Deck 1: Introduction
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/28
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 1: Introduction
1
A portion of the direction field for the differential equation 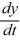 = f(y) is shown below:
= f(y) is shown below:
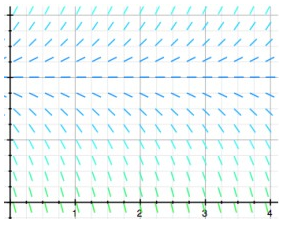
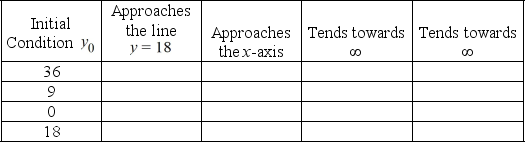
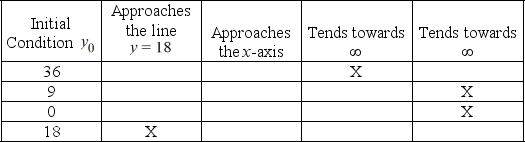
The dotted horizontal line has equation y = 18. Fill in the following chart to indicate the behavior as t of the solution y(t) of the differential equation corresponding to each initial condition
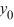 .
.
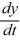 = f(y) is shown below:
= f(y) is shown below:
The dotted horizontal line has equation y = 18. Fill in the following chart to indicate the behavior as t of the solution y(t) of the differential equation corresponding to each initial condition
 .
.
2
A portion of the direction field for the differential equation  = f(y) is shown below:
= f(y) is shown below:
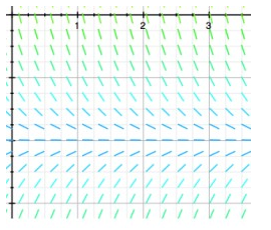
The dotted horizontal line has equation y = -7. Which of the following statements are true? Select all that apply.
A) y(t) = 0 is the solution to the initial-value problem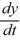 = f(y), y(0) = 0.
= f(y), y(0) = 0.
B) y(t) = -7 is the only equilibrium solution.
C) There is no solution of the initial-value problem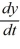 = f(y), y(0) =
= f(y), y(0) = 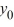 when
when 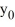 = -7.
= -7.
D) Every solution curve y(t) is increasing toward a negative limit as t .
E) Every solution curve y(t) tends towards -7 as t .
F)F(y) cannot be a linear function of y.
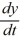 = f(y) is shown below:
= f(y) is shown below:
The dotted horizontal line has equation y = -7. Which of the following statements are true? Select all that apply.
A) y(t) = 0 is the solution to the initial-value problem
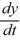 = f(y), y(0) = 0.
= f(y), y(0) = 0.B) y(t) = -7 is the only equilibrium solution.
C) There is no solution of the initial-value problem
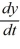 = f(y), y(0) =
= f(y), y(0) = 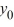 when
when 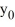 = -7.
= -7.D) Every solution curve y(t) is increasing toward a negative limit as t .
E) Every solution curve y(t) tends towards -7 as t .
F)F(y) cannot be a linear function of y.
y(t) = -7 is the only equilibrium solution.
Every solution curve y(t) tends towards -7 as t .
F(y) cannot be a linear function of y.
Every solution curve y(t) tends towards -7 as t .
F(y) cannot be a linear function of y.
3
Which of the following pairs of values of A and B are such that all solutions of the differential equation 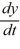 = Ay + B are such that
= Ay + B are such that 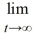 y(t) = 7?
y(t) = 7?
Select all that apply.
A) A = -2, B = 14
B) A = -7, B = 1
C) A = -1, B = 7
D) A = 1, B = -7
E) A = -3, B = 21
F) A = -2, B = -14
G) A = 2, B = -14
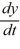 = Ay + B are such that
= Ay + B are such that 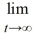 y(t) = 7?
y(t) = 7? Select all that apply.
A) A = -2, B = 14
B) A = -7, B = 1
C) A = -1, B = 7
D) A = 1, B = -7
E) A = -3, B = 21
F) A = -2, B = -14
G) A = 2, B = -14
A = -2, B = 14
A = -1, B = 7
A = -3, B = 21
A = -1, B = 7
A = -3, B = 21
4
Which of the following pairs of values of A and B are such that all solutions of the differential equation 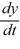 = Ay + B diverge away from the line y = 10 as t ? Select all that apply.
= Ay + B diverge away from the line y = 10 as t ? Select all that apply.
A) A = -2, B = 20
B) A = 3, B = -30
C) A = 1, B = -10
D) A = -1, B = 10
E) A = -2, B = -20
F) A = 10, B = -1
G) A = 2, B = -20
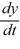 = Ay + B diverge away from the line y = 10 as t ? Select all that apply.
= Ay + B diverge away from the line y = 10 as t ? Select all that apply.A) A = -2, B = 20
B) A = 3, B = -30
C) A = 1, B = -10
D) A = -1, B = 10
E) A = -2, B = -20
F) A = 10, B = -1
G) A = 2, B = -20

