Deck 15: The Importance of Energy Changes and Electron Transfer in Metabolism
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 15: The Importance of Energy Changes and Electron Transfer in Metabolism
1
By definition, a spontaneous reaction is one in which
A) energy is released.
B) energy is absorbed.
C) the energy change is zero.
D) the reaction happens quickly
E) energy is released and the reaction happens quickly
A) energy is released.
B) energy is absorbed.
C) the energy change is zero.
D) the reaction happens quickly
E) energy is released and the reaction happens quickly
A
2
Which best describes the ΔG for hydrolysis of creatine phosphate under cellular conditions in which the concentration of creatine phosphate, creatine, and phosphate all equal 1 mM at 25°C. The ΔG° for the hydrolysis of creatine phosphate at 25°C is −43 kJ/mol.
A) ΔG < −43 kJ/mol
B) ΔG = −43 kJ/mol
C) −43 kJ/mol < ΔG ≤ 0 kJ/mol
D) ΔG > 0 kJ/mol
A) ΔG < −43 kJ/mol
B) ΔG = −43 kJ/mol
C) −43 kJ/mol < ΔG ≤ 0 kJ/mol
D) ΔG > 0 kJ/mol
A
3
Living things are _____
A) a closed system
B) an open system
C) an isolated system
D) none of these
A) a closed system
B) an open system
C) an isolated system
D) none of these
B
4
Consider this rxn which has a ΔG° = +0.4 kJ/mol. succinate + FAD ↔ fumarate + FADH2??1 mM of each compound are mixed & the reaction is allowed to come to equilibrium. Which statement is correct about the resulting concentration of FAD at equilibrium?
A) [FAD] > [FADH2]
B) [FAD] < [FADH2]
C) [FAD] = [FADH2]
D) Cannot be determined from the information provided.
A) [FAD] > [FADH2]
B) [FAD] < [FADH2]
C) [FAD] = [FADH2]
D) Cannot be determined from the information provided.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
An isolated system can exchange ______ with its surroundings
A) energy but not matter
B) matter but not energy
C) both matter and energy
D) neither matter nor energy
A) energy but not matter
B) matter but not energy
C) both matter and energy
D) neither matter nor energy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
In general, catabolism
A) releases energy.
B) absorbs energy.
C) neither absorbs nor releases energy.
A) releases energy.
B) absorbs energy.
C) neither absorbs nor releases energy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Consider this rxn which has a ΔG° = +0.4 kJ/mol. A + B ↔ C + D 1 M A, 1 M B, 0.1 M C and 0.1 M D are added to a container at room temperature. Which of the following statements is true?
A) ΔG < 0 (i.e., it's negative)
B) ΔG = 0
C) ΔG > 0 (i.e., it's positive)
D) Cannot be determined from the information provided.
A) ΔG < 0 (i.e., it's negative)
B) ΔG = 0
C) ΔG > 0 (i.e., it's positive)
D) Cannot be determined from the information provided.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Consider this rxn which has a ΔG° = +0.4 kJ/mol. A + B ↔ C + D 1 M A, 1 M B, 0.1 M C and 0.1 M D are added to a container at room temperature. Which of the following statements is true?
A) The reaction will proceed in the forward direction to reach equilibrium.
B) The reaction will proceed in the backward direction to reach equilibrium.
C) The reaction will not proceed in either direction; it is already at equilibrium.
D) Cannot be determined from the information provided.
A) The reaction will proceed in the forward direction to reach equilibrium.
B) The reaction will proceed in the backward direction to reach equilibrium.
C) The reaction will not proceed in either direction; it is already at equilibrium.
D) Cannot be determined from the information provided.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
A biological reaction with a significantly postive ΔG under cellular conditions may proceed in the forward direction because
A) The cell will change the concentrations of the substrates and products so that the reaction can occur
B) The cell will raise the temperature, thereby affecting the overall thermodynamics of the reaction
C) the reaction can be coupled to a reaction with a more significant negative ΔG
D) reactions with positive ΔG values always proceed in the forward direction
E) None of these
A) The cell will change the concentrations of the substrates and products so that the reaction can occur
B) The cell will raise the temperature, thereby affecting the overall thermodynamics of the reaction
C) the reaction can be coupled to a reaction with a more significant negative ΔG
D) reactions with positive ΔG values always proceed in the forward direction
E) None of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
I am performing a reaction, A → B, with ΔG°' = −5000 kJ/mol. I start the reaction with 10 mM A and no B. After allowing the reaction to proceed for 24 hrs at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, I analyze a sample of the reaction mix to find I now have 8 mM A and 2 mM B. Which of the following conclusions should I make?
A) The reaction has reached equilibrium.
B) I should come back again later; equilibrium has not yet been reached.
C) The formation of B from A is thermodynamically unfavorable, so I should find another starting material to make B.
D) I must've screwed up; there's no way I could get that result with that ΔG°'
A) The reaction has reached equilibrium.
B) I should come back again later; equilibrium has not yet been reached.
C) The formation of B from A is thermodynamically unfavorable, so I should find another starting material to make B.
D) I must've screwed up; there's no way I could get that result with that ΔG°'

