Deck 3: Water and the Fitness of the Environment
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/66
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 3: Water and the Fitness of the Environment
1
Which type of bond must be broken for water to vaporize?
A)ionic bonds
B)nonpolar covalent bonds
C)polar covalent bonds
D)hydrogen bonds
E)covalent bonds
A)ionic bonds
B)nonpolar covalent bonds
C)polar covalent bonds
D)hydrogen bonds
E)covalent bonds
D
2
What gives rise to the cohesiveness of water molecules?
A)hydrophobic interactions
B)nonpolar covalent bonds
C)ionic bonds
D)hydrogen bonds
E)both A and C
A)hydrophobic interactions
B)nonpolar covalent bonds
C)ionic bonds
D)hydrogen bonds
E)both A and C
D
3
When an ionic compound such as sodium chloride (NaCl)is placed in water the component atoms of the NaCl crystal dissociate into individual sodium ions (Na⁺)and chloride ions (Cl⁻). In contrast, the atoms of covalently bonded molecules (e.g., glucose, sucrose, glycerol)do not generally dissociate when placed in aqueous solution. Which of the following solutions would be expected to contain the greatest number of particles (molecules or ions)?
A)1 L of 0.5 M NaCl
B)1 L of 0.5 M glucose
C)1 L of 1.0 M NaCl
D)1 L of 1.0 M glucose
E)C and D will contain equal numbers of particles.
A)1 L of 0.5 M NaCl
B)1 L of 0.5 M glucose
C)1 L of 1.0 M NaCl
D)1 L of 1.0 M glucose
E)C and D will contain equal numbers of particles.
C
4
In a single molecule of water, two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a single oxygen atom by
A)hydrogen bonds.
B)nonpolar covalent bonds.
C)polar covalent bonds.
D)ionic bonds.
E)van der Waals interactions.
A)hydrogen bonds.
B)nonpolar covalent bonds.
C)polar covalent bonds.
D)ionic bonds.
E)van der Waals interactions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
At what temperature is water at its densest?
A)0°C
B)4°C
C)32°C
D)100°C
E)212°C
A)0°C
B)4°C
C)32°C
D)100°C
E)212°C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
How many molecules of glucose (C₆H₂O₆ molecular mass =180 daltons)would be present in one mole of glucose?
A)24
B)342
C)23 × 10¹⁴
D)180 × 10¹⁴
E)6)02 × 10²³
A)24
B)342
C)23 × 10¹⁴
D)180 × 10¹⁴
E)6)02 × 10²³

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The slight negative charge at one end of one water molecule is attracted to the slight positive charge of another water molecule. What is this attraction called?
A)a covalent bond
B)a hydrogen bond
C)an ionic bond
D)a hydrophilic bond
E)a hydrophobic bond
A)a covalent bond
B)a hydrogen bond
C)an ionic bond
D)a hydrophilic bond
E)a hydrophobic bond

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Water is able to form hydrogen bonds because
A)oxygen has a valence of 2.
B)the water molecule is shaped like a tetrahedron.
C)the bonds that hold together the atoms in a water molecule are polar covalent bonds.
D)the oxygen atom in a water molecule has a weak positive charge.
E)each of the hydrogen atoms in a water molecule is weakly negative in charge.
A)oxygen has a valence of 2.
B)the water molecule is shaped like a tetrahedron.
C)the bonds that hold together the atoms in a water molecule are polar covalent bonds.
D)the oxygen atom in a water molecule has a weak positive charge.
E)each of the hydrogen atoms in a water molecule is weakly negative in charge.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Temperature usually increases when water condenses. Which behavior of water is most directly responsible for this phenomenon?
A)the change in density when it condenses to form a liquid or solid
B)reactions with other atmospheric compounds
C)the release of heat by the formation of hydrogen bonds
D)the release of heat by the breaking of hydrogen bonds
E)the high surface tension of water
A)the change in density when it condenses to form a liquid or solid
B)reactions with other atmospheric compounds
C)the release of heat by the formation of hydrogen bonds
D)the release of heat by the breaking of hydrogen bonds
E)the high surface tension of water

