Deck 10: Introduction to Simple Experiments
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 10: Introduction to Simple Experiments
1
A threat to internal validity occurs only if a potential design confound varies with the independent variable.
A)haphazardly
B)systematically
C)spontaneously
D)especially
A)haphazardly
B)systematically
C)spontaneously
D)especially
systematically
2
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
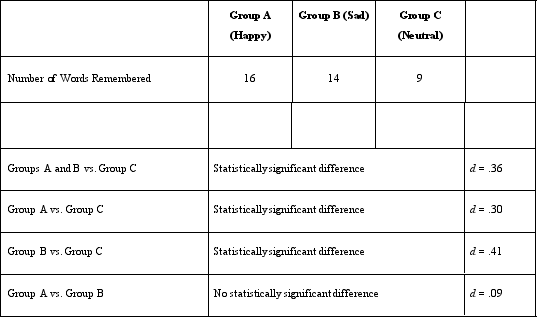
Dr) Lonsbary's study asked participants to report on their mood before completing the memory test. Her decision to include this step was done to address the study's validity.
A)external
B)statistical
C)internal
D)construct
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

Dr) Lonsbary's study asked participants to report on their mood before completing the memory test. Her decision to include this step was done to address the study's validity.
A)external
B)statistical
C)internal
D)construct
construct
3
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
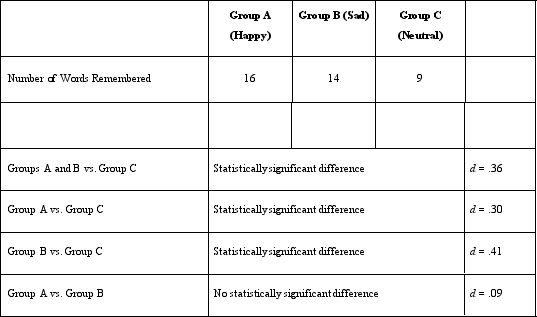
Which of the following provides information about the statistical validity of Dr. Lonsbary's study?
A)The method of random assignment
B)The d coefficient
C)The number of people in each group
D)The mood reported by the participants
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

Which of the following provides information about the statistical validity of Dr. Lonsbary's study?
A)The method of random assignment
B)The d coefficient
C)The number of people in each group
D)The mood reported by the participants
The d coefficient
4
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
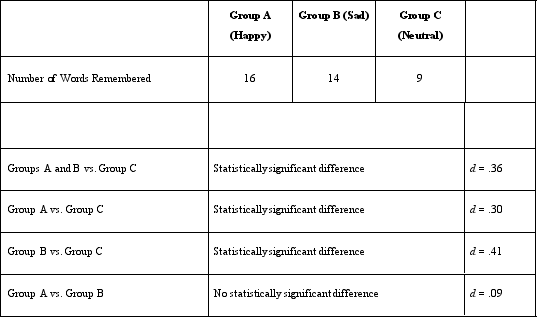
Which of the following is an independent variable in Dr. Lonsbary's study?
A)Number of groups participants were assigned to
B)Feeling happy
C)Participant's mood
D)Number rolled on the die
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

Which of the following is an independent variable in Dr. Lonsbary's study?
A)Number of groups participants were assigned to
B)Feeling happy
C)Participant's mood
D)Number rolled on the die

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
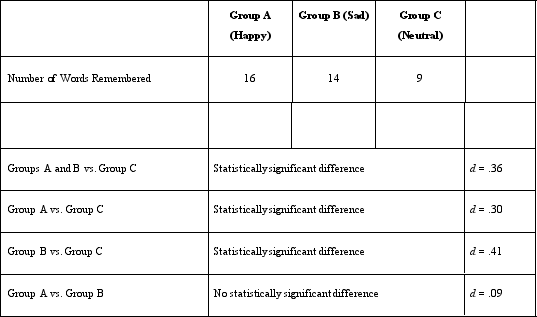
Which of the following is NOT a control variable in Dr. Lonsbary's study?
A)The number of words on the word list
B)The amount of time allowed for remembering/typing the words
C)The amount of time allowed for memorizing the words
D)The mood of the participants
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

Which of the following is NOT a control variable in Dr. Lonsbary's study?
A)The number of words on the word list
B)The amount of time allowed for remembering/typing the words
C)The amount of time allowed for memorizing the words
D)The mood of the participants

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
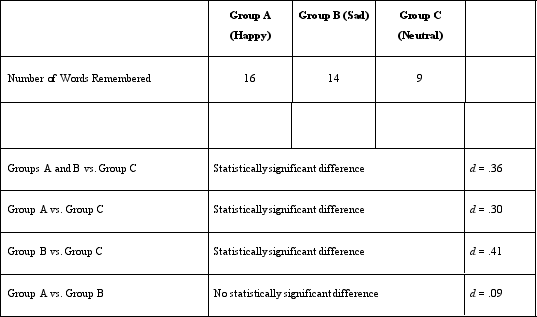
Which of the following allows Dr. Lonsbary to conclude that she met the covariance rule for causality?
A)Noting that there is a difference between the number of words recalled by the happy and neutral people
B)Having people listen to music or silence before they wrote down the list of words they remembered
C)Making sure that all participants were asked to remember the same list of words
D)Putting the 60 participants into equal groups
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

Which of the following allows Dr. Lonsbary to conclude that she met the covariance rule for causality?
A)Noting that there is a difference between the number of words recalled by the happy and neutral people
B)Having people listen to music or silence before they wrote down the list of words they remembered
C)Making sure that all participants were asked to remember the same list of words
D)Putting the 60 participants into equal groups

