of functions y1 = ln t and y1 = t ln t.
Which of these statements is true?
A) Both y1 and y2 can be solutions of the differential equation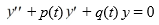 on the interval (0, ), where p(t) and q(t) are continuous on (0, ).
on the interval (0, ), where p(t) and q(t) are continuous on (0, ).
B) The Wronskian for this function pair is strictly positive on (0, ).
C) Abel's theorem implies that y1 and y2 cannot both be solutions of any differential equation of the form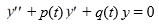 on the interval (0, ).
on the interval (0, ).
D) The pair y1 and y2 constitutes a fundamental set of solutions to some second-order differential equation of the form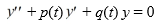 on the interval (0, ).
on the interval (0, ).
Which of these statements is true?
A) Both y1 and y2 can be solutions of the differential equation
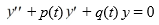 on the interval (0, ), where p(t) and q(t) are continuous on (0, ).
on the interval (0, ), where p(t) and q(t) are continuous on (0, ).B) The Wronskian for this function pair is strictly positive on (0, ).
C) Abel's theorem implies that y1 and y2 cannot both be solutions of any differential equation of the form
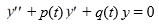 on the interval (0, ).
on the interval (0, ).D) The pair y1 and y2 constitutes a fundamental set of solutions to some second-order differential equation of the form
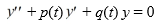 on the interval (0, ).
on the interval (0, ).
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Consider the pair of functions y1 = t and y2 = 3t2.
Which of these statements are true? Select all that apply.
A) W[y1 , y2](t) > 0 for all values of t in the interval (-2, 2).
B) W[y1 , y1](t) = 3t2
C) The pair y1 and y2 constitutes a fundamental set of solutions to some second-order differential equation of the form > 0 for all values of t in the interval (-2, 2). B) W[y<sub>1</sub> , y<sub>1</sub>](t) = 3t<sup>2</sup> C) The pair y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> constitutes a fundamental set of solutions to some second-order differential equation of the form on the interval (-2, 2). D) Abel's theorem implies that y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> cannot both be solutions of any differential equation of the form on the interval (-2, 2). E) Since there exists a value of t<sub>0</sub> in the interval (-2, 2) for which W[y<sub>1</sub> ,y<sub>2</sub> ](t) = 0, there must exist a differential equation of the form for which the pair y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> constitute a fundamental set of solutions on the interval (-2, 2).](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_704b_e927_9020_fd80e61b2acf_TBW1042_11.jpg) on the interval (-2, 2).
on the interval (-2, 2).
D) Abel's theorem implies that y1 and y2 cannot both be solutions of any differential equation of the form > 0 for all values of t in the interval (-2, 2). B) W[y<sub>1</sub> , y<sub>1</sub>](t) = 3t<sup>2</sup> C) The pair y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> constitutes a fundamental set of solutions to some second-order differential equation of the form on the interval (-2, 2). D) Abel's theorem implies that y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> cannot both be solutions of any differential equation of the form on the interval (-2, 2). E) Since there exists a value of t<sub>0</sub> in the interval (-2, 2) for which W[y<sub>1</sub> ,y<sub>2</sub> ](t) = 0, there must exist a differential equation of the form for which the pair y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> constitute a fundamental set of solutions on the interval (-2, 2).](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_704b_e928_9020_dddc4b82d31e_TBW1042_11.jpg) on the interval (-2, 2).
on the interval (-2, 2).
E) Since there exists a value of t0 in the interval (-2, 2) for which W[y1 ,y2 ](t) = 0, there must exist a differential equation of the form > 0 for all values of t in the interval (-2, 2). B) W[y<sub>1</sub> , y<sub>1</sub>](t) = 3t<sup>2</sup> C) The pair y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> constitutes a fundamental set of solutions to some second-order differential equation of the form on the interval (-2, 2). D) Abel's theorem implies that y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> cannot both be solutions of any differential equation of the form on the interval (-2, 2). E) Since there exists a value of t<sub>0</sub> in the interval (-2, 2) for which W[y<sub>1</sub> ,y<sub>2</sub> ](t) = 0, there must exist a differential equation of the form for which the pair y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> constitute a fundamental set of solutions on the interval (-2, 2).](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_704b_e929_9020_5196a9f7a558_TBW1042_11.jpg) for which the pair y1 and y2 constitute a fundamental set of solutions on the interval (-2, 2).
for which the pair y1 and y2 constitute a fundamental set of solutions on the interval (-2, 2).
