Deck 21: Viruses,bacteria,archaea,and Protists: the Diversity of Life 1
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/68
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 21: Viruses,bacteria,archaea,and Protists: the Diversity of Life 1
1
The life cycle of viruses involves:
A)production of new virus particles on the outside of a cell.
B)reproducing on the surface of a cell.
C)filling the host cell with viral particles.
D)attaching viral DNA to the surface of a cell.
A)production of new virus particles on the outside of a cell.
B)reproducing on the surface of a cell.
C)filling the host cell with viral particles.
D)attaching viral DNA to the surface of a cell.
C
2
A major difference between bacteria and eukaryotes is that bacteria have:
A)a rod-shaped nucleus.
B)no membrane-bound organelles.
C)faster mitosis as their method of sexual reproduction.
D)no ribosomes.
A)a rod-shaped nucleus.
B)no membrane-bound organelles.
C)faster mitosis as their method of sexual reproduction.
D)no ribosomes.
B
3
The human immunodeficiency virus targets:
A)lymph nodes.
B)all white blood cells.
C)helper T cells.
D)bone marrow cells.
A)lymph nodes.
B)all white blood cells.
C)helper T cells.
D)bone marrow cells.
C
4
The antibiotic penicillin inhibits the ability of bacteria to:
A)make cell walls.
B)synthesize protein.
C)copy DNA.
D)undergo respiration.
A)make cell walls.
B)synthesize protein.
C)copy DNA.
D)undergo respiration.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Which of the following is true of Domain Archaea compared to other groups?
A)They are the only anaerobes on Earth.
B)Their cell wall and membrane biochemistry is unique.
C)Most of their genes are similar to those found in bacteria.
D)None of their genes work like those found in eukaryotes.
A)They are the only anaerobes on Earth.
B)Their cell wall and membrane biochemistry is unique.
C)Most of their genes are similar to those found in bacteria.
D)None of their genes work like those found in eukaryotes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
If antibiotics seem effective against a human illness,then this illness is probably caused by a/an:
A)protist.
B)autoimmune disease.
C)virus.
D)bacterium.
A)protist.
B)autoimmune disease.
C)virus.
D)bacterium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which phrase most accurately describes the genome of most viruses?
A)surprisingly complex, with tens of thousands of genes
B)surprisingly complex, with around 1 million genes
C)the same as most bacteria, with hundreds of genes
D)relatively simple, with around a dozen genes or fewer
A)surprisingly complex, with tens of thousands of genes
B)surprisingly complex, with around 1 million genes
C)the same as most bacteria, with hundreds of genes
D)relatively simple, with around a dozen genes or fewer

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The main decomposers on Earth are the:
A)viruses and protists.
B)plants and animals.
C)bacteria and fungi.
D)plants and fungi.
A)viruses and protists.
B)plants and animals.
C)bacteria and fungi.
D)plants and fungi.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The viral capsid is:
A)a fatty membrane surrounding the virus.
B)the genetic material at the core.
C)a protein coat around the genetic material.
D)the viral offspring that rupture the cell and escape.
A)a fatty membrane surrounding the virus.
B)the genetic material at the core.
C)a protein coat around the genetic material.
D)the viral offspring that rupture the cell and escape.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
In general,most antibiotics work by:
A)exploiting differences between human and bacterial cells.
B)preventing bacteria from entering human cells.
C)preventing viruses from entering human cells.
D)boosting the human immune system.
A)exploiting differences between human and bacterial cells.
B)preventing bacteria from entering human cells.
C)preventing viruses from entering human cells.
D)boosting the human immune system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Which organisms accomplish most of the work of converting atmospheric nitrogen into a form usable to green plants?
A)bacteria and archaea
B)viruses
C)protists
D)fungi
A)bacteria and archaea
B)viruses
C)protists
D)fungi