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
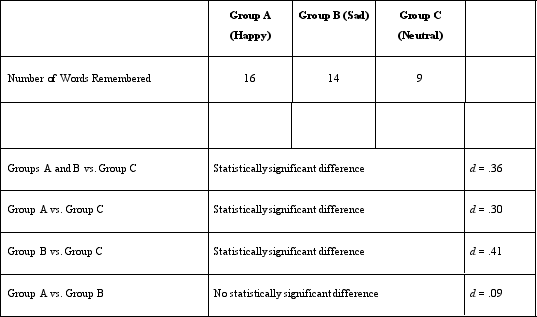
What type of design did Dr. Lonsbary use in her study?
A)Matched-group design
B)Within-groups design
C)Independent-groups design
D)Pretest/posttest design
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

What type of design did Dr. Lonsbary use in her study?
A)Matched-group design
B)Within-groups design
C)Independent-groups design
D)Pretest/posttest design

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
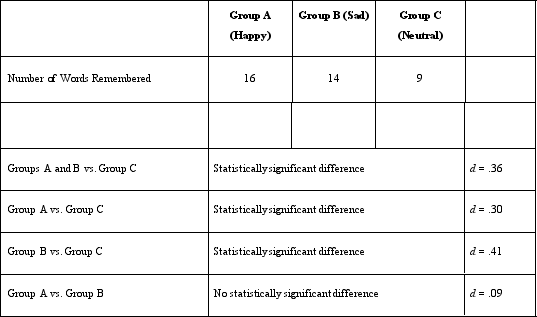
Which of the following allows Dr. Lonsbary to conclude that she met the temporal precedence rule for causality?
A)Noting that there is a difference between the number of words recalled by the happy and neutral people
B)Having people listen to music or silence before they wrote down the list of words they remembered
C)Making sure that all participants were asked to remember the same list of words
D)Putting the 60 participants into equal groups
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

Which of the following allows Dr. Lonsbary to conclude that she met the temporal precedence rule for causality?
A)Noting that there is a difference between the number of words recalled by the happy and neutral people
B)Having people listen to music or silence before they wrote down the list of words they remembered
C)Making sure that all participants were asked to remember the same list of words
D)Putting the 60 participants into equal groups

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
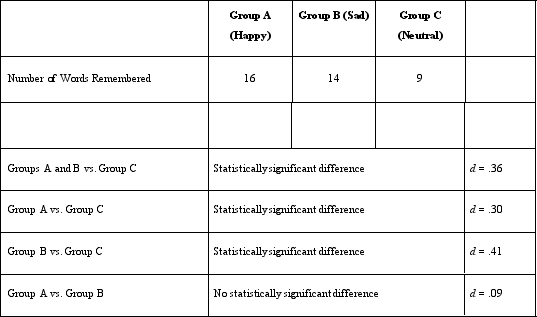
Which of the following should Dr. Lonsbary NOT conclude from her study?
A)Being in a mood other than neutral causes people to have a better memory.
B)Listening to music can cause changes in mood.
C)Being in a happy mood does not cause more of a change in memory than being in a sad mood.
D)Being in an angry mood likely has the same effect on memory as being in a sad mood.
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

Which of the following should Dr. Lonsbary NOT conclude from her study?
A)Being in a mood other than neutral causes people to have a better memory.
B)Listening to music can cause changes in mood.
C)Being in a happy mood does not cause more of a change in memory than being in a sad mood.
D)Being in an angry mood likely has the same effect on memory as being in a sad mood.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which of the following is NOT true of control variables?
A)Control variables help define the control group.
B)Control variables help establish internal validity.
C)Control variables are essential in experimental designs.
D)Control variables are kept the same for all participants.
A)Control variables help define the control group.
B)Control variables help establish internal validity.
C)Control variables are essential in experimental designs.
D)Control variables are kept the same for all participants.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
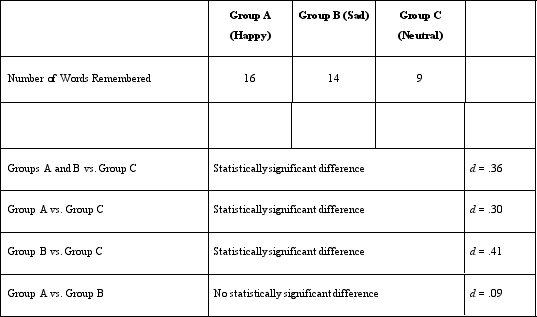
In Dr. Lonsbary's study, which of the following is NOT present?
A)A control variable
B)A treatment group
C)A placebo group
D)A manipulation check
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

In Dr. Lonsbary's study, which of the following is NOT present?
A)A control variable
B)A treatment group
C)A placebo group
D)A manipulation check

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
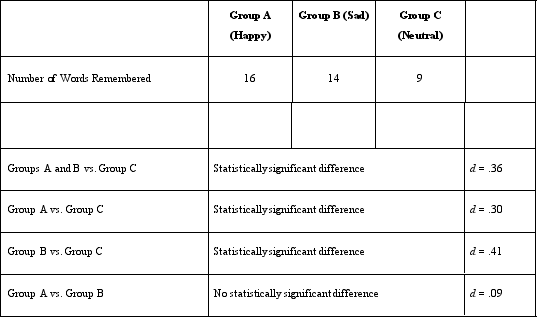
Dr) Lonsbary's colleague, Dr. Chavis, recommended randomly assigning the participants to the three groups. His recommendation was designed to avoid which of the following?
A)An order effect
B)A selection effect
C)A practice effect
D)A carryover effect
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

Dr) Lonsbary's colleague, Dr. Chavis, recommended randomly assigning the participants to the three groups. His recommendation was designed to avoid which of the following?
A)An order effect
B)A selection effect
C)A practice effect
D)A carryover effect

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
When conducting an experiment, what is provided by the independent variable?
A)A comparison group
B)Random assignment
C)Proof of temporal precedence
D)Confirmation of internal validity
A)A comparison group
B)Random assignment
C)Proof of temporal precedence
D)Confirmation of internal validity

