Deck 13: Recursion
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: Recursion
1
One reason modular programming is encouraged is that it is an efficient way to manage computer memory.
True
2
Because variables declared in a module are local, and arguments passed by value are copied into local variables, a module can run like an independent program.
True
3
Variables declared in a module are also available to other modules.
False
4
The factorial of a number is the product of all positive integers from that number down to 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Any recursive procedure can be described nonrecursively.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The following algorithm defines a nonrecursive Fibonacci function:
Function Numeric factorial(Numeric num)
// Declare variables
Declare Numeric fact = 1 // factorial result
Declare Numeric index // loop index
// Loop
For index = num to 1 Step -1
fact = fact * index
End For
Return fact
End Function
Function Numeric factorial(Numeric num)
// Declare variables
Declare Numeric fact = 1 // factorial result
Declare Numeric index // loop index
// Loop
For index = num to 1 Step -1
fact = fact * index
End For
Return fact
End Function

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The factorial of 4 is the same as 4 times the factorial of 3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The factorial of 3 is the same as 2 times the factorial of 2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The factorial of 7 is 504.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The factorial of 6 is 720.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
A factorial can be defined as factorial(n) = n * factorial(n - 1), with factorial(1) defined as 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The Fibonacci number at any position (after the first two numbers in the sequence) is the sum of the Fibonacci number at two positions before the current one and the Fibonacci number at one position before the current one.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
For any integer n greater than or equal to 2, you can represent its position in the Fibonacci sequence, starting the position numbering at 0, as follows:
fibonacci(n) = fibonacci(n - 2) + fibonacci(n - 1)
fibonacci(n) = fibonacci(n - 2) + fibonacci(n - 1)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The Fibonacci sequence was mentioned in the 2006 movie The DaVinci Code.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
For any positive number n, the sum of squares equals 1<sup>2</sup> + 2<sup>2</sup> + 3<sup>2</sup>, and so on up to n<sup>2</sup>.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The sum of squares of 3 and 5 is 24.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The sum of squares of -3 and -8 is 72.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Legend says that when the Towers of Hanoi puzzle is completed, the world will come to an end.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The Towers of Hanoi puzzle is attributed to the French mathematician Edouard Lucas and is based on a legend about a temple in Vietnam, with 64 golden discs stacked on three posts.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The Towers of Hanoi puzzle can be solved with recursion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The greatest common denominator (GCD) of two numbers is the largest integer that can be divided by both numbers evenly (with no remainder).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The mathematician Euclid discovered a method for computing the GCD.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The greatest common denominator of 79 and 51 is 3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The greatest common denominator of 62 and 22 is 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Constructor functions cannot be called recursively.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
____ is a process in which a module calls itself.
A) Stack overflow
B) Short-circuit evaluation
C) Recursion
D) Garbage collection
A) Stack overflow
B) Short-circuit evaluation
C) Recursion
D) Garbage collection

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
To prevent a neverending recursion process, you must make sure to build a(n) ____ into the procedure.
A) base case
B) sentinel
C) index
D) constructor
A) base case
B) sentinel
C) index
D) constructor

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A(n) ____ is an event that does not call itself and must be reached eventually.
A) base case
B) sentinel
C) index
D) constructor
A) base case
B) sentinel
C) index
D) constructor

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
A program's main module occupies a designated place in memory called the ____.
A) branch
B) stub
C) stack
D) base
A) branch
B) stub
C) stack
D) base

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
A memory stack contains the main program, and when another module is running, it is said to be placed, or ____ the memory stack until it is finished executing.
A) deposited onto
B) pushed onto
C) withdrawn from
D) popped from
A) deposited onto
B) pushed onto
C) withdrawn from
D) popped from

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
____ occurs if a recursive procedure contains no base case.
A) Field testing
B) Housekeeping
C) Stack overflow
D) Data hiding
A) Field testing
B) Housekeeping
C) Stack overflow
D) Data hiding

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
5! * 5! is ____.
A) 120
B) 720
C) 5040
D) 14400
A) 120
B) 720
C) 5040
D) 14400

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
6! / (2! * 4!) = ____.
A) 2
B) 15
C) 24
D) 32
A) 2
B) 15
C) 24
D) 32

