Deck 9: Skeletal Muscle Tissue
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/115
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 9: Skeletal Muscle Tissue
1
Muscle fibers differ from "typical cells" in that muscle fibers
A) lack a plasma membrane.
B) have many nuclei.
C) are very small.
D) lack mitochondria.
E) all of the above
A) lack a plasma membrane.
B) have many nuclei.
C) are very small.
D) lack mitochondria.
E) all of the above
B
2
Muscle tissue, one of the four basic tissue groups, consists chiefly of cells that are highly specialized for
A) conduction.
B) contraction.
C) peristalsis.
D) cushioning
E) any of the above
A) conduction.
B) contraction.
C) peristalsis.
D) cushioning
E) any of the above
B
3
Skeletal muscle fibers are formed from embryonic cells called
A) sarcomeres.
B) myofibrils.
C) myoblasts.
D) fascicles.
E) myomeres.
A) sarcomeres.
B) myofibrils.
C) myoblasts.
D) fascicles.
E) myomeres.
C
4
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) The contractions of skeletal muscles pull on tendons and move bones of the skeleton.
B) Skeletal muscles store nutrient reserves.
C) Skeletal muscles are responsible for the pumping action of the heart.
D) Skeletal muscles support the weight of some internal organs.
E) Skeletal muscle contractions help maintain body temperature.
A) The contractions of skeletal muscles pull on tendons and move bones of the skeleton.
B) Skeletal muscles store nutrient reserves.
C) Skeletal muscles are responsible for the pumping action of the heart.
D) Skeletal muscles support the weight of some internal organs.
E) Skeletal muscle contractions help maintain body temperature.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Each skeletal muscle fiber contains ________ myofibrils.
A) 50 to 100
B) 100 to 150
C) 150 to 200
D) 200 to 500
E) hundreds to thousands
A) 50 to 100
B) 100 to 150
C) 150 to 200
D) 200 to 500
E) hundreds to thousands

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
At each end of the muscle, the collagen fibers of the epimysium, and each perimysium and endomysium, come together to form a
A) tendon.
B) satellite cell.
C) ligament.
D) tenosynovium.
E) sheath.
A) tendon.
B) satellite cell.
C) ligament.
D) tenosynovium.
E) sheath.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The advantage of having many nuclei in a skeletal muscle fiber is
A) the ability to contract.
B) the ability to produce more ATP with little oxygen.
C) the ability to store extra DNA for metabolism.
D) the ability to produce large amounts of the muscle proteins needed for muscle contraction.
E) all of the above
A) the ability to contract.
B) the ability to produce more ATP with little oxygen.
C) the ability to store extra DNA for metabolism.
D) the ability to produce large amounts of the muscle proteins needed for muscle contraction.
E) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The repeating unit of a skeletal muscle fiber is the
A) sarcolemma.
B) sarcomere.
C) sarcoplasmic reticulum.
D) myofibril.
E) myofilament.
A) sarcolemma.
B) sarcomere.
C) sarcoplasmic reticulum.
D) myofibril.
E) myofilament.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The plasma membrane of skeletal muscle is called the
A) sarcolemma.
B) sarcomere.
C) sarcosome.
D) sarcoplasmic reticulum.
E) sarcoplasm.
A) sarcolemma.
B) sarcomere.
C) sarcosome.
D) sarcoplasmic reticulum.
E) sarcoplasm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The delicate connective tissue that surrounds the skeletal muscle fibers and ties adjacent muscle fibers together is the
A) endomysium.
B) perimysium.
C) epimysium.
D) superficial fascia.
E) periosteum.
A) endomysium.
B) perimysium.
C) epimysium.
D) superficial fascia.
E) periosteum.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Individual muscle cells are surrounded by
A) endomysium.
B) perimysium.
C) sarcolemma.
D) sarcomere.
E) myofibrils.
A) endomysium.
B) perimysium.
C) sarcolemma.
D) sarcomere.
E) myofibrils.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of the following is a recognized function of skeletal muscle?
A) produce movement
B) maintain posture
C) maintain body temperature
D) guard body entrances and exits
E) all of the above
A) produce movement
B) maintain posture
C) maintain body temperature
D) guard body entrances and exits
E) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Which of the following best describes the term sarcomere?
A) protein that accounts for elasticity of resting muscle
B) repeating unit of striated myofibrils
C) storage site for calcium ions
D) thin filaments are anchored here
E) largely made of myosin molecules
A) protein that accounts for elasticity of resting muscle
B) repeating unit of striated myofibrils
C) storage site for calcium ions
D) thin filaments are anchored here
E) largely made of myosin molecules