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
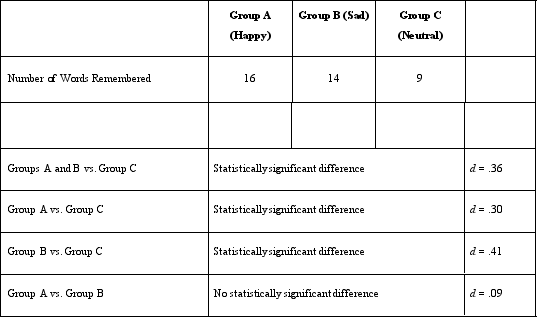
How many conditions/levels of the independent variable were in Dr. Lonsbary's study?
A)Two
B)Three
C)Five
D)Nine
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

How many conditions/levels of the independent variable were in Dr. Lonsbary's study?
A)Two
B)Three
C)Five
D)Nine

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
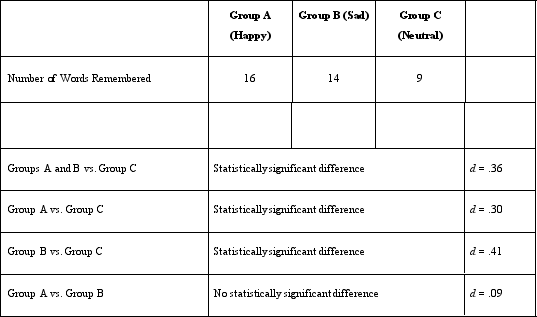
Dr) Lonsbary's study contains which of the following techniques designed to address a threat to construct validity?
A)Counterbalancing
B)A placebo group
C)A demand characteristic
D)A manipulation check
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

Dr) Lonsbary's study contains which of the following techniques designed to address a threat to construct validity?
A)Counterbalancing
B)A placebo group
C)A demand characteristic
D)A manipulation check

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
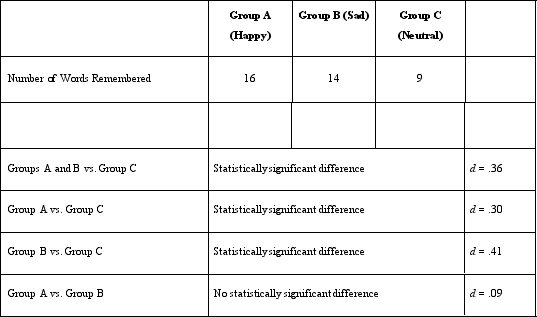
Dr) Lonsbary is considering doing a follow-up study in which instead of asking participants to listen to music to induce mood, she has them write either a story about a character who just won the lottery or a story about a character who just experienced the death of their spouse. This change in the mood variable is designed to enhance the study's validity.
A)external
B)statistical
C)internal
D)construct
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

Dr) Lonsbary is considering doing a follow-up study in which instead of asking participants to listen to music to induce mood, she has them write either a story about a character who just won the lottery or a story about a character who just experienced the death of their spouse. This change in the mood variable is designed to enhance the study's validity.
A)external
B)statistical
C)internal
D)construct

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Dr. Kline, an environmental psychologist, conducts a study to examine whether visiting zoos causes people to have more positive attitudes toward environmental conservation. He asks a group of 45 people attending the zoo on a Saturday morning about their attitudes. He finds that 69% of the people report having a positive attitude after their visit. Which of the following is true?
A)His control group is people who did not visit the zoo.
B)He does not have a dependent variable.
C)He can make a strong causal claim about the effect of zoo visits on environmental attitudes.
D)His study does not qualify as an experiment.
A)His control group is people who did not visit the zoo.
B)He does not have a dependent variable.
C)He can make a strong causal claim about the effect of zoo visits on environmental attitudes.
D)His study does not qualify as an experiment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
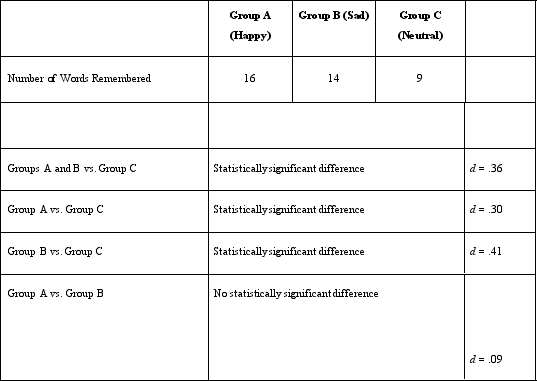
Which of the following is a dependent variable in Dr. Lonsbary's study?
A)Number of words on the list
B)Time given to type the words remembered
C)Time given to memorize the words
D)Number of words remembered
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

Which of the following is a dependent variable in Dr. Lonsbary's study?
A)Number of words on the list
B)Time given to type the words remembered
C)Time given to memorize the words
D)Number of words remembered

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
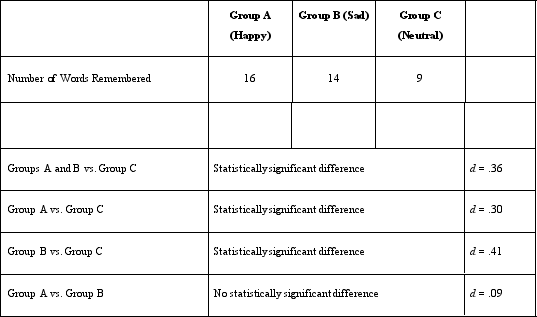
Prior to conducting the current study, Dr. Lonsbary asked her research assistant to use the same mood manipulation with a sample of 30 college students to determine if people's moods really did change after listening to the music. Running this preliminary study helps establish validity.
A)external
B)statistical
C)internal
D)construct
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

