Deck 2: First-Order Differential Equations
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 2: First-Order Differential Equations
1
Find the general solution to the differential equation tan( 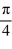 x)
x)
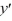 + y = -5 sin(
+ y = -5 sin( 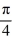 x).
x).
A)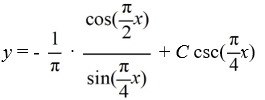
B)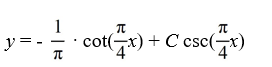
C)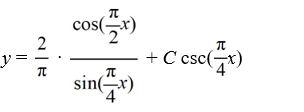
D)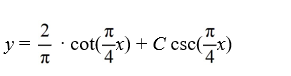
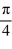 x)
x) 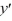 + y = -5 sin(
+ y = -5 sin( 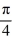 x).
x).A)
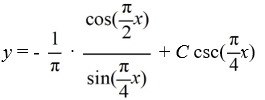
B)
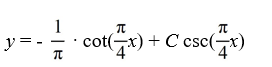
C)
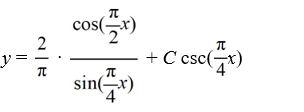
D)
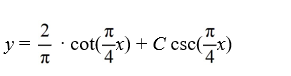
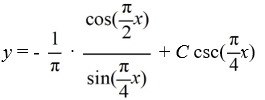
2
Find the general solution of the differential equation x  - 2y =
- 2y = 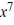 , x > 0.
, x > 0.
A) y = 4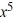 + C
+ C 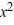
B) y = 4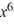 + C
+ C 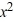
C) y =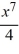 + C
+ C 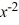
D) y =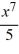 + C
+ C 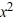
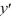 - 2y =
- 2y = 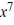 , x > 0.
, x > 0.A) y = 4
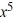 + C
+ C 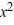
B) y = 4
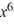 + C
+ C 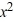
C) y =
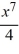 + C
+ C 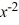
D) y =
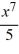 + C
+ C 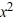
y = 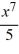 + C
+ C 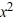
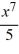 + C
+ C 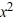
3
Which of the following first-order differential equations are linear in y? Select all that apply.
A) (x + 7)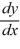 = -3y + 3
= -3y + 3
B)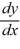 =
= 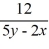
C)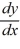 = 6x +
= 6x + 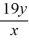 + 14
+ 14
D)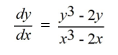
E)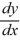 = 2y + 7y2
= 2y + 7y2
A) (x + 7)
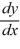 = -3y + 3
= -3y + 3B)
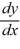 =
= 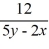
C)
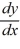 = 6x +
= 6x + 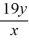 + 14
+ 14D)
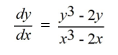
E)
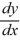 = 2y + 7y2
= 2y + 7y2(x + 7) 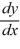 = -3y + 3
= -3y + 3
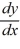 = 6x +
= 6x + 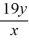 + 14
+ 14
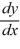 = -3y + 3
= -3y + 3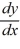 = 6x +
= 6x + 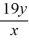 + 14
+ 14 4
Consider the differential equation 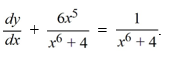
Which of the following is the general solution of this equation?
A)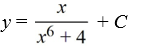
B)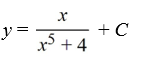
C)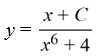
D)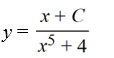
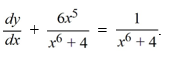
Which of the following is the general solution of this equation?
A)
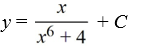
B)
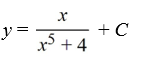
C)
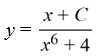
D)
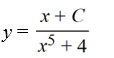

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Consider the differential equation 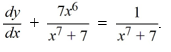
.What choice of the arbitrary constant in the general solution ensures that the solution curve passes through the point (1, 4)?
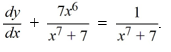
.What choice of the arbitrary constant in the general solution ensures that the solution curve passes through the point (1, 4)?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Consider the differential equation 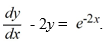
Which of these is the general solution to the equation?
A)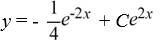
B)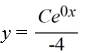
C)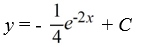
D)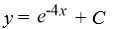
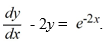
Which of these is the general solution to the equation?
A)
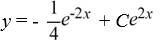
B)
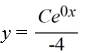
C)
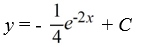
D)
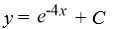

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Consider the differential equation 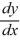 - 3y =
- 3y = 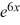 .
.
What choice of the arbitrary constant in the general solution ensures that the solution satisfies the initial condition y(0) = 7?
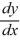 - 3y =
- 3y = 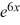 .
.What choice of the arbitrary constant in the general solution ensures that the solution satisfies the initial condition y(0) = 7?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
What is the general solution of this first-order differential equation?
x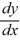 + 2y = 4
+ 2y = 4 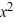
A)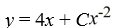
B)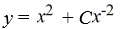
C)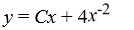
D)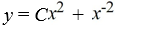
x
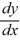 + 2y = 4
+ 2y = 4 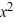
A)
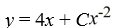
B)
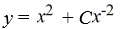
C)
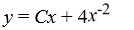
D)
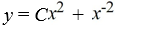

