Deck 14: Audit sampling
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/146
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 14: Audit sampling
1
Which one of the following statements is NOT correct?
A) It is acceptable for auditors to use statistical sampling methods.
B) The primary benefit of statistical sampling methods is the quantification of sampling risk.
C) An advantage of using statistical sampling is that the cost/benefit ratio is always positive.
D) It is acceptable for auditors to use non-statistical sampling methods.
A) It is acceptable for auditors to use statistical sampling methods.
B) The primary benefit of statistical sampling methods is the quantification of sampling risk.
C) An advantage of using statistical sampling is that the cost/benefit ratio is always positive.
D) It is acceptable for auditors to use non-statistical sampling methods.
C
2
Non-sampling errors occur when audit tests do NOT uncover existing exceptions in the:
A) planning stage.
B) population.
C) financial statements.
D) sample.
A) planning stage.
B) population.
C) financial statements.
D) sample.
D
3
Which one is NOT a sample selection method commonly associated with non-statistical audit units?
A) haphazard sample selection
B) probability proportional to size sample selection
C) directed sample selection
D) block sample selection
A) haphazard sample selection
B) probability proportional to size sample selection
C) directed sample selection
D) block sample selection
B
4
One of the causes of non-sampling error is:
A) the use of inappropriate or ineffective audit procedures.
B) the use of attributes sampling instead of variables sampling.
C) failure to draw a random sample.
D) failure to draw a representative sample.
A) the use of inappropriate or ineffective audit procedures.
B) the use of attributes sampling instead of variables sampling.
C) failure to draw a random sample.
D) failure to draw a representative sample.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
How can non-sampling risk be eliminated?
A) proper supervision and instruction of the client's employees
B) controls which ensure that the sample drawn is random and representative
C) the use of attributes sampling rather than variables sampling
D) proper supervision and instruction of the audit team
A) proper supervision and instruction of the client's employees
B) controls which ensure that the sample drawn is random and representative
C) the use of attributes sampling rather than variables sampling
D) proper supervision and instruction of the audit team

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A sample in which every possible combination of items in the population has an equal chance of constituting the sample is a:
A) statistical sample.
B) random sample.
C) representative sample.
D) judgement sample.
A) statistical sample.
B) random sample.
C) representative sample.
D) judgement sample.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
When the auditor goes through a population and selects items for the sample without regard to their size, source, or other distinguishing characteristics, it is called:
A) block sample selection.
B) statistical selection.
C) systematic sample selection.
D) haphazard selection.
A) block sample selection.
B) statistical selection.
C) systematic sample selection.
D) haphazard selection.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Sampling risk (sampling error)is an inherent part of sampling which results from:
A) testing less than the entire population.
B) weaknesses in client's internal control system.
C) inappropriate audit procedures.
D) failure to recognise exceptions.
A) testing less than the entire population.
B) weaknesses in client's internal control system.
C) inappropriate audit procedures.
D) failure to recognise exceptions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
When the auditor intends to evaluate a sample statistically, the only acceptable selection method is:
A) probabilistic selection.
B) block sample selection.
C) judgemental selection.
D) haphazard selection.
A) probabilistic selection.
B) block sample selection.
C) judgemental selection.
D) haphazard selection.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
An advantage of using statistical sampling techniques is that such techniques:
A) eliminate the need for judgemental decisions.
B) mathematically measure risk.
C) have been established in the courts to be superior to judgmental sampling.
D) define the values of precision and reliability required to provide audit satisfaction.
A) eliminate the need for judgemental decisions.
B) mathematically measure risk.
C) have been established in the courts to be superior to judgmental sampling.
D) define the values of precision and reliability required to provide audit satisfaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
What is the most important aspect of audit sampling?
A) evaluating the results
B) sample selection
C) performing the audit procedures
D) all of the above
A) evaluating the results
B) sample selection
C) performing the audit procedures
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The process which requires the calculation of an interval and then selects the items based on the size of the interval is:
A) random sample selection.
B) systematic sample selection.
C) computerised sample selection.
D) statistical sampling.
A) random sample selection.
B) systematic sample selection.
C) computerised sample selection.
D) statistical sampling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The risk which the auditor is willing to take in accepting a control as being effective when it is not is the:
A) allowable risk of overreliance (ARO).
B) tolerable deviation rate (TDR).