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The bundle of collagen fibers at the end of a skeletal muscle that attaches the muscle to bone is called a(n)
A) fascicle.
B) tendon.
C) ligament.
D) epimysium.
E) myofibril.
A) fascicle.
B) tendon.
C) ligament.
D) epimysium.
E) myofibril.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The region of the sarcomere that always contains thin filaments is the
A) Z line.
B) M line.
C) H band.
D) A band.
E) I band.
A) Z line.
B) M line.
C) H band.
D) A band.
E) I band.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Which of the following best describes the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
A) protein that accounts for elasticity of resting muscle
B) repeating unit of striated myofibrils
C) storage and release site for calcium ions
D) thin filaments are anchored here
E) largely made of myosin molecules
A) protein that accounts for elasticity of resting muscle
B) repeating unit of striated myofibrils
C) storage and release site for calcium ions
D) thin filaments are anchored here
E) largely made of myosin molecules

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The region of the sarcomere containing the thick filaments is the
A) Z line.
B) M line.
C) H band.
D) A band.
E) I band.
A) Z line.
B) M line.
C) H band.
D) A band.
E) I band.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The dense layer of connective tissue that surrounds an entire skeletal muscle is the
A) tendon.
B) epimysium.
C) endomysium.
D) perimysium.
E) fascicle.
A) tendon.
B) epimysium.
C) endomysium.
D) perimysium.
E) fascicle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The types of muscle tissue include all of the following, except
A) striated muscle.
B) cardiac muscle.
C) smooth muscle.
D) skeletal muscle.
E) none of the above
A) striated muscle.
B) cardiac muscle.
C) smooth muscle.
D) skeletal muscle.
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Nerves and blood vessels that service the muscle fibers are located in the connective tissues of the
A) endomysium.
B) perimysium.
C) sarcolemma.
D) sarcomere.
E) myofibrils.
A) endomysium.
B) perimysium.
C) sarcolemma.
D) sarcomere.
E) myofibrils.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
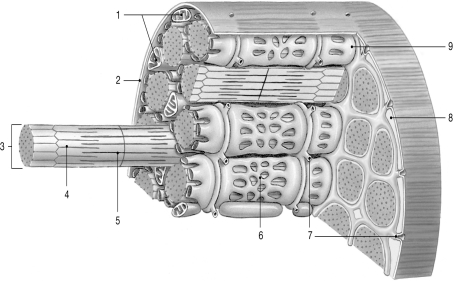
Figure 9-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 9-1 to answer the following questions:
What is released from the structure labeled "9"?
A) sarcoplasm
B) acetylcholine
C) protein
D) calcium ions
E) acetylcholinesterase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Each thin filament consists of
A) two protein strands coiled helically around each other.
B) chains of myosin molecules.
C) six molecules in a rod like structure.
D) a rod-shaped structure with "heads" projecting from each end.
E) a double strand of myosin molecules.
A) two protein strands coiled helically around each other.
B) chains of myosin molecules.
C) six molecules in a rod like structure.
D) a rod-shaped structure with "heads" projecting from each end.
E) a double strand of myosin molecules.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Compared to a "typical" body cell, skeletal muscle cells are
A) larger than normal cells.
B) multinucleate.
C) filled with cylindrical structures containing contractile proteins.
D) capable of rapid shortening against a load.
E) all of the above
A) larger than normal cells.
B) multinucleate.
C) filled with cylindrical structures containing contractile proteins.
D) capable of rapid shortening against a load.
E) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24