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Why does ice float in liquid water?
A)The liquid water molecules have more kinetic energy and thus support the ice.
B)The ionic bonds between the molecules in ice prevent the ice from sinking.
C)Ice always has air bubbles that keep it afloat.
D)Hydrogen bonds stabilize and keep the molecules of ice farther apart than the water molecules of liquid water.
E)The crystalline lattice of ice causes it to be denser than liquid water.
A)The liquid water molecules have more kinetic energy and thus support the ice.
B)The ionic bonds between the molecules in ice prevent the ice from sinking.
C)Ice always has air bubbles that keep it afloat.
D)Hydrogen bonds stabilize and keep the molecules of ice farther apart than the water molecules of liquid water.
E)The crystalline lattice of ice causes it to be denser than liquid water.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Water's high specific heat is mainly a consequence of the
A)small size of the water molecules.
B)high specific heat of oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
C)absorption and release of heat when hydrogen bonds break and form.
D)fact that water is a poor heat conductor.
E)inability of water to dissipate heat into dry air.
A)small size of the water molecules.
B)high specific heat of oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
C)absorption and release of heat when hydrogen bonds break and form.
D)fact that water is a poor heat conductor.
E)inability of water to dissipate heat into dry air.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The following question is based on Figure 3.1: solute molecule surrounded by a hydration shell of water.
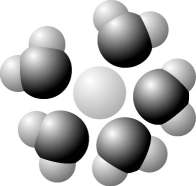
Figure 3.1
Based on your knowledge of the polarity of water molecules, the solute molecule is most likely
A)positively charged.
B)negatively charged.
C)without charge.
D)hydrophobic.
E)nonpolar.

Figure 3.1
Based on your knowledge of the polarity of water molecules, the solute molecule is most likely
A)positively charged.
B)negatively charged.
C)without charge.
D)hydrophobic.
E)nonpolar.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Hydrophobic substances such as vegetable oil are
A)nonpolar substances that repel water molecules.
B)nonpolar substances that have an attraction for water molecules.
C)polar substances that repel water molecules.
D)polar substances that have an affinity for water.
E)charged molecules that hydrogen-bond with water molecules.
A)nonpolar substances that repel water molecules.
B)nonpolar substances that have an attraction for water molecules.
C)polar substances that repel water molecules.
D)polar substances that have an affinity for water.
E)charged molecules that hydrogen-bond with water molecules.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which of the following takes place as an ice cube cools a drink?
A)Molecular collisions in the drink increase.
B)Kinetic energy in the drink decreases.
C)A calorie of heat energy is transferred from the ice to the water of the drink.
D)The specific heat of the water in the drink decreases.
E)Evaporation of the water in the drink increases.
A)Molecular collisions in the drink increase.
B)Kinetic energy in the drink decreases.
C)A calorie of heat energy is transferred from the ice to the water of the drink.
D)The specific heat of the water in the drink decreases.
E)Evaporation of the water in the drink increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
An example of a hydrogen bond is the bond between
A)C and H in methane (CH₄).
B)the H of one water molecule and the O of another water molecule.
C)Na⁺and Cl⁻ in salt.
D)the two hydrogen atoms in a molecule of hydrogen gas (H₂).
E)Mg⁺and Cl⁻ in MgCl₂.
A)C and H in methane (CH₄).
B)the H of one water molecule and the O of another water molecule.
C)Na⁺and Cl⁻ in salt.
D)the two hydrogen atoms in a molecule of hydrogen gas (H₂).
E)Mg⁺and Cl⁻ in MgCl₂.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Which of the following effects is produced by the high surface tension of water?
A)Lakes don't freeze solid in winter, despite low temperatures.
B)A water strider can walk across the surface of a small pond.
C)Organisms resist temperature changes, although they give off heat due to chemical reactions.
D)Water can act as a solvent.
E)The pH of water remains exactly neutral.
A)Lakes don't freeze solid in winter, despite low temperatures.
B)A water strider can walk across the surface of a small pond.
C)Organisms resist temperature changes, although they give off heat due to chemical reactions.
D)Water can act as a solvent.
E)The pH of water remains exactly neutral.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The nutritional information on a cereal box shows that one serving of a dry cereal has 200 kilocalories. If one were to burn one serving of the cereal, the amount of heat given off would be sufficient to raise the temperature of 20 kg of water how many degrees Celsius?
A)0)2°C
B)1)0°C
C)2)0°C
D)10.0°C
E)20.0°C
A)0)2°C
B)1)0°C
C)2)0°C
D)10.0°C
E)20.0°C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements correctly defines a kilocalorie?
A)the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°F
B)the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C
C)the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°F
D)the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°C
E)the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1,000 g of water by 1°F
A)the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°F
B)the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C
C)the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°F
D)the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°C
E)the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1,000 g of water by 1°F

