Deck 8: The Sensorimotor System
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/118
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: The Sensorimotor System
1
Some of the supplementary motor area is in the
A) longitudinal fissure.
B) lateral fissure.
C) parietal cortex.
D) temporal cortex.
E) inferotemporal cortex.
A) longitudinal fissure.
B) lateral fissure.
C) parietal cortex.
D) temporal cortex.
E) inferotemporal cortex.
longitudinal fissure.
2
Large lesions to the right parietal lobe sometimes produce
A) ipsilateral astereognosia.
B) contralateral neglect.
C) apraxia.
D) all of the above
E) both A and C
A) ipsilateral astereognosia.
B) contralateral neglect.
C) apraxia.
D) all of the above
E) both A and C
contralateral neglect.
3
Apraxia typically affects
A) only the left side of the body.
B) only the right side of the body.
C) both sides of the body.
D) only the arms.
E) only the legs.
A) only the left side of the body.
B) only the right side of the body.
C) both sides of the body.
D) only the arms.
E) only the legs.
both sides of the body.
4
The supplementary motor area and the premotor cortex are in the
A) frontal lobe.
B) temporal lobe.
C) parietal lobe.
D) occipital lobe.
E) limbic lobe.
A) frontal lobe.
B) temporal lobe.
C) parietal lobe.
D) occipital lobe.
E) limbic lobe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Which kinds of movements are NOT influenced by sensory feedback?
A) innate movements
B) unpracticed movements
C) practiced movements
D) ballistic movements
E) reflexive movements
A) innate movements
B) unpracticed movements
C) practiced movements
D) ballistic movements
E) reflexive movements

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A neurological patient who shaves only the right side of his face and does not put his left arm into his sweater likely has a lesion in his right
A) premotor area.
B) supplementary motor cortex.
C) posterior parietal lobe.
D) dorsolateral frontal lobe.
E) primary motor area.
A) premotor area.
B) supplementary motor cortex.
C) posterior parietal lobe.
D) dorsolateral frontal lobe.
E) primary motor area.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Like the sensory systems,the sensorimotor system is
A) hierarchical.
B) parallel.
C) functionally segregated.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) hierarchical.
B) parallel.
C) functionally segregated.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The dorsolateral prefrontal association cortex
A) appears to be important in the initiation of complex voluntary movements.
B) sends projections to the primary and secondary motor cortices.
C) plays a critical role in the elicitation and blocking of reflexes.
D) both A and B
E) both B and C
A) appears to be important in the initiation of complex voluntary movements.
B) sends projections to the primary and secondary motor cortices.
C) plays a critical role in the elicitation and blocking of reflexes.
D) both A and B
E) both B and C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
In general,the various areas of secondary motor cortex are thought to
A) terminate response sequences.
B) specialize in guiding learned sequences.
C) program specific patterns of movement.
D) mediate reflexes.
E) provide the major input to spinal motor circuits.
A) terminate response sequences.
B) specialize in guiding learned sequences.
C) program specific patterns of movement.
D) mediate reflexes.
E) provide the major input to spinal motor circuits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The supplementary motor area and the premotor cortex are considered to be areas of
A) the parietal lobe.
B) association cortex.
C) secondary somatosensory cortex.
D) secondary motor cortex.
E) the primary motor cortex.
A) the parietal lobe.
B) association cortex.
C) secondary somatosensory cortex.
D) secondary motor cortex.
E) the primary motor cortex.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Contralateral neglect is usually associated with large lesions of the
A) right parietal lobe.
B) left parietal lobe.
C) right frontal lobe.
D) left frontal lobe.
E) right temporal lobe.
A) right parietal lobe.
B) left parietal lobe.
C) right frontal lobe.
D) left frontal lobe.
E) right temporal lobe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Small areas of secondary motor cortex were discovered in the
A) dorsolateral frontal lobe.
B) lateral prefrontal lobe.
C) cingulate gyrus.
D) posterior parietal lobe.
E) cerebellum.
A) dorsolateral frontal lobe.
B) lateral prefrontal lobe.
C) cingulate gyrus.
D) posterior parietal lobe.
E) cerebellum.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
During sensorimotor learning,
A) the locus of control is often shifted to lower levels of the sensorimotor hierarchy.
B) the locus of control is often shifted from conscious to unconscious control mechanisms.
C) individual responses are often integrated into continuous motor programs.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
A) the locus of control is often shifted to lower levels of the sensorimotor hierarchy.
B) the locus of control is often shifted from conscious to unconscious control mechanisms.
C) individual responses are often integrated into continuous motor programs.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Without the sensory feedback carried by the somatosensory nerves of the arms,human neurological patients,such as G.O.,have difficulty
A) swatting a fly.
B) maintaining a constant appropriate level of manual muscle contraction.
C) adjusting the output of the muscles of their arms to compensate for unexpected external disturbances (e.g., somebody brushing against an arm).
D) all of the above
E) both B and C
A) swatting a fly.
B) maintaining a constant appropriate level of manual muscle contraction.
C) adjusting the output of the muscles of their arms to compensate for unexpected external disturbances (e.g., somebody brushing against an arm).
D) all of the above
E) both B and C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Much of the output of the posterior parietal cortex goes to the
A) dorsolateral prefrontal association cortex.
B) frontal eye fields.
C) various areas of secondary motor cortex.
D) all of the above
E) both B and C
A) dorsolateral prefrontal association cortex.
B) frontal eye fields.
C) various areas of secondary motor cortex.
D) all of the above
E) both B and C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
With respect to sensorimotor learning,the advantage of transferring control to lower circuits of the neural hierarchy is that it
A) frees the higher levels of the nervous system to deal with more complex issues.
B) increases the reliability of movements.
C) increases validity.
D) increases conscious awareness of the response.
E) all of the above
A) frees the higher levels of the nervous system to deal with more complex issues.
B) increases the reliability of movements.
C) increases validity.
D) increases conscious awareness of the response.
E) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Evidence suggests that the decision to initiate a voluntary response comes from the ____________ in concert with other areas of cortex.
A) posterior occipital cortex
B) dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
C) primary motor cortex
D) premotor cortex
E) supplementary motor area
A) posterior occipital cortex
B) dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
C) primary motor cortex
D) premotor cortex
E) supplementary motor area