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Identify the integrating factor for this linear differential equation:
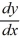 - 2y =
- 2y = 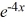
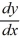 - 2y =
- 2y = 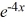

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Identify the integrating factor for this linear differential equation: 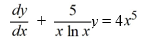
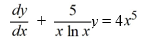

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Identify the integrating factor for this linear differential equation:
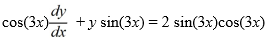
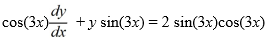

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Identify the integrating factor for this linear differential equation:
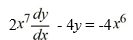
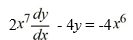

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Which of these is the general solution of this homogeneous differential equation?
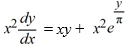
A)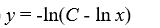
B)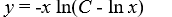
C)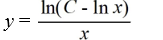
D)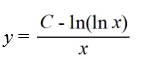
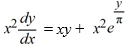
A)
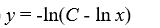
B)
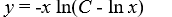
C)
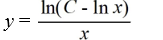
D)
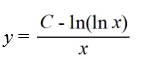

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Consider the differential equation
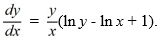
(i) Which of these is the general solution of this equation?
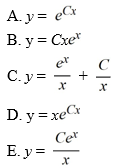
(ii) What choice of the arbitrary constant in the general solution ensures that the solution curve passes through the point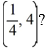
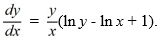
(i) Which of these is the general solution of this equation?
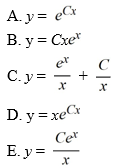
(ii) What choice of the arbitrary constant in the general solution ensures that the solution curve passes through the point
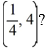

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
What is the general solution of the differential equation 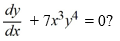
A)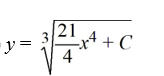
B)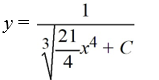
C)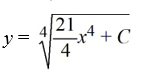
D)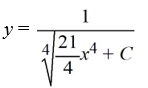
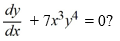
A)
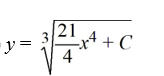
B)
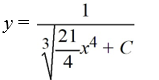
C)
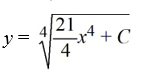
D)
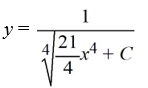

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
What is the general solution of the differential equation (1 + 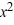 )
) 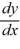 = 1 +
= 1 + 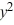 ?
?
A)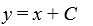
B)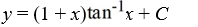
C)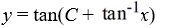
D)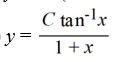
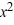 )
) 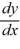 = 1 +
= 1 + 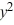 ?
?A)
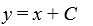
B)
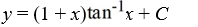
C)
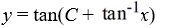
D)
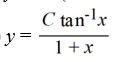

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
What is the general solution of the differential equation 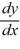 = y sin x + 6sin x?
= y sin x + 6sin x?
A)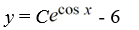
B)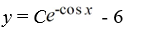
C)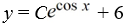
D)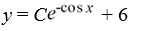
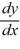 = y sin x + 6sin x?
= y sin x + 6sin x?A)
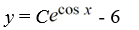
B)
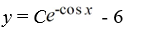
C)
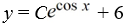
D)
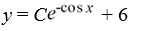

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
What is the solution of this initial value problem?
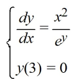
A)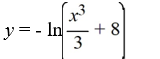
B)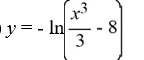
C)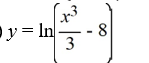
D)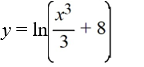
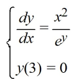
A)
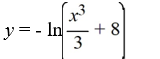
B)
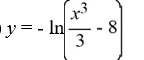
C)
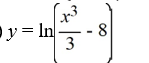
D)
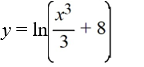

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
What is the solution of this initial value problem?
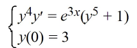
A)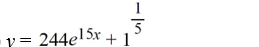
B)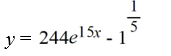
C)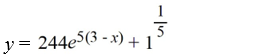
D)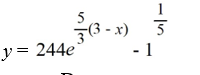
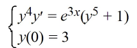
A)
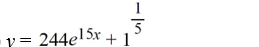
B)
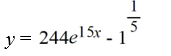
C)
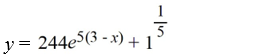
D)
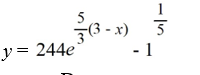

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Consider this initial value problem:
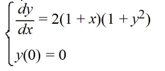
What is the solution of this initial value problem?
A)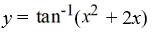
B)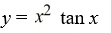
C)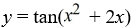
D)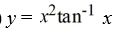
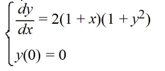
What is the solution of this initial value problem?
A)
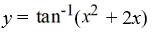
B)
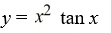
C)
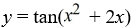
D)
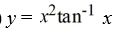

