Deck 13: Fiscal Policy
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/163
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: Fiscal Policy
1
'Fiscal policy' (discretionary fiscal policy)is defined as changes in federal ________ and ________ to achieve macroeconomic objectives such as price stability, healthy rates of economic growth and high employment.
A)taxes; interest rates
B)taxes; financial liquidity in the economy
C)interest rates; financial liquidity in the economy
D)taxes; purchases
A)taxes; interest rates
B)taxes; financial liquidity in the economy
C)interest rates; financial liquidity in the economy
D)taxes; purchases
taxes; purchases
2
In 2015/2016, the largest share of Australian federal government welfare payments went to:
A)unemployment benefits.
B)age pensions and services to the aged.
C)disability pensions and expenditures.
D)payments to families with children.
A)unemployment benefits.
B)age pensions and services to the aged.
C)disability pensions and expenditures.
D)payments to families with children.
age pensions and services to the aged.
3
Government expenditure in Australia as a percentage of GDP has consistently trended upward since the 1960s.
False
4
What is 'fiscal policy' and who is responsible for fiscal policy?
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Which of the following does not function as an automatic stabiliser?
A)Unemployment benefit payments.
B)Government expenditure on road building programs.
C)The Goods and Services Tax (GST).
D)The personal income tax system.
A)Unemployment benefit payments.
B)Government expenditure on road building programs.
C)The Goods and Services Tax (GST).
D)The personal income tax system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The increase in revenue taxation received by the government during an economic boom is due to discretionary fiscal policy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The largest source of revenue for the Australian federal government is:
A)personal income tax.
B)company and petroleum resource tax.
C)petrol excise.
D)superannuation tax.
A)personal income tax.
B)company and petroleum resource tax.
C)petrol excise.
D)superannuation tax.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Which of the following would be considered a fiscal policy action?
A)A city changes its rates of land tax.
B)A federal government creates a subsidy for hybrid cars to encourage the purchase of fuel-efficient cars.
C)Foreign aid is given to Indonesia.
D)A tax cut is designed to stimulate spending during an economic contraction.
A)A city changes its rates of land tax.
B)A federal government creates a subsidy for hybrid cars to encourage the purchase of fuel-efficient cars.
C)Foreign aid is given to Indonesia.
D)A tax cut is designed to stimulate spending during an economic contraction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Federal government expenditure as a proportion of GDP in Australia between 1980 and 2010 has varied between:
A)8% and 12%.
B)15% and 20%.
C)22% and 28%.
D)40% and 45%.
A)8% and 12%.
B)15% and 20%.
C)22% and 28%.
D)40% and 45%.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which of the following is a government 'expenditure' and not a government 'purchase'?
A)The federal government buys a new ship for the defence force.
B)The federal government pays the salary of police.
C)The federal government pays unemployment benefits.
D)The federal government pays to support medical research on AIDS.
A)The federal government buys a new ship for the defence force.
B)The federal government pays the salary of police.
C)The federal government pays unemployment benefits.
D)The federal government pays to support medical research on AIDS.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
During which decade was government expenditure in Australia the highest as a proportion of GDP?
A)1970s
B)1980s
C)1990s
D)2000s
A)1970s
B)1980s
C)1990s
D)2000s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of the following is an automatic stabiliser?
A)Interest rate changes.
B)Increases in government spending on schools.
C)Reductions in nominal wages as inflation rates rise.
D)Unemployment benefit payments to the unemployed.
A)Interest rate changes.
B)Increases in government spending on schools.
C)Reductions in nominal wages as inflation rates rise.
D)Unemployment benefit payments to the unemployed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Which of the following is an example of discretionary fiscal policy?
A)An increase in the number unemployment benefit payments during a recession due to rising unemployment.
B)An increase in income tax receipts during an expansion because incomes are rising.
C)Tax increases to combat rising inflation.
D)A decrease in income tax receipts during a recession because incomes are falling.
A)An increase in the number unemployment benefit payments during a recession due to rising unemployment.
B)An increase in income tax receipts during an expansion because incomes are rising.
C)Tax increases to combat rising inflation.
D)A decrease in income tax receipts during a recession because incomes are falling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
'Fiscal policy' refers to the:
A)government's ability to regulate the functioning of financial markets.
B)policy by the Reserve Bank of Australia to affect the cash rate.
C)techniques used by firms to reduce their tax liability.
D)spending and tax policies used by the government to influence the level of economy activity.
A)government's ability to regulate the functioning of financial markets.
B)policy by the Reserve Bank of Australia to affect the cash rate.
C)techniques used by firms to reduce their tax liability.
D)spending and tax policies used by the government to influence the level of economy activity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
An 'automatic stabiliser' is:
A)a policy for growth of an economy where the current account of the balance of payments is kept in balance.
B)a monetary or fiscal policy that aims to smooth out the business cycle.
C)the tendency for inflation to fall as unemployment rises.
D)a tax or form of government expenditure that has the effect of reducing the size of business cycle fluctuations.
A)a policy for growth of an economy where the current account of the balance of payments is kept in balance.
B)a monetary or fiscal policy that aims to smooth out the business cycle.
C)the tendency for inflation to fall as unemployment rises.
D)a tax or form of government expenditure that has the effect of reducing the size of business cycle fluctuations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Discretionary fiscal policy is when:
A)existing taxation policy automatically smoothes out business cycle fluctuations in the economy.
B)the government changes the levels of expenditure or taxation to achieve a macroeconomic aim.
C)policy is left to the discretion of the Reserve Bank of Australia.
D)politicians are discrete about policy changes and do not advise consumers or producers of new policies.
A)existing taxation policy automatically smoothes out business cycle fluctuations in the economy.
B)the government changes the levels of expenditure or taxation to achieve a macroeconomic aim.
C)policy is left to the discretion of the Reserve Bank of Australia.
D)politicians are discrete about policy changes and do not advise consumers or producers of new policies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Active changes in tax and spending by government intended to smooth out the business cycle are called ________, and changes in taxes and spending that occur passively over the business cycle are called ________.
A)automatic stabilisers; discretionary fiscal policy
B)discretionary fiscal policy; automatic stabilisers
C)automatic stabilisers; monetary policy
D)discretionary fiscal policy; conscious fiscal policy
A)automatic stabilisers; discretionary fiscal policy
B)discretionary fiscal policy; automatic stabilisers
C)automatic stabilisers; monetary policy
D)discretionary fiscal policy; conscious fiscal policy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Government purchases and transfer payments are included in the measure of government expenditures.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
In 2015/2016, after social security and welfare payments, which of the following is the second largest category of Australian federal government expenditures at nearly 16% of the total?
A)defence spending
B)education
C)interest on the debt
D)health care
A)defence spending
B)education
C)interest on the debt
D)health care

