Deck 12: International Financial Crises
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/90
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 12: International Financial Crises
1
Exchange rates and banking systems are often the variables through which the contagion effects of a crisis are spread from one country to another.
True
2
Small devaluations are usually sufficient to stem capital flight.
False
3
A fixed exchange rate system crisis may be accompanied or followed by
A)unexpected gains of international reserves.
B)revaluation of a currency.
C)devaluation of a currency.
D)deflationary pressures within the country.
A)unexpected gains of international reserves.
B)revaluation of a currency.
C)devaluation of a currency.
D)deflationary pressures within the country.
C
4
When expansionary fiscal and monetary policies are joined with a ________ exchange rate system,the various components of economic policy often interact in ways that lead to a crisis followed by a steep recession.
A)fixed
B)floating
C)crawling peg
D)flexible
A)fixed
B)floating
C)crawling peg
D)flexible

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Deficits financed by borrowed money lead to inflation,and in a fixed or crawling peg exchange rate system,this leads to the real exchange rate being undervalued.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A flexible exchange rate system crisis involves
A)a revaluation of the currency.
B)a rapid and uncontrolled depreciation of the currency.
C)a decrease in the dollar value of the country's international debt.
D)a sure political collapse of the ruling government.
A)a revaluation of the currency.
B)a rapid and uncontrolled depreciation of the currency.
C)a decrease in the dollar value of the country's international debt.
D)a sure political collapse of the ruling government.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Disintermediation is a problem associated with a banking crisis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The most common type of macroeconomic imbalance is overly expansionary fiscal policies that create large government budget deficits,often financed by a high growth rate of the money supply.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Exchange rate crises are only associated with fixed exchange rate systems.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
An exchange rate crisis is caused by
A)a sudden and an unexpected collapse in the value of a nation's currency.
B)the inability of the IMF to predict the immediate collapse of the currency of a country.
C)the adoption of a flexible exchange rate system by a country or group of countries.
D)the adoption of a fixed exchange rate system by a country or group of countries.
A)a sudden and an unexpected collapse in the value of a nation's currency.
B)the inability of the IMF to predict the immediate collapse of the currency of a country.
C)the adoption of a flexible exchange rate system by a country or group of countries.
D)the adoption of a fixed exchange rate system by a country or group of countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
All of the following are possible outcomes of a financial crisis except
A)bank failings and disintermediation.
B)a recession.
C)an increase in domestic consumption.
D)depreciation or devaluation of a currency.
A)bank failings and disintermediation.
B)a recession.
C)an increase in domestic consumption.
D)depreciation or devaluation of a currency.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
An exchange rate crisis may lead to a banking crisis and disintermediation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Many developing countries make the government budget one of the primary tools of long-run industrial development,with the government owning and operating industries such as steel mills,airlines,and phone companies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A flexible exchange rate system guarantees a country will not experience an exchange rate crisis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
All of the following are possible outcomes of a banking crisis except
A)depositors, but not banks, may lose all or a portion of their assets.
B)a recession due to decreases in consumption by households.
C)decreases in investment.
D)a contagion effect of the crisis from vulnerable banks to financial institutions on sound basis.
A)depositors, but not banks, may lose all or a portion of their assets.
B)a recession due to decreases in consumption by households.
C)decreases in investment.
D)a contagion effect of the crisis from vulnerable banks to financial institutions on sound basis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Current research suggests that countries that adopt a pegged exchange rate may be more vulnerable to an exchange rate crisis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which of the following does not occur in resolving a debt crisis?
A)Debts are restructured
B)Repayment periods are shortened
C)Interest rates are reduced
D)Some partial debt forgiveness
A)Debts are restructured
B)Repayment periods are shortened
C)Interest rates are reduced
D)Some partial debt forgiveness

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Tax systems in developing countries tend to be efficient and reliable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which of the following is NOT likely to occur when a bank fails?
A)Everyone that deposits money in the bank loses all or a portion of their money, unless the country has a functioning deposit insurance system.
B)The loss of savings (or the feared loss of savings)causes households to cut back on consumption, which spreads the recessionary effect wider through the country.
C)Unaffected banks may stop making loans as they take a cautious approach, slowing or stopping new investment.
D)Other banks make too many loans to make up for the loans not made by the failed bank, kicking off a cycle of stimulation and inflation.
A)Everyone that deposits money in the bank loses all or a portion of their money, unless the country has a functioning deposit insurance system.
B)The loss of savings (or the feared loss of savings)causes households to cut back on consumption, which spreads the recessionary effect wider through the country.
C)Unaffected banks may stop making loans as they take a cautious approach, slowing or stopping new investment.