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Consider this initial value problem:
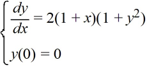
What is approximately the interval where the solution applies? Round each of the endpoints of the interval to the nearest hundredth.
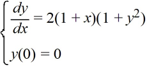
What is approximately the interval where the solution applies? Round each of the endpoints of the interval to the nearest hundredth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
What is the general solution of the differential equation 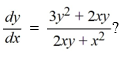
A)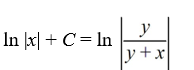
B)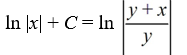
C)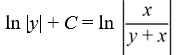
D)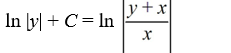
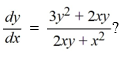
A)
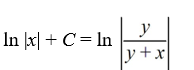
B)
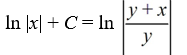
C)
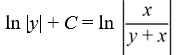
D)
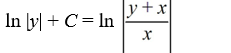

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Which of the following first-order differential equations are separable? Select all that apply.
A)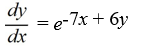
B)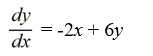
C)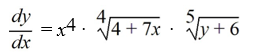
D)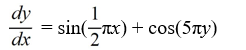
E)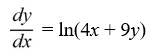
A)
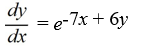
B)
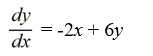
C)
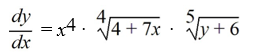
D)
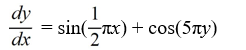
E)
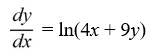

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
A city's water reservoir contains 7 billion cubic meters (bcm) of water. The purification system ensures that the concentration of pollutants remains constant at 0.5 kilograms per bcm, and sensors will trigger an alarm if the concentration of pollutants rises above 1 kilogram per bcm. Water flows in and out of the reservoir at the same rate of 0.20 bcm per day, and the concentration of pollutants in the inflow is 1.9 kilograms per bcm. At all times, the reservoir is well mixed.Set up a differential equation whose solution x(t) is the amount of pollutant in the reservoir at time t.
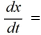 ________________
________________
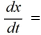 ________________
________________
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A city's water reservoir contains 7 billion cubic meters (bcm) of water. The purification system ensures that the concentration of pollutants remains constant at 0.3 kilograms per bcm, and sensors will trigger an alarm if the concentration of pollutants rises above 1 kilogram per bcm. Water flows in and out of the reservoir at the same rate of 0.20 bcm per day, and the concentration of pollutants in the inflow is 1.9 kilograms per bcm. At all times, the reservoir is well mixed.Set up a differential equation whose solution x(t) is the amount of pollutant in the reservoir at time t and find the general solution of the equation.x(t) = _________________

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
A city's water reservoir contains 7 billion cubic meters (bcm) of water. The purification system ensures that the concentration of pollutants remains constant at 0.6 kilograms per bcm, and sensors will trigger an alarm if the concentration of pollutants rises above 1 kilogram per bcm. Water flows in and out of the reservoir at the same rate of 0.25 bcm per day, and the concentration of pollutants in the inflow is 2 kilograms per bcm. At all times, the reservoir is well mixed.Set up a differential equation whose solution x(t) is the amount of pollutant in the reservoir at time t. Let t = 0 be the time when the purification system fails. What is x(0)?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
A city's water reservoir contains 6 billion cubic meters (bcm) of water. The purification system ensures that the concentration of pollutants remains constant at 0.2 kilograms per bcm, and sensors will trigger an alarm if the concentration of pollutants rises above 1 kilogram per bcm. Water flows in and out of the reservoir at the same rate of 0.20 bcm per day, and the concentration of pollutants in the inflow is 1.9 kilograms per bcm. At all times, the reservoir is well mixed.Set up a differential equation whose solution x(t) is the amount of pollutant in the reservoir at time t and find the particular solution of the differential equation satisfying the initial condition x(0) at time t = 0 when the purification system fails.x(t) = ____________________

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A city's water reservoir contains 6 billion cubic meters (bcm) of water. The purification system ensures that the concentration of pollutants remains constant at 0.5 kilograms per bcm, and sensors will trigger an alarm if the concentration of pollutants rises above 1 kilogram per bcm. Water flows in and out of the reservoir at the same rate of 0.25 bcm per day, and the concentration of pollutants in the inflow is 1.9 kilograms per bcm. At all times, the reservoir is well mixed.If the purification system fails, how much time (in days) elapses before the alarm is triggered? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth of a day.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
A ball is thrown from the top of a tall building with a speed of 12 meters per second. Suppose the ball hits the ground with a speed of 69 meters per second. (Recall that the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s2.)What is the time 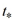 (in seconds) of impact? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth of a second.
(in seconds) of impact? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth of a second.
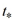 (in seconds) of impact? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth of a second.
(in seconds) of impact? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth of a second.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
A ball is thrown from the top of a tall building with a speed of 14 meters per second. Suppose the ball hits the ground with a speed of 69 meters per second. (Recall that the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s2.)How tall (in meters) is the building? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth of a meter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Which of these differential equations models the following situation?In a town with 4 million people, the rate at which the inhabitants hear a rumor is proportional to the number of people who have not heard the rumor. Use N(t) for the number of people (in millions) who have heard the rumor at time t.
A)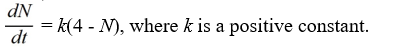
B)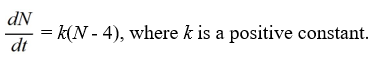
C)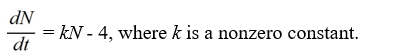
D)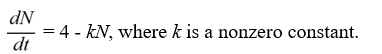
A)
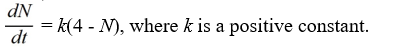
B)
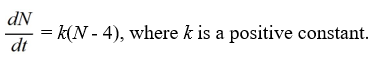
C)
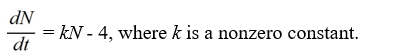
D)
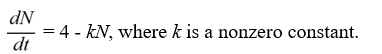