Prior to conducting the current study, Dr. Lonsbary asked her research assistant to use the same mood manipulation with a sample of 30 college students to determine if people's moods really did change after listening to the music. Running this preliminary study helps establish validity.
A)external
B)statistical
C)internal
D)construct

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
RESEARCH STUDY 10.1: Dr. Lonsbary is a cognitive psychologist who is curious about how mood affects memory. She recruited 60 high school students and divided them into three groups. Group A listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel happy ("Happy" by Pharrell). Group B listened to a 5-minute piece of music intended to make them feel sad (a song titled "Home Is Such a Lonely Place" by Blink-182). Group C listened to no music and instead was asked to sit quietly for 5 minutes (thought to make them feel neutral).
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.
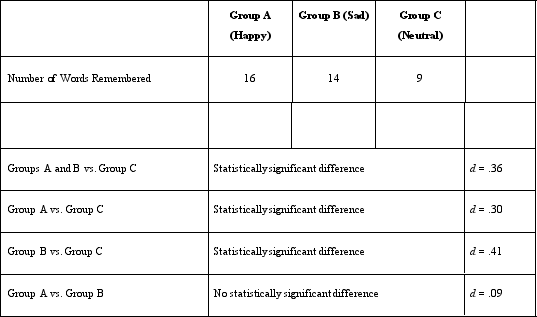
Prior to conducting the current study, Dr. Lonsbary asked her research assistant to use the same mood manipulation with a sample of 30 college students to determine if people's moods really did change after listening to the music. This preliminary study is known as a study.
A)pretest/posttest
B)concurrent measure
C)pilot
D)pretest-only
When a participant would come to her laboratory, Dr. Lonsbary would greet the participant and then ask him or her to roll a six-sided die. Participants who rolled a 1 or 2 were assigned to Group A. Participants who rolled a 3 or 4 were assigned to Group B. Participants who rolled a 5 or 6 were assigned to Group C. The participants were then given an unlabeled CD to listen to based on their group assignment. The CD contained either the song selection or 5 minutes of silence. They were then escorted into a different room, where they were greeted by a research assistant who conducted the experiment. The research assistant sat the participants in front of a computer screen and told them that a list of 25 words would be displayed on the screen. They were instructed to listen to the CD with headphones while trying to memorize the list of words. All participants were given the same list of 25 common words to remember (e.g., desk, gray, plane, car, mask).
When 5 minutes had passed, the screen displayed a question asking them whether they felt happy, sad, or neutral. After the participant responded, a new screen was displayed asking them to type in all the words they could remember from the list of 25 words. All participants were given 3 minutes to type the words they remembered. Afterward, the participant was thanked and dismissed. In response to the mood question, a majority of Group A participants said they were happy, a majority of Group B participants said they were sad, and a majority of Group C participants said they were neutral in their mood. Dr. Lonsbary found the following results in response to the number of words remembered.

Prior to conducting the current study, Dr. Lonsbary asked her research assistant to use the same mood manipulation with a sample of 30 college students to determine if people's moods really did change after listening to the music. This preliminary study is known as a study.
A)pretest/posttest
B)concurrent measure
C)pilot
D)pretest-only

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
RESEARCH STUDY 10.2: Dr. Dormeur studies sleep and sleep disorders. She is curious as to whether technology exposure before bedtime causes people to fall asleep more slowly. She recruits a sample of 60 middle-aged women from a local church who reported no history of sleep problems. She creates three conditions. All participants come to the sleep lab for three nights in a row and experience all three conditions. In the first condition (A), participants were asked to play an online game (Candy Crush) on an iPad for 10 minutes prior to going to bed. In the second condition (B), participants were asked to read an article using an iPad that discussed tricks and tips for improving one's score on Candy Crush (which took about 10 minutes). In the third condition (C), participants were asked to read a newspaper article about the inventor of Candy Crush (which took about 10 minutes). With the use of an electroencephalograph (EEG), the researcher measures how long it takes participants to fall asleep.
Dr) Dormeur was concerned that asking participants how long it took them to fall asleep would lead them to suspect that was the purpose of the study. Her decision to measure how long it took participants to go to sleep using the EEG instead of self-report was meant to decrease which of the following?
A)Order effects
B)Selection effects
C)Demand characteristics
D)Counterbalancing effects
Dr) Dormeur was concerned that asking participants how long it took them to fall asleep would lead them to suspect that was the purpose of the study. Her decision to measure how long it took participants to go to sleep using the EEG instead of self-report was meant to decrease which of the following?
A)Order effects
B)Selection effects
C)Demand characteristics
D)Counterbalancing effects

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Which of the following is NOT true of selection effects?
A)Selection effects are a type of confound.
B)Selection effects can occur when experimenters allow participants to choose their own treatment group.
C)Selection effects are unimportant for interrogating internal validity.
D)Selection effects can occur when researchers assign one type of person to one treatment group and another type of person to another treatment group.
A)Selection effects are a type of confound.
B)Selection effects can occur when experimenters allow participants to choose their own treatment group.
C)Selection effects are unimportant for interrogating internal validity.
D)Selection effects can occur when researchers assign one type of person to one treatment group and another type of person to another treatment group.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Experiments use random assignment to avoid which of the following?
A)Random selection
B)Selection effects
C)Carryover effects
D)Demand characteristics
A)Random selection
B)Selection effects
C)Carryover effects
D)Demand characteristics

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
is used to control order effects in an experiment.
A)Random assignment
B)A design confound
C)Increasing demand characteristics
D)Counterbalancing
A)Random assignment
B)A design confound
C)Increasing demand characteristics
D)Counterbalancing