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Eight differential equations and four slope fields are given below
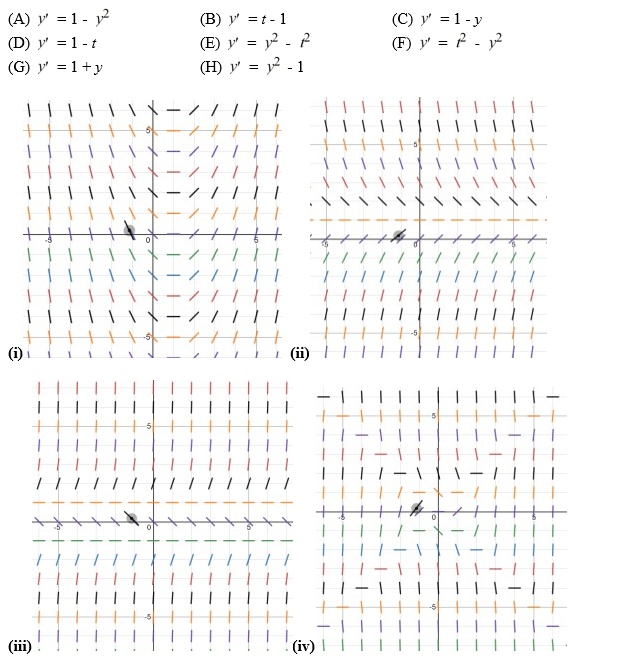
Which of the following are the zero isoclines for the differential equation in (A)? Select all that apply.
A) y = 0
B) y = 1
C) y = -1
D) y = t
E) y = -t

Which of the following are the zero isoclines for the differential equation in (A)? Select all that apply.
A) y = 0
B) y = 1
C) y = -1
D) y = t
E) y = -t

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Eight differential equations and four slope fields are given below.
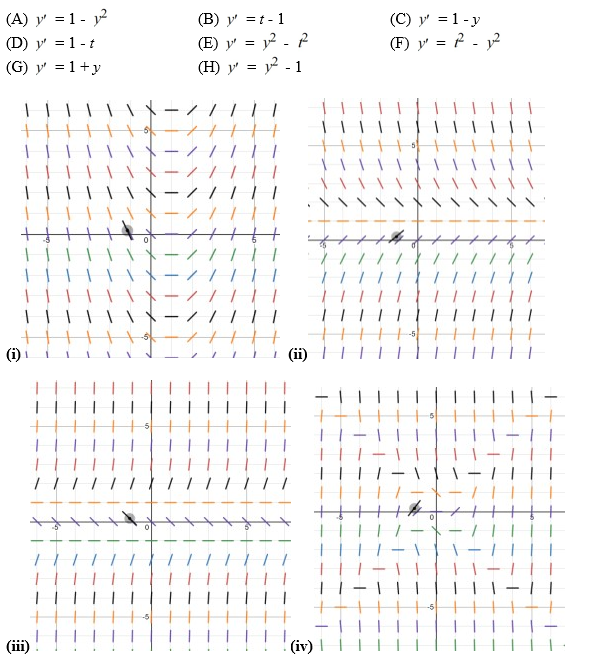
Determine the differential equation that corresponds to each slope field. Fill in the correct letter next to each number below:
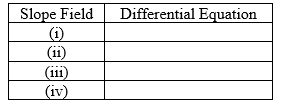