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
A deliberate policy change in taxes and government spending to influence the level of aggregate demand is called:
A)an automatic stabiliser.
B)discretionary fiscal policy.
C)a fiscal deficit.
D)a fiscal surplus.
A)an automatic stabiliser.
B)discretionary fiscal policy.
C)a fiscal deficit.
D)a fiscal surplus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Refer to Figure 13.1 for the following questions.
Figure 13.1
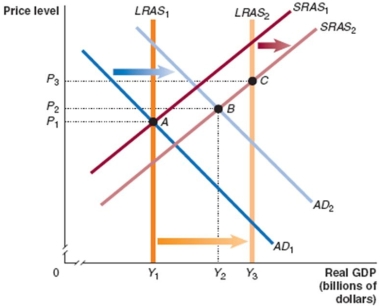
In Figure 13.1, if fiscal policy successfully moves the economy from point B to equilibrium at potential GDP, this will:
A)increase the price level from P₂ to P₃.
B)increase the price level from P₁ to P₂.
C)decrease the price level from P₃ to P₂.
D)decrease the price level from P₂ to P₁.
Figure 13.1

In Figure 13.1, if fiscal policy successfully moves the economy from point B to equilibrium at potential GDP, this will:
A)increase the price level from P₂ to P₃.
B)increase the price level from P₁ to P₂.
C)decrease the price level from P₃ to P₂.
D)decrease the price level from P₂ to P₁.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Consider the hypothetical information in the following table for potential GDP, real GDP and the price level in 2017 and in 2018 if the government does not use fiscal policy.
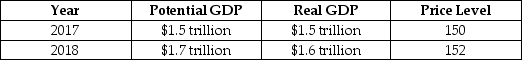
If the government wants to keep real GDP at its potential level in 2014, it should:
A)decrease income taxes.
B)decrease government purchases.
C)decrease interest rates.
D)increase interest rates.

