Deck 32: Nuclear Medicine
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/18
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 32: Nuclear Medicine
1
PET scanning is an examination that can visualize a patient's:
A) physiology.
B) anatomy.
C) soft tissue.
D) bone detail.
A) physiology.
B) anatomy.
C) soft tissue.
D) bone detail.
physiology.
2
PET scanners have to be close to the source of positrons because:
A) the positrons cannot travel very far.
B) the nuclides are so unstable.
C) of the examination radioactivity of the nuclides.
D) of the short half-lives of the nuclides.
A) the positrons cannot travel very far.
B) the nuclides are so unstable.
C) of the examination radioactivity of the nuclides.
D) of the short half-lives of the nuclides.
of the short half-lives of the nuclides.
3
When a positron and an electron combine, the result is annihilation radiation of:
A) two photons of 1.022 MeV.
B) two photons of 0.511 MeV.
C) two photons of 180 MeV.
D) multiple gamma photons.
A) two photons of 1.022 MeV.
B) two photons of 0.511 MeV.
C) two photons of 180 MeV.
D) multiple gamma photons.
two photons of 0.511 MeV.
4
Scintillation detectors or gamma cameras use crystals that change:
A) x-rays into electrons.
B) radioactive emissions into light photons.
C) radioactive emissions into electrons.
D) radioactive emissions into electrical pulses.
A) x-rays into electrons.
B) radioactive emissions into light photons.
C) radioactive emissions into electrons.
D) radioactive emissions into electrical pulses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
An array of photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) is located:
A) in front of the crystal.
B) to the back of the crystal.
C) after the pulse height analyzer.
D) after the collimator.
A) in front of the crystal.
B) to the back of the crystal.
C) after the pulse height analyzer.
D) after the collimator.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
One of the major benefits of fusion imaging with PET and CT is:
A) attenuation coefficients are the same.
B) radiation dose is less.
C) metabolic and anatomic evaluation is easier.
D) the same detector can be used for both.
A) attenuation coefficients are the same.
B) radiation dose is less.
C) metabolic and anatomic evaluation is easier.
D) the same detector can be used for both.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
One desirable characteristic of a radiopharmaceutical is:
A) long physical half-life in days.
B) millisecond effective half-life.
C) easily absorbed in surrounding tissues.
D) primary photon energy between 100 and 140 keV.
A) long physical half-life in days.
B) millisecond effective half-life.
C) easily absorbed in surrounding tissues.
D) primary photon energy between 100 and 140 keV.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Half-life (T 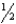 ) is described as the time required for:
) is described as the time required for:
A) half the nuclide to leave the body.
B) half the nuclide to disappear.
C) the nuclide to decay to half its original activity.
D) the original activity to increase by one half.
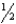 ) is described as the time required for:
) is described as the time required for:A) half the nuclide to leave the body.
B) half the nuclide to disappear.
C) the nuclide to decay to half its original activity.
D) the original activity to increase by one half.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Unwanted photons or "noise" are reduced by using a:
A) pulse height analyzer.
B) collimator.
C) Geiger counter.
D) scintillator.
A) pulse height analyzer.
B) collimator.
C) Geiger counter.
D) scintillator.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The crystal used in gamma cameras is made of:
A) sodium iodide.
B) cesium-activated iodide.
C) thallium-activated sodium iodide.
D) lithium fluoride.
A) sodium iodide.
B) cesium-activated iodide.
C) thallium-activated sodium iodide.
D) lithium fluoride.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Naturally occurring radionuclides are not used for nuclear medicine imaging because:
A) synthetic ones are cheaper.
B) there is a high patient dose from natural ones.
C) synthetic ones decay differently.
D) they are not strong emitters.
A) synthetic ones are cheaper.
B) there is a high patient dose from natural ones.
C) synthetic ones decay differently.
D) they are not strong emitters.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
If only one photon is detected and no other photon is observed during the time window for an annihilation pair, then:
A) the original event is discarded.
B) only the one photon is recorded.
C) the computer estimates the probable location.
D) the examination must be repeated in an hour.
A) the original event is discarded.
B) only the one photon is recorded.
C) the computer estimates the probable location.
D) the examination must be repeated in an hour.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Collimators are used in nuclear medicine to:
A) cone down the beam.
B) limit patient dose from the radiation.
C) maintain signal strength.
D) keep scattered rays from entering the camera.
A) cone down the beam.
B) limit patient dose from the radiation.
C) maintain signal strength.
D) keep scattered rays from entering the camera.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The most common radionuclide used in nuclear medicine is:
A) technetium (99mTc).
B) iodine (123I).
C) thallium (201Tl).
D) xenon (133Xe).
A) technetium (99mTc).
B) iodine (123I).
C) thallium (201Tl).
D) xenon (133Xe).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The radiotracer for PET scanning is chosen for:
A) studies that will show only anatomy.
B) its long half-life compared with nuclear medicine.
C) its similarity to naturally occurring biochemicals.
D) faster examination times.
A) studies that will show only anatomy.
B) its long half-life compared with nuclear medicine.
C) its similarity to naturally occurring biochemicals.
D) faster examination times.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Positron-emitting radionuclides have a:
1)neutron-deficient nucleus.
2)proton-deficient nucleus.
3)similar size to electrons.
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)neutron-deficient nucleus.
2)proton-deficient nucleus.
3)similar size to electrons.
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The most common device used to produce nuclides for PET scanning is the:
A) high-frequency generator.
B) compact medical cyclotron.
C) linear accelerator.
D) pulse height analyzer.
A) high-frequency generator.
B) compact medical cyclotron.
C) linear accelerator.
D) pulse height analyzer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
SPECT imaging produces images that:
A) are similar to those done in CT.
B) will show only large lesions.
C) require increased amounts of radionuclides.
D) show only motion.
A) are similar to those done in CT.
B) will show only large lesions.
C) require increased amounts of radionuclides.
D) show only motion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