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
One mole (mol)of a substance is
A)6)02 × 10²³ molecules of the substance.
B)1 g of the substance dissolved in 1 L of solution.
C)the largest amount of the substance that can be dissolved in 1 L of solution.
D)the molecular mass of the substance expressed in grams.
E)A and D only
A)6)02 × 10²³ molecules of the substance.
B)1 g of the substance dissolved in 1 L of solution.
C)the largest amount of the substance that can be dissolved in 1 L of solution.
D)the molecular mass of the substance expressed in grams.
E)A and D only

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
How many molecules of glycerol (C₃H₈O₃)would be present in 1 L of a 1 M glycerol solution?
A)1
B)14
C)92
D)1 × 10⁷
E)6)02 × 10²³
A)1
B)14
C)92
D)1 × 10⁷
E)6)02 × 10²³

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The molecular weight of water is 18 daltons. What is the molarity of 1 liter of pure water?
A)55.6M
B)18M
C)37M
D)0)66M
E)1)0M
A)55.6M
B)18M
C)37M
D)0)66M
E)1)0M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
A solution contains 0.0000001(10⁻⁷)moles of hydroxyl ions [OH⁻] per liter. Which of the following best describes this solution?
A)acidic: H⁺ acceptor
B)basic: H⁺ acceptor
C)acidic: H⁺ donor
D)basic: H⁺ donor
E)neutral
A)acidic: H⁺ acceptor
B)basic: H⁺ acceptor
C)acidic: H⁺ donor
D)basic: H⁺ donor
E)neutral

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Which of the following statements is completely correct?
A)H₂CO₃ is a weak acid, and NaOH is a weak base (alkali).
B)H₂CO₃ is a strong acid, and NaOH is a strong base (alkali).
C)NH₃ is a weak base (alkali), and H₂CO₃ is a strong acid.
D)NH₃ is a weak base (alkali), and HCl is a strong acid.
E)NH₃ is a strong base (alkali), and HCl is a weak acid.
A)H₂CO₃ is a weak acid, and NaOH is a weak base (alkali).
B)H₂CO₃ is a strong acid, and NaOH is a strong base (alkali).
C)NH₃ is a weak base (alkali), and H₂CO₃ is a strong acid.
D)NH₃ is a weak base (alkali), and HCl is a strong acid.
E)NH₃ is a strong base (alkali), and HCl is a weak acid.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The molecular mass of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆)is 180 g. Which of the following procedures should you carry out to make a 0.5 M solution of glucose?
A)Dissolve 0.5 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of solution is 1 L.
B)Dissolve 90 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
C)Dissolve 180 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
D)Dissolve 0.5 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
E)Dissolve 180 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
A)Dissolve 0.5 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of solution is 1 L.
B)Dissolve 90 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
C)Dissolve 180 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
D)Dissolve 0.5 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
E)Dissolve 180 g of glucose in 1 L of water.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
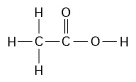
How many grams of the molecule in Figure 3.2 would be required to make 1 L of a 0.5 M solution of the molecule?
(Carbon = 12, Oxygen = 16, Hydrogen = 1)
A)29
B)30
C)60
D)150
E)342

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The molecular mass of glucose is 180 g. Which of the following procedures should you carry out to make a 1 M solution of glucose?
A)Dissolve 1 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
B)Dissolve 180 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
C)Dissolve 180 g of glucose in 100 g of water.
D)Dissolve 180 mg (milligrams)of glucose in 1 L of water.
E)Dissolve 180 g of glucose in water, and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
A)Dissolve 1 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
B)Dissolve 180 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
C)Dissolve 180 g of glucose in 100 g of water.
D)Dissolve 180 mg (milligrams)of glucose in 1 L of water.
E)Dissolve 180 g of glucose in water, and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
You have a freshly-prepared 1M solution of glucose in water. You carefully pour out a 100 mL sample of that solution. How many glucose molecules are included in that 100 mL sample?
A)6)02 × 10²³
B)3)01 × 10²³
C)6)02 × 10²⁴
D)12.04 × 10²³
E)6)02 × 10²²
A)6)02 × 10²³
B)3)01 × 10²³
C)6)02 × 10²⁴
D)12.04 × 10²³
E)6)02 × 10²²