If the government wants to keep real GDP at its potential level in 2014, it should:
A)decrease income taxes.
B)decrease government purchases.
C)decrease interest rates.
D)increase interest rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
To ameliorate the effects of a recession, a government could enact appropriate policies including:
A)increasing tax rates.
B)increasing taxes by a fixed amount.
C)increasing government purchases.
D)decreasing defence spending.
A)increasing tax rates.
B)increasing taxes by a fixed amount.
C)increasing government purchases.
D)decreasing defence spending.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
A contractionary fiscal policy would cause the:
A)aggregate demand curve to the right.
B)aggregate demand curve to the left.
C)short-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
D)short-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
A)aggregate demand curve to the right.
B)aggregate demand curve to the left.
C)short-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
D)short-run aggregate supply curve to the left.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Expansionary fiscal policy ________ the price level and ________ equilibrium real GDP.
A)decreases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)increases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
A)decreases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)increases; increases
D)decreases; decreases

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
What is the difference between 'discretionary fiscal policy' and 'automatic stabilisers'?
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Refer to Figure 13.1 for the following questions.
Figure 13.1

If the economy moves from A to B in Figure 13.1, which of the following would be the appropriate fiscal policy to achieve potential GDP?
A)increase taxes
B)increase government spending
C)contractionary fiscal policy
D)decrease interest rates
Figure 13.1

If the economy moves from A to B in Figure 13.1, which of the following would be the appropriate fiscal policy to achieve potential GDP?
A)increase taxes
B)increase government spending
C)contractionary fiscal policy
D)decrease interest rates

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
To help fight a recession, the government could:
A)increase taxes to increase aggregate demand.
B)increase government spending and run a budget deficit.
C)lower interest rates by decreasing the cash rate.
D)conduct contractionary fiscal policy by raising taxes.
A)increase taxes to increase aggregate demand.
B)increase government spending and run a budget deficit.
C)lower interest rates by decreasing the cash rate.
D)conduct contractionary fiscal policy by raising taxes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
If policy makers are concerned that the economy is in danger of rising inflation because aggregate demand is increasing faster than aggregate supply, the appropriate fiscal policy response is to:
A)increase taxes.
B)increase government spending.
C)use expansionary fiscal policy.
D)increase interest rates.
A)increase taxes.
B)increase government spending.
C)use expansionary fiscal policy.
D)increase interest rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Give examples of 'automatic stabilisers'. Explain how automatic stabilisers work when there is an economic boom.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
If the economy were in a recession, we would expect government expenditure to be:
A)high and tax revenues to be high, probably leading to a budget deficit.
B)high and tax revenues to be low, probably leading to a budget deficit.
C)low and tax revenues to be low, probably leading to a budget surplus.
D)high and tax revenues to be low, probably leading to a budget surplus.
A)high and tax revenues to be high, probably leading to a budget deficit.
B)high and tax revenues to be low, probably leading to a budget deficit.
C)low and tax revenues to be low, probably leading to a budget surplus.
D)high and tax revenues to be low, probably leading to a budget surplus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Which is the largest source of federal government revenue and which is the largest single area of government expenditure in Australia?
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
If the government wants to try to reduce unemployment, it could ________ spending and/or taxes should be ________.
A)increase; decreased
B)decrease; decreased
C)decrease; increased
D)increase; increased
A)increase; decreased
B)decrease; decreased
C)decrease; increased
D)increase; increased

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A decrease in individual income taxes ________ disposable income, which ________ consumption spending.
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Refer to Figure 13.2 for the following question.
Figure 13.2
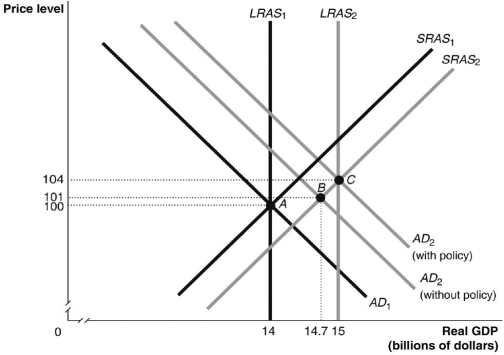
In Figure 13.2, suppose the economy in Year 1 is at point A and expected in Year 2 to be at point B. Which of the following policies could the government use to move the economy to point C?
A)decrease income taxes
B)decrease government purchases
C)increase income taxes
D)sell commonwealth government bonds and securities
Figure 13.2