C) estimated population deviation rate.
D) sample deviation rate (SDR).
A) allowable risk of overreliance (ARO).
B) tolerable deviation rate (TDR).
C) estimated population deviation rate.
D) sample deviation rate (SDR).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A sample in which the characteristics of the sample are the same as those of the population is:
A) an attributes sample.
B) a variables sample.
C) a representative sample.
D) a random sample.
A) an attributes sample.
B) a variables sample.
C) a representative sample.
D) a random sample.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Which one of the following BEST illustrates the concept of sampling risk?
A) The documents related to the chosen sample may not be available for inspection.
B) An auditor may select audit procedures that are not appropriate to achieve the specific objective.
C) A randomly chosen sample may not be representative of the population as a whole on the characteristics of interest.
D) An auditor may fail to recognise errors in the documents examined for the chosen sample.
A) The documents related to the chosen sample may not be available for inspection.
B) An auditor may select audit procedures that are not appropriate to achieve the specific objective.
C) A randomly chosen sample may not be representative of the population as a whole on the characteristics of interest.
D) An auditor may fail to recognise errors in the documents examined for the chosen sample.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Which one of the following statements is NOT correct regarding probabilistic and non-probabilistic sample selection?
A) In probabilistic selection, every population item has a known chance of being selected.
B) It is not acceptable to make non-statistical evaluations using probabilistic selection.
C) Probabilistic selection is required for all statistical sampling methods.
D) Both methods are acceptable and commonly used.
A) In probabilistic selection, every population item has a known chance of being selected.
B) It is not acceptable to make non-statistical evaluations using probabilistic selection.
C) Probabilistic selection is required for all statistical sampling methods.
D) Both methods are acceptable and commonly used.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
There are many situations in auditing where it is advantageous to select samples that emphasise population items that have larger recorded amounts.Which one of the following would NOT be a way to obtain such a sample?
A) Take a sample where the probability of selecting any individual population items is proportional to its recorded amount
B) Use stratified sampling
C) Use probability-proportional-to-size sampling
D) Use block sample selection
A) Take a sample where the probability of selecting any individual population items is proportional to its recorded amount
B) Use stratified sampling
C) Use probability-proportional-to-size sampling
D) Use block sample selection

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
One of the ways to reduce sampling risk is to:
A) provide proper supervision and instruction of the audit team.
B) carefully design the audit procedures to be used.
C) use variables sampling rather than attributes sampling.
D) use an appropriate method of selecting sample items from the population.
A) provide proper supervision and instruction of the audit team.
B) carefully design the audit procedures to be used.
C) use variables sampling rather than attributes sampling.
D) use an appropriate method of selecting sample items from the population.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which one of the following statements is a valid criticism of the use of non-statistical sampling methods?
A) Conclusions may be drawn in more precise ways when using statistical sampling methods.
B) Non-statistical sampling does not differ substantially from statistical sampling methods.
C) The cost of performing random selection of testing often exceeds the benefits.
D) Many audit texts, such as footing of journals, must be performed outside a statistical sampling context.
A) Conclusions may be drawn in more precise ways when using statistical sampling methods.
B) Non-statistical sampling does not differ substantially from statistical sampling methods.
C) The cost of performing random selection of testing often exceeds the benefits.
D) Many audit texts, such as footing of journals, must be performed outside a statistical sampling context.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The deviation rate the auditor will permit in the population and still be willing to use the assessed level of control risk established during planning is called the:
A) tolerable deviation rate (TDR).
B) sample deviation rate (SDR).
C) acceptable risk of overreliance (ARO).
D) estimated population deviation rate.
A) tolerable deviation rate (TDR).
B) sample deviation rate (SDR).
C) acceptable risk of overreliance (ARO).
D) estimated population deviation rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The deviation rate in a representative sample is the:
A) number of items in the population containing a particular attribute.
B) auditor's best estimate of the deviation rate.
C) auditor's calculation of the error rate in the population.
D) none of the above
A) number of items in the population containing a particular attribute.
B) auditor's best estimate of the deviation rate.
C) auditor's calculation of the error rate in the population.
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Since auditors are interested in the occurrence of deviations in populations, they refer to the occurrence rate as the:
A) deviation rate.
B) confidence level.
C) populations rate.
D) probability rate.
A) deviation rate.