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
On another planet, a ball dropped from a height of 5 meters takes 3 seconds to hit the ground.
Let g be the acceleration due to gravity on this planet, v0 the initial velocity of the ball, and x0 the initial height of the ball above the ground. Write a formula for the height of the ball, x(t), above the ground at time t.
Let g be the acceleration due to gravity on this planet, v0 the initial velocity of the ball, and x0 the initial height of the ball above the ground. Write a formula for the height of the ball, x(t), above the ground at time t.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
On another planet, a ball dropped from a height of 5 meters takes 4 seconds to hit the ground.Determine the value of g.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
On another planet, a ball dropped from a height of 5 meters takes 4.5 seconds to hit the ground.Find the amount of time it takes the ball to hit the ground if it is dropped from a height of 122 meters. Round your answer to the nearest tenth of a second.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
A pie is moved from the oven at 475 degrees Fahrenheit to a freezer at 25 degrees Fahrenheit. After 10 minutes, the pie has cooled to 425 degrees Fahrenheit.
Let T(t) be the temperature of the pie t minutes after it has been moved to the freezer. Formulate an initial-value problem whose solution is T(t).
Let T(t) be the temperature of the pie t minutes after it has been moved to the freezer. Formulate an initial-value problem whose solution is T(t).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
A pie is moved from the oven at 425 degrees Fahrenheit to a freezer at 18 degrees Fahrenheit. After 10 minutes, the pie has cooled to 375 degrees Fahrenheit.Let T(t) be the temperature of the pie t minutes after it has been moved to the freezer. Formulate and solve an initial-value problem for T(t).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The amount of medicine in the bloodstream decays exponentially with a half-life of 7 hours. There must be at least 30 milligrams of medicine per pound of body weight to keep the patient safe during a one-hour procedure.
Set up an initial value problem whose solution is the amount of medicine, x(t) (measured in milligrams), in the bloodstream at time t. Let t = 0 correspond to the time when the procedure begins, and assume that x(0) = x0
Set up an initial value problem whose solution is the amount of medicine, x(t) (measured in milligrams), in the bloodstream at time t. Let t = 0 correspond to the time when the procedure begins, and assume that x(0) = x0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The amount of medicine in the bloodstream decays exponentially with a half-life of 4 hours. There must be at least 25 milligrams of medicine per pound of body weight to keep the patient safe during a one-hour procedure.
Set up an initial value problem whose solution is the amount of medicine, x(t) (measured in milligrams), in the bloodstream at time t. Let t = 0 correspond to the time when the procedure begins, and assume that x(0) = x0. Determine the exact value of proportionality constant in the differential equation from.
Set up an initial value problem whose solution is the amount of medicine, x(t) (measured in milligrams), in the bloodstream at time t. Let t = 0 correspond to the time when the procedure begins, and assume that x(0) = x0. Determine the exact value of proportionality constant in the differential equation from.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
The amount of medicine in the bloodstream decays exponentially with a half-life of 5 hours. There must be at least 25 milligrams of medicine per pound of body weight to keep the patient safe during a one-hour procedure.If a patient weighs 130 pounds, how much medicine should be administered at the beginning of the procedure? Round your answer to the nearest milligram.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
What is the general solution of the differential equation 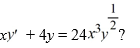
A)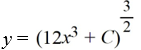
B)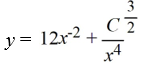
C)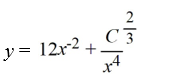
D)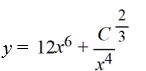
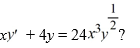
A)
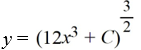
B)
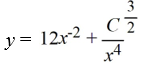
C)
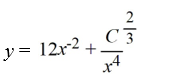
D)
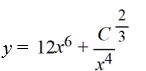