In Figure 13.2, suppose the economy in Year 1 is at point A and expected in Year 2 to be at point B. Which of the following policies could the government use to move the economy to point C?
A)decrease income taxes
B)decrease government purchases
C)increase income taxes
D)sell commonwealth government bonds and securities

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
How could the existence of unemployment benefits or other transfer programs reduce the severity of an economic contraction?
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
If real equilibrium GDP is below the long-run aggregate supply curve, an appropriate fiscal policy would be to:
A)increase government purchases and increase a budget deficit.
B)pursue a contractionary fiscal policy by increasing the budget surplus.
C)increase individual income taxes to balance the budget.
D)increase business income taxes to increase tax fairness.
A)increase government purchases and increase a budget deficit.
B)pursue a contractionary fiscal policy by increasing the budget surplus.
C)increase individual income taxes to balance the budget.
D)increase business income taxes to increase tax fairness.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Which of the following is considered 'expansionary fiscal policy'?
A)The government decreases the income tax rate.
B)The government increases defence spending due to a change in priorities.
C)Legislation that increases education expense deductions from federal income taxes.
D)A state (not federal)government cuts highway spending to balance its budget.
A)The government decreases the income tax rate.
B)The government increases defence spending due to a change in priorities.
C)Legislation that increases education expense deductions from federal income taxes.
D)A state (not federal)government cuts highway spending to balance its budget.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Refer to Figure 13.3 for the following question.
Figure 13.3
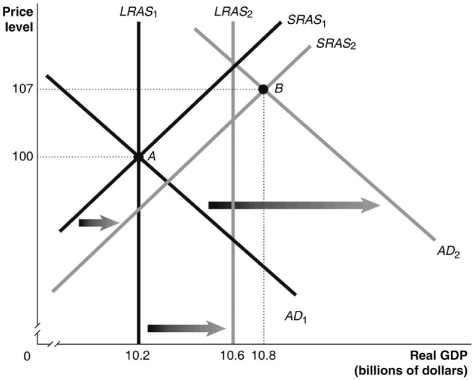
Refer to Figure 13.3. Given that the economy has moved from A to B in the graph above, which of the following would be the appropriate fiscal policy to achieve potential GDP?
A)increase interest rates
B)increase government spending
C)decrease interest rates
D)increase taxes
Figure 13.3

Refer to Figure 13.3. Given that the economy has moved from A to B in the graph above, which of the following would be the appropriate fiscal policy to achieve potential GDP?
A)increase interest rates
B)increase government spending
C)decrease interest rates
D)increase taxes

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
What is the difference between 'federal purchases' and 'federal expenditures'?
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
What is 'expansionary fiscal policy' and under what circumstances would it be used?
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
An initial increase in government purchases of $200 billion will shift the aggregate demand curve to the right by:
A)$200 billion.
B)less than $200 billion.
C)more than $200 billion.
D)None of these options is correct. This policy shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve.
A)$200 billion.
B)less than $200 billion.
C)more than $200 billion.
D)None of these options is correct. This policy shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
'Expansionary fiscal policy' is used by the government in an attempt to fight rising inflation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
If economists predict that the inflation will increase, the government should:
A)decrease government spending.
B)decrease taxes.
C)lower interest rates.
D)conduct expansionary fiscal policy.
A)decrease government spending.
B)decrease taxes.
C)lower interest rates.
D)conduct expansionary fiscal policy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Consider the hypothetical information in the following table for potential GDP, real GDP and the price level in 2016 and in 2017 if the government does not use fiscal policy.
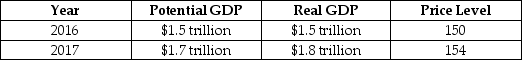
If the government wants control inflation while keeping real GDP at its potential level in 2017, it should:
A)increase income taxes.
B)increase government purchases.
C)decrease interest rates.
D)increase interest rates.

If the government wants control inflation while keeping real GDP at its potential level in 2017, it should:
A)increase income taxes.
B)increase government purchases.
C)decrease interest rates.
D)increase interest rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
By decreasing government spending and aggregate demand, the policy ________ the price level and ________ equilibrium real GDP, ceteris paribus.
A)decreases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)increases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
A)decreases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)increases; increases
D)decreases; decreases