Which of these statements are true? Select all that apply.
A) W[y1 , y2](t) > 0 for all values of t in the interval (-2, 2).
B) W[y1 , y1](t) = 3t2
C) The pair y1 and y2 constitutes a fundamental set of solutions to some second-order differential equation of the form
 > 0 for all values of t in the interval (-2, 2). B) W[y<sub>1</sub> , y<sub>1</sub>](t) = 3t<sup>2</sup> C) The pair y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> constitutes a fundamental set of solutions to some second-order differential equation of the form on the interval (-2, 2). D) Abel's theorem implies that y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> cannot both be solutions of any differential equation of the form on the interval (-2, 2). E) Since there exists a value of t<sub>0</sub> in the interval (-2, 2) for which W[y<sub>1</sub> ,y<sub>2</sub> ](t) = 0, there must exist a differential equation of the form for which the pair y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> constitute a fundamental set of solutions on the interval (-2, 2).](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_704b_e927_9020_fd80e61b2acf_TBW1042_11.jpg) on the interval (-2, 2).
on the interval (-2, 2).D) Abel's theorem implies that y1 and y2 cannot both be solutions of any differential equation of the form
 > 0 for all values of t in the interval (-2, 2). B) W[y<sub>1</sub> , y<sub>1</sub>](t) = 3t<sup>2</sup> C) The pair y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> constitutes a fundamental set of solutions to some second-order differential equation of the form on the interval (-2, 2). D) Abel's theorem implies that y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> cannot both be solutions of any differential equation of the form on the interval (-2, 2). E) Since there exists a value of t<sub>0</sub> in the interval (-2, 2) for which W[y<sub>1</sub> ,y<sub>2</sub> ](t) = 0, there must exist a differential equation of the form for which the pair y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> constitute a fundamental set of solutions on the interval (-2, 2).](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_704b_e928_9020_dddc4b82d31e_TBW1042_11.jpg) on the interval (-2, 2).
on the interval (-2, 2).E) Since there exists a value of t0 in the interval (-2, 2) for which W[y1 ,y2 ](t) = 0, there must exist a differential equation of the form
 > 0 for all values of t in the interval (-2, 2). B) W[y<sub>1</sub> , y<sub>1</sub>](t) = 3t<sup>2</sup> C) The pair y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> constitutes a fundamental set of solutions to some second-order differential equation of the form on the interval (-2, 2). D) Abel's theorem implies that y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> cannot both be solutions of any differential equation of the form on the interval (-2, 2). E) Since there exists a value of t<sub>0</sub> in the interval (-2, 2) for which W[y<sub>1</sub> ,y<sub>2</sub> ](t) = 0, there must exist a differential equation of the form for which the pair y<sub>1</sub> and y<sub>2</sub> constitute a fundamental set of solutions on the interval (-2, 2).](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_704b_e929_9020_5196a9f7a558_TBW1042_11.jpg) for which the pair y1 and y2 constitute a fundamental set of solutions on the interval (-2, 2).
for which the pair y1 and y2 constitute a fundamental set of solutions on the interval (-2, 2).
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Which of these is a fundamental set of solutions for the differential equation 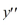
Select all that apply.
A) and
B) and
C) and
D) and
E) and
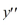
Select all that apply.
A) and
B) and
C) and
D) and
E) and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The pair of functions 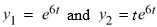
forms a fundamental set of solutions for the differential equation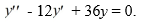
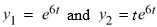
forms a fundamental set of solutions for the differential equation
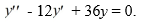

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
What is the characteristic equation for the second-order homogeneous differential equation 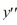 + 36y=0?
+ 36y=0?
A)
B)
C)
D)
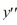 + 36y=0?
+ 36y=0?A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
For which of these differential equations is the characteristic equation given by 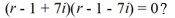
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
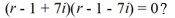
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Which of the following are solutions to the homogeneous second-order differential equation 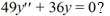
Select all that apply.
A)
B) , where is any real constant
C)
D)
E) where and are any real constants
F)
G) , where is any real constant
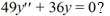
Select all that apply.