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
4!/0! = ____.
A) 2
B) 15
C) 24
D) 32
A) 2
B) 15
C) 24
D) 32

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
(10! / 5!) / 10 = ____.
A) 720
B) 1440
C) 3024
D) 5040
A) 720
B) 1440
C) 3024
D) 5040

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which of the following represents the factorial function?
A) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Call function recursively until reaching 0 or 1
If num == 0 Or num == 1 Then
Return num
Else
Return unKnown(num - 2) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
B) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Base case returns 1
If (num == 1) Then
Return 1
Else
Return (num * num) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
C) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Declare variables
Declare Numeric fact = 1
Declare Numeric index // loop index
// Loop
For index = num to 1 Step -1
Fact = fact * index
End For
Return fact
End Function
D) Module unKnown(Integer n, sourcePeg, targetPeg, sparePeg)
If (n > 0) Then
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sourcePeg, sparePeg, targetPeg)
// Move disc from sourcePeg to targetPeg
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sparePeg, targetPeg, sourcePeg)
End If
End Module
A) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Call function recursively until reaching 0 or 1
If num == 0 Or num == 1 Then
Return num
Else
Return unKnown(num - 2) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
B) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Base case returns 1
If (num == 1) Then
Return 1
Else
Return (num * num) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
C) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Declare variables
Declare Numeric fact = 1
Declare Numeric index // loop index
// Loop
For index = num to 1 Step -1
Fact = fact * index
End For
Return fact
End Function
D) Module unKnown(Integer n, sourcePeg, targetPeg, sparePeg)
If (n > 0) Then
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sourcePeg, sparePeg, targetPeg)
// Move disc from sourcePeg to targetPeg
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sparePeg, targetPeg, sourcePeg)
End If
End Module

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The following sequence is known as the ____.
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144 ...
A) sum of squares
B) Towers of Hanoi
C) Fibonacci sequence
D) factorial sequence
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144 ...
A) sum of squares
B) Towers of Hanoi
C) Fibonacci sequence
D) factorial sequence

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Which of the following represents the Fibonnacci sequence?
A) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Call function recursively until reaching 0 or 1
If num == 0 Or num == 1 Then
Return num
Else
Return unKnown(num - 2) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
B) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Base case returns 1
If (num == 1) Then
Return 1
Else
Return (num * num) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
C) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Declare variables
Declare Numeric fact = 1 // factorial result
Declare Numeric index // loop index
// Loop
For index = num to 1 Step -1
Fact = fact * index
End For
Return fact
End Function
D) Module unKnown(Integer n, sourcePeg, targetPeg, sparePeg)
If (n > 0) Then
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sourcePeg, sparePeg, targetPeg)
// Move disc from sourcePeg to targetPeg
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sparePeg, targetPeg, sourcePeg)
End If
End Module
A) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Call function recursively until reaching 0 or 1
If num == 0 Or num == 1 Then
Return num
Else
Return unKnown(num - 2) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
B) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Base case returns 1
If (num == 1) Then
Return 1
Else
Return (num * num) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
C) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Declare variables
Declare Numeric fact = 1 // factorial result
Declare Numeric index // loop index
// Loop
For index = num to 1 Step -1
Fact = fact * index
End For
Return fact
End Function
D) Module unKnown(Integer n, sourcePeg, targetPeg, sparePeg)
If (n > 0) Then
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sourcePeg, sparePeg, targetPeg)
// Move disc from sourcePeg to targetPeg
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sparePeg, targetPeg, sourcePeg)
End If
End Module

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Which of the following represents the sum of squares?
A) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Call function recursively until reaching 0 or 1
If num == 0 Or num == 1 Then
Return num
Else
Return unKnown(num - 2) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
B) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Base case returns 1
If (num == 1) Then
Return 1
Else
Return (num * num) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
C) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Declare variables
Declare Numeric fact = 1
Declare Numeric index // loop index
// Loop
For index = num to 1 Step -1
Fact = fact * index
End For
Return fact
End Function
D) Module unKnown(Integer n, sourcePeg, targetPeg, sparePeg)
If (n > 0) Then
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sourcePeg, sparePeg, targetPeg)
// Move disc from sourcePeg to targetPeg
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sparePeg, targetPeg, sourcePeg)
End If
End Module
A) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Call function recursively until reaching 0 or 1
If num == 0 Or num == 1 Then
Return num
Else
Return unKnown(num - 2) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
B) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Base case returns 1
If (num == 1) Then
Return 1
Else
Return (num * num) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
C) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Declare variables
Declare Numeric fact = 1
Declare Numeric index // loop index
// Loop
For index = num to 1 Step -1
Fact = fact * index
End For
Return fact
End Function
D) Module unKnown(Integer n, sourcePeg, targetPeg, sparePeg)
If (n > 0) Then
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sourcePeg, sparePeg, targetPeg)
// Move disc from sourcePeg to targetPeg
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sparePeg, targetPeg, sourcePeg)
End If
End Module