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which of the following is NOT a reason that a researcher might choose a pretest/posttest design?
A)To ensure that random assignment made the treatment/comparison groups equal
B)To determine how groups change over the course of the experiment
C)To allow for the study of spontaneous behaviors
D)To make a strong causal claim
A)To ensure that random assignment made the treatment/comparison groups equal
B)To determine how groups change over the course of the experiment
C)To allow for the study of spontaneous behaviors
D)To make a strong causal claim

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
All of the following are advantages of within-groups designs EXCEPT:
A)Participants in the treatment/control groups will be equivalent.
B)It is less time-consuming for the participants.
C)It gives researchers more power to find differences between conditions.
D)They require fewer participants.
A)Participants in the treatment/control groups will be equivalent.
B)It is less time-consuming for the participants.
C)It gives researchers more power to find differences between conditions.
D)They require fewer participants.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Which of the following research designs is used to address possible selection effects?
A)Posttest-only designs
B)Matched-groups designs
C)Pretest/posttest designs
D)Correlational designs
A)Posttest-only designs
B)Matched-groups designs
C)Pretest/posttest designs
D)Correlational designs

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
RESEARCH STUDY 10.2: Dr. Dormeur studies sleep and sleep disorders. She is curious as to whether technology exposure before bedtime causes people to fall asleep more slowly. She recruits a sample of 60 middle-aged women from a local church who reported no history of sleep problems. She creates three conditions. All participants come to the sleep lab for three nights in a row and experience all three conditions. In the first condition (A), participants were asked to play an online game (Candy Crush) on an iPad for 10 minutes prior to going to bed. In the second condition (B), participants were asked to read an article using an iPad that discussed tricks and tips for improving one's score on Candy Crush (which took about 10 minutes). In the third condition (C), participants were asked to read a newspaper article about the inventor of Candy Crush (which took about 10 minutes). With the use of an electroencephalograph (EEG), the researcher measures how long it takes participants to fall asleep.
Which of the following designs is Dr. Dormeur using?
A)Pretest/posttest design
B)Concurrent-measures design
C)Repeated-measures design
D)Posttest-only design
Which of the following designs is Dr. Dormeur using?
A)Pretest/posttest design
B)Concurrent-measures design
C)Repeated-measures design
D)Posttest-only design

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Using a matched-group design is especially important in which of the following cases?
A)When you have only a few people in your study
B)When you have at least three levels/conditions of the independent variable
C)When you do not have a control group
D)When you have a complex dependent variable
A)When you have only a few people in your study
B)When you have at least three levels/conditions of the independent variable
C)When you do not have a control group
D)When you have a complex dependent variable

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Generally, what is the main priority for experimental studies?
A)Construct validity
B)External validity
C)Internal validity
D)Statistical validity
A)Construct validity
B)External validity
C)Internal validity
D)Statistical validity

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The ability for a study to reveal a statistically significant difference between the levels of an independent variable when one truly exists is known as:
A)covariance.
B)power.
C)effect size.
D)statistical validity.
A)covariance.
B)power.
C)effect size.
D)statistical validity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Which of the following is an advantage of within-groups designs?
A)These designs avoid order effects.
B)These designs avoid demand characteristics.
C)These designs are always possible.
D)These designs rely on fewer participants.
A)These designs avoid order effects.
B)These designs avoid demand characteristics.
C)These designs are always possible.
D)These designs rely on fewer participants.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
What is the primary difference between pretest/posttest designs and within-groups designs?
A)The number of participants used
B)The number of times the dependent variable is measured
C)The number of levels of the independent variable participants are exposed to
D)There is no difference between the two designs.
A)The number of participants used
B)The number of times the dependent variable is measured
C)The number of levels of the independent variable participants are exposed to
D)There is no difference between the two designs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
RESEARCH STUDY 10.2: Dr. Dormeur studies sleep and sleep disorders. She is curious as to whether technology exposure before bedtime causes people to fall asleep more slowly. She recruits a sample of 60 middle-aged women from a local church who reported no history of sleep problems. She creates three conditions. All participants come to the sleep lab for three nights in a row and experience all three conditions. In the first condition (A), participants were asked to play an online game (Candy Crush) on an iPad for 10 minutes prior to going to bed. In the second condition (B), participants were asked to read an article using an iPad that discussed tricks and tips for improving one's score on Candy Crush (which took about 10 minutes). In the third condition (C), participants were asked to read a newspaper article about the inventor of Candy Crush (which took about 10 minutes). With the use of an electroencephalograph (EEG), the researcher measures how long it takes participants to fall asleep.
Dr) Dormeur's participants have only agreed to participate in the study for three nights each. Which type of counterbalancing can she use?
A)Partial counterbalancing
B)Full counterbalancing
C)Minimal counterbalancing
D)Carryover counterbalancing
Dr) Dormeur's participants have only agreed to participate in the study for three nights each. Which type of counterbalancing can she use?
A)Partial counterbalancing
B)Full counterbalancing
C)Minimal counterbalancing
D)Carryover counterbalancing

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Practice effects and carryover effects are examples of effects.
A)order
B)scientific
C)between-person
D)causal
A)order
B)scientific
C)between-person
D)causal

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Dr. Alfonse, a developmental psychologist, conducts a study to determine whether children prefer books with drawn illustrations or with photographs. A group of 30 preschoolers are shown two copies of a book (Ferdinand the Bull) at the same time. Although the story is the same, one book is illustrated with drawings and the other is illustrated with photos. Students are then asked to indicate which book they prefer. This is an example of which of the following designs?
A)Longitudinal design
B)Repeated-measures design
C)Concurrent-measures design
D)Posttest-only design
A)Longitudinal design
B)Repeated-measures design
C)Concurrent-measures design
D)Posttest-only design