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Apraxia is usually caused by lesions to the
A) the left parietal lobe.
B) the right parietal lobe.
C) the right primary motor cortex.
D) the right secondary motor cortex.
E) either temporal lobe.
A) the left parietal lobe.
B) the right parietal lobe.
C) the right primary motor cortex.
D) the right secondary motor cortex.
E) either temporal lobe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which structure is thought to be involved in the integration of the sensory information that is the basis for initiating a movement?
A) posterior parietal cortex
B) primary somatosensory cortex
C) primary auditory cortex
D) frontal cortex
E) primary visual cortex
A) posterior parietal cortex
B) primary somatosensory cortex
C) primary auditory cortex
D) frontal cortex
E) primary visual cortex

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a principle of sensorimotor organization?
A) The sensorimotor system is hierarchically organized.
B) Motor output is guided by sensory input.
C) Learning changes the nature and locus of sensorimotor control.
D) all of the above
E) both B and C
A) The sensorimotor system is hierarchically organized.
B) Motor output is guided by sensory input.
C) Learning changes the nature and locus of sensorimotor control.
D) all of the above
E) both B and C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Current theories of the function of the basal ganglia emphasize their
A) role in modulating motor output.
B) involvement in a variety of cognitive processes.
C) systematic anatomical organization.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
A) role in modulating motor output.
B) involvement in a variety of cognitive processes.
C) systematic anatomical organization.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The cerebellum is thought to
A) correct ongoing movements that deviate from their intended course.
B) play a major role in motor learning, particularly when timing is critical.
C) mediate astereognosia.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
A) correct ongoing movements that deviate from their intended course.
B) play a major role in motor learning, particularly when timing is critical.
C) mediate astereognosia.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Which of the following receives information from various parts of the cortex and feeds it back to motor cortex?
A) basal ganglia
B) cerebellum
C) red nucleus
D) reticular formation
E) substantia nigra
A) basal ganglia
B) cerebellum
C) red nucleus
D) reticular formation
E) substantia nigra