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
What is the pH of a solution with a hydrogen ion [H⁺] concentration of 10⁻⁸ M?
A)pH 2
B)pH 4
C)pH 6
D)pH 8
E)pH 10
A)pH 2
B)pH 4
C)pH 6
D)pH 8
E)pH 10

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29

How many grams of the molecule in Figure 3.2 would be equal to 1 mol of the molecule?
(Carbon = 12, Oxygen = 16, Hydrogen = 1)
A)29
B)30
C)60
D)150
E)342

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which of the following solutions has the greatest concentration of hydroxyl ions [OH⁻]?
A)lemon juice at pH 2
B)vinegar at pH 3
C)tomato juice at pH 4
D)urine at pH 6
E)seawater at pH 8
A)lemon juice at pH 2
B)vinegar at pH 3
C)tomato juice at pH 4
D)urine at pH 6
E)seawater at pH 8

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
You have a freshly-prepared 0.1M solution of glucose in water. Each liter of this solution contains how many glucose molecules?
A)6)02 × 10²³
B)3)01 × 10²³
C)6)02 × 10²⁴
D)12.04 × 10²³
E)6)02 × 10²²
A)6)02 × 10²³
B)3)01 × 10²³
C)6)02 × 10²⁴
D)12.04 × 10²³
E)6)02 × 10²²

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Which of the following ionizes completely in solution and is considered to be a strong base (alkali)?
A)NaCl
B)HCl
C)NH₃
D)H₂CO₃
E)NaOH
A)NaCl
B)HCl
C)NH₃
D)H₂CO₃
E)NaOH

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Which of the following ionizes completely in solution and is considered to be a strong acid?
A)NaOH
B)HCl
C)NH₃
D)H₂CO₃
E)CH₃COOH
A)NaOH
B)HCl
C)NH₃
D)H₂CO₃
E)CH₃COOH

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
What is the pH of a solution with a hydroxyl ion [OH⁻] concentration of 10⁻¹² M?
A)pH 2
B)pH 4
C)pH 10
D)pH 12
E)pH 14
A)pH 2
B)pH 4
C)pH 10
D)pH 12
E)pH 14

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
A given solution contains 0.0001(10⁻⁴)moles of hydrogen ions [H⁺] per liter. Which of the following best describes this solution?
A)acidic: H⁺ acceptor
B)basic: H⁺ acceptor
C)acidic: H⁺ donor
D)basic: H⁺ donor
E)neutral
A)acidic: H⁺ acceptor
B)basic: H⁺ acceptor
C)acidic: H⁺ donor
D)basic: H⁺ donor
E)neutral

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which of the following solutions has the greatest concentration of hydrogen ions [H⁺]?
A)gastric juice at pH 2
B)vinegar at pH 3
C)tomato juice at pH 4
D)black coffee at pH 5
E)household bleach at pH 12
A)gastric juice at pH 2
B)vinegar at pH 3
C)tomato juice at pH 4
D)black coffee at pH 5
E)household bleach at pH 12

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
A small birthday candle is weighed, then lighted and placed beneath a metal can containing 100 mL of water. Careful records are kept as the temperature of the water rises. Data from this experiment are shown on the graph. What amount of heat energy is released in the burning of candle wax?
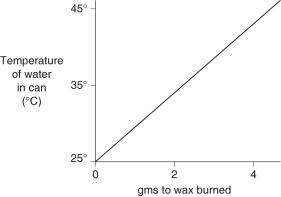
A)0)5 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
B)5 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
C)10 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
D)20 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
E)50 kilocalories per gram of wax burned

A)0)5 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
B)5 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
C)10 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
D)20 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
E)50 kilocalories per gram of wax burned

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Identical heat lamps are arranged to shine on identical containers of water and methanol (wood alcohol), so that each liquid absorbs the same amount of energy minute by minute. The covalent bonds of methanol molecules are non-polar, so there are no hydrogen bonds among methanol molecules. Which of the following graphs correctly describes what will happen to the temperature of the water and the methanol?
A)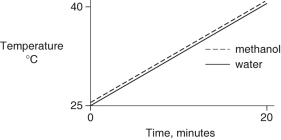
B)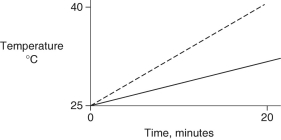
C)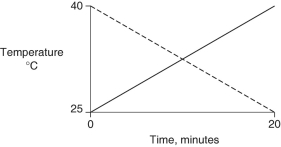
D)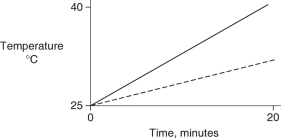
E)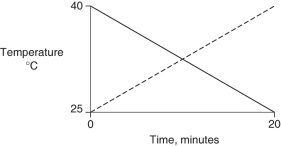
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39

