Deck 14: Managerial Decision-Making Under Uncertainty
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 14: Managerial Decision-Making Under Uncertainty
1
If an event is certain to occur, it has a probability (pr)of
A)0.
B)0 < pr < 1.
C)1.
D)Not enough information to determine.
A)0.
B)0 < pr < 1.
C)1.
D)Not enough information to determine.
1.
2
Probability
A)is a number between 0 and 1, inclusive.
B)indicates how likely an outcome is to occur.
C)is larger the more likely the event is to occur.
D)All of the above.
A)is a number between 0 and 1, inclusive.
B)indicates how likely an outcome is to occur.
C)is larger the more likely the event is to occur.
D)All of the above.
All of the above.
3
People in a certain group have a 0.3% chance of dying this year. If a person in this group buys a life insurance policy for $3,300 that pays $1,000,000 to her family if she dies this year and $0 otherwise, what is the expected value of a policy to the insurance company?
A)$0
B)$300
C)$3,000
D)$3,300
A)$0
B)$300
C)$3,000
D)$3,300
$300
4
Although he is very poor, Al plays the million-dollar lottery everyday because he is certain that one day he will win. Al makes this calculation based upon
A)the frequency of past outcomes.
B)subjective probability.
C)knowledge of all possible outcomes.
D)tossing a coin.
A)the frequency of past outcomes.
B)subjective probability.
C)knowledge of all possible outcomes.
D)tossing a coin.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Best guesses of an event occurring in the future are based on
A)estimates derived from the frequency of the event occurring in the past.
B)coin flips.
C)subjective probability.
D)the wisdom of crowds.
A)estimates derived from the frequency of the event occurring in the past.
B)coin flips.
C)subjective probability.
D)the wisdom of crowds.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Which of the following sets of outcomes is exhaustive?
A)win, lose, tie
B)employed full-time, employed part-time, unemployed
C)married, single, widowed
D)All of the above.
A)win, lose, tie
B)employed full-time, employed part-time, unemployed
C)married, single, widowed
D)All of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
If an event is likely to occur, which probability is a reasonable estimate?
A)0.32
B)0.79
C)1
D)Not enough information to determine.
A)0.32
B)0.79
C)1
D)Not enough information to determine.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
If outcomes are ________, exactly one of the outcomes will occur and the probabilities add up to ________.
A)probabilistic; between 0 and 1
B)exhaustive and mutually exclusive; 1
C)exhaustive; 1
D)mutually exclusive; between 0 and 1
A)probabilistic; between 0 and 1
B)exhaustive and mutually exclusive; 1
C)exhaustive; 1
D)mutually exclusive; between 0 and 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
You draw colored balls out of a bag. You draw a red ball 30% of the time and a blue ball 70% of the time. For each draw, the blue outcome and the red outcome are
A)mutually exclusive.
B)exhaustive.
C)Both A and B.
D)None of the above.
A)mutually exclusive.
B)exhaustive.
C)Both A and B.
D)None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
On any given day, a salesman can earn $0 with a 20% probability, $100 with a 40% probability, or $300 with a 20% probability. His expected earnings equal
A)$0.
B)$100 because that is the most likely outcome.
C)$100 because that is what he will earn on average.
D)$200 because that is what he will earn on average.
A)$0.
B)$100 because that is the most likely outcome.
C)$100 because that is what he will earn on average.
D)$200 because that is what he will earn on average.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Your friend Dimitre tells you that he thinks that his favorite basketball team has a 70% chance of winning the next game. This is an example of a(n)
A)objective probability.
B)subjective probability.
C)risk-averse statement.
D)Friedman-Savage preference.
A)objective probability.
B)subjective probability.
C)risk-averse statement.
D)Friedman-Savage preference.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of the following sets of outcomes is mutually exclusive?
A)win, lose, tie
B)employed full-time, employed part-time, unemployed
C)married, single, widowed
D)All of the above.
A)win, lose, tie
B)employed full-time, employed part-time, unemployed
C)married, single, widowed
D)All of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Sarah buys little stuffed animals for $5 each. They come in different varieties. If the producer stops making (retires)a certain variety, a stuffed animal of that variety will be worth $100; otherwise it is worth $0. There is 50% chance that any variety will be retired. When Sarah buys her next stuffed animal, the expected value is
A)$50.
B)$47.50.
C)$45.00.
D)$0.
A)$50.
B)$47.50.
C)$45.00.
D)$0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
On any given day, a salesman can earn $0 with a 30% probability, $100 with a 20% probability, or $300 with a 50% probability. His expected earnings equal
A)$0.
B)$100.
C)$150.
D)$170.
A)$0.
B)$100.
C)$150.
D)$170.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
If an event will NOT occur, it has a probability (pr)of
A)0.
B)0 < pr < 1.
C)1.
D)Not enough information to determine.
A)0.
B)0 < pr < 1.
C)1.
D)Not enough information to determine.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Expected value represents
A)the actual payment one expects to receive.
B)the average of all payments one would receive if one undertook the risky event many times.
C)the payment one receives if he or she makes the correct decision.
D)the payment that is most likely to occur.
A)the actual payment one expects to receive.
B)the average of all payments one would receive if one undertook the risky event many times.
C)the payment one receives if he or she makes the correct decision.
D)the payment that is most likely to occur.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
On any given day we know a salesman can earn $0 with a 30% probability, $100 with a 20% probability or $300 with 40% probability. His expected earnings equal
A)$0.
B)$140.
C)$300.
D)It cannot be determined from the available information.
A)$0.
B)$140.
C)$300.
D)It cannot be determined from the available information.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
A(n)________ relates each possible outcome to its probability of occurrence.
A)probability distribution
B)frequency
C)expected value
D)coin toss
A)probability distribution
B)frequency
C)expected value
D)coin toss