A)
B) , where is any real constant
C)
D)
E) where and are any real constants
F)
G) , where is any real constant

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which of the following are solutions to the homogeneous second-order differential equation 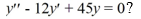
Select all that apply.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) , where is any real constant
F)
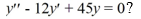
Select all that apply.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) , where is any real constant
F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Which of the following is the general solution of the homogeneous second-order differential equation 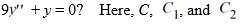
are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
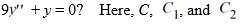
are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Which of the following is the general solution of the homogeneous second-order differential equation 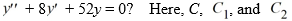
are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
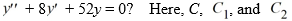
are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
What is the solution of this initial value problem: 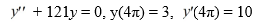
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
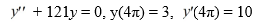
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
What is the solution of this initial value problem:
![<strong>What is the solution of this initial value problem: </strong> A) y=e^{3 t}\left[3 \cos (7 t)-\frac{4}{7} \sin (7 t)\right] B) y=e^{-3 t}(3 \cos (7 t)+2 \sin (7 t)) C) y=e^{7 t}\left(3 \cos (3 t)+\frac{14}{3} \sin (3 t)\right) D) y=e^{-7 t}\left[3 \cos (3 t)-\frac{4}{3} \sin (3 t)\right]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_704c_375c_9020_039bad32b3eb_TBW1042_00.jpg)
A)
B)
C)
D)
![<strong>What is the solution of this initial value problem: </strong> A) y=e^{3 t}\left[3 \cos (7 t)-\frac{4}{7} \sin (7 t)\right] B) y=e^{-3 t}(3 \cos (7 t)+2 \sin (7 t)) C) y=e^{7 t}\left(3 \cos (3 t)+\frac{14}{3} \sin (3 t)\right) D) y=e^{-7 t}\left[3 \cos (3 t)-\frac{4}{3} \sin (3 t)\right]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_704c_375c_9020_039bad32b3eb_TBW1042_00.jpg)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Consider the initial value problem:
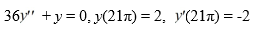
What is the solution of this initial value problem?
A)
B)
C)
D)
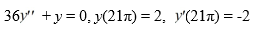
What is the solution of this initial value problem?
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Consider the initial value problem:
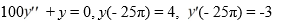
Which of the following is an accurate description of the long-term behavior of the solution?
A) y(t) decreases to 0 as t .
B) y(t) is periodic with period 20 .
C) y(t) oscillates toward 0 as t .
D) y(t) becomes unbounded in both the positive and negative y-directions as t .
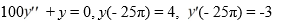
Which of the following is an accurate description of the long-term behavior of the solution?
A) y(t) decreases to 0 as t .
B) y(t) is periodic with period 20 .
C) y(t) oscillates toward 0 as t .
D) y(t) becomes unbounded in both the positive and negative y-directions as t .

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Which of the following is an accurate description of the long-term behavior of the solution of the initial value problem
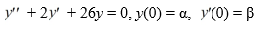
For any choice of and satisfying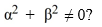
A) y is periodic with period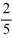 .
.
B) y is periodic with period 2 .
C) y becomes unbounded in both the positive and negative y-directions as t .
D) y oscillates toward 0 as t .
E) y increases toward + if > 0, and decreases toward - if < 0.
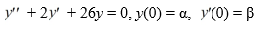
For any choice of and satisfying
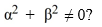
A) y is periodic with period
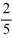 .
.B) y is periodic with period 2 .
C) y becomes unbounded in both the positive and negative y-directions as t .
D) y oscillates toward 0 as t .
E) y increases toward + if > 0, and decreases toward - if < 0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Which of the following are solutions to the homogeneous second-order Cauchy Euler differential equation 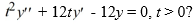 . Select all that apply.
. Select all that apply.
A)
B) , where is any real constant
C)
D) , where is any real constant
E) , where is any real constant
F) , where , and are arbitrary real constants
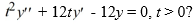 . Select all that apply.
. Select all that apply.A)
B) , where is any real constant
C)
D) , where is any real constant
E) , where is any real constant
F) , where , and are arbitrary real constants

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Consider the homogeneous second-order Cauchy Euler differential equation
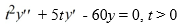
What is the general solution of this differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B) .
C)
D) .
E)
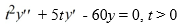
What is the general solution of this differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B) .
C)
D) .
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Consider the homogeneous second-order Cauchy Euler differential equation
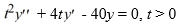
What is the solution of the initial value problem comprised of this differential equation and the initial conditions y(1) = α,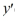 (1) = 4?
(1) = 4?
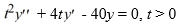
What is the solution of the initial value problem comprised of this differential equation and the initial conditions y(1) = α,
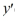 (1) = 4?
(1) = 4?