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Which of the following statements are true for this initial-value problem? Select all that apply 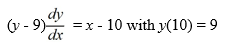
A) A locally unique solution is not guaranteed to exist by the local existence and uniqueness theorem for first-order differential equations because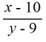 is not continuous at the point .
is not continuous at the point .
B) y = x - 19 is the only solution of this initial value problem.
C) y = x - 19 and y = 1 - x are both solutions of this initial value problem.
D) This initial value problem cannot have a solution because the conditions of the existence and uniqueness theorem for first-order linear equations are not satisfied.
E) The existence and uniqueness theorem for first-order linear equations ensures the existence of a unique local solution of this initial value problem because x - 10 is continuous at the point (10, 9).
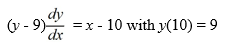
A) A locally unique solution is not guaranteed to exist by the local existence and uniqueness theorem for first-order differential equations because
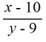 is not continuous at the point .
is not continuous at the point .B) y = x - 19 is the only solution of this initial value problem.
C) y = x - 19 and y = 1 - x are both solutions of this initial value problem.
D) This initial value problem cannot have a solution because the conditions of the existence and uniqueness theorem for first-order linear equations are not satisfied.
E) The existence and uniqueness theorem for first-order linear equations ensures the existence of a unique local solution of this initial value problem because x - 10 is continuous at the point (10, 9).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Which of the following is an accurate conclusion that can be made using the existence and uniqueness theorem for first-order differential equations for this initial value problem?
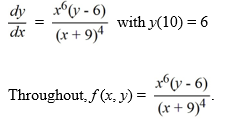
A) The initial value problem has a unique solution because f (x, y) is continuous on a rectangle containing the point (10, 6).
B) The initial value problem is not guaranteed to have a unique solution because fx (x, y) is not continuous when x = -9.
C) The initial value problem has a unique solution because both f (x, y) and fy(x, y) are continuous on a rectangle containing the point (10, 6).
D) The initial value problem does not have a solution because fx (x, y) and fy (x, y) are not both continuous on a rectangle containing the point (10, 6).
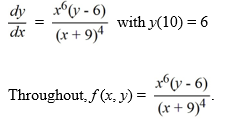
A) The initial value problem has a unique solution because f (x, y) is continuous on a rectangle containing the point (10, 6).
B) The initial value problem is not guaranteed to have a unique solution because fx (x, y) is not continuous when x = -9.
C) The initial value problem has a unique solution because both f (x, y) and fy(x, y) are continuous on a rectangle containing the point (10, 6).
D) The initial value problem does not have a solution because fx (x, y) and fy (x, y) are not both continuous on a rectangle containing the point (10, 6).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Which of the following is an accurate conclusion that can be made using the existence and uniqueness theorem for first-order nonlinear equations for this initial value problem?
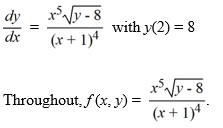
A) The initial value problem has a unique solution because f (x, y) is continuous on a rectangle containing the point (2, 8) on its boundary.
B) The initial value problem is not guaranteed to have a unique solution because fx (x, y) is not continuous when x = -1.
C) The initial value problem has a unique solution because both f (x, y) and fy (x, y) are continuous on a rectangle containing the point (2, 8).
D) The initial value problem is not guaranteed to have a unique local solution because there is no rectangle surrounding the point (2, 8) on which both f (x, y) and fy(x, y) are continuous.
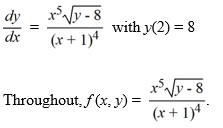
A) The initial value problem has a unique solution because f (x, y) is continuous on a rectangle containing the point (2, 8) on its boundary.
B) The initial value problem is not guaranteed to have a unique solution because fx (x, y) is not continuous when x = -1.
C) The initial value problem has a unique solution because both f (x, y) and fy (x, y) are continuous on a rectangle containing the point (2, 8).
D) The initial value problem is not guaranteed to have a unique local solution because there is no rectangle surrounding the point (2, 8) on which both f (x, y) and fy(x, y) are continuous.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Which of these is the general solution of the differential equation 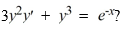
A)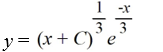
B)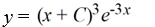
C)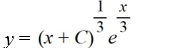
D)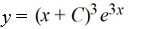
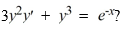
A)
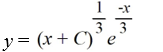
B)
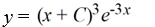
C)
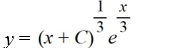
D)
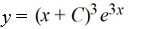