How many grams of the molecule in Figure 3.2 would be required to make 2.5 L of a 1 M solution of the molecule?
(Carbon = 12, Oxygen = 16, Hydrogen = 1)
A)29
B)30
C)60
D)150
E)342

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
If the pH of a solution is decreased from 9 to 8, it means that the
A)concentration of H⁺ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10)what it was at pH 9.
B)concentration of H⁺ has increased 10-fold (10X)compared to what it was at pH 9.
C)concentration of OH⁻ has increased 10-fold (10X)compared to what it was at pH 9.
D)concentration of OH⁻ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10)what it was at pH 9.
E)Both B and D are correct.
A)concentration of H⁺ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10)what it was at pH 9.
B)concentration of H⁺ has increased 10-fold (10X)compared to what it was at pH 9.
C)concentration of OH⁻ has increased 10-fold (10X)compared to what it was at pH 9.
D)concentration of OH⁻ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10)what it was at pH 9.
E)Both B and D are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
You have two beakers. One contains a solution of HCl at pH = 1.0. The other contains a solution of NaOH at pH = 13. Into a third beaker, you slowly and cautiously pour 20 mL of the HCL and 20 mL of the NaOH. After complete stirring, the pH of the mixture will be
A)2)0.
B)12.0.
C)7)0.
D)5)0.
E)9)0.
A)2)0.
B)12.0.
C)7)0.
D)5)0.
E)9)0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The bonds that are broken when water vaporizes are
A)ionic bonds.
B)hydrogen bonds between water molecules.
C)covalent bonds between atoms within water molecules.
D)polar covalent bonds.
E)nonpolar covalent bonds
A)ionic bonds.
B)hydrogen bonds between water molecules.
C)covalent bonds between atoms within water molecules.
D)polar covalent bonds.
E)nonpolar covalent bonds

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Assume that acid rain has lowered the pH of a particular lake to pH 4.0. What is the hydroxyl ion concentration of this lake?
A)1 × 10⁻¹⁰ mol of hydroxyl ion per liter of lake water
B)1 × 10⁻⁴ mol of hydroxyl ion per liter of lake water
C)10.0 M with regard to hydroxyl ion concentration
D)4)0 M with regard to hydroxyl ion concentration
E)both B and D
A)1 × 10⁻¹⁰ mol of hydroxyl ion per liter of lake water
B)1 × 10⁻⁴ mol of hydroxyl ion per liter of lake water
C)10.0 M with regard to hydroxyl ion concentration
D)4)0 M with regard to hydroxyl ion concentration
E)both B and D

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Pure, freshly-distilled water has a pH of 7. This means that
A)there are no H⁺ ions in the water.
B)there are no OH⁻ ions in the water.
C)the concentration of H⁺ ions in the water equals the concentration of OH⁻ ions in the water.
D)the concentration of H⁺ ions in the water is 7 times the concentration of OH⁻ ions in the water.
E)The concentration of OH⁻ ions in the water is 7 times the concentration of H⁺ ions in the water.
A)there are no H⁺ ions in the water.
B)there are no OH⁻ ions in the water.
C)the concentration of H⁺ ions in the water equals the concentration of OH⁻ ions in the water.
D)the concentration of H⁺ ions in the water is 7 times the concentration of OH⁻ ions in the water.
E)The concentration of OH⁻ ions in the water is 7 times the concentration of H⁺ ions in the water.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Equal volumes of vinegar from a freshly-opened bottle are added to each of the following solutions. After complete mixing, which of the mixtures will have the highest pH?
A)100 mL of pure water
B)100 mL of freshly-brewed coffee
C)100 mL of household cleanser containing 0.5M ammonia
D)100 mL of freshly-squeezed orange juice
E)100 mL of tomato juice
A)100 mL of pure water
B)100 mL of freshly-brewed coffee
C)100 mL of household cleanser containing 0.5M ammonia
D)100 mL of freshly-squeezed orange juice
E)100 mL of tomato juice