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
If there are 10,000 people in your age bracket, and 10 of them died last year, an insurance company believes that the probability of someone in that age bracket dying this year would be
A)0.
B).001.
C).0001.
D)1,000.
A)0.
B).001.
C).0001.
D)1,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
If an event is unlikely to occur, which probability is a reasonable estimate?
A)0
B)0.23
C)0.82
D)Not enough information to determine.
A)0
B)0.23
C)0.82
D)Not enough information to determine.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Sarah buys little stuffed animals for $5 each. They come in different varieties. If the producer stops making (retires)a certain variety, a stuffed animal of that variety will be worth $100; otherwise it is worth $0. There is 50% chance that any variety will be retired. For the purchase of an individual stuffed animal, what is the value to Sarah of knowing ahead of time whether the variety will be retired?
A)$50
B)$5
C)$2.50
D)$0
A)$50
B)$5
C)$2.50
D)$0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
On any given day, a salesman can earn $0 with a 20% probability, $100 with a 40% probability, or $300 with a 20% probability. Calculate the expected value and variance of his earnings, and interpret.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Variance is a measure of ________ and the higher the variance, ________.
A)expected profit; the greater the profit
B)risk; the greater the risk
C)standard deviation; greater the standard deviation
D)risk; the lower the risk
A)expected profit; the greater the profit
B)risk; the greater the risk
C)standard deviation; greater the standard deviation
D)risk; the lower the risk

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
A fair bet is one where
A)the player has a 50/50 chance of winning.
B)the player's utility function is convex.
C)the expected value is zero.
D)the expected value is positive.
A)the player has a 50/50 chance of winning.
B)the player's utility function is convex.
C)the expected value is zero.
D)the expected value is positive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Someone who is risk-averse has
A)diminishing marginal utility of wealth.
B)constant marginal utility of wealth.
C)increasing marginal utility of wealth.
D)less marginal utility of wealth than someone who is risk-neutral.
A)diminishing marginal utility of wealth.
B)constant marginal utility of wealth.
C)increasing marginal utility of wealth.
D)less marginal utility of wealth than someone who is risk-neutral.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
John's utility from an additional dollar increases more when he has $1,000 than when he has $10,000. From this, we can conclude that John
A)is risk averse.
B)is risk loving.
C)is risk neutral.
D)has a negative marginal utility of wealth.
A)is risk averse.
B)is risk loving.
C)is risk neutral.
D)has a negative marginal utility of wealth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Rahul has a concave utility function. Therefore, if there are two choices he will pick the ________ if ________ expected value.
A)fair bet; both have the same
B)less risky choice;both have the same
C)more risky choice; both have the same
D)less risky choice; it has a lower
A)fair bet; both have the same
B)less risky choice;both have the same
C)more risky choice; both have the same
D)less risky choice; it has a lower