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Consider the initial value problem
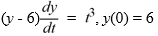
What can be said about the applicability of the existence and uniqueness theorem to this initial value problem?
A) The theorem does not apply because the initial condition is prescribed at t = 0 and the function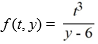 equals 0 when evaluated at such a point.
equals 0 when evaluated at such a point.
B) The theorem does not apply because the function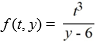 is discontinuous at any point of the form (t, 6).
is discontinuous at any point of the form (t, 6).
C) The theorem applies and ensures the existence of a unique local solution of this initial value problem.
D) The theorem does not apply because the differential equation is nonlinear.
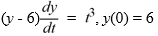
What can be said about the applicability of the existence and uniqueness theorem to this initial value problem?
A) The theorem does not apply because the initial condition is prescribed at t = 0 and the function
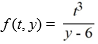 equals 0 when evaluated at such a point.
equals 0 when evaluated at such a point.B) The theorem does not apply because the function
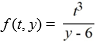 is discontinuous at any point of the form (t, 6).
is discontinuous at any point of the form (t, 6).C) The theorem applies and ensures the existence of a unique local solution of this initial value problem.
D) The theorem does not apply because the differential equation is nonlinear.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Consider the initial value problem
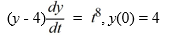
Find all solutions of this initial value problem.
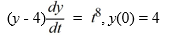
Find all solutions of this initial value problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Consider the autonomous differential equation
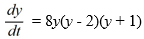
Which of these is an equilibrium solution of this differential equation? Select all that apply.
A) y = 0
B) y = 2
C) y = 1
D) y = -2
E) y = -1
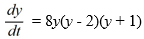
Which of these is an equilibrium solution of this differential equation? Select all that apply.
A) y = 0
B) y = 2
C) y = 1
D) y = -2
E) y = -1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Consider the autonomous differential equation
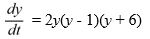
Which of the following statements are true? Select all that apply.
A) y = 1 is asymptotically stable.
B) y = -6 is unstable.
C) y = 0 is asymptotically stable.
D) y = 6 is unstable.
E) y = 1 is semi-stable.
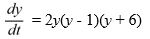
Which of the following statements are true? Select all that apply.
A) y = 1 is asymptotically stable.
B) y = -6 is unstable.
C) y = 0 is asymptotically stable.
D) y = 6 is unstable.
E) y = 1 is semi-stable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Consider the autonomous differential equation
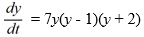
Determine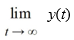 for the initial condition y(t0 ) = (8, -4).
for the initial condition y(t0 ) = (8, -4).
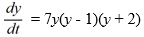
Determine
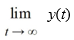 for the initial condition y(t0 ) = (8, -4).
for the initial condition y(t0 ) = (8, -4).
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Consider the autonomous differential equation
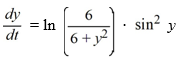
Which of these is a complete list of the equilibrium solutions of this differential equation?
A) , where is an integer
B)
C) , where is an integer
D) , where is an integer
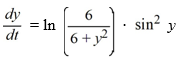
Which of these is a complete list of the equilibrium solutions of this differential equation?
A) , where is an integer
B)
C) , where is an integer
D) , where is an integer

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Consider the autonomous differential equation
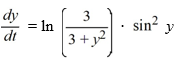
Which of the following statements is true?
A) All nonequilibrium solutions tend toward - as t .
B) y = 2k is stable and y = (2k + 1) is unstable, for any integer k.
C) y = 2k is unstable and y = (2k + 1) is stable, for any integer k.
D) All equilibrium solutions are semi-stable.
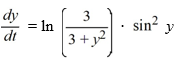
Which of the following statements is true?
A) All nonequilibrium solutions tend toward - as t .
B) y = 2k is stable and y = (2k + 1) is unstable, for any integer k.
C) y = 2k is unstable and y = (2k + 1) is stable, for any integer k.
D) All equilibrium solutions are semi-stable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Consider the autonomous differential equation
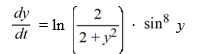
Determine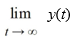 for the initial condition
for the initial condition 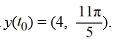 Enter the exact answer.
Enter the exact answer.
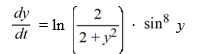
Determine
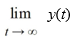 for the initial condition
for the initial condition 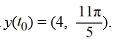 Enter the exact answer.
Enter the exact answer.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Consider the autonomous differential equation
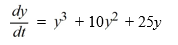
Which of these is an equilibrium solution of this differential equation? Select all that apply.
A) y = -5
B) y = 5
C) y = 0
D) y = -10
E) y = 10
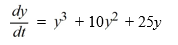
Which of these is an equilibrium solution of this differential equation? Select all that apply.
A) y = -5
B) y = 5
C) y = 0
D) y = -10
E) y = 10

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Consider the autonomous differential equation
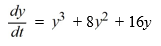
dentify the following statement as TRUE or FALSE:A solution curve passing through the point (0, -2) tends to 0 as t .
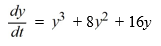
dentify the following statement as TRUE or FALSE:A solution curve passing through the point (0, -2) tends to 0 as t .