Determine the differential equation that corresponds to each slope field. Fill in the correct letter next to each number below:


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A pond initially contains 70,000 gallons of water and an unknown amount of pesticide. Water containing 0.07 grams of pesticide per gallon flows into the pond at a rate of 360 gallons per hour. The mixture flows out of the pond at the same rate, so the amount of water in the pond remains constant. Assume the pesticide is uniformly mixed throughout the pond.
Which of these is the differential equation for the amount of pesticide, P(t), in the pond at any time t?
A)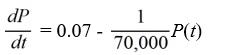
B)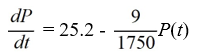
C)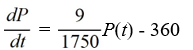
D)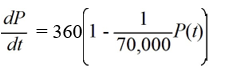
Which of these is the differential equation for the amount of pesticide, P(t), in the pond at any time t?
A)
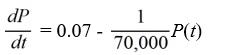
B)
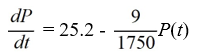
C)
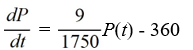
D)
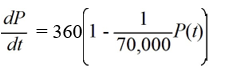

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A pond initially contains 150,000 gallons of water and an unknown amount of pesticide. Water containing 0.08 grams of pesticide per gallon flows into the pond at a rate of 400 gallons per hour. The mixture flows out of the pond at the same rate, so the amount of water in the pond remains constant. Assume the pesticide is uniformly mixed throughout the pond.How much pesticide will be in the pond after a very long time? ________ grams.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
A pond initially contains 70,000 gallons of water and an unknown amount of pesticide. Water containing 0.05 grams of pesticide per gallon flows into the pond at a rate of 300 gallons per hour. The mixture flows out of the pond at the same rate, so the amount of water in the pond remains constant. Assume the pesticide is uniformly mixed throughout the pond.Which of these is the general solution of the differential equation for the amount of pesticide, P(t), in the pond at any time t?
A)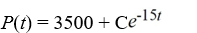
B)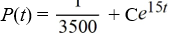
C)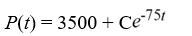
D)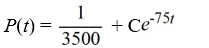
A)
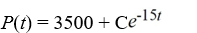
B)
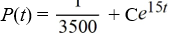
C)
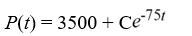
D)
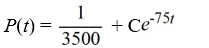

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
A pond initially contains 100,000 gallons of water and an unknown amount of pesticide. Water containing 0.07 grams of pesticide per gallon flows into the pond at a rate of 320 gallons per hour. The mixture flows out of the pond at the same rate, so the amount of water in the pond remains constant. Assume the pesticide is uniformly mixed throughout the pond.Which of these is the solution of the initial-value problem comprised of the differential equation for the amount of pesticide, P(t), in the pond at any time t and the initial condition P(0) = P0?
A)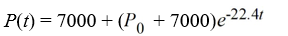
B)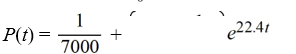
C)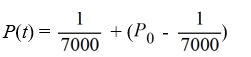
D)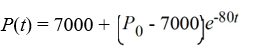
A)
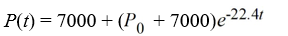
B)
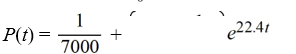
C)
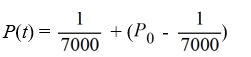
D)
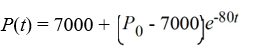