Figure 9-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 9-1 to answer the following questions:
Which structure contains the motor end plate?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 5
E) 8

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
The skeletal muscle complex known as the triad consists of
A) actin, myosin, and filaments.
B) a transverse tubule and two terminal cisternae.
C) filaments, myofibrils, and sarcomeres.
D) A bands, H bands, and I bands.
E) actin, myosin, and sarcomeres.
A) actin, myosin, and filaments.
B) a transverse tubule and two terminal cisternae.
C) filaments, myofibrils, and sarcomeres.
D) A bands, H bands, and I bands.
E) actin, myosin, and sarcomeres.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26

Figure 9-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 9-1 to answer the following questions:
What physiological process occurs in the structure labeled "7"?
A) release of neurotransmitter
B) conduction of the action potential into the cell interior
C) activity of acetylcholinesterase
D) release of protein into the muscle fiber
E) the sliding filament theory

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
At rest, active sites on the actin are blocked by
A) myosin molecules.
B) troponin molecules.
C) tropomyosin molecules.
D) calcium ions.
E) ATP molecules.
A) myosin molecules.
B) troponin molecules.
C) tropomyosin molecules.
D) calcium ions.
E) ATP molecules.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28

Figure 9-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 9-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure where ATP is produced.
A) 6
B) 7
C) 1
D) 3
E) 2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Which of the following best describes the term titin?
A) protein that accounts for elasticity of resting muscle
B) repeating unit of striated myofibrils
C) storage site for calcium ions
D) where thin filaments are anchored
E) largely made of myosin molecules
A) protein that accounts for elasticity of resting muscle
B) repeating unit of striated myofibrils
C) storage site for calcium ions
D) where thin filaments are anchored
E) largely made of myosin molecules

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30

Figure 9-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 9-1 to answer the following questions:
Where is ATP is consumed?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 6
E) 3 and 6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
In a sarcomere, thick filaments are linked laterally by proteins of the
A) Z line.
B) M line.
C) H band.
D) A band.
E) I band.
A) Z line.
B) M line.
C) H band.
D) A band.
E) I band.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32

Figure 9-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 9-1 to answer the following questions:
Which of the following are found in the structure labeled "3"?
A) actin
B) myosin
C) titin
D) tropomyosin
E) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Which statement about the microscopic anatomy of skeletal muscle fibers is True ?
A) Tubular extensions of the sarcolemma penetrate the fiber transversely.
B) Cross striations result from the lateral alignment of thick and thin filaments.
C) Each fiber has many nuclei.
D) Muscle fibers are continuous from tendon to tendon.
E) All are True .
A) Tubular extensions of the sarcolemma penetrate the fiber transversely.
B) Cross striations result from the lateral alignment of thick and thin filaments.
C) Each fiber has many nuclei.
D) Muscle fibers are continuous from tendon to tendon.
E) All are True .

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The area in the center of the A band that contains no thin filaments is the
A) Z line.
B) M line.
C) H band.
D) I band.
E) zone of overlap.
A) Z line.
B) M line.
C) H band.
D) I band.
E) zone of overlap.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Which of the following best describes the term Z line?
A) protein that accounts for elasticity of resting muscle
B) repeating unit of striated myofibrils
C) storage site for calcium ions
D) where thin filaments are anchored
E) largely made of myosin molecules
A) protein that accounts for elasticity of resting muscle
B) repeating unit of striated myofibrils
C) storage site for calcium ions
D) where thin filaments are anchored
E) largely made of myosin molecules

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36

Figure 9-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 9-1 to answer the following questions:
Where would calcium ion be predominately found?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 8
E) 9

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37

Figure 9-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 9-1 to answer the following questions:
Which structure actively pumps calcium ions out of the sarcoplasm to produce relaxation?
A) 6
B) 7
C) 1
D) 3
E) 2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38