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The sum of squares of -5 and -7 is ____.
A) 28
B) 74
C) 82
D) 94
A) 28
B) 74
C) 82
D) 94

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The sum of squares of the first two even integers is ____.
A) 5
B) 10
C) 15
D) 20
A) 5
B) 10
C) 15
D) 20

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The sum of squares can be defined as ____.
A) (num) + sumOfSquares(num - 1)
B) (num / num) + sumOfSquares(num - 1)
C) (num * num) + sumOfSquares(num - 1)
D) (num * num) + sumOfSquares(num)
A) (num) + sumOfSquares(num - 1)
B) (num / num) + sumOfSquares(num - 1)
C) (num * num) + sumOfSquares(num - 1)
D) (num * num) + sumOfSquares(num)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Which of the following is played with three pegs and a stack of discs?
A) The Towers of Hanoi
B) Chess
C) The sum of squares
D) Checkers
A) The Towers of Hanoi
B) Chess
C) The sum of squares
D) Checkers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
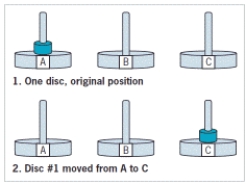
-The accompanying figure represents the ____.
A) Towers of Hanoi
B) Fibonacci sequence
C) sum of squares
D) factorial sequence

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Which of the following represents the Towers of Hanoi?
A) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Call function recursively until reaching 0 or 1
If num == 0 Or num == 1 Then
Return num
Else
Return unKnown(num - 2) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
B) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Base case returns 1
If (num == 1) Then
Return 1
Else
Return (num * num) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
C) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Declare variables
Declare Numeric fact = 1
Declare Numeric index // loop index
// Loop
For index = num to 1 Step -1
Fact = fact * index
End For
Return fact
End Function
D) Module unKnown(Integer n, sourcePeg, targetPeg, sparePeg)
If (n > 0) Then
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sourcePeg, sparePeg, targetPeg)
// Move disc from sourcePeg to targetPeg
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sparePeg, targetPeg, sourcePeg)
End If
End Module
A) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Call function recursively until reaching 0 or 1
If num == 0 Or num == 1 Then
Return num
Else
Return unKnown(num - 2) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
B) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Base case returns 1
If (num == 1) Then
Return 1
Else
Return (num * num) + unKnown(num - 1)
End If
End Function
C) Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric num)
// Declare variables
Declare Numeric fact = 1
Declare Numeric index // loop index
// Loop
For index = num to 1 Step -1
Fact = fact * index
End For
Return fact
End Function
D) Module unKnown(Integer n, sourcePeg, targetPeg, sparePeg)
If (n > 0) Then
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sourcePeg, sparePeg, targetPeg)
// Move disc from sourcePeg to targetPeg
MoveDiscs(n - 1, sparePeg, targetPeg, sourcePeg)
End If
End Module

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
What is the greatest common denominator of 30 and 36?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
What is the greatest common denominator of 87 and 41?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
What is the greatest common denominator of 36 and 22?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
What is the greatest common denominator of 105 and 35?
A) 5
B) 15
C) 25
D) 35
A) 5
B) 15
C) 25
D) 35

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The following algorithm represents the ____.
Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric x, Numeric y)
If y = 0 Then
Return x
Else
Return GCD(y, x % y)
End If
End Function
A) sum of squares
B) Fibonacci series
C) GCD function
D) factorial series
Function Numeric unKnown(Numeric x, Numeric y)
If y = 0 Then
Return x
Else
Return GCD(y, x % y)
End If
End Function
A) sum of squares
B) Fibonacci series
C) GCD function
D) factorial series

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