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The somatotopic map of the primary motor cortex is called the
A) motor homunculus.
B) somatosensory homunculus.
C) stereognosis.
D) somatotopic homunculus.
E) supplementary map.
A) motor homunculus.
B) somatosensory homunculus.
C) stereognosis.
D) somatotopic homunculus.
E) supplementary map.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A study of the firing of primary motor cortex neurons while monkeys moved freely about indicated that their firing was often related to the
A) direction of the movement.
B) speed of the movement.
C) end point (i.e., target) of the movement.
D) acceleration of the movement.
E) purpose of the movement.
A) direction of the movement.
B) speed of the movement.
C) end point (i.e., target) of the movement.
D) acceleration of the movement.
E) purpose of the movement.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Which part of the body has been found to be doubly represented in each primary motor area of monkeys?
A) tongue
B) contralateral lip
C) contralateral hand
D) genitals
E) contralateral foot
A) tongue
B) contralateral lip
C) contralateral hand
D) genitals
E) contralateral foot

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
In 1937,the primary motor cortex was mapped by electrically stimulating the cortex of conscious human patients who were undergoing neurosurgery.This was accomplished by
A) Hebb.
B) Pinel.
C) Jackson.
D) Penfield and Boldrey.
E) Sperry.
A) Hebb.
B) Pinel.
C) Jackson.
D) Penfield and Boldrey.
E) Sperry.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The consequences of widespread cerebellar damage include
A) difficulty in maintaining steady postures.
B) inability to precisely control the direction, force, velocity, and amplitude of movements.
C) inability to adapt patterns of motor output to changing conditions.
D) severe disturbances of balance, gait, speech, and eye movement.
E) all of the above
A) difficulty in maintaining steady postures.
B) inability to precisely control the direction, force, velocity, and amplitude of movements.
C) inability to adapt patterns of motor output to changing conditions.
D) severe disturbances of balance, gait, speech, and eye movement.
E) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Long bursts of stimulation applied to the primary motor cortex elicit
A) simple movements of one joint.
B) simple contractions of one muscle.
C) complex natural-looking response sequences.
D) reflexes.
E) either A or B
A) simple movements of one joint.
B) simple contractions of one muscle.
C) complex natural-looking response sequences.
D) reflexes.
E) either A or B

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The only parts of each motor homunculus to receive somatosensory feedback directly from the skin are the
A) genital areas.
B) lip areas.
C) hand areas.
D) foot areas.
E) face areas.
A) genital areas.
B) lip areas.
C) hand areas.
D) foot areas.
E) face areas.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
It has been estimated that over half the neurons of the brain are in a structure that constitutes only 10% of the brain's total mass.This structure is the
A) neocortex.
B) cerebellum.
C) hippocampus.
D) brain stem.
E) corpus callosum.
A) neocortex.
B) cerebellum.
C) hippocampus.
D) brain stem.
E) corpus callosum.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
In the primary motor cortex,the neurons that participate in the movement of a particular finger are
A) located in one somatotopically segregated finger area.
B) widely distributed over the somatotopic hand area.
C) all located in a single column.
D) all located in the left parietal lobe.
E) all located in the right parietal lobe.
A) located in one somatotopically segregated finger area.
B) widely distributed over the somatotopic hand area.
C) all located in a single column.
D) all located in the left parietal lobe.
E) all located in the right parietal lobe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The primary motor cortex receives cutaneous feedback from only one part of the body: the hands.This feedback likely plays an important role in
A) stereognosis.
B) astereognosia.
C) the homunculus.
D) the cingulate motor areas.
E) apraxia.
A) stereognosis.
B) astereognosia.
C) the homunculus.
D) the cingulate motor areas.
E) apraxia.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Which structure is part of a neural loop including the cortex and the basal ganglia?
A) thalamus
B) vestibular nucleus
C) cerebellum
D) red nucleus
E) substantia nigra
A) thalamus
B) vestibular nucleus
C) cerebellum
D) red nucleus
E) substantia nigra