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which statement about the relationship between bacteria and the human body is most accurate?
A)Although many tissues are kept bacteria-free, around 100 trillion bacteria live on or in us.
B)About one-tenth of our body weights are due to bacteria
C)Bacteria are found in the mouth, stomach, and intestines in about equal amounts.
D)Most bacteria are transient; that is, they come for brief periods and then are gone.
A)Although many tissues are kept bacteria-free, around 100 trillion bacteria live on or in us.
B)About one-tenth of our body weights are due to bacteria
C)Bacteria are found in the mouth, stomach, and intestines in about equal amounts.
D)Most bacteria are transient; that is, they come for brief periods and then are gone.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A bacterium that is pathogenic:
A)is flexible regarding use of metabolic pathways.
B)has genes similar to viruses.
C)is a disease-causing organism.
D)benefits from living inside humans and produces nutrients for us.
A)is flexible regarding use of metabolic pathways.
B)has genes similar to viruses.
C)is a disease-causing organism.
D)benefits from living inside humans and produces nutrients for us.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which of the following is the best description of a virus?
A)A virus is the smallest living thing.
B)A virus is a life-form that can reproduce inside cells or independently.
C)A virus is a tiny spore-producing cell.
D)A virus is a noncellular, replicating entity.
A)A virus is the smallest living thing.
B)A virus is a life-form that can reproduce inside cells or independently.
C)A virus is a tiny spore-producing cell.
D)A virus is a noncellular, replicating entity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Bacteria that benefit from living in or on us while we are unaffected by the relationship are termed:
A)commensal.
B)pathogenic.
C)mutualistic.
D)probiotic.
A)commensal.
B)pathogenic.
C)mutualistic.
D)probiotic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The process by which viruses can exchange genetic sequences to come up with a "new" virus such as H1N1 is:
A)recombination.
B)reassortment.
C)independent assortment.
D)conjugation.
A)recombination.
B)reassortment.
C)independent assortment.
D)conjugation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The material in the core of HIV (AIDS virus)is:
A)protein.
B)xarbohydrate.
C)DNA.
D)RNA.
A)protein.
B)xarbohydrate.
C)DNA.
D)RNA.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which of the following would support the hypothesis that bacteria have mutually beneficial relationships with us?
A)Bacteria derive benefit from waste materials in our intestines.
B)Mice that were made "germ free" did not absorb and metabolize nutrients as well.
C)Bacteria can metabolize food using alternate pathways.
D)Most intestinal bacteria cannot live outside the body.
A)Bacteria derive benefit from waste materials in our intestines.
B)Mice that were made "germ free" did not absorb and metabolize nutrients as well.
C)Bacteria can metabolize food using alternate pathways.
D)Most intestinal bacteria cannot live outside the body.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which of the following would support the statement that bacteria represent the most fundamentally diverse group on Earth?
A)Bacteria exist in varieties with and without cell walls.
B)Bacteria accomplish all characteristics of life as small, single cells.
C)Bacteria are metabolically diverse regarding oxygen and food requirements.
D)Bacteria come in several different shapes.
A)Bacteria exist in varieties with and without cell walls.
B)Bacteria accomplish all characteristics of life as small, single cells.
C)Bacteria are metabolically diverse regarding oxygen and food requirements.
D)Bacteria come in several different shapes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The botulism bacterium can kill a person by:
A)killing muscle cells.
B)secreting a toxin that paralyzes muscles.
C)causing brain hemorrhages.
D)producing lethally high fevers.
A)killing muscle cells.
B)secreting a toxin that paralyzes muscles.
C)causing brain hemorrhages.
D)producing lethally high fevers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Which statement best describes our current understanding of protist evolution?
A)Protists evolved from the Archaea while other eukaryotes did not.
B)Protists evolved from multicellular eukaryotes.
C)Protists evolved from separate branches off the early eukaryotic line.
D)Protists evolved from eukaryotic parasites.
A)Protists evolved from the Archaea while other eukaryotes did not.
B)Protists evolved from multicellular eukaryotes.
C)Protists evolved from separate branches off the early eukaryotic line.
D)Protists evolved from eukaryotic parasites.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Refer to the scenario below, and then answer the following question(s).
As part of your field biology independent study, you visit a small lake with an extremely high salt concentration. Searching with nets and other sampling devices, you find no fish, plants, algae, or any visible signs of life in the lake. Still, you decide to take a few samples of the water back to the lab. You find the sample teeming with very small cells, hundreds of times smaller than a typical human cell. These cells have cell walls, which you analyze chemically and find they are not made of peptidoglycan or cellulose.
Based upon the chemical experiments you performed,how would you classify these life-forms?
A)protists
B)fungi
C)bacteria
D)archaea
As part of your field biology independent study, you visit a small lake with an extremely high salt concentration. Searching with nets and other sampling devices, you find no fish, plants, algae, or any visible signs of life in the lake. Still, you decide to take a few samples of the water back to the lab. You find the sample teeming with very small cells, hundreds of times smaller than a typical human cell. These cells have cell walls, which you analyze chemically and find they are not made of peptidoglycan or cellulose.
Based upon the chemical experiments you performed,how would you classify these life-forms?
A)protists
B)fungi
C)bacteria
D)archaea