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
RESEARCH STUDY 10.2: Dr. Dormeur studies sleep and sleep disorders. She is curious as to whether technology exposure before bedtime causes people to fall asleep more slowly. She recruits a sample of 60 middle-aged women from a local church who reported no history of sleep problems. She creates three conditions. All participants come to the sleep lab for three nights in a row and experience all three conditions. In the first condition (A), participants were asked to play an online game (Candy Crush) on an iPad for 10 minutes prior to going to bed. In the second condition (B), participants were asked to read an article using an iPad that discussed tricks and tips for improving one's score on Candy Crush (which took about 10 minutes). In the third condition (C), participants were asked to read a newspaper article about the inventor of Candy Crush (which took about 10 minutes). With the use of an electroencephalograph (EEG), the researcher measures how long it takes participants to fall asleep.
Given that there are three conditions/levels of the independent variable, how many orders of the conditions are possible in Dr. Dormeur's study?
A)Three
B)Six
C)Nine
D)Twelve
Given that there are three conditions/levels of the independent variable, how many orders of the conditions are possible in Dr. Dormeur's study?
A)Three
B)Six
C)Nine
D)Twelve

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Random selection enhances validity and random assignment enhances validity.
A)internal; internal
B)external; external
C)internal; external
D)external; internal
A)internal; internal
B)external; external
C)internal; external
D)external; internal

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
An independent-groups design is also known as a design.
A)between-subjects
B)matched-groups
C)within-groups
D)mixed
A)between-subjects
B)matched-groups
C)within-groups
D)mixed

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Which of the following is a threat to internal validity found in within-groups designs but not in independent-groups designs?
A)Selection effects
B)Design confounds
C)Demand characteristics
D)Practice effects
A)Selection effects
B)Design confounds
C)Demand characteristics
D)Practice effects

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
In true experiments, is to dependent variable as is to independent variable.
A)measuring; manipulating
B)controlling; manipulating
C)recording; measuring
D)manipulating; measuring
A)measuring; manipulating
B)controlling; manipulating
C)recording; measuring
D)manipulating; measuring

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
In the study depicted in the figure above, why might researchers have measured blood pressure twice? 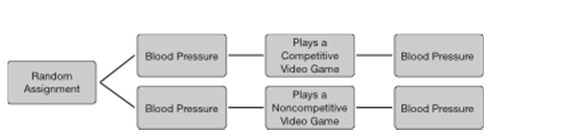
A) To make sure the first measurement could be trusted
B) To decrease testing effects
C) To make sure the two groups were equal before the manipulation
D) To establish temporal precedence

A) To make sure the first measurement could be trusted
B) To decrease testing effects
C) To make sure the two groups were equal before the manipulation
D) To establish temporal precedence

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
RESEARCH STUDY 10.3: Dr. Phillips is a cognitive-developmental psychologist who studies how children learn mathematical principles. His current interest is in studying how children learn multiplication. He recruits 54 second-graders who have not yet learned how to multiply numbers to participate in his study. He is curious as to whether different teaching styles lead to better mastery of the subject. One condition (A) involves having students read a chapter on multiplication from their textbook. One condition (B) involves having students watch a video of cartoon characters explaining multiplication. One condition (C) involves having students being taught multiplication by a teacher. One condition (D) involves having students being taught multiplication by a fourth-grader. In all conditions, participants spend 30 minutes learning the fundamentals of multiplication and are then given the same 15-question multiplication test. The number of questions answered correctly is recorded. The data are below.
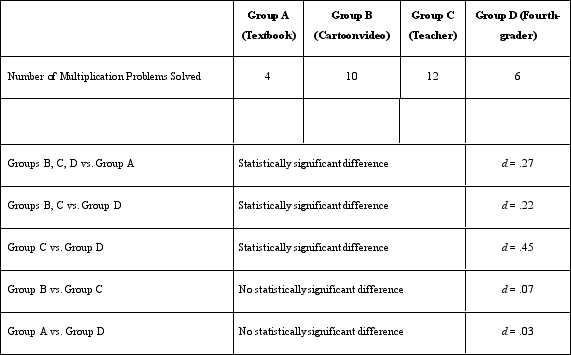
Write a question you would ask of Dr. Phillips' study to interrogate each of the four validities.

Write a question you would ask of Dr. Phillips' study to interrogate each of the four validities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Considering a measure's face validity is:
A)a good way to interrogate the construct validity of the dependent variable.
B)not necessary in experiments.
C)only done if an experiment uses observational measures.
D)the first step in establishing causation.
A)a good way to interrogate the construct validity of the dependent variable.
B)not necessary in experiments.
C)only done if an experiment uses observational measures.
D)the first step in establishing causation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
RESEARCH STUDY 10.3: Dr. Phillips is a cognitive-developmental psychologist who studies how children learn mathematical principles. His current interest is in studying how children learn multiplication. He recruits 54 second-graders who have not yet learned how to multiply numbers to participate in his study. He is curious as to whether different teaching styles lead to better mastery of the subject. One condition (A) involves having students read a chapter on multiplication from their textbook. One condition (B) involves having students watch a video of cartoon characters explaining multiplication. One condition (C) involves having students being taught multiplication by a teacher. One condition (D) involves having students being taught multiplication by a fourth-grader. In all conditions, participants spend 30 minutes learning the fundamentals of multiplication and are then given the same 15-question multiplication test. The number of questions answered correctly is recorded. The data are below.
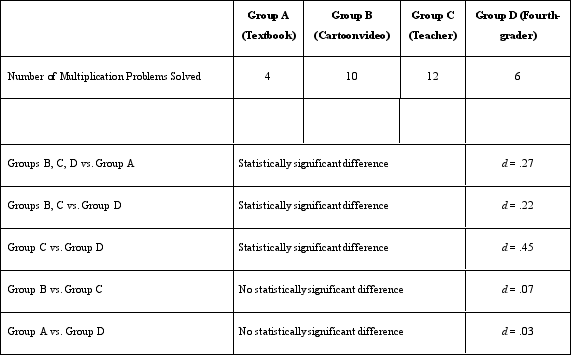
Name two ways that Dr. Phillips could avoid selection threat when he is assigning participants to conditions and explain why each of these methods avoids selection threat.