Figure 9-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 9-1 to answer the following questions:
Where are the myosin molecules located?
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7
E) 8

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Interactions between actin and myosin filaments of the sarcomere are responsible for
A) muscle fatigue.
B) the conduction of neural stimulation to the muscle fiber.
C) muscle contraction.
D) muscle relaxation.
E) the striped appearance of skeletal muscle.
A) muscle fatigue.
B) the conduction of neural stimulation to the muscle fiber.
C) muscle contraction.
D) muscle relaxation.
E) the striped appearance of skeletal muscle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40

Figure 9-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 9-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structures labeled " 1."
A) mitochondria
B) glycogen
C) ATP
D) myofibril
E) synaptic vesicle

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The narrow space between the synaptic terminal and the muscle fiber is the
A) synaptic knob.
B) motor end plate.
C) motor unit.
D) synaptic cleft.
E) M line.
A) synaptic knob.
B) motor end plate.
C) motor unit.
D) synaptic cleft.
E) M line.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The cytoplasm of the neuromuscular synaptic terminal contains vesicles filled with molecules of the neurotransmitter
A) epinephrine.
B) norepinephrine.
C) acetylcholine.
D) antidiuretic hormone.
E) all of the above
A) epinephrine.
B) norepinephrine.
C) acetylcholine.
D) antidiuretic hormone.
E) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Each skeletal muscle fiber is controlled by a motor neuron at a single
A) synaptic knob.
B) sarcomere.
C) neuromuscular junction.
D) synaptic cleft.
E) transverse tubule.
A) synaptic knob.
B) sarcomere.
C) neuromuscular junction.
D) synaptic cleft.
E) transverse tubule.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Triggering of the muscle action potential occurs after
A) acetylcholine binds to chemically gated channels in the motor end plate membrane.
B) acetylcholinesterase binds to receptors on the end plate.
C) calcium ion binds to channels on the end plate.
D) the nerve action potential jumps across the neuromuscular junction.
E) Any of the above can produce an action potential in the muscle cell.
A) acetylcholine binds to chemically gated channels in the motor end plate membrane.
B) acetylcholinesterase binds to receptors on the end plate.
C) calcium ion binds to channels on the end plate.
D) the nerve action potential jumps across the neuromuscular junction.
E) Any of the above can produce an action potential in the muscle cell.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Receptors for acetylcholine are located on the
A) synaptic knob.
B) motor end plate.
C) sarcomere.
D) synaptic cleft.
E) transverse tubule.
A) synaptic knob.
B) motor end plate.
C) sarcomere.
D) synaptic cleft.
E) transverse tubule.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Cross-bridges are portions of
A) actin molecules.
B) myosin molecules.
C) troponin molecules.
D) tropomyosin molecules.
E) calcium ions.
A) actin molecules.
B) myosin molecules.
C) troponin molecules.
D) tropomyosin molecules.
E) calcium ions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Physical evidence that supports the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction includes
A) constant distance between Z lines during contraction.
B) decreased width of the H band during contraction.
C) increased width of the I band during contraction.
D) decreased width of the A band during contraction.
E) the I band and H band distance is constant during contraction.
A) constant distance between Z lines during contraction.
B) decreased width of the H band during contraction.
C) increased width of the I band during contraction.
D) decreased width of the A band during contraction.
E) the I band and H band distance is constant during contraction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
At rest, the tropomyosin molecule is held in place by
A) actin molecules.
B) myosin molecules.
C) troponin molecules.
D) ATP molecules.
E) calcium ions.
A) actin molecules.
B) myosin molecules.
C) troponin molecules.
D) ATP molecules.
E) calcium ions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The most important factor in decreasing the intracellular concentration of calcium ion after contraction is
A) active transport of calcium across the sarcolemma.
B) active transport of calcium into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C) active transport of calcium into the synaptic cleft.
D) diffusion of calcium out of the cell.
E) diffusion of calcium into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
A) active transport of calcium across the sarcolemma.
B) active transport of calcium into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C) active transport of calcium into the synaptic cleft.
D) diffusion of calcium out of the cell.
E) diffusion of calcium into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
When acetylcholine binds to receptors at the motor end plate, the end plate membrane becomes
A) more permeable to sodium ions.
B) less permeable to sodium ions.
C) more permeable to calcium ions.
D) less permeable to potassium ions.
E) repolarized.
A) more permeable to sodium ions.
B) less permeable to sodium ions.
C) more permeable to calcium ions.
D) less permeable to potassium ions.
E) repolarized.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
In response to action potentials arriving along the transverse tubules, the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases
A) acetylcholine.
B) sodium ions.
C) potassium ions.
D) calcium ions.
E) hydrogen ions.
A) acetylcholine.
B) sodium ions.
C) potassium ions.
D) calcium ions.
E) hydrogen ions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Which of the following become connected by myosin cross-bridges during muscle contraction?
A) thin filaments and thick filaments
B) thick filaments and titin filaments
C) z disks and actin filaments
D) thick filaments and t-tubules
E) thin filaments and t-tubules
A) thin filaments and thick filaments
B) thick filaments and titin filaments
C) z disks and actin filaments
D) thick filaments and t-tubules
E) thin filaments and t-tubules