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Use the dynamic aggregate demand and aggregate supply model and start with Year 1 in a long-run macroeconomic equilibrium. For Year 2, graph aggregate demand, long-run aggregate supply, and short-run aggregate supply such that the condition of the economy will induce the government to conduct contractionary fiscal policy. Briefly explain the condition of the economy and what the government is attempting to do.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
An appropriate fiscal policy response when aggregate demand is growing at a faster rate than aggregate supply is to increase interest rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Refer to Figure 13.4 for the following questions.
Figure 13.4
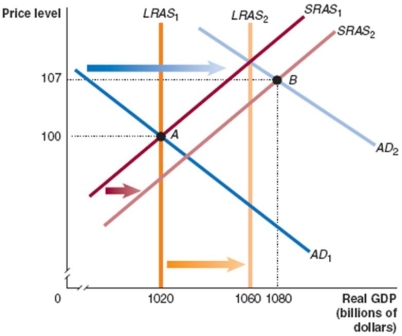
Given that the economy has moved from A to B in Figure 13.4, which of the following would be the appropriate fiscal policy to achieve potential GDP?
A)decrease taxes
B)decrease government spending
C)expansionary fiscal policy
D)increase interest rates
Figure 13.4

Given that the economy has moved from A to B in Figure 13.4, which of the following would be the appropriate fiscal policy to achieve potential GDP?
A)decrease taxes
B)decrease government spending
C)expansionary fiscal policy
D)increase interest rates

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The 'multiplier effect' is the series of ________ increases in ________ expenditures that result from an initial increase in ________ expenditures.
A)induced; investment; autonomous
B)induced; consumption; autonomous
C)autonomous; consumption; induced
D)autonomous; investment; induced
A)induced; investment; autonomous
B)induced; consumption; autonomous
C)autonomous; consumption; induced
D)autonomous; investment; induced

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
If the economy is growing beyond potential GDP, which of the following would be an appropriate fiscal policy to bring the economy back to long-run aggregate supply? An increase in:
A)liquidity and a decrease in interest rates.
B)government purchases.
C)oil prices.
D)taxes.
A)liquidity and a decrease in interest rates.
B)government purchases.
C)oil prices.
D)taxes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Refer to Figure 13.5 for the following question.
Figure 13.5
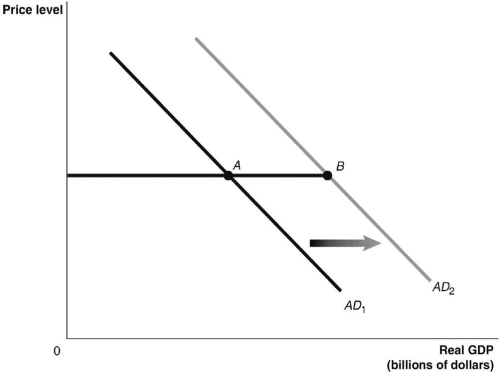
Refer to Figure 13.5. If government purchases increase by $100 billion and lead to an ultimate increase in aggregate demand as shown in the graph, the difference in real GDP between point A and point B will be:
A)$100 billion.
B)less than $100 billion.
C)more than $100 billion.
D)There is insufficient information given here to make a conclusion.
Figure 13.5

Refer to Figure 13.5. If government purchases increase by $100 billion and lead to an ultimate increase in aggregate demand as shown in the graph, the difference in real GDP between point A and point B will be:
A)$100 billion.
B)less than $100 billion.
C)more than $100 billion.
D)There is insufficient information given here to make a conclusion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Refer to Figure 13.4 for the following questions.
Figure 13.4

In Figure 13.4, if fiscal policy is successful at moving the economy from point B to equilibrium at potential GDP, which of the following will occur?
A)the price level will rise
B)deflation will occur
C)unemployment will fall
D)unemployment will rise
Figure 13.4

In Figure 13.4, if fiscal policy is successful at moving the economy from point B to equilibrium at potential GDP, which of the following will occur?
A)the price level will rise
B)deflation will occur
C)unemployment will fall
D)unemployment will rise

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
What is 'contractionary fiscal policy' and under what circumstances would it be used?
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Suppose the economy is in the state described by the following table.
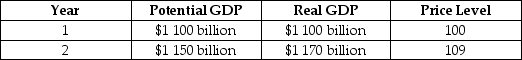
What problem will occur in the economy if no policy is pursued? What fiscal policy tools could be used to combat the problem? Draw a dynamic aggregate demand and supply graph to illustrate the appropriate fiscal policy to use in this situation.
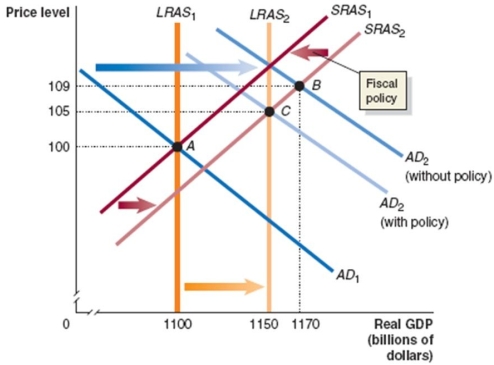
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