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
An example of a protist intestinal parasite would be:
A)Clostridium botulinum.
B)Yersinia pestis.
C)Chlamydomonas.
D)Giardia.
A)Clostridium botulinum.
B)Yersinia pestis.
C)Chlamydomonas.
D)Giardia.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
In what type of environment would you be most likely to find anaerobes?
A)high temperature
B)high acidity
C)high salt content
D)no oxygen
A)high temperature
B)high acidity
C)high salt content
D)no oxygen

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
What is the benefit of sexual reproduction in protists?
A)greater variation among offspring
B)fast increase in numbers
C)availability of more environments
D)ease of finding a mate
A)greater variation among offspring
B)fast increase in numbers
C)availability of more environments
D)ease of finding a mate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Which of the following areas/conditions would be favored by thermophiles?
A)anaerobic conditions
B)deep-sea volcanic vents
C)the arctic tundra
D)the stomachs of herbivores
A)anaerobic conditions
B)deep-sea volcanic vents
C)the arctic tundra
D)the stomachs of herbivores

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Organisms called plasmodial slime molds move by which process?
A)beating of cilia
B)cytoplasmic streaming
C)contractile cytoskeleton movements
D)growth in the direction of sunlight
A)beating of cilia
B)cytoplasmic streaming
C)contractile cytoskeleton movements
D)growth in the direction of sunlight

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Refer to the scenario below, and then answer the following question(s).
As part of your field biology independent study, you visit a small lake with an extremely high salt concentration. Searching with nets and other sampling devices, you find no fish, plants, algae, or any visible signs of life in the lake. Still, you decide to take a few samples of the water back to the lab. You find the sample teeming with very small cells, hundreds of times smaller than a typical human cell. These cells have cell walls, which you analyze chemically and find they are not made of peptidoglycan or cellulose.
Based upon the environment in which you found these life-forms,how would you categorize them?
A)thermophiles
B)halophiles
C)anaerobes
D)methanogens
As part of your field biology independent study, you visit a small lake with an extremely high salt concentration. Searching with nets and other sampling devices, you find no fish, plants, algae, or any visible signs of life in the lake. Still, you decide to take a few samples of the water back to the lab. You find the sample teeming with very small cells, hundreds of times smaller than a typical human cell. These cells have cell walls, which you analyze chemically and find they are not made of peptidoglycan or cellulose.
Based upon the environment in which you found these life-forms,how would you categorize them?
A)thermophiles
B)halophiles
C)anaerobes
D)methanogens

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Volvox and Paramecium share which characteristic?
A)photosynthetic ability
B)movement
C)true multicellularity
D)anaerobic respiration
A)photosynthetic ability
B)movement
C)true multicellularity
D)anaerobic respiration

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Cells such as those of golden algae that form stable associations but do not take on specialized roles are described as:
A)incomplete unicellular.
B)selective multicellularity.
C)true multicellularity.
D)colonial multicellularity.
A)incomplete unicellular.
B)selective multicellularity.
C)true multicellularity.
D)colonial multicellularity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Which organisms form the basic foundation of the food chain in the ocean?
A)shrimp
B)krill
C)phytoplankton
D)jellyfish
A)shrimp
B)krill
C)phytoplankton
D)jellyfish