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Biochemists use a modified value for standard ΔG values because
A) all reagents are not at a 1 molar concentration.
B) the pH in living systems is seldom, if ever, near 0.
C) the concentration of water is not at 1 molar concentration.
D) the reagents are not one molar and the pH = 7.
E) All of these justify why biochemists use a special ΔG value.
A) all reagents are not at a 1 molar concentration.
B) the pH in living systems is seldom, if ever, near 0.
C) the concentration of water is not at 1 molar concentration.
D) the reagents are not one molar and the pH = 7.
E) All of these justify why biochemists use a special ΔG value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements concerning the free energy change (ΔG) is false?
A) The energy change for a reaction depends only on the initial and final states, and is independent of the path taken.
B) The overall energy change for a reaction could be calculated by summing the energy changes for a series of separate reactions that could convert the reactants to the products.
C) The rate of a reaction can be determined from the energy change.
D) The energy change is a function of the concentrations of the products and reactants at start.
E) All of the answers are true
A) The energy change for a reaction depends only on the initial and final states, and is independent of the path taken.
B) The overall energy change for a reaction could be calculated by summing the energy changes for a series of separate reactions that could convert the reactants to the products.
C) The rate of a reaction can be determined from the energy change.
D) The energy change is a function of the concentrations of the products and reactants at start.
E) All of the answers are true

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
I am performing a reaction, A → B, with ΔG°' = −0.3 kJ/mol. I start the reaction with 10 mM A and no B. After allowing the reaction to proceed for 24 hrs at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, I analyze a sample of the reaction mix to find I now have 1 mM A and 9 mM B. Which of the following conclusions should I make?
A) The reaction has reached equilibrium.
B) I should come back again later; equilibrium has not yet been reached.
C) The formation of B from A is thermodynamically unfavorable, so I should find another starting material to make B.
D) I must've screwed up; there's no way I could get that result with that ΔG°'
A) The reaction has reached equilibrium.
B) I should come back again later; equilibrium has not yet been reached.
C) The formation of B from A is thermodynamically unfavorable, so I should find another starting material to make B.
D) I must've screwed up; there's no way I could get that result with that ΔG°'

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements apply to anabolism?
A) proceeds in stages
B) requires energy
C) requires reducing agents
D) all of these
A) proceeds in stages
B) requires energy
C) requires reducing agents
D) all of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The standard state usually used in biochemistry (ΔG°') includes
A) all concentrations at 1 M.
B) all concentrations at 1 M, except for [H+], which is 10−7 M.
C) same as a), but at 25° C.
D) same as b), but at 25° C.
E) None of the answers
A) all concentrations at 1 M.
B) all concentrations at 1 M, except for [H+], which is 10−7 M.
C) same as a), but at 25° C.
D) same as b), but at 25° C.
E) None of the answers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Which of the following is not true concerning standard states?
A) For pure liquids, the standard state is 1M
B) For pure solids, the standard state is the pure solid itself
C) For gases, the standard state is 1 atmosphere
D) For solutes, the standard state is 1M
E) All of the answers are true
A) For pure liquids, the standard state is 1M
B) For pure solids, the standard state is the pure solid itself
C) For gases, the standard state is 1 atmosphere
D) For solutes, the standard state is 1M
E) All of the answers are true

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
In general, catabolism
A) is an oxidative process that releases energy
B) is a reductive process that releases energy
C) is an oxidative process that requires energy
D) is a reductive process that requires energy
E) none of these
A) is an oxidative process that releases energy
B) is a reductive process that releases energy
C) is an oxidative process that requires energy
D) is a reductive process that requires energy
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
"Metabolism" refers to
A) the breakdown of larger molecules into smaller ones.
B) the production of larger molecules from smaller ones.
C) both of these
D) none of these
A) the breakdown of larger molecules into smaller ones.
B) the production of larger molecules from smaller ones.
C) both of these
D) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The standard state of a solution is taken as
A) 1 atmosphere of pressure.
B) the pure solute.
C) 1 molar concentration.
D) 1 % by weight
E) none of the above.
A) 1 atmosphere of pressure.
B) the pure solute.
C) 1 molar concentration.
D) 1 % by weight
E) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The production of larger molecules from smaller ones is called
A) metabolism.
B) catabolism.
C) anabolism.
D) none of these
A) metabolism.
B) catabolism.
C) anabolism.
D) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Exhibit 15A Consider the reaction of alcohol dehydrogenase.
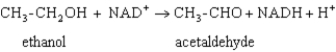
Refer to Exhibit 15A. Which is the oxidizing agent?
A) Ethanol
B) NAD+
C) Acetaldehyde
D) NADH
E) H+