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by
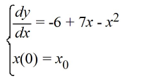
Which of these is an equilibrium solution of this differential equation? Select all that apply.
A) y = 0
B) y = -1
C) y = 6
D) y = 1
E) y = -6
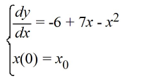
Which of these is an equilibrium solution of this differential equation? Select all that apply.
A) y = 0
B) y = -1
C) y = 6
D) y = 1
E) y = -6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by
![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f01_9020_7f6daacd1e54_TBW1042_00.jpg)
For what values of![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f02_9020_0b7e9743c9ee_TBW1042_11.jpg) does the fish population become extinct?
does the fish population become extinct?
A) For all![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f03_9020_c3a2fcaf95d5_TBW1042_11.jpg) in (0, 1].
in (0, 1].
B) For all![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f04_9020_01c9a87b21b1_TBW1042_11.jpg) in (0, 1).
in (0, 1).
C) For all![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f05_9020_611beaccef4b_TBW1042_11.jpg) in (0, 5).
in (0, 5).
D) For all![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f06_9020_a3faa61f8beb_TBW1042_11.jpg) in (0, 5].
in (0, 5].
E) For all![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f07_9020_6dbddfd7f700_TBW1042_11.jpg) in (1, 5).
in (1, 5).
F) For all![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f08_9020_1d4b8965d75f_TBW1042_11.jpg) in [1, 5].
in [1, 5].
![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f01_9020_7f6daacd1e54_TBW1042_00.jpg)
For what values of
![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f02_9020_0b7e9743c9ee_TBW1042_11.jpg) does the fish population become extinct?
does the fish population become extinct?A) For all
![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f03_9020_c3a2fcaf95d5_TBW1042_11.jpg) in (0, 1].
in (0, 1].B) For all
![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f04_9020_01c9a87b21b1_TBW1042_11.jpg) in (0, 1).
in (0, 1).C) For all
![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f05_9020_611beaccef4b_TBW1042_11.jpg) in (0, 5).
in (0, 5).D) For all
![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f06_9020_a3faa61f8beb_TBW1042_11.jpg) in (0, 5].
in (0, 5].E) For all
![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f07_9020_6dbddfd7f700_TBW1042_11.jpg) in (1, 5).
in (1, 5).F) For all
![<strong>A model of a fishery which grows logistically and is harvested at a constant rate is given by For what values of does the fish population become extinct?</strong> A) For all in (0, 1]. B) For all in (0, 1). C) For all in (0, 5). D) For all in (0, 5]. E) For all in (1, 5). F) For all in [1, 5].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1042/11eeb833_7050_2f08_9020_1d4b8965d75f_TBW1042_11.jpg) in [1, 5].
in [1, 5].
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Consider the differential equation 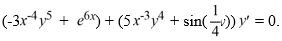
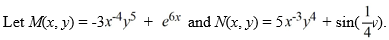
Which of the following statements regarding this differential equation is true?
A) It is not exact because .
B) It is exact because .
C) It is exact because .
D) It is not exact because .
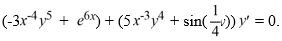
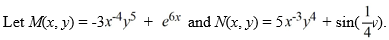
Which of the following statements regarding this differential equation is true?
A) It is not exact because .
B) It is exact because .
C) It is exact because .
D) It is not exact because .

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Consider the differential equation 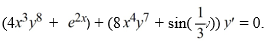
What is the general solution of this differential equation?
A)
B)
C)
D)
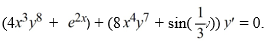
What is the general solution of this differential equation?
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Solve this initial value problem:
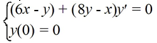
A)
B)
C)
D)
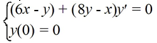
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Which of the following first-order differential equations are exact? Select all that apply.
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Which of the following is the general solution of the differential equation
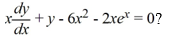
A)
B)
C)
D)
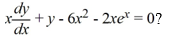
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
For what value of K is this differential equation exact? Enter the exact answer, not a decimal approximation.
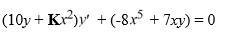
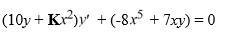

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
For what value of K is this differential equation exact? Enter the exact answer, not a decimal approximation
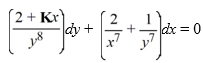
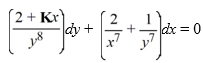

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Consider the differential equation 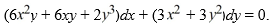 Find an integrating factor μ(x) so that the following differential equation is exact:
Find an integrating factor μ(x) so that the following differential equation is exact:
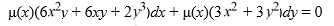
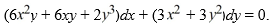 Find an integrating factor μ(x) so that the following differential equation is exact:
Find an integrating factor μ(x) so that the following differential equation is exact: 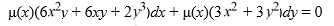

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Consider the following initial value problem:
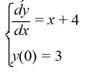
(i) Use Euler's method with two equal steps to find an approximation of y(1). Enter the exact answer, not an approximation.
(ii) Solve the initial value problem and compute the solution at x = 1. Enter the exact answer, not an approximation.
(iii) What is the error in Euler's method in making this approximation?
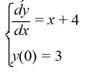
(i) Use Euler's method with two equal steps to find an approximation of y(1). Enter the exact answer, not an approximation.
(ii) Solve the initial value problem and compute the solution at x = 1. Enter the exact answer, not an approximation.
(iii) What is the error in Euler's method in making this approximation?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Consider the following initial value problem:
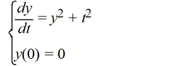
Determine the first two iterations of Picard's iteration method.
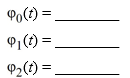
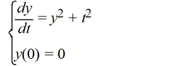
Determine the first two iterations of Picard's iteration method.
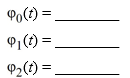