Name two ways that Dr. Phillips could avoid selection threat when he is assigning participants to conditions and explain why each of these methods avoids selection threat.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
RESEARCH STUDY 10.3: Dr. Phillips is a cognitive-developmental psychologist who studies how children learn mathematical principles. His current interest is in studying how children learn multiplication. He recruits 54 second-graders who have not yet learned how to multiply numbers to participate in his study. He is curious as to whether different teaching styles lead to better mastery of the subject. One condition (A) involves having students read a chapter on multiplication from their textbook. One condition (B) involves having students watch a video of cartoon characters explaining multiplication. One condition (C) involves having students being taught multiplication by a teacher. One condition (D) involves having students being taught multiplication by a fourth-grader. In all conditions, participants spend 30 minutes learning the fundamentals of multiplication and are then given the same 15-question multiplication test. The number of questions answered correctly is recorded. The data are below.
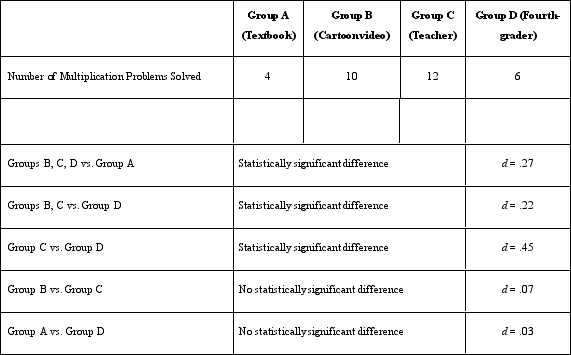
Explain why Dr. Phillips cannot conduct a within-groups design.

Explain why Dr. Phillips cannot conduct a within-groups design.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
RESEARCH STUDY 10.3: Dr. Phillips is a cognitive-developmental psychologist who studies how children learn mathematical principles. His current interest is in studying how children learn multiplication. He recruits 54 second-graders who have not yet learned how to multiply numbers to participate in his study. He is curious as to whether different teaching styles lead to better mastery of the subject. One condition (A) involves having students read a chapter on multiplication from their textbook. One condition (B) involves having students watch a video of cartoon characters explaining multiplication. One condition (C) involves having students being taught multiplication by a teacher. One condition (D) involves having students being taught multiplication by a fourth-grader. In all conditions, participants spend 30 minutes learning the fundamentals of multiplication and are then given the same 15-question multiplication test. The number of questions answered correctly is recorded. The data are below.
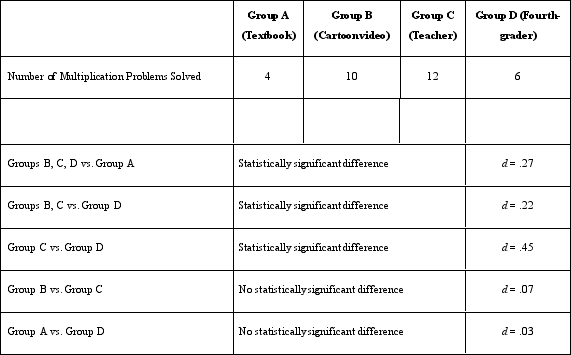
Based on the results of his study, Dr. Phillips hopes to make a causal statement. Explain how his study does or does not meet the three rules of causation.

Based on the results of his study, Dr. Phillips hopes to make a causal statement. Explain how his study does or does not meet the three rules of causation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
RESEARCH STUDY 10.3: Dr. Phillips is a cognitive-developmental psychologist who studies how children learn mathematical principles. His current interest is in studying how children learn multiplication. He recruits 54 second-graders who have not yet learned how to multiply numbers to participate in his study. He is curious as to whether different teaching styles lead to better mastery of the subject. One condition (A) involves having students read a chapter on multiplication from their textbook. One condition (B) involves having students watch a video of cartoon characters explaining multiplication. One condition (C) involves having students being taught multiplication by a teacher. One condition (D) involves having students being taught multiplication by a fourth-grader. In all conditions, participants spend 30 minutes learning the fundamentals of multiplication and are then given the same 15-question multiplication test. The number of questions answered correctly is recorded. The data are below.
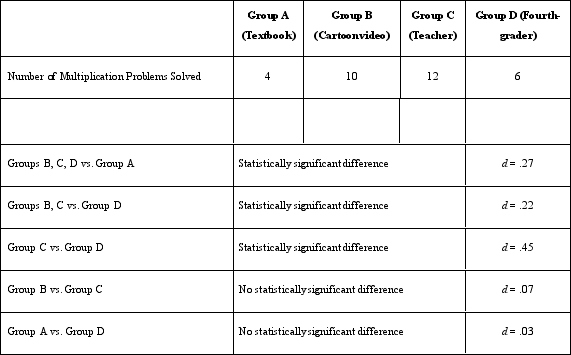
Using Dr. Phillips' study as an example, explain the difference between a control group and a comparison group. Why did Dr. Phillips' study not have a control group?