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
How would the loss of acetylcholinesterase from the motor end plate affect skeletal muscle?
A) It would make the muscles less excitable.
B) It would produce muscle weakness.
C) It would cause spastic paralysis (muscles are contracted and unable to relax).
D) It would cause flaccid paralysis (muscles are relaxed and unable to contract).
E) It would have little effect on skeletal muscles.
A) It would make the muscles less excitable.
B) It would produce muscle weakness.
C) It would cause spastic paralysis (muscles are contracted and unable to relax).
D) It would cause flaccid paralysis (muscles are relaxed and unable to contract).
E) It would have little effect on skeletal muscles.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The thin filaments of striated muscle are made of which protein(s)?
A) actin
B) tropomyosin
C) troponin
D) nebulin
E) all of the above
A) actin
B) tropomyosin
C) troponin
D) nebulin
E) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitters are released by ________ when the action potential arrives.
A) endocytosis
B) apoptosis
C) exocytosis
D) hydrolysis
E) sodium
A) endocytosis
B) apoptosis
C) exocytosis
D) hydrolysis
E) sodium

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
When calcium ion binds to troponin,
A) tropomyosin moves into the groove between the helical actin strands.
B) active sites on the myosin are exposed.
C) actin heads will bind to myosin.
D) muscle relaxation occurs.
E) myosin shortens.
A) tropomyosin moves into the groove between the helical actin strands.
B) active sites on the myosin are exposed.
C) actin heads will bind to myosin.
D) muscle relaxation occurs.
E) myosin shortens.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Since each myofibril is attached at either end of the muscle fiber, when sarcomeres shorten, the muscle fiber
A) lengthens.
B) shortens.
C) strengthens.
D) weakens.
E) not enough information to say
A) lengthens.
B) shortens.
C) strengthens.
D) weakens.
E) not enough information to say