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Recent fMRI studies have challenged the traditional view of the cerebellum by suggesting that in addition to its sensorimotor functions it is involved in
A) motor learning.
B) control and learning of cognitive responses.
C) learning motor sequences.
D) correcting motor sequences.
E) integrating motor sequences.
A) motor learning.
B) control and learning of cognitive responses.
C) learning motor sequences.
D) correcting motor sequences.
E) integrating motor sequences.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The effects of damage to the primary motor cortex include
A) astereognosia.
B) difficulty in moving one part of the body independently of others.
C) paralysis.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
A) astereognosia.
B) difficulty in moving one part of the body independently of others.
C) paralysis.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Signals from the left primary motor cortex descend through the spinal cord white matter in one of
A) three major tracts.
B) four major tracts.
C) five major tracts.
D) six major tracts.
E) eight major tracts.
A) three major tracts.
B) four major tracts.
C) five major tracts.
D) six major tracts.
E) eight major tracts.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A deficit in the ability to recognize objects by touch is called
A) apraxia.
B) asomatognosia.
C) stereognosis.
D) astereognosia.
E) homunculus.
A) apraxia.
B) asomatognosia.
C) stereognosis.
D) astereognosia.
E) homunculus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Neurons that fire in response to making a particular response,observing somebody else making the response,or just thinking about the response are called
A) supplementary motor neurons.
B) premotor neurons.
C) mirror neurons.
D) ballistic neurons.
E) somatotopic neurons.
A) supplementary motor neurons.
B) premotor neurons.
C) mirror neurons.
D) ballistic neurons.
E) somatotopic neurons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
In a remarkable demonstration,Belle,the owl monkey,controlled the movements of a robotic arm
A) by pressing buttons.
B) with the activity of neurons in her primary motor cortex.
C) with speech sounds.
D) with monkey calls.
E) by providing visual feedback to the arm.
A) by pressing buttons.
B) with the activity of neurons in her primary motor cortex.
C) with speech sounds.
D) with monkey calls.
E) by providing visual feedback to the arm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The cell bodies of Betz cells are found in the
A) premotor cortex.
B) primary motor cortex.
C) supplementary motor cortex.
D) cerebellum.
E) basal ganglia.
A) premotor cortex.
B) primary motor cortex.
C) supplementary motor cortex.
D) cerebellum.
E) basal ganglia.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The motor units of the thumb,fingers,and face contain the
A) fewest muscle fibers.
B) most muscle fibers.
C) fewest motor neurons.
D) most motor neurons.
E) most extensors.
A) fewest muscle fibers.
B) most muscle fibers.
C) fewest motor neurons.
D) most motor neurons.
E) most extensors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The axons of Betz cells are part of the
A) dorsolateral corticospinal tract.
B) dorsolateral corticorubrospinal tract.
C) anterolateral pathway.
D) ventromedial cortico-brainstem-spinal tract.
E) ventromedial corticospinal tract.
A) dorsolateral corticospinal tract.
B) dorsolateral corticorubrospinal tract.
C) anterolateral pathway.
D) ventromedial cortico-brainstem-spinal tract.
E) ventromedial corticospinal tract.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The descending pathway illustrated here is the
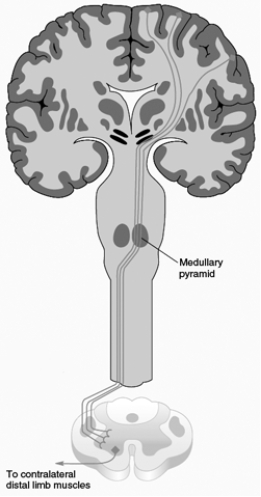
A) dorsolateral corticorubrospinal tract.
B) dorsolateral corticospinal tract.
C) ventromedial corticospinal tract.
D) ventromedial cortico-brainstem-spinal tract.
E) none of the above