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
For a given expected value, the smaller the standard deviation of the expected value, the larger the risk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Which of the following games involving the roll of a single die is a fair bet?
A)Bet $1 and receive $1 if 3 or 4 comes up.
B)Bet $1 and receive $1 if 3, 4, or 5 comes up.
C)Bet $1 and receive $4 if 6 comes up.
D)None of the bets is a fair bet.
A)Bet $1 and receive $1 if 3 or 4 comes up.
B)Bet $1 and receive $1 if 3, 4, or 5 comes up.
C)Bet $1 and receive $4 if 6 comes up.
D)None of the bets is a fair bet.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The key economic difference between expected utility and expected value is that
A)expected value only considers the value of outcomes, whereas expected utility considers the tradeoff between value and risk.
B)expected utility only considers the value of outcomes, whereas expected value considers the tradeoff between value and risk.
C)expected utility is the maximum value obtained, whereas expect value is the mean of the values from a set of possible outcomes.
D)None of the above-the differences are mathematical not economic.
A)expected value only considers the value of outcomes, whereas expected utility considers the tradeoff between value and risk.
B)expected utility only considers the value of outcomes, whereas expected value considers the tradeoff between value and risk.
C)expected utility is the maximum value obtained, whereas expect value is the mean of the values from a set of possible outcomes.
D)None of the above-the differences are mathematical not economic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
From the expected value of a game, we
A)cannot determine the risk.
B)can determine the risk.
C)can determine exactly how much a player will receive.
D)can infer the subjective probabilities of each possible outcome.
A)cannot determine the risk.
B)can determine the risk.
C)can determine exactly how much a player will receive.
D)can infer the subjective probabilities of each possible outcome.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
John derives more utility from having $1,000 than from having $100. From this, we can conclude that John
A)is risk averse.
B)is risk loving.
C)is risk neutral.
D)has a positive marginal utility of wealth.
A)is risk averse.
B)is risk loving.
C)is risk neutral.
D)has a positive marginal utility of wealth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Expected value represents the average of all outcomes if one were to undertake the risky event many times over and over again.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A risk premium
A)is required to get a risk-neutral person to make a fair bet.
B)is the maximum amount needed to compensate a decision-maker to willingly take a risk.
C)is the maximum amount a decision-maker would pay to avoid taking a risk.
D)is the minimum amount a decision-maker would pay to avoid taking a risk.
A)is required to get a risk-neutral person to make a fair bet.
B)is the maximum amount needed to compensate a decision-maker to willingly take a risk.
C)is the maximum amount a decision-maker would pay to avoid taking a risk.
D)is the minimum amount a decision-maker would pay to avoid taking a risk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Sarah buys little stuffed animals for $5 each. They come in different varieties. If the producer stops making (retires)a certain variety, a stuffed animal of that variety will be worth $100; otherwise it is worth $0. There is 25% chance that any variety will be retired. For the purchase of an individual animal, what is the value to Sarah of knowing ahead of time whether or not that variety will be retired?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Catherine is risk-averse. When faced with a choice between a gamble and a certain level of wealth she will
A)always prefer the gamble.
B)always prefer the certain level of wealth.
C)prefer the gamble if the expected utility from it is higher than the utility from the certain level of wealth.
D)prefer the certain level of wealth if the expected utility from the gamble is higher than the utility of the certain level of wealth.
A)always prefer the gamble.
B)always prefer the certain level of wealth.
C)prefer the gamble if the expected utility from it is higher than the utility from the certain level of wealth.
D)prefer the certain level of wealth if the expected utility from the gamble is higher than the utility of the certain level of wealth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Variance is a measure of ________ and the lower the variance, ________.
A)expected profit; the lower the profit
B)risk; the lower the risk
C)standard deviation; lower the standard deviation
D)risk; the greater the risk
A)expected profit; the lower the profit
B)risk; the lower the risk
C)standard deviation; lower the standard deviation
D)risk; the greater the risk