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Consider the homogeneous second-order Cauchy Euler differential equation
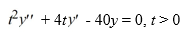
For what value α does the solution of the initial value problem comprised of this differential equation and the initial conditions y(1) = α,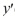 (1) = 6 tend to 0 as t → ∞? Enter your answer as a simplified fraction. If there is no such value of α, enter 'none'.
(1) = 6 tend to 0 as t → ∞? Enter your answer as a simplified fraction. If there is no such value of α, enter 'none'.
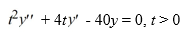
For what value α does the solution of the initial value problem comprised of this differential equation and the initial conditions y(1) = α,
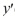 (1) = 6 tend to 0 as t → ∞? Enter your answer as a simplified fraction. If there is no such value of α, enter 'none'.
(1) = 6 tend to 0 as t → ∞? Enter your answer as a simplified fraction. If there is no such value of α, enter 'none'.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Consider the homogeneous second-order Cauchy Euler differential equation
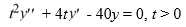
For what value α does the solution of the initial value problem comprised of this differential equation and the initial conditions y(1) = α,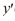 (1) = 4 remain bounded as
(1) = 4 remain bounded as 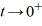 ? Enter your answer as a simplified fraction. If there is no such value of α, enter 'none'.
? Enter your answer as a simplified fraction. If there is no such value of α, enter 'none'.
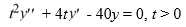
For what value α does the solution of the initial value problem comprised of this differential equation and the initial conditions y(1) = α,
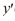 (1) = 4 remain bounded as
(1) = 4 remain bounded as 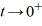 ? Enter your answer as a simplified fraction. If there is no such value of α, enter 'none'.
? Enter your answer as a simplified fraction. If there is no such value of α, enter 'none'.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
For what value(s) of is y = 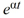 a solution of the second-order homogeneous differential equation
a solution of the second-order homogeneous differential equation 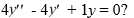
A)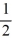
B) 0 and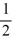
C) 0 and -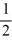
D) -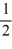
E) -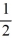 and
and 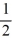
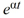 a solution of the second-order homogeneous differential equation
a solution of the second-order homogeneous differential equation 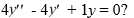
A)
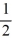
B) 0 and
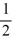
C) 0 and -
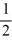
D) -
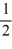
E) -
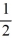 and
and 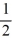

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Which of the following are solutions to the homogeneous second-order differential equation 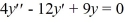 ?
?
Select all that apply.
A)
B)
C) , where and are arbitrary real constants
D)
E)
F) 42_00
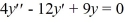 ?
?Select all that apply.
A)
B)
C) , where and are arbitrary real constants
D)
E)
F) 42_00

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Which of the following is the general solution of the homogeneous second-order differential equation 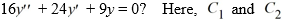
arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
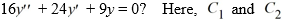
arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
What is the solution of this initial value problem:
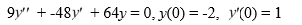
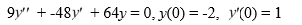

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Consider this initial value problem:
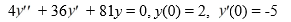
What is the solution of this initial value problem?
A)
B)
C)
D)
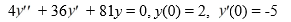
What is the solution of this initial value problem?
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Consider this initial value problem:
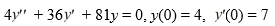
Which of the following is an accurate description of the long-term behavior of the solution?
A) y(t) tends to 0 as t .
B) y(t) is strictly increasing and approaches as t .
C) y(t) is strictly decreasing and approaches - as t .
D) y(t) becomes unbounded in both the positive and negative y-direction as t .
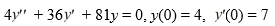
Which of the following is an accurate description of the long-term behavior of the solution?
A) y(t) tends to 0 as t .
B) y(t) is strictly increasing and approaches as t .
C) y(t) is strictly decreasing and approaches - as t .
D) y(t) becomes unbounded in both the positive and negative y-direction as t .

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Consider this initial value problem:
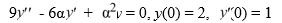
For what values of does the solution tend to 0 as t ?
A) all real numbers
B) all nonzero real numbers
C) all positive real numbers
D) all negative real numbers
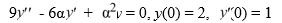
For what values of does the solution tend to 0 as t ?
A) all real numbers
B) all nonzero real numbers
C) all positive real numbers
D) all negative real numbers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Use the method of reduction of order to find a second solution of the differential equation 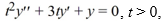 using the fact that y1 = t-1 is a solution. is a solution.
using the fact that y1 = t-1 is a solution. is a solution.
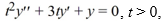 using the fact that y1 = t-1 is a solution. is a solution.
using the fact that y1 = t-1 is a solution. is a solution.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Use the method of reduction of order to find a second solution of the differential equation , 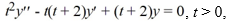 using the fact that y1 = t is a solution.
using the fact that y1 = t is a solution.