B) confidence level.
C) populations rate.
D) probability rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The final step in the evaluation of the audit results is the decision to:
A) determine the error in each sample.
B) project the point estimate.
C) determine sampling error and calculate the estimated total population error.
D) decide the acceptability of the population.
A) determine the error in each sample.
B) project the point estimate.
C) determine sampling error and calculate the estimated total population error.
D) decide the acceptability of the population.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
When the computed upper deviation rate is greater than the tolerable deviation rate, it is necessary for the auditor to take specific action.Which of the following courses of action would be most difficult to defend if the auditor is ever subject to review by a court?
A) Write a letter to management.
B) Expand the sample size.
C) Revise the assessed control risk.
D) Revise and relax the tolerable deviation rate (TDR) or the acceptable risk of assessing control risk too low (ARO).
A) Write a letter to management.
B) Expand the sample size.
C) Revise the assessed control risk.
D) Revise and relax the tolerable deviation rate (TDR) or the acceptable risk of assessing control risk too low (ARO).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
How are tests of controls affected when the auditor decides to assess control risk at the maximum level?
A) increased in number
B) reduced in number
C) not performed
D) unchanged from prior planned settings
A) increased in number
B) reduced in number
C) not performed
D) unchanged from prior planned settings

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
When using systematic selection procedures with monetary-unit sampling of accounts receivable, the interval is determined by:
A) dividing the sample size by the account with the largest dollar value.
B) consulting a random number table.
C) dividing the population size by the account receivable with the largest dollar value.
D) dividing the population size by the desired sample size.
A) dividing the sample size by the account with the largest dollar value.
B) consulting a random number table.
C) dividing the population size by the account receivable with the largest dollar value.
D) dividing the population size by the desired sample size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Which one of the following is an advantage of systematic sample selection over random number sampling?
A) There may be correlation between the location of items in the population, the feature of sampling interest, and the sampling interval.
B) It does not require establishment of correspondence between random numbers and items in the population.
C) It provides a stronger basis for statistical conclusions.
D) It enables the auditor to use the more efficient sampling with replacement tables.
A) There may be correlation between the location of items in the population, the feature of sampling interest, and the sampling interval.
B) It does not require establishment of correspondence between random numbers and items in the population.
C) It provides a stronger basis for statistical conclusions.
D) It enables the auditor to use the more efficient sampling with replacement tables.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The advantage of systematic sample selection is that:
A) it is easy to use.
B) it is unnecessary to determine if the population is arranged randomly.
C) there is limited possibility of it being biased.
D) all of the above
A) it is easy to use.
B) it is unnecessary to determine if the population is arranged randomly.
C) there is limited possibility of it being biased.
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Non-probabilistic sample selection methods are NOT based on strict mathematical probabilities; therefore:
A) they are discouraged by the Corporations Act.
B) they are not as good as statistical sampling.
C) they are forbidden by the Statements of Auditing Standards.
D) the representativeness of the sample may be difficult to determine.
A) they are discouraged by the Corporations Act.
B) they are not as good as statistical sampling.
C) they are forbidden by the Statements of Auditing Standards.
D) the representativeness of the sample may be difficult to determine.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The auditor must consider the possibility that the true population misstatement is greater than the amount of misstatement that is tolerable when the auditor is performing:
A) statistical sampling.
B) non-statistical sampling.
C) both A and B
D) none of the above
A) statistical sampling.
B) non-statistical sampling.
C) both A and B
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
When selecting a stratified sample, the sample size is:
A) determined for the unstratified population and then apportioned to each stratum.
B) determined for each stratum and selected from that stratum.
C) determined for each stratum and selected randomly from the entire unstratified population.
D) always larger than if unstratified sampling had been used.
A) determined for the unstratified population and then apportioned to each stratum.
B) determined for each stratum and selected from that stratum.
C) determined for each stratum and selected randomly from the entire unstratified population.
D) always larger than if unstratified sampling had been used.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
If all other factors specified in a sampling plan remain constant, changing the estimated population deviation rate from 2% to 4% would cause the required sample size to:
A) decrease.
B) remain the same.
C) increase.
D) become indeterminate.
A) decrease.
B) remain the same.
C) increase.
D) become indeterminate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
In systematic sample selection, the population size is divided by the number of sample items desired in order to determine the:
A) interval.