What problem will occur in the economy if no policy is pursued? What fiscal policy tools could be used to combat the problem? Draw a dynamic aggregate demand and supply graph to illustrate the appropriate fiscal policy to use in this situation.

_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Identify each of the following as (i)part of an expansionary fiscal policy; (ii)part of a contractionary fiscal policy; or (iii)not part of fiscal policy.
a.The personal income tax rate is lowered.
b.The government increases spending on defence due to a change in spending priorities.
c.The company income tax rate is lowered.
d.The State of New South Wales builds a new tollway in an attempt to expand employment and ease traffic congestion.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
a.The personal income tax rate is lowered.
b.The government increases spending on defence due to a change in spending priorities.
c.The company income tax rate is lowered.
d.The State of New South Wales builds a new tollway in an attempt to expand employment and ease traffic congestion.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Tax increases on business income slow down the rate of increase in aggregate demand by decreasing:
A)business investment spending.
B)consumption spending.
C)government spending.
D)wage rates.
A)business investment spending.
B)consumption spending.
C)government spending.
D)wage rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
If the equilibrium real GDP were higher than potential GDP, then a contractionary fiscal policy would cause the inflation rate to be ________ and real GDP to be ________.
A)higher; higher
B)higher; lower
C)lower; higher
D)lower; lower
A)higher; higher
B)higher; lower
C)lower; higher
D)lower; lower

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
'Contractionary fiscal policy' aims to reduce the rate of increase in aggregate demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
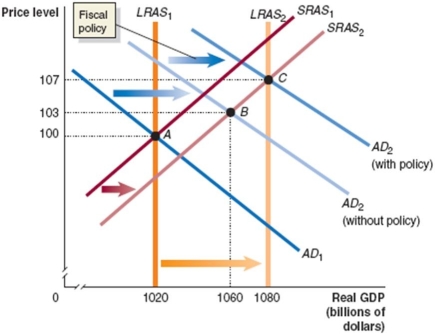
Assume that the economy is in the state described by the following table.
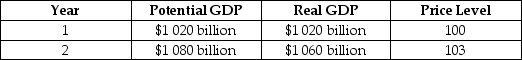
Draw a dynamic aggregate demand and aggregate supply diagram to illustrate the state of the economy in year 1 and year 2, assuming that no policy is pursued. Then illustrate the appropriate fiscal policy to use in this situation. Assume that the policy results in the economy producing at potential GDP. Provide an explanation.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

Draw a dynamic aggregate demand and aggregate supply diagram to illustrate the state of the economy in year 1 and year 2, assuming that no policy is pursued. Then illustrate the appropriate fiscal policy to use in this situation. Assume that the policy results in the economy producing at potential GDP. Provide an explanation.

_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
The tax multiplier is calculated as 'one minus the government purchases multiplier'.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
The government purchases multiplier is defined as:
A)
B)
C)
D)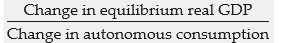
A)

B)

C)