A) dorsolateral corticorubrospinal tract.
B) dorsolateral corticospinal tract.
C) ventromedial corticospinal tract.
D) ventromedial cortico-brainstem-spinal tract.
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
In general,the dorsolateral corticospinal tract controls the muscles of the
A) thighs.
B) body core.
C) hands and feet.
D) proximal limbs.
E) legs.
A) thighs.
B) body core.
C) hands and feet.
D) proximal limbs.
E) legs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Which of the following brain stem structures receives direct sensory information about balance?
A) cerebellum
B) reticular formation
C) vestibular nucleus
D) tectum
E) red nucleus
A) cerebellum
B) reticular formation
C) vestibular nucleus
D) tectum
E) red nucleus

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
In contrast to the descending dorsolateral motor pathways,the ventromedial pathways
A) control the trunk.
B) are more diffuse.
C) are more strictly contralateral.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
A) control the trunk.
B) are more diffuse.
C) are more strictly contralateral.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
In general,the ventromedial descending motor tracts control the muscles of the
A) thumbs.
B) fingers.
C) trunk.
D) toes.
E) face.
A) thumbs.
B) fingers.
C) trunk.
D) toes.
E) face.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
When a motor neuron fires,all of the muscle fibers of its motor
A) unit contract together.
B) pool contract together.
C) segment contract together.
D) equivalence contract together.
E) feedback contract together.
A) unit contract together.
B) pool contract together.
C) segment contract together.
D) equivalence contract together.
E) feedback contract together.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
In neuroanatomy,"rubro" refers to the
A) substantia nigra.
B) vestibular system.
C) caudate.
D) red nucleus.
E) cerebellum.
A) substantia nigra.
B) vestibular system.
C) caudate.
D) red nucleus.
E) cerebellum.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
In contrast to the axons of the descending dorsolateral motor pathways,individual axons of the ventromedial pathways often terminate
A) directly on motor neurons.
B) in two or more segments.
C) on both sides of the spinal cord.
D) both A and B
E) both B and C
A) directly on motor neurons.
B) in two or more segments.
C) on both sides of the spinal cord.
D) both A and B
E) both B and C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Most axons of the dorsolateral corticorubrospinal tract synapse on
A) muscles of the fingers and thumb.
B) muscles of the hands and wrists.
C) interneurons of the spinal gray matter that in turn synapse on motor neurons that project to the distal muscles of the arms and legs.
D) motor neurons that project to the fingers.
E) Betz cells.
A) muscles of the fingers and thumb.
B) muscles of the hands and wrists.
C) interneurons of the spinal gray matter that in turn synapse on motor neurons that project to the distal muscles of the arms and legs.
D) motor neurons that project to the fingers.
E) Betz cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Only primates and a few other species,such as hamsters and raccoons,have cortical neurons that synapse directly on
A) muscles.
B) muscles of the fingers and thumb.
C) motor neurons that project to the muscles of the fingers and thumb.
D) spinal interneurons.
E) targets in the PNS.
A) muscles.
B) muscles of the fingers and thumb.
C) motor neurons that project to the muscles of the fingers and thumb.
D) spinal interneurons.
E) targets in the PNS.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
In the classic experiments of Lawrence and Kuypers,the descending motor tracts of monkeys were transected.The results of these experiments suggest that the function of the ventromedial pathways is the control of
A) posture.
B) movements of the body core and associated arm movements.
C) reaching for objects.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
A) posture.
B) movements of the body core and associated arm movements.
C) reaching for objects.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
In one classic experiment,monkeys had difficulty letting go of food after their
A) dorsolateral corticorubrospinal tracts were transected.
B) dorsolateral corticospinal tracts were transected.
C) ventromedial corticospinal tracts were transected.
D) cerebellum was lesioned.
E) basal ganglia were lesioned.
A) dorsolateral corticorubrospinal tracts were transected.
B) dorsolateral corticospinal tracts were transected.
C) ventromedial corticospinal tracts were transected.
D) cerebellum was lesioned.
E) basal ganglia were lesioned.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
In contrast to the ventromedial corticospinal tract,before descending to the spinal cord,the ventromedial cortico-brainstem-spinal tract interacts with the
A) tectum.
B) reticular formation.
C) vestibular nuclei.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) tectum.
B) reticular formation.
C) vestibular nuclei.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
In which of the following structures would the motor units likely be the smallest?
A) finger
B) leg
C) arm
D) foot
E) back
A) finger
B) leg
C) arm
D) foot
E) back