B) mean.
C) computed upper exceptions rate.
D) tolerable exception rate.
A) interval.
B) mean.
C) computed upper exceptions rate.
D) tolerable exception rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Which one of the following material occurrences would be most likely to attract the auditor's attention?
A) deviations from client's established control procedures
B) monetary errors or irregularities in populations of account balance details
C) deviations from client's budgeted values
D) both A and B
A) deviations from client's established control procedures
B) monetary errors or irregularities in populations of account balance details
C) deviations from client's budgeted values
D) both A and B

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Which one of the following BEST describes what the auditor means by the rate of occurrence in the audit sampling plan?
A) the frequency with which a certain characteristic occurs within a population
B) the dollar range within which the true population total can be expected to fall
C) the degree of confidence that the sample is representative of the population
D) the number of errors that can reasonably be expected to be found in a population
A) the frequency with which a certain characteristic occurs within a population
B) the dollar range within which the true population total can be expected to fall
C) the degree of confidence that the sample is representative of the population
D) the number of errors that can reasonably be expected to be found in a population

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
In performing a review of his client's cash disbursements, an auditor uses systematic sample selection with a random start.The primary disadvantage of systematic sample selection is that population items:
A) must be reordered in a systematic pattern before the sample can be drawn.
B) may occur twice in the sample.
C) must be replaced in the population after sampling to permit valid statistical inference.
D) may occur in a systematic pattern, thus negating the randomness of the sample.
A) must be reordered in a systematic pattern before the sample can be drawn.
B) may occur twice in the sample.
C) must be replaced in the population after sampling to permit valid statistical inference.
D) may occur in a systematic pattern, thus negating the randomness of the sample.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Which of the following factors is generally NOT considered in determining sample size for a test of controls?
A) risk of assessing control risk too low
B) expected population deviation rate
C) tolerable deviation rate
D) population size
A) risk of assessing control risk too low
B) expected population deviation rate
C) tolerable deviation rate
D) population size

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Audit sampling would be an appropriate method to use on which one of the following procedures in an audit program?
A) Review the aged schedule of accounts receivable to determine if receivables from officers are included.
B) Review sales transactions for large and unreasonable amounts.
C) Examine a sample of duplicate sales invoices for credit approval by the credit manager.
D) Observe whether the duties of the accounts receivable clerk are separate from handling cash.
A) Review the aged schedule of accounts receivable to determine if receivables from officers are included.
B) Review sales transactions for large and unreasonable amounts.
C) Examine a sample of duplicate sales invoices for credit approval by the credit manager.
D) Observe whether the duties of the accounts receivable clerk are separate from handling cash.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
A method of sampling in which all the items in the population are divided into two or more subpopulations is:
A) attributes sampling.
B) stratified sampling.
C) divisible sampling.
D) variables sampling.
A) attributes sampling.
B) stratified sampling.
C) divisible sampling.
D) variables sampling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Which one of the following statements regarding block sampling is NOT true?
A) It is acceptable to use block sampling for tests of transactions only if a reasonable number of blocks are used.
B) Once the first item in the block is selected, the remainder of the block is chosen automatically.
C) Block sampling is the selection of several items in sequence.
D) A 'reasonable number' for most situations is probably at least six blocks from six different months.
A) It is acceptable to use block sampling for tests of transactions only if a reasonable number of blocks are used.
B) Once the first item in the block is selected, the remainder of the block is chosen automatically.
C) Block sampling is the selection of several items in sequence.
D) A 'reasonable number' for most situations is probably at least six blocks from six different months.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
If the size of the sample to be used in a particular test of attributes has NOT been determined by using statistical concepts, but the sample has been chosen in accordance with random selection procedures:
A) the auditor may or may not achieve the tolerable deviation rate at the acceptable risk of assessing control risk too low.
B) the auditor will have to evaluate the results by reference to the principles of discovery sampling.
C) no inferences can be drawn from the sample.
D) the auditor has committed a non-sampling error.
A) the auditor may or may not achieve the tolerable deviation rate at the acceptable risk of assessing control risk too low.
B) the auditor will have to evaluate the results by reference to the principles of discovery sampling.
C) no inferences can be drawn from the sample.
D) the auditor has committed a non-sampling error.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The risk the auditor is willing to take of accepting a balance as correct when the true error in the balance is greater than the tolerable misstatement is the:
A) lower bound.