D)Other banks make too many loans to make up for the loans not made by the failed bank, kicking off a cycle of stimulation and inflation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Unlike a banking crisis,an exchange rate crisis rarely results in a deep recession.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
A financial crisis brought on by macroeconomic imbalances
A)is usually inevitable given underlying conditions.
B)often happens to countries with strong international positions.
C)is often preceded by capital inflows and an increase in foreign liabilities.
D)is usually the result of fragility in the banking sector.
A)is usually inevitable given underlying conditions.
B)often happens to countries with strong international positions.
C)is often preceded by capital inflows and an increase in foreign liabilities.
D)is usually the result of fragility in the banking sector.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Which of the following was NOT a cause or a characteristic of the 1994/95 Mexican peso crisis?
A)An overvalued exchange rate
B)An inflow of large foreign portfolio capital
C)The inability of the IMF, the world bank, and the NAFTA member countries (i.e., the United States and Canada)to predict the looming financial crisis
D)Shifts by the world capital markets toward more conservative and risk-averse investments because of interest and exchange rate movements around the world
A)An overvalued exchange rate
B)An inflow of large foreign portfolio capital
C)The inability of the IMF, the world bank, and the NAFTA member countries (i.e., the United States and Canada)to predict the looming financial crisis
D)Shifts by the world capital markets toward more conservative and risk-averse investments because of interest and exchange rate movements around the world

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Financial crises due to weak financial sectors can often be avoided if international lenders respond appropriately.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
A debt crisis may lead to a banking crisis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
All of the following are symptoms of definite and identifiable macroeconomic imbalances except
A)large budget deficits.
B)an overvalued currency.
C)a current account deficit.
D)the discovery of emerging markets by financial investors who want to diversify their portfolios.
A)large budget deficits.
B)an overvalued currency.
C)a current account deficit.
D)the discovery of emerging markets by financial investors who want to diversify their portfolios.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Consider the following two statements. I. The East Asian financial crisis was an example of macroeconomic imbalances.
II) The Latin American debt crisis was an example of macroeconomic imbalances.
A)Both statements are true.
B)I is true, and II is false.
C)I is false and II is true.
D)Both statements are false.
II) The Latin American debt crisis was an example of macroeconomic imbalances.
A)Both statements are true.
B)I is true, and II is false.
C)I is false and II is true.
D)Both statements are false.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a financial crisis caused by macroeconomic imbalances?
A)Crises can be unpredictable.
B)Crises can be predictable.
C)Crises can by expansionary fiscal policies accompanied by high budget deficits.
D)Crises can be caused by budget surpluses.
A)Crises can be unpredictable.
B)Crises can be predictable.
C)Crises can by expansionary fiscal policies accompanied by high budget deficits.
D)Crises can be caused by budget surpluses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
If the banking sector borrows internationally and lends locally,how does this intensify a financial crisis?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The Mexican peso crisis of 1994 and 1995 was directly related to
A)a large capital account surplus.
B)a large capital account deficit.
C)an undervalued peso.
D)a large current account surplus.
A)a large capital account surplus.
B)a large capital account deficit.
C)an undervalued peso.
D)a large current account surplus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
It is normal and typical in a debt crisis for debtors to completely repudiate all their debts.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Although financial crises can be unpredictable,they are usually preceded by identifiable vulnerabilities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Which of the following is a true statement about crises caused by volatile capital flows?
A)Volatile capital flows rarely cause contagion effects.
B)Technological advances have increased the volatility of capital flows.
C)Exchange rates appreciate when there are capital outflows.
D)Budget deficits decrease when there are capital outflows.
A)Volatile capital flows rarely cause contagion effects.
B)Technological advances have increased the volatility of capital flows.
C)Exchange rates appreciate when there are capital outflows.
D)Budget deficits decrease when there are capital outflows.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
A large and growing current account deficit can be an indicator of a potential crisis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
It should be possible to avoid intensifying crises when there are weak financial sectors if
A)banks pay closer attention to the maturity match between their debts and assets.
B)governments do not run budget deficits.
C)current account deficits are moderate.
D)banks do not lend to unworthy creditors.
A)banks pay closer attention to the maturity match between their debts and assets.
B)governments do not run budget deficits.
C)current account deficits are moderate.
D)banks do not lend to unworthy creditors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The 2007 subprime crisis spread easily because
A)the United States is an important economy.
B)banks in other countries had purchased assets that depended on the U.S. housing market.
C)there was speculation against the U.S. dollar.
D)the Fed failed to act at the right time.
A)the United States is an important economy.
B)banks in other countries had purchased assets that depended on the U.S. housing market.