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Which midbrain structure receives visual and auditory information about spatial location?
A) tectum
B) cerebellum
C) basal ganglia
D) tegmentum
E) vestibular nucleus
A) tectum
B) cerebellum
C) basal ganglia
D) tegmentum
E) vestibular nucleus

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
In the classic transection experiments of Lawrence and Kuypers,monkeys with all their dorsolateral motor pathways transected sat with their arms hanging limply by their sides.However,these same monkeys had no difficulty
A) picking up pieces of food and then releasing them.
B) using their arms for standing, walking, and climbing.
C) reaching for moving objects.
D) moving their fingers independently.
E) all of the above
A) picking up pieces of food and then releasing them.
B) using their arms for standing, walking, and climbing.
C) reaching for moving objects.
D) moving their fingers independently.
E) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The decussation in the medullary pyramids is part of the
A) dorsolateral corticospinal tract.
B) dorsolateral corticorubrospinal tract.
C) ventromedial corticospinal tract.
D) ventromedial cortico-brainstem-spinal tract.
E) both C and D
A) dorsolateral corticospinal tract.
B) dorsolateral corticorubrospinal tract.
C) ventromedial corticospinal tract.
D) ventromedial cortico-brainstem-spinal tract.
E) both C and D

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
The biceps and triceps are
A) synergistic.
B) dynamic.
C) isometric.
D) extensors.
E) antagonistic.
A) synergistic.
B) dynamic.
C) isometric.
D) extensors.
E) antagonistic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
About how many motor neurons are there in the typical motor unit?
A) 4
B) 1
C) 100
D) 1,000
E) 150
A) 4
B) 1
C) 100
D) 1,000
E) 150

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
During a stretch reflex,the extrafusal motor neuron is excited directly by the
A) intrafusal motor neuron.
B) muscle spindle receptor.
C) spindle afferent neuron.
D) intrafusal muscle.
E) muscle.
A) intrafusal motor neuron.
B) muscle spindle receptor.
C) spindle afferent neuron.
D) intrafusal muscle.
E) muscle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The tension of a muscle can be increased by increasing
A) the number of active neurons in its motor pool.
B) the level of activity of neurons in its motor pool.
C) the number of active neurons in its motor unit.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
A) the number of active neurons in its motor pool.
B) the level of activity of neurons in its motor pool.
C) the number of active neurons in its motor unit.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Muscle spindles provide the CNS with information about muscle
A) fatigue.
B) length.
C) tension.
D) color.
E) location.
A) fatigue.
B) length.
C) tension.
D) color.
E) location.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
So-called fast muscle fibers
A) are pale.
B) are bright red.
C) can generate great force for long periods.
D) are found exclusively in extensors.
E) are found exclusively in flexors.
A) are pale.
B) are bright red.
C) can generate great force for long periods.
D) are found exclusively in extensors.
E) are found exclusively in flexors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
The patellar tendon reflex is a
A) withdrawal reflex.
B) reciprocal reflex.
C) stretch reflex.
D) recurrent reflex.
E) multisynaptic reflex.
A) withdrawal reflex.
B) reciprocal reflex.
C) stretch reflex.
D) recurrent reflex.
E) multisynaptic reflex.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Bob tried to open a jar of pickles,but the lid did not budge.As he struggled against the unmoving lid,the muscles of his hands and arms were
A) in isometric contraction.
B) in dynamic contraction.
C) locked in a stretch reflex.
D) in motor pools.
E) in extension.
A) in isometric contraction.
B) in dynamic contraction.
C) locked in a stretch reflex.
D) in motor pools.
E) in extension.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
The latency of withdrawal reflexes indicates that they involve
A) no synapses.
B) at least 1 synapse.
C) at least 2 synapses.
D) at least 3 synapses.
E) more than 3 synapses.
A) no synapses.
B) at least 1 synapse.
C) at least 2 synapses.
D) at least 3 synapses.
E) more than 3 synapses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
The tiny muscle at the end of the pointer line is
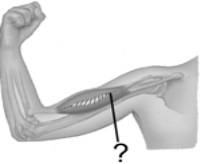
A) an intrafusal muscle.
B) an extrafusal muscle.
C) a skeletal muscle.
D) both A and C
E) Both B and C