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
A pond initially contains 120,000 gallons of water and an unknown amount of pesticide. Water containing 0.08 grams of pesticide per gallon flows into the pond at a rate of 260 gallons per hour. The mixture flows out of the pond at the same rate, so the amount of water in the pond remains constant. Assume the pesticide is uniformly mixed throughout the pond.Which of these equations would you need to solve to find the time T (in hours) after which P(t) is within 2% of its limiting behavior?
A)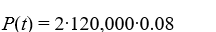
B)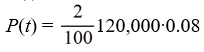
C)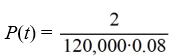
D)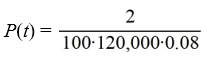
A)
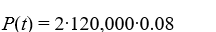
B)
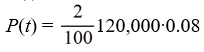
C)
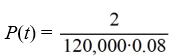
D)
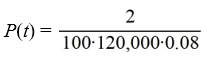

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Newton's Law of Cooling states that the temperature of an object changes at a rate proportional to the difference between the temperature of the object itself and the temperature of its surroundings (typically the ambient temperature). Suppose the ambient temperature is 77°F and the rate constant is 0.09 per minute.Which of these is a differential equation for the temperature of the object, T(t), at any time t?
A)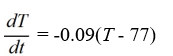
B)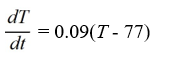
C)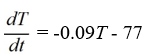
D)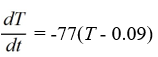
E)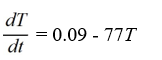
A)
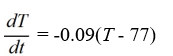
B)
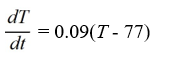
C)
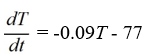
D)
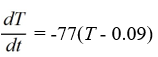
E)
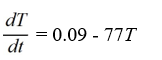

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Newton's Law of Cooling states that the temperature of an object changes at a rate proportional to the difference between the temperature of the object itself and the temperature of its surroundings (typically the ambient temperature). Suppose the ambient temperature is 72°F and the rate constant is 0.11 per minute.What is the general solution of the differential equation for the temperature of the object, T(t), at any time t?
A)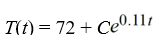
B)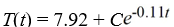
C)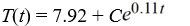
D)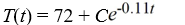
E)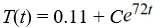
A)
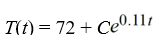
B)
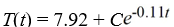
C)
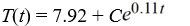
D)
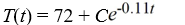
E)
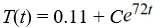

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Newton's Law of Cooling states that the temperature of an object changes at a rate proportional to the difference between the temperature of the object itself and the temperature of its surroundings (typically the ambient temperature). Suppose the ambient temperature is 72°F and the rate constant is 0.1 per minute.Suppose the temperature of the object is initially 107°F. What is the solution to the initial-value problem comprised of the differential equation for the temperature of the object, T(t), at any time t and the initial condition T(0) = 107?
A)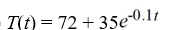
B)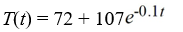
C)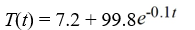
D)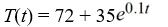
E)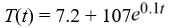
A)
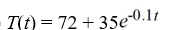
B)
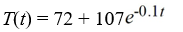
C)
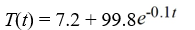
D)
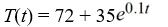
E)
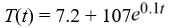