C)there was speculation against the U.S. dollar.
D)the Fed failed to act at the right time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Describe the Mexican peso crisis in terms of the imbalances that caused it,the policies Mexico used to respond,and the lessons learned.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Carefully explain two reasons why domestic crises can become international crises.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A financial crisis brought on by volatile capital flows
A)is usually inevitable given underlying conditions.
B)does not happen to countries with strong international positions.
C)is often preceded by capital inflows and an increase in foreign liabilities.
D)is usually the result of high budget deficits.
A)is usually inevitable given underlying conditions.
B)does not happen to countries with strong international positions.
C)is often preceded by capital inflows and an increase in foreign liabilities.
D)is usually the result of high budget deficits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
An austerity policy is
A)an increase in the money supply.
B)an expenditure reduction and expenditure switching policy.
C)an expansionary fiscal policy accompanied by decreases in taxes, increases in expenditures, or both.
D)an exchange rate switching policy from a fixed to a flexible exchange rate system.
A)an increase in the money supply.
B)an expenditure reduction and expenditure switching policy.
C)an expansionary fiscal policy accompanied by decreases in taxes, increases in expenditures, or both.
D)an exchange rate switching policy from a fixed to a flexible exchange rate system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Sovereign default refers to
A)default due to excessive money supply growth.
B)default on private debt instruments.
C)default on government debt instruments.
D)bankruptcy of firms, resulting in equity losses.
A)default due to excessive money supply growth.
B)default on private debt instruments.
C)default on government debt instruments.
D)bankruptcy of firms, resulting in equity losses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Which of the following may NOT help avoid a financial crisis?
A)Maintaining credible and sustainable fiscal policies
B)Regulation and supervision of the financial system
C)Immediately bailing out financial intermediaries and standing ready to bail out others in case a financial crisis occurs
D)Maintaining credible and sustainable monetary policies
A)Maintaining credible and sustainable fiscal policies
B)Regulation and supervision of the financial system
C)Immediately bailing out financial intermediaries and standing ready to bail out others in case a financial crisis occurs
D)Maintaining credible and sustainable monetary policies

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
A temporary limitation on capital flows may help stop a financial crisis that has begun.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The Basel Capital Accord does NOT include
A)requiring bank owners to invest into and have some capital ownership in the banks they own.
B)supervision of banks by an oversight board.
C)information disclosure designed to encourage market discipline.
D)denying access to foreign capital by a country that defaults on its international loans.
A)requiring bank owners to invest into and have some capital ownership in the banks they own.
B)supervision of banks by an oversight board.
C)information disclosure designed to encourage market discipline.
D)denying access to foreign capital by a country that defaults on its international loans.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
All of the following statements are true about the real exchange rate, 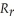 =
= 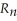
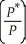 ,except
,except
A)a greater change in P (domestic price)compared to a change in P* (foreign price)necessitates a rise in the nominal rate, Rn, to keep the real rate unchanged.
B)a pegged exchange rate system requires tight control of the money supply.
C)there is a one-to-one correspondence between the real and nominal exchange rates.
D)an expansionary monetary policy raises the real exchange rate.
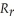 =
= 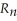
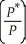 ,except
,exceptA)a greater change in P (domestic price)compared to a change in P* (foreign price)necessitates a rise in the nominal rate, Rn, to keep the real rate unchanged.
B)a pegged exchange rate system requires tight control of the money supply.
C)there is a one-to-one correspondence between the real and nominal exchange rates.
D)an expansionary monetary policy raises the real exchange rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Capital controls for banks
A)reduce the chance of bank failures.
B)have been demonstrated to be effective in preventing financial crises.
C)increase the problem of moral hazard.
D)increase the profitability of banks.
A)reduce the chance of bank failures.
B)have been demonstrated to be effective in preventing financial crises.
C)increase the problem of moral hazard.
D)increase the profitability of banks.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Which of the following is NOT a true statement about capital controls?
A)Countries are more able to prevent capital inflows than they were in the 1970s.
B)Capital controls may reduce world welfare by preventing capital from moving to its most valuable use.
C)It is unclear whether it is best to limit capital inflows, capital outflows, or both.
D)Restricting the movement of capital cannot stop a crisis once it has begun.
A)Countries are more able to prevent capital inflows than they were in the 1970s.
B)Capital controls may reduce world welfare by preventing capital from moving to its most valuable use.
C)It is unclear whether it is best to limit capital inflows, capital outflows, or both.
D)Restricting the movement of capital cannot stop a crisis once it has begun.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
If a country has a collapsing currency due to large budget deficits financed by monetary expansion,the cure is to
A)default on sovereign debt and restructure the economy.