B) allowable risk of incorrect acceptance.
C) tolerable risk.
D) upper bound.
A) lower bound.
B) allowable risk of incorrect acceptance.
C) tolerable risk.
D) upper bound.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The tolerable deviation rate (TDR)has a significant effect on sample size.The relationship of TDR to sample size is:
A) inverse (larger TDR = smaller sample).
B) direct (larger TDR = larger sample).
C) variable (sometimes larger, sometimes smaller).
D) not determinable.
A) inverse (larger TDR = smaller sample).
B) direct (larger TDR = larger sample).
C) variable (sometimes larger, sometimes smaller).
D) not determinable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The initial sample size is so-called because:
A) the auditor must take several samples to ensure randomness.
B) there is always another sample to be done.
C) the deviations must be evaluated before deciding whether the sample is sufficiently large to achieve the objectives.
D) the auditor must take several samples to ensure that the final sample is representative of the population.
A) the auditor must take several samples to ensure randomness.
B) there is always another sample to be done.
C) the deviations must be evaluated before deciding whether the sample is sufficiently large to achieve the objectives.
D) the auditor must take several samples to ensure that the final sample is representative of the population.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
If the result obtained from a particular sample will be critical (that is, the auditor would not be able to render an unqualified opinion unless every item in the population were examined), which of the following is the most important to the auditor?
A) estimated population deviation rate
B) tolerable deviation rate
C) acceptable risk of assessing control risk too low
D) size of the population
A) estimated population deviation rate
B) tolerable deviation rate
C) acceptable risk of assessing control risk too low
D) size of the population

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
When errors are found, a common assumption in practice is to assume:
A) a 100% assumption for all errors.
B) that the population errors are smaller than the sample errors.
C) that the population errors are larger than the sample errors.
D) that misstatements in the unaudited population are proportional to the misstatements in the sample.
A) a 100% assumption for all errors.
B) that the population errors are smaller than the sample errors.
C) that the population errors are larger than the sample errors.
D) that misstatements in the unaudited population are proportional to the misstatements in the sample.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
As a result of tests of controls, an auditor assessed control risk too low and decreased substantive testing.This occurred because the true deviation rate in the population was:
A) more than the deviation rate in the auditor's sample.
B) less than the deviation rate in the auditor's sample.
C) less than the risk of assessing control risk too low based on the auditor's sample.
D) more than the risk of assessing control risk too low based on the auditor's sample.
A) more than the deviation rate in the auditor's sample.
B) less than the deviation rate in the auditor's sample.
C) less than the risk of assessing control risk too low based on the auditor's sample.
D) more than the risk of assessing control risk too low based on the auditor's sample.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
An increase in the sample size has the effect of decreasing the sampling error if the:
A) actual sample deviation rate increases.
B) actual sample deviation rate does not increase.
C) number of deviations in the sample increases.
D) number of deviations in the sample does not increase.
A) actual sample deviation rate increases.
B) actual sample deviation rate does not increase.
C) number of deviations in the sample increases.
D) number of deviations in the sample does not increase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Establishing the tolerable deviation rate (TDR)requires:
A) auditor judgement.
B) a computer program.
C) random number tables.
D) statistical frequency probability tables.
A) auditor judgement.
B) a computer program.
C) random number tables.
D) statistical frequency probability tables.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Acceptable risk of assessing control risk too low (ARO)is the auditor's measure of:
A) non-sampling risk.
B) inherent risk.
C) control risk.
D) sampling risk.
A) non-sampling risk.
B) inherent risk.
C) control risk.
D) sampling risk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
In audit sampling, an advance estimate of the deviation rate is necessary to plan the appropriate sample size.The relationship of estimated population deviation rate (EPDR)to sample size is:
A) direct (small EPDR = small sample).
B) indeterminate.
C) inverse (small EPDR = large sample).
D) a variable (sometimes small, sometimes large) dependent on other factors present.
A) direct (small EPDR = small sample).
B) indeterminate.
C) inverse (small EPDR = large sample).
D) a variable (sometimes small, sometimes large) dependent on other factors present.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The acceptable risk of assessing control risk too low (ARO)is a measure of the level of risk that:
A) is predicted by the statistical frequency table.
B) the auditor is willing to take.