A) an intrafusal muscle.
B) an extrafusal muscle.
C) a skeletal muscle.
D) both A and C
E) Both B and C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Increases in muscle tension in the absence of any shortening of the muscle are said to be
A) contractions.
B) dynamic.
C) extensions.
D) isometric.
E) synergistic.
A) contractions.
B) dynamic.
C) extensions.
D) isometric.
E) synergistic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
All of the motor neurons that innervate the fibers of a single muscle are called its
A) motor unit.
B) discharge unit.
C) motor pool.
D) antagonists.
E) agonists.
A) motor unit.
B) discharge unit.
C) motor pool.
D) antagonists.
E) agonists.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
The tiny motor neuron illustrated here is
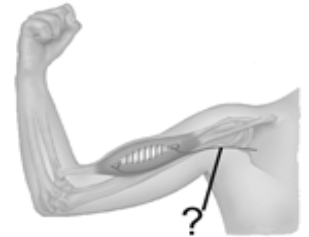
A) a spindle afferent neuron.
B) an intrafusal neuron.
C) an extrafusal neuron.
D) an agonist neuron.
E) an antagonist neuron.

A) a spindle afferent neuron.
B) an intrafusal neuron.
C) an extrafusal neuron.
D) an agonist neuron.
E) an antagonist neuron.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Intrafusal is to extrafusal as
A) voluntary is to ballistic.
B) muscle spindle is to skeletal muscle.
C) voluntary is to reflex.
D) dynamic is to static.
E) CNS is to PNS.
A) voluntary is to ballistic.
B) muscle spindle is to skeletal muscle.
C) voluntary is to reflex.
D) dynamic is to static.
E) CNS is to PNS.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Which of the following requires an inhibitory interneuron?
A) reciprocal innervation
B) recurrent collateral inhibition
C) isometric contraction
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
A) reciprocal innervation
B) recurrent collateral inhibition
C) isometric contraction
D) all of the above
E) both A and B

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Which of the following helps distribute the work between different motor neurons of a muscle's motor pool?
A) cocontraction
B) recurrent collateral inhibition
C) reciprocal inhibition
D) muscle-spindle feedback
E) withdrawal reflex
A) cocontraction
B) recurrent collateral inhibition
C) reciprocal inhibition
D) muscle-spindle feedback
E) withdrawal reflex

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Muscles are protected from damage caused by excessive contraction by
A) gamma efferents.
B) spindle afferents.
C) extrafusal motor pools.
D) Golgi tendon organs.
E) synergistic muscles.
A) gamma efferents.
B) spindle afferents.
C) extrafusal motor pools.
D) Golgi tendon organs.
E) synergistic muscles.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Recurrent collateral inhibition is mediated by
A) cocontraction.
B) Renshaw cells.
C) Golgi organs.
D) muscle spindles.
E) reciprocal innervation.
A) cocontraction.
B) Renshaw cells.
C) Golgi organs.
D) muscle spindles.
E) reciprocal innervation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
The patellar tendon reflex is a
A) conditioned reflex.
B) stretch reflex.
C) withdrawal reflex.
D) monosynaptic reflex.
E) both B and D
A) conditioned reflex.
B) stretch reflex.
C) withdrawal reflex.
D) monosynaptic reflex.
E) both B and D

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Illustrated here is a
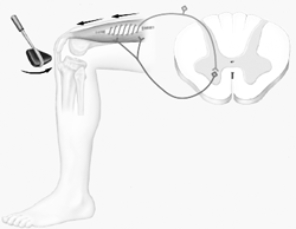
A) patellar tendon reflex.
B) withdrawal reflex.
C) stretch reflex.
D) both A and B
E) both A and C

A) patellar tendon reflex.
B) withdrawal reflex.
C) stretch reflex.
D) both A and B
E) both A and C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 118 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