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
When a skeletal muscle fiber contracts,
A) the H bands and I bands get smaller.
B) the zones of overlap get larger.
C) the Z lines get closer together.
D) the width of the A band remains constant.
E) all of the above
A) the H bands and I bands get smaller.
B) the zones of overlap get larger.
C) the Z lines get closer together.
D) the width of the A band remains constant.
E) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The action potential is conducted into a skeletal muscle fiber by
A) motor end plates.
B) neuromuscular junctions.
C) transverse tubules.
D) triads.
E) sarcoplasmic reticulum.
A) motor end plates.
B) neuromuscular junctions.
C) transverse tubules.
D) triads.
E) sarcoplasmic reticulum.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
How would a drug that blocks acetylcholine receptors at the motor end plate affect skeletal muscle?
A) It would make the muscles more excitable.
B) It would produce uncontrolled muscle spasms.
C) It would cause spastic paralysis (muscles are contracted and unable to relax).
D) It would cause flaccid paralysis (muscles are relaxed and unable to contract).
E) It would have little effect on skeletal muscles.
A) It would make the muscles more excitable.
B) It would produce uncontrolled muscle spasms.
C) It would cause spastic paralysis (muscles are contracted and unable to relax).
D) It would cause flaccid paralysis (muscles are relaxed and unable to contract).
E) It would have little effect on skeletal muscles.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
The increase in muscle tension that is produced by increasing the number of active motor units is called
A) incomplete tetanus.
B) complete tetanus.
C) treppe.
D) wave summation.
E) recruitment.
A) incomplete tetanus.
B) complete tetanus.
C) treppe.
D) wave summation.
E) recruitment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
The rapid rise and fall in force produced by a muscle fiber after a single action potential is
A) a tetanus.
B) an unfused tetanus.
C) a twitch.
D) an end plate potential.
E) a muscle action potential.
A) a tetanus.
B) an unfused tetanus.
C) a twitch.
D) an end plate potential.
E) a muscle action potential.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Which of the following muscles would contract more forcefully?
A) a muscle receiving 10 to 15 action potentials per second
B) a muscle receiving 20 to 25 action potentials per second
A) a muscle receiving 10 to 15 action potentials per second
B) a muscle receiving 20 to 25 action potentials per second

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Which of the following acts as an ATPase during the contraction cycle of muscle?
A) actin molecules
B) troponin molecules
C) tropomyosin molecules
D) the head portion of the myosin molecule
E) the tail portion of the myosin molecule
A) actin molecules
B) troponin molecules
C) tropomyosin molecules
D) the head portion of the myosin molecule
E) the tail portion of the myosin molecule

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Which of the following is greater?
A) the concentration of calcium ion in the sarcoplasm of a resting muscle
B) the concentration of calcium ion in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a resting muscle
A) the concentration of calcium ion in the sarcoplasm of a resting muscle
B) the concentration of calcium ion in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a resting muscle

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
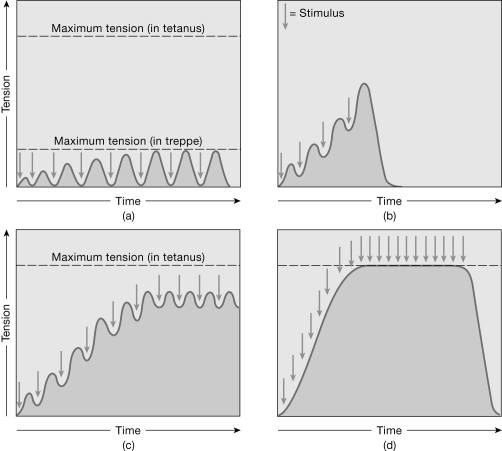
Figure 9-2 Muscle Contractions
Use Figure 9-2 to answer the following questions:
What is the contraction in graph (d) called?
A) complete tetanus
B) incomplete tetanus
C) twitch
D) wave summation
E) treppe

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Calcium ions are binding to troponin during the ________ of a muscle twitch.
A) latent period
B) contraction phase
C) recovery phase
D) relaxation phase
E) latent period and the contraction phase
A) latent period
B) contraction phase
C) recovery phase
D) relaxation phase
E) latent period and the contraction phase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
In which of the following would the motor units have the fewest muscle fibers?
A) muscles of the neck
B) postural muscles of the back
C) muscles that control the eyes
D) thigh muscles
E) calf muscles
A) muscles of the neck
B) postural muscles of the back
C) muscles that control the eyes
D) thigh muscles
E) calf muscles