Refer to Exhibit 15A. Which is the oxidizing agent?
A) Ethanol
B) NAD+
C) Acetaldehyde
D) NADH
E) H+

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
What happens to the entropy when ATP is hydrolysed to ADP?
A) Entropy increases
B) Entropy decreases.
C) Entropy doesn't change.
D) ATP has no entropy.
A) Entropy increases
B) Entropy decreases.
C) Entropy doesn't change.
D) ATP has no entropy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
In biological redox reactions, hydrogen ions are usually transferred along with electrons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which of the following is not true?
A) Molecular oxygen is always a substrate in oxidation reactions.
B) Oxidation reactions involve the movement of electrons from one molecule to another
C) When a molecule is oxidized, it loses electrons
D) Reduction involves the gain of electrons
A) Molecular oxygen is always a substrate in oxidation reactions.
B) Oxidation reactions involve the movement of electrons from one molecule to another
C) When a molecule is oxidized, it loses electrons
D) Reduction involves the gain of electrons

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
The conversion of NAD+ to NADH is an example of reduction because
A) the pyridine ring loses electrons (and a hydrogen)
B) the pyridine ring gains electrons (and a hydrogen)
C) the adenine ring loses electrons
D) the adenine ring gains electrons
A) the pyridine ring loses electrons (and a hydrogen)
B) the pyridine ring gains electrons (and a hydrogen)
C) the adenine ring loses electrons
D) the adenine ring gains electrons

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
During reduction
A) electrons are lost.
B) electrons are gained.
C) electrons may either be lost or gained.
D) hydrogen is formed.
A) electrons are lost.
B) electrons are gained.
C) electrons may either be lost or gained.
D) hydrogen is formed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
In general, the anabolic pathways tend to involve oxidation reactions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
An organism that is at equilibrium would be
A) in a steady state
B) an open system
C) dead
D) energetically balanced
A) in a steady state
B) an open system
C) dead
D) energetically balanced

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
"Oxidation" refers to
A) the loss of oxygen.
B) the gain of oxygen.
C) the loss of electrons.
D) the gain of electrons.
A) the loss of oxygen.
B) the gain of oxygen.
C) the loss of electrons.
D) the gain of electrons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Consider these reactions: ATP → ADP + Pi
ΔG°' = −31 kJ/mol
Glucose-6-phosphate → glucose + Pi
ΔG°' = −13 kJ/mol
Glucose + ATP → glucose-6-phosphate + ADP
ΔG°' = ?
What is the ΔG°' of the last reaction?
A) −44 kJ/mol
B) −18 kJ/mol
C) +18 kJ/mol
D) +44 kJ/mol
E) Cannot be determined from the information provided.
ΔG°' = −31 kJ/mol
Glucose-6-phosphate → glucose + Pi
ΔG°' = −13 kJ/mol
Glucose + ATP → glucose-6-phosphate + ADP
ΔG°' = ?
What is the ΔG°' of the last reaction?
A) −44 kJ/mol
B) −18 kJ/mol
C) +18 kJ/mol
D) +44 kJ/mol
E) Cannot be determined from the information provided.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Exhibit 15A Consider the reaction of alcohol dehydrogenase.

Refer to Exhibit 15A. Which molecule is reduced?
A) Ethanol
B) NAD+
C) Acetaldehyde
D) NADH
E) H+

Refer to Exhibit 15A. Which molecule is reduced?
A) Ethanol
B) NAD+
C) Acetaldehyde
D) NADH
E) H+