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Many mammals control their body temperature by sweating. Which property of water is most directly responsible for the ability of sweat to lower body temperature?
A)water's change in density when it condenses
B)water's ability to dissolve molecules in the air
C)the release of heat by the formation of hydrogen bonds
D)the absorption of heat by the breaking of hydrogen bonds
E)water's high surface tension
A)water's change in density when it condenses
B)water's ability to dissolve molecules in the air
C)the release of heat by the formation of hydrogen bonds
D)the absorption of heat by the breaking of hydrogen bonds
E)water's high surface tension

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Research indicates that acid precipitation can damage living organisms by
A)buffering aquatic systems such as lakes and streams.
B)decreasing the H⁺ concentration of lakes and streams.
C)increasing the OH⁻ concentration of lakes and streams.
D)washing away certain mineral ions that help buffer soil solution and are essential nutrients for plant growth.
E)both B and C
A)buffering aquatic systems such as lakes and streams.
B)decreasing the H⁺ concentration of lakes and streams.
C)increasing the OH⁻ concentration of lakes and streams.
D)washing away certain mineral ions that help buffer soil solution and are essential nutrients for plant growth.
E)both B and C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
You have two beakers; one contains pure water, the other contains pure methanol (wood alcohol). The covalent bonds of methanol molecules are nonpolar, so there are no hydrogen bonds among methanol molecules. You pour crystals of table salt (NaCl)into each beaker. Predict what will happen.
A)Equal amounts of NaCl crystals will dissolve in both water and methanol.
B)NaCl crystals will NOT dissolve in either water or methanol.
C)NaCl crystals will dissolve readily in water but will not dissolve in methanol.
D)NaCl crystals will dissolve readily in methanol but will not dissolve in water.
E)When the first crystals of NaCl are added to water or to methanol, they will not dissolve; but as more crystals are added, the crystals will begin to dissolve faster and faster.
A)Equal amounts of NaCl crystals will dissolve in both water and methanol.
B)NaCl crystals will NOT dissolve in either water or methanol.
C)NaCl crystals will dissolve readily in water but will not dissolve in methanol.
D)NaCl crystals will dissolve readily in methanol but will not dissolve in water.
E)When the first crystals of NaCl are added to water or to methanol, they will not dissolve; but as more crystals are added, the crystals will begin to dissolve faster and faster.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
A 100 mL beaker contains 10 mL of NaOH solution at pH = 13. A technician carefully pours into the beaker, 10 mL of HCl at pH = 1. Which of the following statements correctly describes the results of this mixing?
A)The concentration of Na⁺ ion rises.
B)The concentration of Cl⁻ ion falls.
C)The concentration of undissociated H₂O molecules remains unchanged.
D)The pH of the beaker's contents rises.
E)The pH of the beaker's contents falls.
A)The concentration of Na⁺ ion rises.
B)The concentration of Cl⁻ ion falls.
C)The concentration of undissociated H₂O molecules remains unchanged.
D)The pH of the beaker's contents rises.
E)The pH of the beaker's contents falls.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Carbon dioxide (CO₂)is readily soluble in water, according to the equation CO₂ + H₂O → H₂CO₃. Carbonic acid (H₂CO₃)is a weak acid. If CO₂ is bubbled into a beaker containing pure, freshly-distilled water, which of the following graphs correctly describes the results?
A)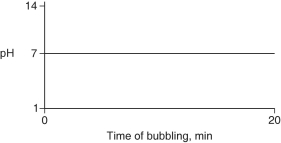
B)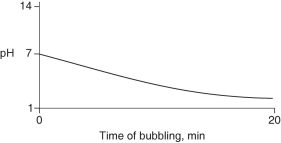
C)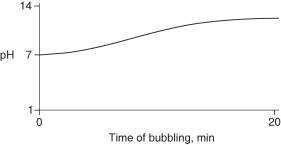
D)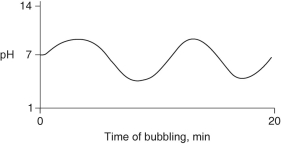
E)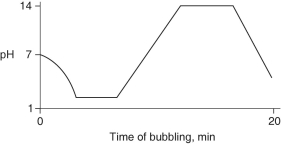
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
One liter of a solution of pH 2 has how many more hydrogen ions (H⁺)than 1 L of a solution of pH 6?
A)4 times more
B)400 times more
C)4,000 times more
D)10,000 times more
E)100,000 times more
A)4 times more
B)400 times more
C)4,000 times more
D)10,000 times more
E)100,000 times more