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Muscular force can be adjusted to match different loads by
A) varying the frequency of action potentials in motor neurons.
B) recruiting larger motor units.
C) recruiting more motor units.
D) all of the above
E) None of the above.muscle contraction is all-or-none.
A) varying the frequency of action potentials in motor neurons.
B) recruiting larger motor units.
C) recruiting more motor units.
D) all of the above
E) None of the above.muscle contraction is all-or-none.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
If a second stimulus arrives before the relaxation phase has ended, a second, more powerful contraction occurs. This is called
A) incomplete tetanus.
B) complete tetanus.
C) treppe.
D) wave summation.
E) recruitment.
A) incomplete tetanus.
B) complete tetanus.
C) treppe.
D) wave summation.
E) recruitment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Which statement about excitation-contraction coupling is incorrect?
A) Calcium ion is released from the transverse tubule.
B) Calcium ion is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C) Tropomyosin moves to expose myosin binding sites on actin.
D) Troponin binds calcium ion and signals tropomyosin to move.
E) Relaxation requires uptake of calcium ions by the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
A) Calcium ion is released from the transverse tubule.
B) Calcium ion is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C) Tropomyosin moves to expose myosin binding sites on actin.
D) Troponin binds calcium ion and signals tropomyosin to move.
E) Relaxation requires uptake of calcium ions by the sarcoplasmic reticulum.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
A single motor neuron together with all the muscle fibers it innervates is called
A) an end foot.
B) an end plate.
C) a motor unit.
D) a dermatome.
E) a myotome.
A) an end foot.
B) an end plate.
C) a motor unit.
D) a dermatome.
E) a myotome.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73

Figure 9-2 Muscle Contractions
Use Figure 9-2 to answer the following questions:
To produce a contraction similar to the one in graph (b), the muscle
A) must be stimulated to the point of fatigue.
B) must be stimulated again before it has relaxed from the previous stimulation.
C) is excited by a stimulus of increasing intensity.
D) is caused to produce isolated twitches.
E) gradually warms up.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
What is thought to happen in a muscle during the response shown in graph (a)?
A) It is getting stronger with exercise.
B) There is a gradual increase in the concentration of calcium ions in the sarcoplasm.
C) It is fatigued and must make repeated efforts to twitch normally.
D) It is aged and has lost contractile proteins.
E) It is producing more ATP as tension increases.
A) It is getting stronger with exercise.
B) There is a gradual increase in the concentration of calcium ions in the sarcoplasm.
C) It is fatigued and must make repeated efforts to twitch normally.
D) It is aged and has lost contractile proteins.
E) It is producing more ATP as tension increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
A muscle producing tension that peaks and falls at intermediate stimulus rates is said to be in
A) incomplete tetanus.
B) complete tetanus.
C) treppe.
D) wave summation.
E) recruitment.
A) incomplete tetanus.
B) complete tetanus.
C) treppe.
D) wave summation.
E) recruitment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Which of the following motor units would produce the greatest tension?
A) a motor unit in a back muscle
B) a motor unit in a hand muscle
C) a motor unit in an eye muscle
A) a motor unit in a back muscle
B) a motor unit in a hand muscle
C) a motor unit in an eye muscle

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
The type of contraction in which the muscle fibers do not shorten is called
A) tetany.
B) treppe.
C) concentric.
D) isotonic.
E) isometric.
A) tetany.
B) treppe.
C) concentric.
D) isotonic.
E) isometric.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78

Figure 9-2 Muscle Contractions
Use Figure 9-2 to answer the following questions:
What is the single response to each stimulus of a skeletal muscle called?
A) complete tetanus
B) incomplete tetanus
C) twitch
D) wave summation
E) treppe

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79

Figure 9-2 Muscle Contractions
Use Figure 9-2 to answer the following questions:
Why is there partial relaxation in graph (c)?
A) Calcium ion release is slow.
B) The muscle is starting to fatigue.
C) Stimulation intensity is fluctuating.
D) ATP reserves are cycling.
E) Nerve stimulation frequency is below maximum.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
When a muscle is stimulated repeatedly at a high rate, the amount of tension gradually increases to a steady maximum tension. This is called
A) incomplete tetanus.
B) complete tetanus.
C) a twitch.
D) wave summation.
E) recruitment.
A) incomplete tetanus.
B) complete tetanus.
C) a twitch.
D) wave summation.
E) recruitment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