C) is predicted by the random number table.
D) is generated as a result of the auditor's knowledge of the true population deviation rate.
A) is predicted by the statistical frequency table.
B) the auditor is willing to take.
C) is predicted by the random number table.
D) is generated as a result of the auditor's knowledge of the true population deviation rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
In estimating the population misstatement, the first step in projecting from the sample to the population is to:
A) calculate the precision interval.
B) revise the upper error bound.
C) determine the population mean.
D) make a point estimate.
A) calculate the precision interval.
B) revise the upper error bound.
C) determine the population mean.
D) make a point estimate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The relationship between sample size and the acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance is:
A) indeterminate.
B) variable; that is, larger acceptable risk = sometimes larger sample size and sometimes not.
C) direct; that is, larger acceptable risk = larger sample size.
D) inverse; that is, larger acceptable risk = smaller sample size.
A) indeterminate.
B) variable; that is, larger acceptable risk = sometimes larger sample size and sometimes not.
C) direct; that is, larger acceptable risk = larger sample size.
D) inverse; that is, larger acceptable risk = smaller sample size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Statistical theory proves that in most types of populations to which audit sampling applies, the population size is:
A) a minor consideration in determining sample size.
B) the determining factor in determining sample size.
C) a major consideration in determining sample size.
D) not a consideration in determining sample size.
A) a minor consideration in determining sample size.
B) the determining factor in determining sample size.
C) a major consideration in determining sample size.
D) not a consideration in determining sample size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
What is an auditor's evaluation of a statistical sample for attributes when a test of 100 documents results in 4 deviations, assuming the tolerable deviation rate is 5%, the expected population deviation rate is 3% and the allowance for sampling risk is 2%?
A) Modify planned reliance on the control because the tolerable rate plus the allowance for sampling risk exceeds the expected population deviation rate.
B) Accept the sample results as support for planned reliance on the control because the tolerable rate less the allowance or sampling risk equals the expected population deviation rate.
C) Modify planned reliance on the control because the sample deviation rate plus the allowance for sampling risk exceeds the tolerable rate.
D) Accept the sample results as support for planned reliance on the control because the sample deviation rate plus the allowance for sampling risk exceeds the tolerable rate.
A) Modify planned reliance on the control because the tolerable rate plus the allowance for sampling risk exceeds the expected population deviation rate.
B) Accept the sample results as support for planned reliance on the control because the tolerable rate less the allowance or sampling risk equals the expected population deviation rate.
C) Modify planned reliance on the control because the sample deviation rate plus the allowance for sampling risk exceeds the tolerable rate.
D) Accept the sample results as support for planned reliance on the control because the sample deviation rate plus the allowance for sampling risk exceeds the tolerable rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
When an auditor performs tests of details of balances, the concern is determining:
A) both the effectiveness of controls and the monetary correctness of the transactions.
B) whether the deviation rate in the population is sufficiently low to justify reducing substantive testing.
C) whether the account balance being audited is fairly stated.
D) all of the above
A) both the effectiveness of controls and the monetary correctness of the transactions.
B) whether the deviation rate in the population is sufficiently low to justify reducing substantive testing.
C) whether the account balance being audited is fairly stated.
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Which one of the following statements regarding the process of defining the population is NOT correct? The
A) population represents the body of data about which the auditor wishes to generalise.
B) auditor can define the population to include whatever data is desired.
C) auditor can randomly sample from whatever part of the population he or she chooses.
D) auditor may generalise only about that population which has been sampled.
A) population represents the body of data about which the auditor wishes to generalise.
B) auditor can define the population to include whatever data is desired.
C) auditor can randomly sample from whatever part of the population he or she chooses.
D) auditor may generalise only about that population which has been sampled.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Of the four factors which determine the initial sample size (population size, tolerable deviation rate, acceptable risk of over-reliance, and expected population deviation rate), which combination of two factors has the greatest effect on sample size?
A) acceptable risk of overreliance minus tolerable deviation rate
B) expected population deviation rate plus acceptable risk of overreliance
C) population size times expected population deviation rate
D) tolerable deviation rate minus expected population deviation rate
A) acceptable risk of overreliance minus tolerable deviation rate
B) expected population deviation rate plus acceptable risk of overreliance
C) population size times expected population deviation rate
D) tolerable deviation rate minus expected population deviation rate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The allowable risk of overreliance (ARO)has a significant effect on sample size.The relationship of ARO to sample size is:
A) variable (sometimes larger, sometimes smaller).