B)peg the currency to something different.
C)cut the deficit and raise interest rates.
D)increase the rate of inflation to reduce the real value of government debt.
A)default on sovereign debt and restructure the economy.
B)peg the currency to something different.
C)cut the deficit and raise interest rates.
D)increase the rate of inflation to reduce the real value of government debt.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
A crisis caused by sudden capital flight
A)is easy to resolve with capital controls.
B)might be lessened if investor confidence can be increased.
C)has a clear and unique equilibrium outcome.
D)can be corrected through currency devaluation.
A)is easy to resolve with capital controls.
B)might be lessened if investor confidence can be increased.
C)has a clear and unique equilibrium outcome.
D)can be corrected through currency devaluation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Crawling pegs
A)are anti-inflationary because they require monetary discipline.
B)are designed to stabilize real exchange rates when domestic inflation is less than inflation in other nations.
C)reduce a nation's vulnerability to financial crises.
D)lead to undervaluation of the domestic currency.
A)are anti-inflationary because they require monetary discipline.
B)are designed to stabilize real exchange rates when domestic inflation is less than inflation in other nations.
C)reduce a nation's vulnerability to financial crises.
D)lead to undervaluation of the domestic currency.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
In theory,the free movement of capital raises world welfare because
A)it reduces inflation in some countries.
B)it reduces the chance of financial crises.
C)it allows countries to invest more than they could with domestic savings alone.
D)it increases world income equality.
A)it reduces inflation in some countries.
B)it reduces the chance of financial crises.
C)it allows countries to invest more than they could with domestic savings alone.
D)it increases world income equality.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Economists agree that the free movement of capital is desirable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Explain how the global financial crisis of 2007-2009 was the result of macroeconomic imbalances.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
It is relatively easy to prescribe a cure for financial crises that result from inconsistent macroeconomic policies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The main policy advice given by the IMF to East Asian countries facing the financial crises of 1997/1998 was
A)raising their domestic interest rates to stabilize the collapsing currencies.
B)using their monetary and fiscal policies alone.
C)use capital controls.
D)adopting a flexible exchange rate system.
A)raising their domestic interest rates to stabilize the collapsing currencies.
B)using their monetary and fiscal policies alone.
C)use capital controls.
D)adopting a flexible exchange rate system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Which one of the following countries refused to accept the IMF conditions during the East Asian financial crisis?
A)South Korea
B)Malaysia
C)Thailand
D)Singapore
A)South Korea
B)Malaysia
C)Thailand
D)Singapore

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Austerity programs involving budget cuts and higher interest rates may not be politically feasible.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
With crises caused by macroeconomic imbalances,
A)it is usually difficult to avoid a recession.
B)austerity programs are not needed.
C)expansionary policies can be used to correct the crisis.
D)the money supply should be increased.
A)it is usually difficult to avoid a recession.
B)austerity programs are not needed.
C)expansionary policies can be used to correct the crisis.
D)the money supply should be increased.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Which of the following was NOT one of the causes of the Asian financial crises of 1997 and 1998?
A)A current account deficit and financial account surpluses
B)The use of exports as an engine of economic growth by the countries involved
C)China's 1994 devaluation of its fixed exchange rate
D)The appreciation of the U.S. dollar and depreciation of the Japanese yen
A)A current account deficit and financial account surpluses
B)The use of exports as an engine of economic growth by the countries involved
C)China's 1994 devaluation of its fixed exchange rate
D)The appreciation of the U.S. dollar and depreciation of the Japanese yen

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
All of the following involve a moral hazard problem except
A)an individual driving carelessly after buying a comprehensive insurance policy for a Ford Pinto.
B)the IMF bailing Mexico out of a financial crisis, with promises to do the same for other nations that might face financial problems.
C)the requirement of banking institutions that owners invest a substantial portion of their own capital in their bank.
D)membership in FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation)by your local bank.
A)an individual driving carelessly after buying a comprehensive insurance policy for a Ford Pinto.
B)the IMF bailing Mexico out of a financial crisis, with promises to do the same for other nations that might face financial problems.
C)the requirement of banking institutions that owners invest a substantial portion of their own capital in their bank.
D)membership in FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation)by your local bank.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
How does a weak financial sector intensify the problems created by volatile capital flows?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
What are the costs of capital mobility?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
IMF conditionality may include
A)changes in the fiscal and monetary policies of the country facing the financial crisis.
B)changes in the exchange rate policies.
C)regulating and restructuring the financial sector of the economy of the country in crisis.
D)political regime change.
A)changes in the fiscal and monetary policies of the country facing the financial crisis.