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A lottery game pays $500 with .001 probability and $0 otherwise. The variance of the payout is
A)15.8.
B)249.50.
C)249.75.
D)499.
A)15.8.
B)249.50.
C)249.75.
D)499.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
All else held constant, as the variance of a payoff increases, the
A)expected value of the payoff increases.
B)risk of the payoff increases.
C)expected value of the payoff decreases.
D)risk of the payoff decreases.
A)expected value of the payoff increases.
B)risk of the payoff increases.
C)expected value of the payoff decreases.
D)risk of the payoff decreases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Expected utility is
A)the maximum utility that a person can get from a set of possible outcomes.
B)the probability-weighted mean of the utility gained from a set of possible outcomes.
C)negative for risk-averse people.
D)indeterminant for risk preferring people.
A)the maximum utility that a person can get from a set of possible outcomes.
B)the probability-weighted mean of the utility gained from a set of possible outcomes.
C)negative for risk-averse people.
D)indeterminant for risk preferring people.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
If a person is risk neutral, then she
A)is indifferent about taking a fair bet.
B)will pay a premium to avoid a fair bet.
C)has a horizontal utility function.
D)has zero marginal utility of wealth.
A)is indifferent about taking a fair bet.
B)will pay a premium to avoid a fair bet.
C)has a horizontal utility function.
D)has zero marginal utility of wealth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
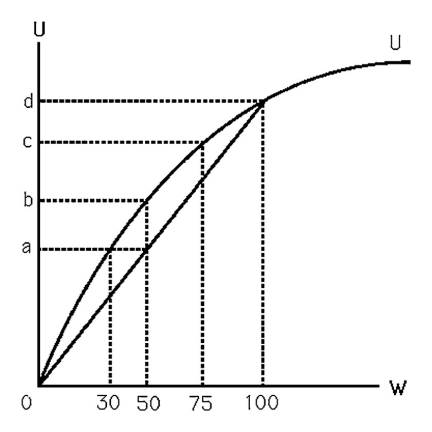
The above figure shows Bob's utility function. He currently has $100 of wealth, but there is a 50% chance that it could all be stolen. Bob's expected utility is
A)a.
B)b.
C)c.
D)d.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43

The above figure shows Bob's utility function. He currently has $100 of wealth, but there is a 50% chance that it could all be stolen. Bob is risk averse because
A)his utility function is convex.
B)he has negative marginal utility of wealth.
C)he is willing to pay a premium to avoid a risky situation.
D)All of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Someone who is risk-preferring has
A)diminishing marginal utility of wealth.
B)constant marginal utility of wealth.
C)increasing marginal utility of wealth.
D)less marginal utility of wealth than someone who is risk-preferring.
A)diminishing marginal utility of wealth.
B)constant marginal utility of wealth.
C)increasing marginal utility of wealth.
D)less marginal utility of wealth than someone who is risk-preferring.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45

The above figure shows Bob's utility function. He currently has $100 of wealth, but there is a 50% chance that it could all be stolen. Bob's expected wealth is
A)$0.
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46

The above figure shows Bob's utility function. He currently has $100 of wealth, but there is a 50% chance that it could all be stolen. Bob is risk averse because
A)his utility function is concave.
B)he has diminishing marginal utility of wealth.
C)he is willing to pay a premium to avoid a risky situation.
D)All of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Bob invests $25 in an investment that has a 50% chance of being worth $100 and a 50% chance of being worth $0. From this information we can conclude that Bob is
A)risk preferring.
B)risk neutral.
C)risk averse.
D)Any of the above.
A)risk preferring.
B)risk neutral.
C)risk averse.
D)Any of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Bob invests $75 in an investment that has a 50% chance of being worth $100 and a 50% chance of being worth $0. From this information we can conclude that Bob is
A)risk preferring.
B)risk neutral.
C)risk averse.
D)irrational.
A)risk preferring.
B)risk neutral.
C)risk averse.
D)irrational.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Someone who is risk-neutral has
A)diminishing marginal utility of wealth.
B)constant marginal utility of wealth.
C)increasing marginal utility of wealth.
D)less marginal utility of wealth than someone who is risk-preferring.
A)diminishing marginal utility of wealth.
B)constant marginal utility of wealth.
C)increasing marginal utility of wealth.
D)less marginal utility of wealth than someone who is risk-preferring.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
A risk-preferring person is willing to pay
A)a risk premium.
B)a fee to make a fair bet.
C)to obtain decreasing marginal utility.
D)None of the above.
A)a risk premium.
B)a fee to make a fair bet.
C)to obtain decreasing marginal utility.
D)None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Natasha is going to buy a risky asset that has an expected value of $62, which yields an expected utility of 146. Her risk premium is $19. What is her certainty equivalent?
A)$19
B)$43
C)$81
D)$208
A)$19
B)$43
C)$81
D)$208