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Consider the difference equation 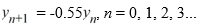
Find the explicit solution of this difference equation in terms of y0 .
A)
B)
C)
D)
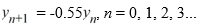
Find the explicit solution of this difference equation in terms of y0 .
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Consider the difference equation 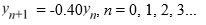
Which of the following is an accurate description of the behavior of the solutions to this difference equation in terms of y0?
A) If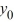 0, then the sequence {
0, then the sequence { 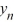 } diverges in an oscillatory manner.
} diverges in an oscillatory manner.
B) If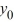 > 0, then the sequence {} converges to 0 as n ; for all other choices of , the sequence {
> 0, then the sequence {} converges to 0 as n ; for all other choices of , the sequence { 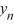 } diverges.
} diverges.
C) If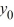 0, then the sequence {
0, then the sequence { 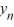 } diverges toward - as n .
} diverges toward - as n .
D) The sequence {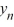 } converges to 0 as n for all values of
} converges to 0 as n for all values of 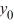 .
.
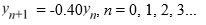
Which of the following is an accurate description of the behavior of the solutions to this difference equation in terms of y0?
A) If
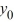 0, then the sequence {
0, then the sequence { 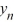 } diverges in an oscillatory manner.
} diverges in an oscillatory manner.B) If
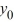 > 0, then the sequence {} converges to 0 as n ; for all other choices of , the sequence {
> 0, then the sequence {} converges to 0 as n ; for all other choices of , the sequence { 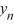 } diverges.
} diverges.C) If
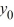 0, then the sequence {
0, then the sequence { 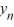 } diverges toward - as n .
} diverges toward - as n .D) The sequence {
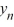 } converges to 0 as n for all values of
} converges to 0 as n for all values of 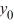 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Consider the difference equation 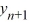 = 0.50
= 0.50 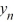 + 6, n = 0, 1, 2, 3...Find the explicit solution of this difference equation in terms of
+ 6, n = 0, 1, 2, 3...Find the explicit solution of this difference equation in terms of 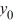 .
.
A)
B)
C)
D)
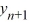 = 0.50
= 0.50 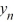 + 6, n = 0, 1, 2, 3...Find the explicit solution of this difference equation in terms of
+ 6, n = 0, 1, 2, 3...Find the explicit solution of this difference equation in terms of 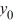 .
.A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Consider the difference equation 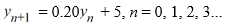
Which of the following is an accurate description of the behavior of the solutions to this difference equation in terms of y0 . ?
A) If y0 (\neq\) 0, then the sequence {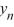 } diverges to as n .
} diverges to as n .
B) The sequence {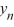 } converges to 6.25 as n for all values of .
} converges to 6.25 as n for all values of .
C) If y0 > 0, then the sequence {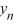 } converges to 6.25 as n ; for all other choices of y0 , the sequence {
} converges to 6.25 as n ; for all other choices of y0 , the sequence { 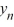 } converges to 0 as n .
} converges to 0 as n .
D) D) If y0 0, then the sequence {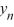 } converges to 6.25 as n ; for all other choices of y0 , the sequence {
} converges to 6.25 as n ; for all other choices of y0 , the sequence { 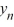 } converges to 0 as n .
} converges to 0 as n .
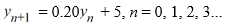
Which of the following is an accurate description of the behavior of the solutions to this difference equation in terms of y0 . ?
A) If y0 (\neq\) 0, then the sequence {
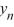 } diverges to as n .
} diverges to as n .B) The sequence {
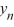 } converges to 6.25 as n for all values of .
} converges to 6.25 as n for all values of .C) If y0 > 0, then the sequence {
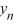 } converges to 6.25 as n ; for all other choices of y0 , the sequence {
} converges to 6.25 as n ; for all other choices of y0 , the sequence { 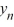 } converges to 0 as n .
} converges to 0 as n .D) D) If y0 0, then the sequence {
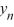 } converges to 6.25 as n ; for all other choices of y0 , the sequence {
} converges to 6.25 as n ; for all other choices of y0 , the sequence { 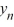 } converges to 0 as n .
} converges to 0 as n .
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
What is the two-parameter family of solutions of the second-order differential equation
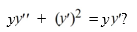
A)
B)
C)
D)
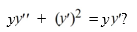
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
What is the two-parameter family of solutions of the second-order differential equation
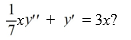
A)
B)
C)
D)
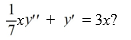
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
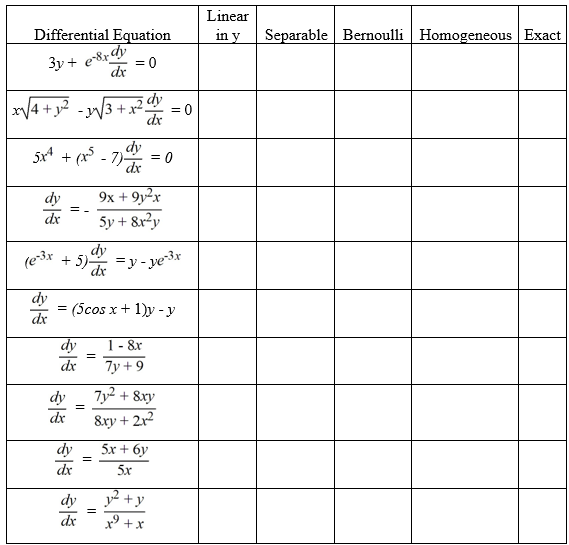
For each differential equation, select each category in which it falls.


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 73 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