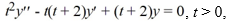 using the fact that y1 = t is a solution.
using the fact that y1 = t is a solution.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
What is the general solution of the homogeneous second-order Cauchy Euler differential equation 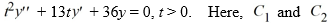 are arbitrary real constants.
are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
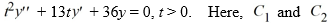 are arbitrary real constants.
are arbitrary real constants.A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
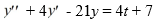
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
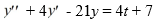
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
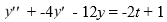
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is to be used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
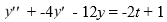
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is to be used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
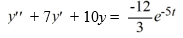
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
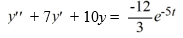
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
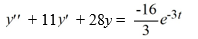
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is to be used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
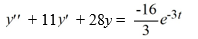
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is to be used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
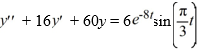
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here,C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
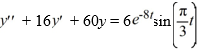
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here,C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
![<strong>Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation: Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is to be used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.</strong> A) Y(t)=A e^{8 t}\left[\sin \frac{\pi}{9} t+\cos \frac{\pi}{9} t\right]+B B) Y(t)=A e^{8 t} \sin \left(\frac{\pi}{9} t\right)+B C) Y(t)=e^{A t}(\sin (B t)+\cos (B t)) D) Y(t)=A e^{8 t} \sin \left(\frac{\pi}{9} t\right) E) Y(t)=e^{8 t}\left(A \sin \frac{\pi}{9} t+B \cos \frac{\pi}{9} t\right)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_704c_d3d1_9020_75ae4888001c_TBW1042_11.jpg)
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is to be used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
![<strong>Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation: Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is to be used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.</strong> A) Y(t)=A e^{8 t}\left[\sin \frac{\pi}{9} t+\cos \frac{\pi}{9} t\right]+B B) Y(t)=A e^{8 t} \sin \left(\frac{\pi}{9} t\right)+B C) Y(t)=e^{A t}(\sin (B t)+\cos (B t)) D) Y(t)=A e^{8 t} \sin \left(\frac{\pi}{9} t\right) E) Y(t)=e^{8 t}\left(A \sin \frac{\pi}{9} t+B \cos \frac{\pi}{9} t\right)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_704c_d3d1_9020_75ae4888001c_TBW1042_11.jpg)
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is to be used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Which of these is the general solution of the second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation 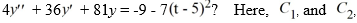
and all capital letters are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
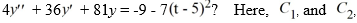
and all capital letters are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
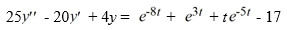
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
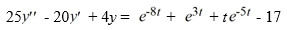
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
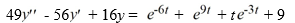
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
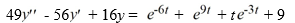
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
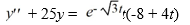
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
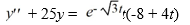
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
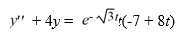
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
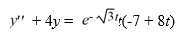
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
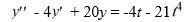
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
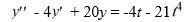
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
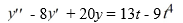
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
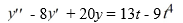
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
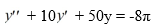
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
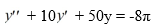
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
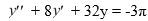
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
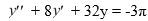
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
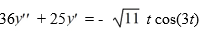
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
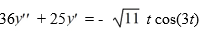
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
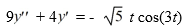
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
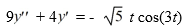
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
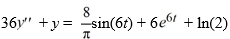
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
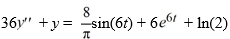
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation:
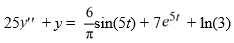
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
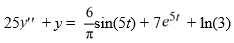
Which of these is a suitable form of a particular solution Y(t) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation if the method of undetermined coefficients is used? Here, all capital letters represent arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Which of these is the general solution of the second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation 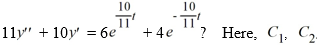 and all capital letters are arbitrary real constants.
and all capital letters are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
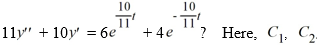 and all capital letters are arbitrary real constants.
and all capital letters are arbitrary real constants.A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Which of these is the general solution of the second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation 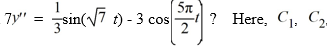 , and all capital letters are arbitrary real constants.
, and all capital letters are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
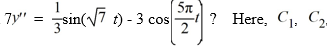 , and all capital letters are arbitrary real constants.
, and all capital letters are arbitrary real constants.A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Consider this second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation: 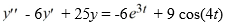 Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
A)
B)
C)
D)
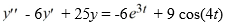 Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.
Which of the following is the form of the solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants.A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