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Newton's Law of Cooling states that the temperature of an object changes at a rate proportional to the difference between the temperature of the object itself and the temperature of its surroundings (typically the ambient temperature). Suppose the ambient temperature is 72°F and the rate constant is 0.12 per minute.Suppose the temperature of the object is initially 97°F. Given the initial condition T(0) = 97, how many minutes does it take the object to reach a temperature of 80.3°F? Round your answer to the nearest tenth of a minute.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
An antibiotic is being administered intravenously to a patient. Fluid containing 6.5 mg/ of the antibiotic enters the patient's bloodstream at a rate of 100 /hour. The antibiotic is absorbed by the body or otherwise leaves the bloodstream at a rate proportional to the amount present, with a rate constant of 0.4 per hour. Assume the antibiotic is always uniformly distributed throughout the bloodstream.Which of these is a differential equation for the amount of antibiotic, A(t), in the bloodstream at any time t?
A)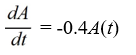
B)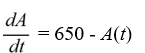
C)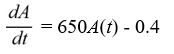
D)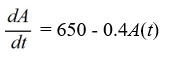
A)
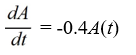
B)
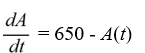
C)
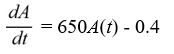
D)
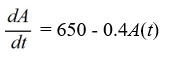

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
An antibiotic is being administered intravenously to a patient. Fluid containing 8.0 mg/Cm3 of the antibiotic enters the patient's bloodstream at a rate of 100 Cm3/hour. The antibiotic is absorbed by the body or otherwise leaves the bloodstream at a rate proportional to the amount present, with a rate constant of 0.6 per hour. Assume the antibiotic is always uniformly distributed throughout the bloodstream.How much of the antibiotic is present in the bloodstream after a very long time? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth of a milligram.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
An antibiotic is being administered intravenously to a patient. Fluid containing 4.5 mg/Cm3 of the antibiotic enters the patient's bloodstream at a rate of 100 Cm3/hour. The antibiotic is absorbed by the body or otherwise leaves the bloodstream at a rate proportional to the amount present, with a rate constant of 0.5 per hour. Assume the antibiotic is always uniformly distributed throughout the bloodstream.What is the general solution to the differential equation for the amount of antibiotic, A(t), in the bloodstream at any time t?
A)
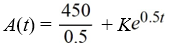
B)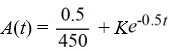
C)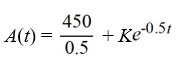
D)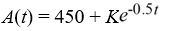
E)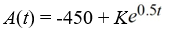
A)
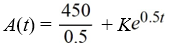
B)
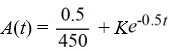
C)
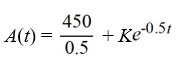
D)
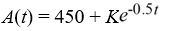
E)
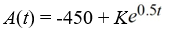

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Consider the differential equation x 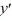 =
= 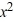 + y.
+ y.
What is the general solution of this equation?
A) y = C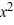 + x
+ x
B) y =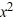 + Cx
+ Cx
C) y = C(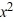 + x)
+ x)
D) y =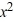 + x + C
+ x + C
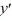 =
= 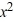 + y.
+ y.What is the general solution of this equation?
A) y = C
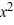 + x
+ xB) y =
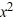 + Cx
+ CxC) y = C(
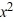 + x)
+ x)D) y =
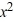 + x + C
+ x + C
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Consider the differential equation x = 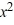 + y.What is the value of the constant C in the general solution corresponding to the initial condition y(2) = 0?
+ y.What is the value of the constant C in the general solution corresponding to the initial condition y(2) = 0?
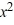 + y.What is the value of the constant C in the general solution corresponding to the initial condition y(2) = 0?
+ y.What is the value of the constant C in the general solution corresponding to the initial condition y(2) = 0?
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
For each of the following ordinary differential equations, identify the order and indicate whether it is linear or nonlinear.
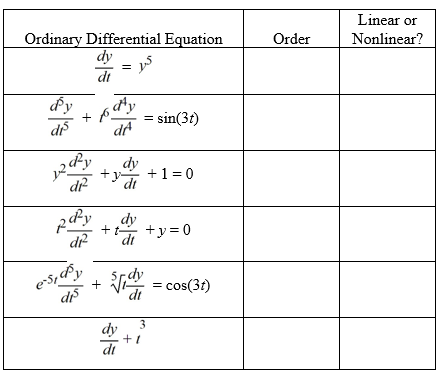


