Deck 10: Series
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/26
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 10: Series
1
Use the nth term test to investigate the series .
A) The series converges.
B) , so the series diverges.
C) , so the test fails to tell us anything about the series.
D) , so the test fails to tell us anything about the series.
A) The series converges.
B) , so the series diverges.
C) , so the test fails to tell us anything about the series.
D) , so the test fails to tell us anything about the series.
, so the series diverges.
2
Use the integral test to investigate the series .
A) The integral , so the series .
B) The integral , so the series converges.
C) The integral , so the series diverges.
D) The integral , so the test fails to tell us anything about the series.
A) The integral , so the series .
B) The integral , so the series converges.
C) The integral , so the series diverges.
D) The integral , so the test fails to tell us anything about the series.
The integral , so the series converges.
3
Use the ratio test to investigate the series .
A) , so the series diverges.
B) , so the series converges.
C) , so the ratio test fails to tell us anything about the series.
D) , so the series converges.
A) , so the series diverges.
B) , so the series converges.
C) , so the ratio test fails to tell us anything about the series.
D) , so the series converges.
, so the series converges.
4
Investigate the alternating series .
A) The p- series converges, so the series converges absolutely.
B) The p-series diverges, so the series converges conditionally.
C) The ratio test gives , so the series diverges.
D) The p-series diverges, so the series diverges.
A) The p- series converges, so the series converges absolutely.
B) The p-series diverges, so the series converges conditionally.
C) The ratio test gives , so the series diverges.
D) The p-series diverges, so the series diverges.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Find the interval of convergence of the power series .
A)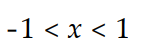
B)
C)
D)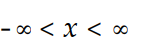
A)
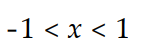
B)
C)
D)
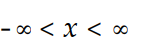

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Find a Maclaurin series expansion forf(x) .
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Find a Taylor series expansion for with .
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Use the first four non- zero terms of the Maclaurin series for to estimate .
A) .7405
B).7399
C) .7407
D).7402
A) .7405
B).7399
C) .7407
D).7402

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Find the Fourier series for the square wave (of period ) given by
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
For the problems below, determine whether each series converges or diverges.
-
-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
For the problems below, determine whether each series converges or diverges.
-
-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
For the problems below, use either the ratio test or the integral test to determine whether each series converges or diverges.
-
-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
For the problems below, use either the ratio test or the integral test to determine whether each series converges or diverges.
-
-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
For the problems below, determine whether each alternating series converges or diverges. If it converges, find whether it converges absolutely or converges conditionally.
-
-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
For the problems below, determine whether each alternating series converges or diverges. If it converges, find whether it converges absolutely or converges conditionally.
-
-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
For the problems below, determine whether each alternating series converges or diverges. If it converges, find whether it converges absolutely or converges conditionally.
-
-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
For the problems below, find the interval of convergences of each series.
-
-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
For the problems below, find the interval of convergences of each series.
-18
-18

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
For the problems below, find a Maclaurin series expansion for each function. Include at least thereetarms.
-
-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
For the problems below, find a Maclaurin series expansion for each function. Include at least thereetarms.
-
-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Find a Maclaurin series expansion for .

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Evaluate . (Use three non-zero terms.) Round to four significant digits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
For the problems below, find the Taylor series expansion for each function for the given value of a. Give at least three terms.
-
-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
For the problems below, find the Taylor series expansion for each function for the given value of a. Give at least three terms.
-
-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Calculate the value of using the first four non- zero terms of a Taylor series. Round to five significant digits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Find the Fourier series expansion of . Write at least four terms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