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Which of the following coenzymes is derived from riboflavin?
A) Coenzyme A
B) NAD+.
C) FAD
D) All of the above.
E) None of the above.
A) Coenzyme A
B) NAD+.
C) FAD
D) All of the above.
E) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
In order to drive the synthesis of ATP, the hydrolysis of an organic phosphate
A) must have a higher free energy change.
B) must have a lower free energy change.
C) must have a free energy change equal to that of ATP.
A) must have a higher free energy change.
B) must have a lower free energy change.
C) must have a free energy change equal to that of ATP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Which of the following coenzymes is not a carrier of electrons in biological redox reactions?
A) Coenzyme A
B) Niacin.
C) Riboflavin.
D) Transition metal ions, such as those of iron or copper.
E) All of these can be intermediate electron carriers.
A) Coenzyme A
B) Niacin.
C) Riboflavin.
D) Transition metal ions, such as those of iron or copper.
E) All of these can be intermediate electron carriers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The oxidation of nutrients supplies the energy to produce ATP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which of the following is not a part of FAD?
A) Ribitol
B) isoalloxazine
C) adenine
D) ribose
E) nicotinamide
A) Ribitol
B) isoalloxazine
C) adenine
D) ribose
E) nicotinamide

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
An oxidizing agent
A) loses oxygen.
B) gains oxygen.
C) loses electrons.
D) gains electrons.
A) loses oxygen.
B) gains oxygen.
C) loses electrons.
D) gains electrons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
In the coenzyme FAD the site to which electrons are transferred is
A) the ribose moiety of the molecule
B) a purine ring system
C) a pyrimidine ring system
D) a nitrogen-containing ring system
A) the ribose moiety of the molecule
B) a purine ring system
C) a pyrimidine ring system
D) a nitrogen-containing ring system

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
ATP is a good source of energy to run metabolic reactions for all the following reasons, except:
A) The pyrophosphate bond has a high energy of hydrolysis.
B) The sugar group is very reactive.
C) The bonds between the phosphates are acid anhydrides.
D) The phosphate groups can combine readily with other molecules.
E) All of these explain why ATP is a good energy source.
A) The pyrophosphate bond has a high energy of hydrolysis.
B) The sugar group is very reactive.
C) The bonds between the phosphates are acid anhydrides.
D) The phosphate groups can combine readily with other molecules.
E) All of these explain why ATP is a good energy source.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Exhibit 15A Consider the reaction of alcohol dehydrogenase.

Refer to Exhibit 15A. Which molecule loses electrons?
A) Ethanol
B) NAD+
C) Acetaldehyde
D) NADH
E) H+

Refer to Exhibit 15A. Which molecule loses electrons?
A) Ethanol
B) NAD+
C) Acetaldehyde
D) NADH
E) H+

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
If the reaction A → B has ΔG = +25 Joule/mol and the reaction B → C has ΔG = −15 Joule/mol, the overall energy change A → C will be
A) −40 Joule/mol.
B) −15 Joule/mol.
C) +10 Joule/mol.
D) +40 Joule/mol.
E) You cannot determine the overall reaction from the given data.
A) −40 Joule/mol.
B) −15 Joule/mol.
C) +10 Joule/mol.
D) +40 Joule/mol.
E) You cannot determine the overall reaction from the given data.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The body allows energy consuming reactions to occur by coupling them with reactions which have a negative ΔG.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The number of degrees of freedom a molecule has is related to the numbers of resonant structures it has.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
When we say that the efficiency of glycolysis is about 33% we mean that
A) 2 ATP are produced and 6 ATP are involved in the overall process
B) 2 ATP are produced in the oxidation of glucose, which contains six carbon atoms
C) the energy used to phosphorylate 2 ATP is 33% of the energy released in the process
D) all of these
A) 2 ATP are produced and 6 ATP are involved in the overall process
B) 2 ATP are produced in the oxidation of glucose, which contains six carbon atoms
C) the energy used to phosphorylate 2 ATP is 33% of the energy released in the process
D) all of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
In metabolism the term "activation" refers to
A) conversion of a component of a metabolic pathway into a reactive compound.
B) addition of a catalyst.
C) bypassing endergonic reactions in a pathway.
D) bypassing the unreactive components of a pathway.
A) conversion of a component of a metabolic pathway into a reactive compound.
B) addition of a catalyst.
C) bypassing endergonic reactions in a pathway.
D) bypassing the unreactive components of a pathway.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Many cells oxidize fatty acids to produce ATP. If no ATP were produced, the ΔG°' of this process would be
A) unchanged
B) a larger positive number
C) a larger negative number
D) impossible to determine
A) unchanged
B) a larger positive number
C) a larger negative number
D) impossible to determine

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
In order to initiate many metabolic pathways it is necessary to activate the starting materials.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Which of the following are examples of exergonic processes?
A) protein synthesis and active transport
B) protein synthesis and oxidation of carbohydrates
C) active transport and oxidation of carbohydrates
D) oxidation of fats and of carbohydrates
A) protein synthesis and active transport
B) protein synthesis and oxidation of carbohydrates
C) active transport and oxidation of carbohydrates
D) oxidation of fats and of carbohydrates