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
A model for the vertical flight of a projectile launched from the ground with velocity V in the absence of air resistance is
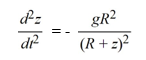
From what single term in this equation can you infer the order of the equation?
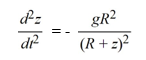
From what single term in this equation can you infer the order of the equation?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
A model for the vertical flight of a projectile launched from the ground with velocity V in the absence of air resistance is
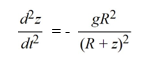
Is this differential equation linear or nonlinear?
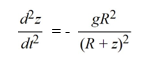
Is this differential equation linear or nonlinear?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
A model for the vertical flight of a projectile launched from the ground with velocity V in the absence of air resistance is
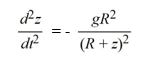
Which of these initial conditions complete the description of the situation? Select all that apply.
A)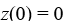
B)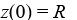
C)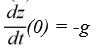
D)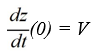
E)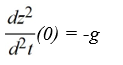
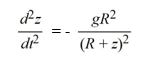
Which of these initial conditions complete the description of the situation? Select all that apply.
A)
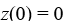
B)
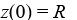
C)
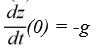
D)
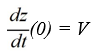
E)
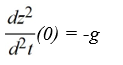

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which of the following are solutions to the differential equation 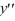 - 16y = 0? Select all that apply.
- 16y = 0? Select all that apply.
A)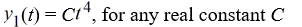
B)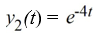
C)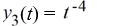
D)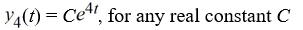
E)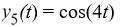
F)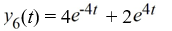
G)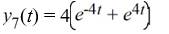
H)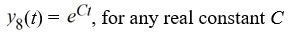
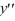 - 16y = 0? Select all that apply.
- 16y = 0? Select all that apply.A)
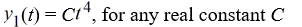
B)
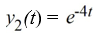
C)
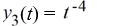
D)
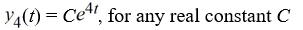
E)
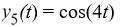
F)
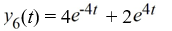
G)
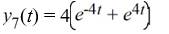
H)
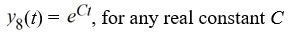

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Which of the following are solutions to the differential equation 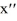 - 2
- 2 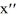 = 0? Select all that apply
= 0? Select all that apply
A)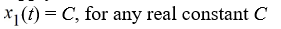
B)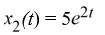
C)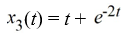
D)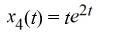
E)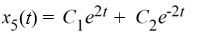
F)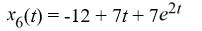
G)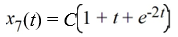
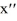 - 2
- 2 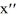 = 0? Select all that apply
= 0? Select all that applyA)
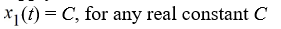
B)
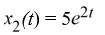
C)
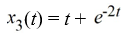
D)
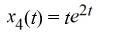
E)
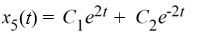
F)
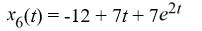
G)
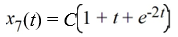

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
For what values of r is y(t) = 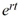 a solution of the differential equation
a solution of the differential equation 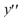 +4
+4 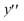 - 12y = 0?
- 12y = 0?
A) 2 and -6
B) 0 and 2
C) -2 and 6
D) 0 and -6
E) 0, 2, and -6
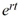 a solution of the differential equation
a solution of the differential equation 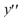 +4
+4 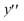 - 12y = 0?
- 12y = 0?A) 2 and -6
B) 0 and 2
C) -2 and 6
D) 0 and -6
E) 0, 2, and -6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
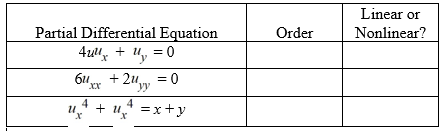
For each of the following partial differential equations, identify the order and indicate whether it is linear or nonlinear.


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