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
One liter of a solution pH 9 has how many more hydroxyl ions (OH⁻)than 1 L of a solution of pH 4?
A)5 times more
B)100 times more
C)1,000 times more
D)10,000 times more
E)100,000 times more
A)5 times more
B)100 times more
C)1,000 times more
D)10,000 times more
E)100,000 times more

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Carbon dioxide (CO₂)is readily soluble in water, according to the equation CO₂ + H₂O → H₂CO₃. Carbonic acid (H₂CO₃)is a weak acid. Respiring cells release CO₂. What prediction can we make about the pH of blood as that blood first comes in contact with respiring cells?
A)Blood pH will decrease slightly.
B)Blood pH will increase slightly.
C)Blood pH will remain unchanged.
D)Blood pH will first increase, then decrease as CO₂ combines with hemoglobin.
E)Blood pH will first decrease, then increase sharply as CO₂ combines with hemoglobin.
A)Blood pH will decrease slightly.
B)Blood pH will increase slightly.
C)Blood pH will remain unchanged.
D)Blood pH will first increase, then decrease as CO₂ combines with hemoglobin.
E)Blood pH will first decrease, then increase sharply as CO₂ combines with hemoglobin.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Buffers are substances that help resist shifts in pH by
A)releasing H⁺ in acidic solutions.
B)donating H⁺ to a solution when they have been depleted.
C)releasing OH⁻ in basic solutions.
D)accepting H⁺ when the are in excess.
E)Both B and D are correct.
A)releasing H⁺ in acidic solutions.
B)donating H⁺ to a solution when they have been depleted.
C)releasing OH⁻ in basic solutions.
D)accepting H⁺ when the are in excess.
E)Both B and D are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Which of the following statements is True about buffer solutions?
A)They maintain a constant pH when bases are added to them but not when acids are added to them.
B)They maintain a constant pH when acids are added to them but not when bases are added to them.
C)They maintain a constant pH of exactly 7 in all living cells and biological fluids.
D)They maintain a relatively constant pH when either acids or bases are added to them.
E)They are found only in living systems and biological fluids.
A)They maintain a constant pH when bases are added to them but not when acids are added to them.
B)They maintain a constant pH when acids are added to them but not when bases are added to them.
C)They maintain a constant pH of exactly 7 in all living cells and biological fluids.
D)They maintain a relatively constant pH when either acids or bases are added to them.
E)They are found only in living systems and biological fluids.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Consider two solutions: solution X has a pH of 4; solution Y has a pH of 7. From this information, we can reasonably conclude that
A)solution Y has no free hydrogen ions (H⁺).
B)the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 30 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y.
C)the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y is 1,000 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X.
D)the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 3 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y.
E)None of the other answer choices correctly describes these solutions.
A)solution Y has no free hydrogen ions (H⁺).
B)the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 30 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y.
C)the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y is 1,000 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X.
D)the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 3 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y.
E)None of the other answer choices correctly describes these solutions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
One of the buffers that contribute to pH stability in human blood is carbonic acid (H₂CO₃). Carbonic acid is a weak acid that dissociates into a bicarbonate ion (HCO₃⁻)and a hydrogen ion (H⁺). Thus, H₂CO₃ ↔ HCO₃⁻ + H⁺
If the pH of the blood drops, one would expect
A)a decrease in the concentration of H₂CO₃ and an increase in the concentration of HCO₃⁻.
B)the concentration of hydroxide ion (OH⁻)to increase.
C)the concentration of bicarbonate ion (HCO₃⁻)to increase.
D)the HCO₃⁻ to act as a base and remove excess H⁺ with the formation of H₂CO₃.
E)the HCO₃⁻ to act as an acid and remove excess H⁺ with the formation of H₂CO₃.
If the pH of the blood drops, one would expect