B)changes in the exchange rate policies.
C)regulating and restructuring the financial sector of the economy of the country in crisis.
D)political regime change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Financial capital is highly volatile,and technological advances have reinforced this volatility.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
International financial flows have changed in meaningful ways,and these changes were brought to the attention of policy makers by the Asian financial crisis.Describe three changes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
What agreement has been reached to reduce the moral hazard problem and what does it require?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
An issue that proposals for international reform agree on is that
A)the IMF should intervene more in financial crises.
B)there must be a lender of last resort.
C)IMF quotas are currently set at an appropriate level.
D)the Basel capital requirements for banks should be increased.
A)the IMF should intervene more in financial crises.
B)there must be a lender of last resort.
C)IMF quotas are currently set at an appropriate level.
D)the Basel capital requirements for banks should be increased.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Implementing short-term capital controls during the Asian crisis caused Malaysia to recover more slowly than other countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
The international institution that serves as a lender of last resort is called the
A)IBRD.
B)WTO.
C)IMF.
D)World Bank.
A)IBRD.
B)WTO.
C)IMF.
D)World Bank.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
With regard to the IMF,"mission creep" means that
A)the IMF was making loans to nonmember countries.
B)the IMF had expanded its lending to an inappropriate level.
C)the IMF had taken on extended responsibilities that it should be authorized to perform.
D)the IMF had taken on responsibilities for which it was not suited.
A)the IMF was making loans to nonmember countries.
B)the IMF had expanded its lending to an inappropriate level.
C)the IMF had taken on extended responsibilities that it should be authorized to perform.
D)the IMF had taken on responsibilities for which it was not suited.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Explain the pros and cons of a crawling peg.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Which of the following is NOT a true statement about IMF lending?
A)The IMF can usually determine the difference between national crises and those likely to cause system-wide problems.
B)Limits on borrowing have not kept up with the growth of national economies.
C)The IMF does not have the funds to provide the support that a large economy might need.
D)Proposals for lending expansion suggest greater IMF intervention if it can stop crises faster.
A)The IMF can usually determine the difference between national crises and those likely to cause system-wide problems.
B)Limits on borrowing have not kept up with the growth of national economies.
C)The IMF does not have the funds to provide the support that a large economy might need.
D)Proposals for lending expansion suggest greater IMF intervention if it can stop crises faster.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
If governments promise to bail out the financial system in the event of a crisis,this creates a moral hazard problem.Describe this problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
IMF quotas
A)depend on the size of an economy and its strength.
B)strictly limit the amount that a country can borrow.
C)should be increased.
D)are equal to the amount that a country can borrow from the IMF.
A)depend on the size of an economy and its strength.
B)strictly limit the amount that a country can borrow.
C)should be increased.
D)are equal to the amount that a country can borrow from the IMF.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
What are the benefits of capital mobility?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
All of the following issues have been discussed as options for reforming the international financial architecture except
A)how high an interest rate the lender of last resort should charge when it makes loans.
B)the length of the payback period.
C)the size of the loans.
D)if the lender of last resort (i.e., the IMF)should consult and collaborate with other international institutions such as the United Nations and the WTO.
A)how high an interest rate the lender of last resort should charge when it makes loans.
B)the length of the payback period.
C)the size of the loans.
D)if the lender of last resort (i.e., the IMF)should consult and collaborate with other international institutions such as the United Nations and the WTO.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Describe the background factors that contributed to the Asian financial crisis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Which of the following is a macroeconomic factor that contributed to the financial crisis in 2007?
A)Global saving and investment imbalances
B)Financial market innovation
C)Deeper levels of integration across financial markets
D)Challenges and failures in financial regulation
A)Global saving and investment imbalances
B)Financial market innovation
C)Deeper levels of integration across financial markets
D)Challenges and failures in financial regulation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
How did the vulnerabilities in Asian economies lead to the Asian financial crisis of 1997-1998.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
A lender of last resort
A)makes loans when no one else will.
B)makes loans without regard for risk.
C)is a firm that is forced to make loans for its own survival.
D)makes loans to all who require them.
A)makes loans when no one else will.
B)makes loans without regard for risk.
C)is a firm that is forced to make loans for its own survival.
D)makes loans to all who require them.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
When a country borrows from the IMF
A)it receives all the funds from the loan at once.
B)it receives funds in tranches, each dependent on the completion of reform targets.
C)it is free of conditions.
D)it can be any amount that the country requests.
A)it receives all the funds from the loan at once.
B)it receives funds in tranches, each dependent on the completion of reform targets.
C)it is free of conditions.
D)it can be any amount that the country requests.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