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52

The above figure shows Bob's utility function. He currently has $100 of wealth, but there is a 50% chance that it could all be stolen. Living with this risk gives Bob the same expected utility as if there was no chance of theft and his wealth was
A)$0.
B)$20.
C)$30.
D)$50.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
A person who is risk-neutral will
A)pay a small risk premium when making a choice.
B)pick a slightly less risky option with a slightly lower expected value.
C)pick the option with the highest expected value.
D)None of the above.
A)pay a small risk premium when making a choice.
B)pick a slightly less risky option with a slightly lower expected value.
C)pick the option with the highest expected value.
D)None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54

The above figure shows Bob's utility function. He currently has $100 of wealth, but there is a 50% chance that it could all be stolen. If Bob could keep $50 with certainty, his utility would be
A)a.
B)b.
C)c.
D)d.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
For a risk-neutral person, the expected utility associated with various levels of wealth
A)is above the person's utility function.
B)is below the person's utility function.
C)is equal to the person's utility function.
D)does not exist.
A)is above the person's utility function.
B)is below the person's utility function.
C)is equal to the person's utility function.
D)does not exist.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Bob invests $50 in an investment that has a 50% chance of being worth $100 and a 50% chance of being worth $0. From this information we can conclude that Bob is NOT
A)risk preferring.
B)risk neutral.
C)risk averse.
D)rational.
A)risk preferring.
B)risk neutral.
C)risk averse.
D)rational.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
If a person is entertained by gambling, then
A)she is not risk averse.
B)she does not understand the concept of a fair game.
C)she may gamble even if it is an unfair game.
D)she will definitely not buy automobile insurance.
A)she is not risk averse.
B)she does not understand the concept of a fair game.
C)she may gamble even if it is an unfair game.
D)she will definitely not buy automobile insurance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58

The above figure shows Bob's utility function. He currently has $100 of wealth, but there is a 50% chance that it could all be stolen. The midpoint of the chord that runs from zero and intersects the utility function where wealth is 100, represents Bob's
A)risk premium.
B)expected utility of receiving $50 with certainty.
C)expected utility of receiving $0 50% of the time and $100 50% of the time.
D)risk neutrality.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Natasha is going to buy a risky asset that has an expected value of $62, which yields an expected utility of 146. Equivalently, she could get utility of 146 from a certainty equivalent of $43. What is Natasha's risk premium?
A)$19
B)$43
C)$103
D)$105
A)$19
B)$43
C)$103
D)$105

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60

The above figure shows Bob's utility function. He currently has $100 of wealth, but there is a 50% chance that it could all be stolen. What is the most Bob would pay for insurance that would replace his $100 should it be stolen?
A)$30
B)$50
C)$70
D)$75