A)a decrease in the concentration of H₂CO₃ and an increase in the concentration of HCO₃⁻.
B)the concentration of hydroxide ion (OH⁻)to increase.
C)the concentration of bicarbonate ion (HCO₃⁻)to increase.
D)the HCO₃⁻ to act as a base and remove excess H⁺ with the formation of H₂CO₃.
E)the HCO₃⁻ to act as an acid and remove excess H⁺ with the formation of H₂CO₃.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
If the pH of a solution is increased from pH 5 to pH 7, it means that the
A)concentration of H⁺ is twice (2X)what it was at pH 5.
B)concentration of H⁺ is half (1/2)what it was at pH 5.
C)concentration of OH⁻ is 100 times greater than what it was at pH 5.
D)concentration of OH⁻ is one-hundredth (0.01X)what it was at pH 5.
E)concentration of H⁺ is 100 times greater and the concentration of OH⁻ is one-hundredth what they were at pH 5.
A)concentration of H⁺ is twice (2X)what it was at pH 5.
B)concentration of H⁺ is half (1/2)what it was at pH 5.
C)concentration of OH⁻ is 100 times greater than what it was at pH 5.
D)concentration of OH⁻ is one-hundredth (0.01X)what it was at pH 5.
E)concentration of H⁺ is 100 times greater and the concentration of OH⁻ is one-hundredth what they were at pH 5.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
A slice of pizza has 500 kcal. If we could burn the pizza and use all the heat to warm a 50-L container of cold water, what would be the approximate increase in the temperature of the water? (Note: A liter of cold water weighs about 1 kg.)
A)50°C
B)5°C
C)10°C
D)100°C
E)1°C
A)50°C
B)5°C
C)10°C
D)100°C
E)1°C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
One of the buffers that contribute to pH stability in human blood is carbonic acid H₂CO₃. Carbonic acid is a weak acid that when placed in an aqueous solution dissociates into a bicarbonate ion (HCO₃⁻)and a hydrogen ion (H⁺). Thus, H₂CO₃ ↔ HCO₃⁻ + H⁺
If the pH of the blood increases, one would expect
A)a decrease in the concentration of H₂CO₃ and an increase in the concentration of H₂O.
B)an increase in the concentration of H₂CO₃ and a decrease in the concentration of H₂O.
C)a decrease in the concentration of HCO₃⁻ and an increase in the concentration of H₂O.
D)an increase in the concentration of HCO₃⁻ and a decrease in the concentration of H₂O.
E)a decrease in the concentration of HCO₃⁻ and an increase in the concentration of both H₂CO₃ and H₂O.
If the pH of the blood increases, one would expect
A)a decrease in the concentration of H₂CO₃ and an increase in the concentration of H₂O.
B)an increase in the concentration of H₂CO₃ and a decrease in the concentration of H₂O.
C)a decrease in the concentration of HCO₃⁻ and an increase in the concentration of H₂O.
D)an increase in the concentration of HCO₃⁻ and a decrease in the concentration of H₂O.
E)a decrease in the concentration of HCO₃⁻ and an increase in the concentration of both H₂CO₃ and H₂O.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
We can be sure that a mole of table sugar and a mole of vitamin C are equal in their
A)mass in daltons.
B)mass in grams.
C)number of molecules.
D)number of atoms.
E)volume.
A)mass in daltons.
B)mass in grams.
C)number of molecules.
D)number of atoms.
E)volume.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
How many grams of acetic acid (C₂H₄O₂)would you use to make 10 L of a 0.1 M aqueous solution of acetic acid? (Note: The atomic masses, in daltons, are approximately 12 for carbon, 1 for hydrogen, and 16 for oxygen.)
A)10.0 g
B)0)1 g
C)6)0 g
D)60.0 g
E)0)6 g
A)10.0 g
B)0)1 g
C)6)0 g
D)60.0 g
E)0)6 g

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Draw three water molecules and label the atoms. Draw solid lines to indicate covalent bonds and dotted lines for hydrogen bonds. Add partial charge labels as appropriate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Which of the following is a hydrophobic material?
A)paper
B)table salt
C)wax
D)sugar
E)pasta
A)paper
B)table salt
C)wax
D)sugar
E)pasta

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
What is the hydroxide ion concentration of the lake described in question 7?
A)10⁻⁷ M
B)10⁻⁴ M
C)10⁻¹⁰ M
D)10⁻¹⁴ M
E)10 M
A)10⁻⁷ M
B)10⁻⁴ M
C)10⁻¹⁰ M
D)10⁻¹⁴ M
E)10 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Measurements show that the pH of a particular lake is 4.0. What is the hydrogen ion concentration of the lake?
A)4)0 M
B)10⁻¹⁰ M
C)10⁻⁴ M
D)10⁴ M
E)4%
A)4)0 M
B)10⁻¹⁰ M
C)10⁻⁴ M
D)10⁴ M
E)4%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