B) nonexistent.
C) inverse (larger ARO = smaller sample).
D) direct (larger ARO = larger sample).
A) variable (sometimes larger, sometimes smaller).
B) nonexistent.
C) inverse (larger ARO = smaller sample).
D) direct (larger ARO = larger sample).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
In monetary-unit sampling, items containing large understatement errors:
A) have an increased probability of being included in the sample.
B) may have a small recorded value due to those errors.
C) are of less concern than those with large overstatement errors.
D) all of the above
A) have an increased probability of being included in the sample.
B) may have a small recorded value due to those errors.
C) are of less concern than those with large overstatement errors.
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
A frequency distribution of the results of all possible samples of a specified size that could be obtained from a population containing some specific parameter is the:
A) sampling distribution.
B) population distribution.
C) sample size.
D) sample deviation rate.
A) sampling distribution.
B) population distribution.
C) sample size.
D) sample deviation rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
When using monetary-unit sampling, the recorded dollar population is a definition of the:
A) items in the population which contain errors.
B) items in the sample which contain errors.
C) population size.
D) items in the population which the auditor has included in the sample.
A) items in the population which contain errors.
B) items in the sample which contain errors.
C) population size.
D) items in the population which the auditor has included in the sample.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The point estimate, by itself, is NOT an adequate measure of the population misstatement because of:
A) population biases.
B) control risk.
C) sampling error.
D) audit risk.
A) population biases.
B) control risk.
C) sampling error.
D) audit risk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Monetary-unit sampling is most commonly used when:
A) the population data are maintained on computer files.
B) zero or few exceptions are expected.
C) a dollar result is desired.
D) all of the above
A) the population data are maintained on computer files.
B) zero or few exceptions are expected.
C) a dollar result is desired.
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
An accounts receivable population contains a total of 4 customers.The accounts, amounts, and cumulative total are shown in the following table:

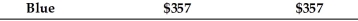
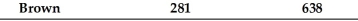
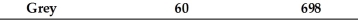
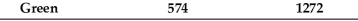
If monetary-unit sampling is used, what is the population size?
A) 1272
B) 574
C) 4
D) unknown

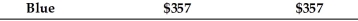
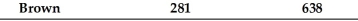
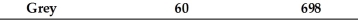
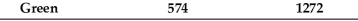
If monetary-unit sampling is used, what is the population size?
A) 1272
B) 574
C) 4
D) unknown

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
When using monetary-unit sampling, evaluating the likelihood of unrecorded items in the population is:
A) an automatic outcome of the process.
B) necessary.
C) impossible.
D) possible but difficult.
A) an automatic outcome of the process.
B) necessary.
C) impossible.
D) possible but difficult.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
If an auditor, planning to use statistical sampling, is concerned with the dollar value of mathematical errors in sales invoices, the auditor would most likely NOT utilise:
A) sampling for attributes.
B) sampling for variables.
C) stratified random sampling.
D) random sampling.
A) sampling for attributes.
B) sampling for variables.
C) stratified random sampling.
D) random sampling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
For monetary-unit sampling, normally the estimate of the population deviation rate is:
A) between 1% and 5%, inclusive.
B) 0%.
C) between 6% and 10%, inclusive.
D) greater than 10%.
A) between 1% and 5%, inclusive.
B) 0%.
C) between 6% and 10%, inclusive.
D) greater than 10%.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
An auditor using non-statistical sampling cannot:
A) determine a point estimate for the population.
B) mathematically measure the precision of the point estimate.
C) draw a random sample.
D) do any of the above.
A) determine a point estimate for the population.
B) mathematically measure the precision of the point estimate.
C) draw a random sample.
D) do any of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
The most commonly used method of statistical sampling for tests of details of balances is:
A) discovery sampling.
B) monetary-unit sampling.
C) variables sampling.
D) attributes sampling.
A) discovery sampling.
B) monetary-unit sampling.
C) variables sampling.
D) attributes sampling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
The major difference between monetary-unit sampling (MUS)and attributes sampling is that in MUS, the:
A) dollars are converted to occurrence rates.
B) rate of occurrence is converted to dollars.