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Spontaneous reaction always occurs at a relatively fast rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
What happens to the entropy when ATP is hydrolysed to ADP?
A) Entropy increases
B) Entropy decreases.
C) Entropy doesn't change.
D) ATP has no entropy.
A) Entropy increases
B) Entropy decreases.
C) Entropy doesn't change.
D) ATP has no entropy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Which of the following are examples of endergonic processes?
A) protein synthesis and active transport
B) protein synthesis and oxidation of carbohydrates
C) active transport and oxidation of carbohydrates
D) oxidation of fats and of carbohydrates
A) protein synthesis and active transport
B) protein synthesis and oxidation of carbohydrates
C) active transport and oxidation of carbohydrates
D) oxidation of fats and of carbohydrates

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Which of the following is not a mechanism used to activate substrates for further metabolism?
A) Addition of a phosphate group.
B) Combination with a vitamin, such as coenzyme A.
C) Hydrolyzing a polymer into its component monomers.
D) Addition of a phosphate group or combining with a vitamin.
E) All of these processes activate substrates.
A) Addition of a phosphate group.
B) Combination with a vitamin, such as coenzyme A.
C) Hydrolyzing a polymer into its component monomers.
D) Addition of a phosphate group or combining with a vitamin.
E) All of these processes activate substrates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
An example of an activation step in metabolism is
A) the hydrolysis of a triacylglycerol.
B) the cis-trans isomerization of retinal.
C) the formation of an acyl derivative of coenzyme A.
D) the formation of the peptide bond.
A) the hydrolysis of a triacylglycerol.
B) the cis-trans isomerization of retinal.
C) the formation of an acyl derivative of coenzyme A.
D) the formation of the peptide bond.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The energy released during metabolism of nutrients can be used to synthesize ATP from ADP and phosphate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The efficiency of aerobic metabolism is greater than that of anaerobic metabolism even though much more energy is released in aerobic than in anaerobic metabolism because
A) aerobic metabolism is linked to oxygen, which is a more powerful oxidizing agent than those in anaerobic metabolism
B) aerobic metabolism produces carbon dioxide and water
C) aerobic metabolism traps much more energy in the form of ATP than does anaerobic metabolism
D) anaerobic metabolism produces two- and three-carbon compounds
A) aerobic metabolism is linked to oxygen, which is a more powerful oxidizing agent than those in anaerobic metabolism
B) aerobic metabolism produces carbon dioxide and water
C) aerobic metabolism traps much more energy in the form of ATP than does anaerobic metabolism
D) anaerobic metabolism produces two- and three-carbon compounds

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
The linking of an exergonic reaction to drive an endergonic reaction is called:
A) coupling
B) a state function
C) resonance
D) catabolsim
A) coupling
B) a state function
C) resonance
D) catabolsim

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Metabolism takes place in stages
A) because enzymes cannot catalyze the process efficiently
B) and allows for efficient production and use of energy
C) because large free energy changes cannot occur in living organisms
D) to use highly unreactive compounds
A) because enzymes cannot catalyze the process efficiently
B) and allows for efficient production and use of energy
C) because large free energy changes cannot occur in living organisms
D) to use highly unreactive compounds

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
What happens to the entropy of a molecule as the number of resonance structures increases?
A) Entropy also increases.
B) Entropy decreases.
C) Entropy has no relationship to the number of resonance structures.
A) Entropy also increases.
B) Entropy decreases.
C) Entropy has no relationship to the number of resonance structures.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The hydrolysis of ATP can be used to drive reactions that have a ΔG°' that is
A) greater than +5 kJ/mol
B) less than +5 kJ/mol
C) between +20 and +40 kJ/mol
D) not possible to determine from the information in this chapter
A) greater than +5 kJ/mol
B) less than +5 kJ/mol
C) between +20 and +40 kJ/mol
D) not possible to determine from the information in this chapter

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The phosphorylation of ADP to produce ATP is endergonic because
A) a negatively charged ion is bonded to a molecule that already carries a negative charge
B) ATP is more stable than ADP
C) the entropy of the products is less than that of the reactants
D) polyphosphate chains are the storage form of phosphorus in living organisms
A) a negatively charged ion is bonded to a molecule that already carries a negative charge
B) ATP is more stable than ADP
C) the entropy of the products is less than that of the reactants
D) polyphosphate chains are the storage form of phosphorus in living organisms

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