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61

The above figure shows Bob's utility function. He currently has $100 of wealth, but there is a 50% chance that it could all be stolen. Bob will buy theft insurance to cover the full $100
A)as long as it does not cost more than $25.
B)as long as it does not cost more than $50.
C)as long as it does not cost more than $70.
D)at any price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
If two events are positively correlated but NOT perfectly correlated, then
A)diversification is not necessary since there is no risk.
B)diversification eliminates all risk.
C)diversification does not reduce risk at all.
D)diversification can reduce risk.
A)diversification is not necessary since there is no risk.
B)diversification eliminates all risk.
C)diversification does not reduce risk at all.
D)diversification can reduce risk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
If a person willingly plays an unfair game that is NOT in his favor, he is risk loving.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
If Stock A and Stock B both increase in value at the same time, they are
A)negatively correlated.
B)uncorrelated.
C)positively correlated.
D)certain bets.
A)negatively correlated.
B)uncorrelated.
C)positively correlated.
D)certain bets.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
If Stock A increases in value when Stock B decreases in value at the same time, they are
A)negatively correlated.
B)uncorrelated.
C)positively correlated.
D)in different industries.
A)negatively correlated.
B)uncorrelated.
C)positively correlated.
D)in different industries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
A fair game is a game in which the chances are 50-50 that you win or lose.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Buying a diversified mutual stock fund allows you to
A)completely avoid all types of risk.
B)avoid only random, unsystematic risk.
C)avoid only systematic risk.
D)avoid risk only when all the stock prices are perfectly correlated.
A)completely avoid all types of risk.
B)avoid only random, unsystematic risk.
C)avoid only systematic risk.
D)avoid risk only when all the stock prices are perfectly correlated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
If Stock A sometimes increases and sometimes decreases in value when Stock B increases in value at the same time, they are
A)negatively correlated.
B)uncorrelated.
C)positively correlated.
D)random bets.
A)negatively correlated.
B)uncorrelated.
C)positively correlated.
D)random bets.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
What type of risk behavior does the person exhibit who is willing to pay $5 for the chance to bet $60 on a game where 20% of the time the bet returns $100, and 80% of the time returns $50? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
The ability of diversification to reduce risk
A)is greater the more negatively correlated the two events are.
B)is greater the more positively correlated the two events are.
C)is greater the more uncorrelated the two events are.
D)is greater the more risk averse the individual is.
A)is greater the more negatively correlated the two events are.
B)is greater the more positively correlated the two events are.
C)is greater the more uncorrelated the two events are.
D)is greater the more risk averse the individual is.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Searching the Internet for information to help select a product that is more reliable is most likely to be done by a
A)risk-averse person.
B)risk-neutral person.
C)risk-preferring person.
D)This cannot be determined with the information provided.
A)risk-averse person.
B)risk-neutral person.
C)risk-preferring person.
D)This cannot be determined with the information provided.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
If Stock A and Stock B both decrease in value at the same time, they are
A)negatively correlated.
B)uncorrelated.
C)positively correlated.
D)bad bets.
A)negatively correlated.
B)uncorrelated.
C)positively correlated.
D)bad bets.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
If two events are perfectly negatively correlated, then
A)diversification can reduce but not eliminate risk.
B)diversification can eliminate risk.
C)diversification has no impact on risk.
D)diversification cuts risk in half.
A)diversification can reduce but not eliminate risk.
B)diversification can eliminate risk.
C)diversification has no impact on risk.
D)diversification cuts risk in half.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
A stock mutual fund is generally
A)less risky than buying individual stocks.
B)more risky than buying individual stocks.
C)just as risky as buying individual stocks.
D)a way for the rich to avoid taxes.
A)less risky than buying individual stocks.
B)more risky than buying individual stocks.
C)just as risky as buying individual stocks.
D)a way for the rich to avoid taxes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
In terms of the stock market, systematic risk refers to the fact that
A)some stocks have higher returns than others.
B)some stocks' returns have a higher variance than others.
C)all stock prices are correlated with the health of the economy.
D)most stock prices are perfectly negatively correlated.
A)some stocks have higher returns than others.
B)some stocks' returns have a higher variance than others.
C)all stock prices are correlated with the health of the economy.
D)most stock prices are perfectly negatively correlated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
If a person is risk averse, then she has negative marginal utility of wealth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Making many risky bets
A)reduces your expected value.
B)is called risk-pooling and can reduce risk.
C)is irrational.
D)is called risk pooling and increases your expected value.
A)reduces your expected value.
B)is called risk-pooling and can reduce risk.
C)is irrational.
D)is called risk pooling and increases your expected value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
If two events are perfectly positively correlated, then
A)diversification is not necessary since there is no risk.
B)diversification eliminates all risk.
C)diversification does not reduce risk at all.
D)diversification only cuts the risk in half.
A)diversification is not necessary since there is no risk.
B)diversification eliminates all risk.
C)diversification does not reduce risk at all.
D)diversification only cuts the risk in half.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
If Stock A sometimes increases and sometimes decreases in value when Stock B decreases in value at the same time, they are
A)negatively correlated.
B)uncorrelated.
C)positively correlated.
D)random bets.
A)negatively correlated.
B)uncorrelated.
C)positively correlated.
D)random bets.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Taking actions that reduce risk
A)raise your expected value.
B)makes you less risk-averse.
C)are impractical in most circumstances.
D)change your utility function.
A)raise your expected value.
B)makes you less risk-averse.
C)are impractical in most circumstances.
D)change your utility function.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 116 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