C) measure is in dollars.
D) measure is the rate of occurrence.
A) dollars are converted to occurrence rates.
B) rate of occurrence is converted to dollars.
C) measure is in dollars.
D) measure is the rate of occurrence.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
The auditor must deal with layers of the computed upper deviation rate (CUDR)from the attributes table because there are different error assumptions for each error.Assume a sample of 100 had found 1 error, and the computed upper deviation rate is shown in the following table:
Number of Errors Upper Precision Limit from Table
0 )023
1 )038
What is the CUDR layer for the first mistake?
A) 6.1%
B) 1.5%
C) 3.8%
D) 2.3%
Number of Errors Upper Precision Limit from Table
0 )023
1 )038
What is the CUDR layer for the first mistake?
A) 6.1%
B) 1.5%
C) 3.8%
D) 2.3%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
The appropriate assumption to make regarding the overall percent of error in those population items containing an error is:
A) set after a quantitative analysis of client's internal control system.
B) based on statistical analysis using confidence limits.
C) determined using random number tables.
D) based on the auditor's personal judgement in the circumstances.
A) set after a quantitative analysis of client's internal control system.
B) based on statistical analysis using confidence limits.
C) determined using random number tables.
D) based on the auditor's personal judgement in the circumstances.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
An example of sampling for attributes would be estimating the:
A) probability of losing a patent infringement case.
B) percentage of sales invoices with no accompanying shipping documents.
C) quantity of specific inventory items.
D) dollar value of accounts receivable.
A) probability of losing a patent infringement case.
B) percentage of sales invoices with no accompanying shipping documents.
C) quantity of specific inventory items.
D) dollar value of accounts receivable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Whenever a statistical method is used, a decision rule determines whether the population is acceptable.The decision rule for monetary-unit sampling is 'Accept the conclusion that the book value is NOT misstated by a material amount if:
A) the overstatement tolerable misstatement amount falls between the lower and upper misstatement bounds.'
B) the upper misstatement bound falls between the understatement and overstatement tolerable misstatement amounts.'
C) both the understatement and overstatement tolerable misstatement amounts fall between the upper and lower misstatement bounds.'
D) both the lower and upper misstatement bounds falls between the understatement and overstatement tolerable misstatement amounts.'
A) the overstatement tolerable misstatement amount falls between the lower and upper misstatement bounds.'
B) the upper misstatement bound falls between the understatement and overstatement tolerable misstatement amounts.'
C) both the understatement and overstatement tolerable misstatement amounts fall between the upper and lower misstatement bounds.'
D) both the lower and upper misstatement bounds falls between the understatement and overstatement tolerable misstatement amounts.'

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Which one of the following is NOT a problem with monetary-unit selection?
A) accounts with small recorded balances that are significantly understated
B) population items that should have a zero balance but do not
C) population items with a zero recorded balance
D) accounts with negative balances
A) accounts with small recorded balances that are significantly understated
B) population items that should have a zero balance but do not
C) population items with a zero recorded balance
D) accounts with negative balances

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
A statistical method used to estimate the proportion of items in a population containing a characteristic of interest is:
A) variables sampling.
B) population-proportional-to-size sampling.
C) attributes sampling.
D) estimation sampling.
A) variables sampling.
B) population-proportional-to-size sampling.
C) attributes sampling.
D) estimation sampling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Which one of the following statements regarding monetary-unit sampling (MUS)is NOT true?
A) An account with a large balance has a greater chance of being included in the sample than an account with a small balance.
B) There is no need to use stratified sampling with MUS; it occurs automatically.
C) MUS automatically places emphasis on physical units with larger recorded balances.
D) The sampling unit in MUS is the account balance.
A) An account with a large balance has a greater chance of being included in the sample than an account with a small balance.
B) There is no need to use stratified sampling with MUS; it occurs automatically.
C) MUS automatically places emphasis on physical units with larger recorded balances.
D) The sampling unit in MUS is the account balance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Before the population can be considered acceptable based on the acceptable risk of assessing control risk too low (ARO), the computed upper deviation rate (CUDR)must be __________ the tolerable deviation rate (TDR).
A) greater than or equal to
B) greater than
C) less than or equal to
D) less than
A) greater than or equal to
B) greater than
C) less than or equal to
D) less than

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 146 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