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Amoeba and phytoplankton differ in that phytoplankton can:
A)perform photosynthesis.
B)eat krill.
C)move with pseudopodia.
D)live on land.
A)perform photosynthesis.
B)eat krill.
C)move with pseudopodia.
D)live on land.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Bacteria are the smallest living things known.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Cilia are:
A)the cytoplasmic extensions or false feet that some cell types use for locomotion.
B)different kinds of cells, each designed to perform a different function.
C)the circular chromosomes of bacteria.
D)many short, hair-like cellular extensions that beat to produce movement.
A)the cytoplasmic extensions or false feet that some cell types use for locomotion.
B)different kinds of cells, each designed to perform a different function.
C)the circular chromosomes of bacteria.
D)many short, hair-like cellular extensions that beat to produce movement.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The core of some viruses is carbohydrate in nature.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
A protist such as Chlamydomonas may switch to sexual reproduction when:
A)there are numerous predators.
B)there is little nutrition.
C)a 90-day cycle is completed.
D)hormones from nearby members of the species are detected.
A)there are numerous predators.
B)there is little nutrition.
C)a 90-day cycle is completed.
D)hormones from nearby members of the species are detected.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Chlamydomonas "mating types" differ in what way?
A)chloroplasts
B)flagella structure
C)interlocking male and female parts
D)membrane phospholipids
A)chloroplasts
B)flagella structure
C)interlocking male and female parts
D)membrane phospholipids

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Plasmodium falciparum is a protozoan that:
A)can switch between plant and animal lifestyles.
B)is closely related to fungi.
C)causes malaria.
D)causes intestinal distress.
A)can switch between plant and animal lifestyles.
B)is closely related to fungi.
C)causes malaria.
D)causes intestinal distress.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Microscopic algae and bacteria produce over half of the oxygen in the atmosphere.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Entamoeba histolytica is a/an:
A)photosynthetic protist.
B)protist that moves using flagella.
C)parasitic protist responsible for dysentery.
D)aggregating protist that can form a "slug-like" organism.
A)photosynthetic protist.
B)protist that moves using flagella.
C)parasitic protist responsible for dysentery.
D)aggregating protist that can form a "slug-like" organism.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The simplest eukaryotes are the bacteria.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Malaria is caused by a bacterium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Some bacteria can obtain their nutrition by photosynthesis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Paramecium is a heterotrophic protist that moves using cilia.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Most bacteria present in the human intestines are pathogenic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Rod-shaped bacteria are called spirochetes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Spherical bacteria are called cocci.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Overuse of antibiotics has likely produced MRSA.MRSA stands for ________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Virus-like entities called viroids lack a ________ and are simply strands of infectious RNA.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
When a virus takes over the machinery of a cell,it forces the cell to manufacture more viral particles.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Bacteria are considered to be a type of protist.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
A long,whip-like tail found in a protist is called a flagellum.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Nearly half the antibiotics used in the United States go into animal feed as growth stimulants.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Bacteria store their DNA within a spherical nucleus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
When bacteria undergo binary fission,they produce identical daughter cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Scientists do not consider viruses to be alive because viruses cannot metabolize outside a host cell.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Most protists are unicellular.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Methanogens are in the ________ category of extremophile.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Refer to the figure below, and then answer the following question(s).
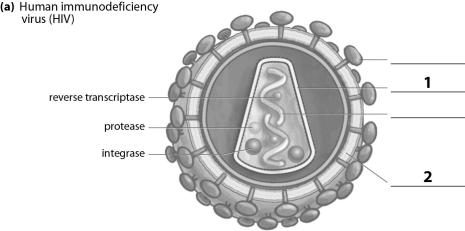
The missing label indicated by a "1" corresponds to the:
A)receptor.
B)capsid.
C)RNA.
D)envelope.

The missing label indicated by a "1" corresponds to the:
A)receptor.
B)capsid.
C)RNA.
D)envelope.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Protists are arguably the most diverse of the eukaryotic kingdoms.Defend that statement using examples to support your ideas.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Scientists mostly agree that viruses are not technically living things.Defend this position based on what you know about what viruses are and how they work.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Defend the position that bacteria are both beneficial and detrimental to humans.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Photosynthetic aquatic microorganisms,such as some bacteria and protists,are known as ________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Some protists have locomotor extensions called ________ and ________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Refer to the figure below, and then answer the following question(s).

The missing label indicated by a "2" corresponds to the:
A)receptor.
B)capsid.
C)RNA.
D)envelope.

The missing label indicated by a "2" corresponds to the:
A)receptor.
B)capsid.
C)RNA.
D)envelope.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