D)
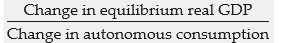

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Suppose real GDP is $13 trillion, potential GDP is $13.5 trillion, and the government plans to use fiscal policy to restore the economy to potential GDP. Assuming a constant price level, the government would need to increase government purchases by:
A)$500 billion.
B)less than $500 billion.
C)more than $500 billion.
D)None of these options is correct. The government must act to decrease government purchases in this case.
A)$500 billion.
B)less than $500 billion.
C)more than $500 billion.
D)None of these options is correct. The government must act to decrease government purchases in this case.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
If the government purchases multiplier equals 2, and real GDP is $14 trillion with potential GDP $14.5 trillion, then government purchases would need to increase by ________ to restore the economy to potential GDP.
A)$7.25 trillion
B)$1 trillion
C)$500 billion
D)$250 billion
A)$7.25 trillion
B)$1 trillion
C)$500 billion
D)$250 billion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
In the case of an upward-sloping aggregate supply curve, the change in real GDP brought about by a change in government spending will be less than that predicted by the simple government purchases multiplier.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Assume that the federal government gives a $5 billion tax cut. Assume that tax rates are fixed, the economy is closed, and the marginal propensity to consume is 0.75. What happens to equilibrium GDP?
A)There is a $20 billion increase in equilibrium GDP.
B)There is a $20 billion decrease in equilibrium GDP.
C)There is a $15 billion increase in equilibrium GDP.
D)There is a $15 billion decrease in equilibrium GDP.
A)There is a $20 billion increase in equilibrium GDP.
B)There is a $20 billion decrease in equilibrium GDP.
C)There is a $15 billion increase in equilibrium GDP.
D)There is a $15 billion decrease in equilibrium GDP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
An equal decrease in government purchases and taxes will cause:
A)a decrease in real GDP.
B)no change in real GDP.
C)an increase in the budget surplus because real GDP increases.
D)a reduction in the structural budget surplus.
A)a decrease in real GDP.
B)no change in real GDP.
C)an increase in the budget surplus because real GDP increases.
D)a reduction in the structural budget surplus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Suppose real GDP is $1.3 trillion and potential GDP is $1.35 trillion. If the government increases government purchases by $0.5 trillion, then the economy will be brought to equilibrium at potential GDP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Outline the differences between the government 'purchases multiplier' and the 'tax multiplier'.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Raising taxes will:
A)raise disposable income and raise spending.
B)raise disposable income and lower spending.
C)lower disposable income and raise spending.
D)lower disposable income and lower spending.
A)raise disposable income and raise spending.
B)raise disposable income and lower spending.
C)lower disposable income and raise spending.
D)lower disposable income and lower spending.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
The government 'purchases multiplier' always has a positive sign and the 'tax multiplier' always has a negative sign.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Induced taxes and transfer payments reduce the multiplier effects.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Suppose that the government allocates $2 billion for new roads. It also raises taxes by $2 billion to keep the deficit from growing. If the marginal propensity to consume = 0.8, what is the effect on equilibrium GDP?
A)GDP does not change
B)GDP increases by $5 billion
C)GDP increases by $800 million
D)GDP increases by $2 billion
A)GDP does not change
B)GDP increases by $5 billion
C)GDP increases by $800 million
D)GDP increases by $2 billion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
The tax multiplier:
A)is negative.
B)is larger in absolute value as compared to the government purchases multiplier.
C)only works when taxes are cut.
D)is less than one.
A)is negative.
B)is larger in absolute value as compared to the government purchases multiplier.
C)only works when taxes are cut.
D)is less than one.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
If the absolute value of the tax multiplier equals 1.5, real GDP is $13 trillion, and potential GDP is $13.6 trillion, then taxes would need to be cut by ________ to restore the economy to potential GDP.
A)$400 billion
B)$450 billion
C)$600 billion
D)None of these options is correct. Taxes should be increased in this case.
A)$400 billion
B)$450 billion
C)$600 billion
D)None of these options is correct. Taxes should be increased in this case.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
A cut in tax rates affects equilibrium real GDP through two channels: ________ disposable income and consumer spending, and ________ the size of the multiplier effect.
A)decreasing; increasing
B)decreasing; decreasing
C)increasing; increasing
D)increasing; decreasing
A)decreasing; increasing
B)decreasing; decreasing
C)increasing; increasing
D)increasing; decreasing

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
The government purchases multiplier will be larger if the marginal income tax rate increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Assume in a closed economy that taxes are fixed and the marginal propensity to consume is equal to 0.8. What is the government purchases multiplier?
A)10
B)5
C)4
D)3
A)10
B)5
C)4
D)3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Reducing taxes by a specific fixed amount will usually:
A)lower income and lower spending.
B)raise income and lower spending.
C)lower income and raise spending.
D)raise income and raise spending.
A)lower income and lower spending.
B)raise income and lower spending.
C)lower income and raise spending.
D)raise income and raise spending.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
A change in tax rates:
A)has a less complicated effect on GDP than does a tax cut of a fixed amount.
B)has a larger multiplier effect the smaller the tax rate.
C)will not affect disposable income.
D)will not affect the size of the multiplier.
A)has a less complicated effect on GDP than does a tax cut of a fixed amount.
B)has a larger multiplier effect the smaller the tax rate.
C)will not affect disposable income.
D)will not affect the size of the multiplier.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 163 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