Using Dr. Phillips' study as an example, explain the difference between a control group and a comparison group. Why did Dr. Phillips' study not have a control group?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
RESEARCH STUDY 10.3: Dr. Phillips is a cognitive-developmental psychologist who studies how children learn mathematical principles. His current interest is in studying how children learn multiplication. He recruits 54 second-graders who have not yet learned how to multiply numbers to participate in his study. He is curious as to whether different teaching styles lead to better mastery of the subject. One condition (A) involves having students read a chapter on multiplication from their textbook. One condition (B) involves having students watch a video of cartoon characters explaining multiplication. One condition (C) involves having students being taught multiplication by a teacher. One condition (D) involves having students being taught multiplication by a fourth-grader. In all conditions, participants spend 30 minutes learning the fundamentals of multiplication and are then given the same 15-question multiplication test. The number of questions answered correctly is recorded. The data are below.
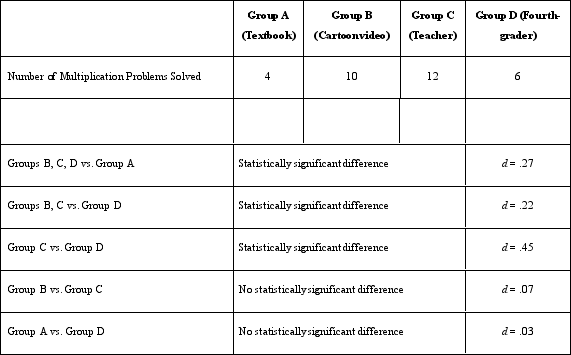
Identify the independent variable(s), dependent variable(s), and a control variable in Dr. Phillips' study.

Identify the independent variable(s), dependent variable(s), and a control variable in Dr. Phillips' study.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Researchers conducting an experiment can ensure temporal precedence by doing which of the following?
A)Having a control group
B)Manipulating the cause before measuring the effect
C)Running a manipulation check
D)Establishing covariance
A)Having a control group
B)Manipulating the cause before measuring the effect
C)Running a manipulation check
D)Establishing covariance

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
When interrogating the construct validity of the dependent variable in an experiment, which of the following questions should be asked?
A)"How well was this variable manipulated?"
B)"How well was this variable controlled by the experimenter?"
C)"How well was this variable explained to participants?"
D)"How well was this variable measured?"
A)"How well was this variable manipulated?"
B)"How well was this variable controlled by the experimenter?"
C)"How well was this variable explained to participants?"
D)"How well was this variable measured?"

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The figure above depicts which type of research design?
A) Repeated-measures design
B) Concurrent-measures design
C) Posttest-only design
D) Pretest/posttest design
A) Repeated-measures design
B) Concurrent-measures design
C) Posttest-only design
D) Pretest/posttest design

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
What type of experimental design is affected by order effects? What can researchers do to address order effects, and how does this fix them?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Which of the following phrases describes a manipulated variable?
A)"Participants wrote down how many text messages they had sent the day before."
B)"Researchers recorded whether participants volunteered to help the student in need or did not volunteer."
C)"Participants were placed in the high tempo music condition, the low tempo music condition, or the no music condition based on which color card they randomly drew from a deck."
D)"Researchers recorded the length of time participants took to complete the anagrams."
A)"Participants wrote down how many text messages they had sent the day before."
B)"Researchers recorded whether participants volunteered to help the student in need or did not volunteer."
C)"Participants were placed in the high tempo music condition, the low tempo music condition, or the no music condition based on which color card they randomly drew from a deck."
D)"Researchers recorded the length of time participants took to complete the anagrams."

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
A variable that the researcher controls is a variable.
A)measured
B)manipulated
C)dependent
D)selection
A)measured
B)manipulated
C)dependent
D)selection

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
What is the difference between concurrent-measures designs and repeated-measures designs? 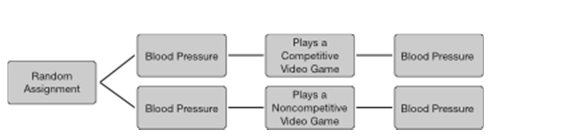
A)Concurrent-measures design is an independent-groups design; repeated-measures design is a within-group design.
B)Concurrent-measures designs expose participants to the levels of the independent variable at roughly the same time; repeated-measures designs expose participants to the levels of the independent variable sequentially.
C)Concurrent-measures designs can have any number of levels of an independent variable; repeated-measures designs can only have two levels of the independent variable.
D)There is no difference; they are two terms for the same design.

A)Concurrent-measures design is an independent-groups design; repeated-measures design is a within-group design.
B)Concurrent-measures designs expose participants to the levels of the independent variable at roughly the same time; repeated-measures designs expose participants to the levels of the independent variable sequentially.
C)Concurrent-measures designs can have any number of levels of an independent variable; repeated-measures designs can only have two levels of the independent variable.
D)There is no difference; they are two terms for the same design.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
What is a design confound? What type of validity is threatened by design confounds, and how is it threatened? Explain why not all problems in a study are necessarily confounds.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
In the study depicted in the figure above, how could a researcher transform the study into a within-groups design? 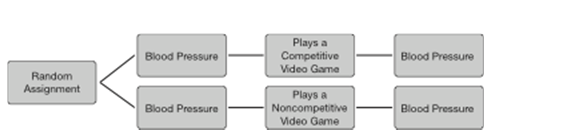
A) Adding a control group
B) Removing the first blood pressure measurement
C) Adding another independent variable
D) Having participants play both the competitive game and the noncompetitive game

A) Adding a control group
B) Removing the first blood pressure measurement
C) Adding another independent variable
D) Having participants play both the competitive game and the noncompetitive game

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Explain why control variables are necessary in experiments and why they are not actually variables.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Explain why experiments are better than your own personal experience at making causal claims.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Name three disadvantages of within-groups designs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
What is the difference between a posttest-only design and a pretest/posttest design? Provide both a benefit and a disadvantage of using a pretest/posttest design.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Explain the difference between full counterbalancing and partial counterbalancing. Why would a researcher choose partial counterbalancing over full counterbalancing?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Define manipulation checks and pilot studies, and explain how they address the construct validity of an experiment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Name three advantages of within-groups designs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








