Deck 7: Foreign Currency Derivatives and Swaps
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 7: Foreign Currency Derivatives and Swaps
1
Which of the following is NOT a difference between a currency futures contract and a forward contract?
A) The futures contract is marked to market daily whereas the forward contract is only due to be settled at maturity.
B) The counterparty to the futures participant is unknown with the clearinghouse stepping into each transaction whereas the forward contract participants are in direct contact setting the forward specifications.
C) A single sales commission covers both the purchase and sale of a futures contract whereas there is no specific sales commission with a forward contract because banks earn a profit through the bid-ask spread.
D) All of the above are true.
A) The futures contract is marked to market daily whereas the forward contract is only due to be settled at maturity.
B) The counterparty to the futures participant is unknown with the clearinghouse stepping into each transaction whereas the forward contract participants are in direct contact setting the forward specifications.
C) A single sales commission covers both the purchase and sale of a futures contract whereas there is no specific sales commission with a forward contract because banks earn a profit through the bid-ask spread.
D) All of the above are true.
All of the above are true.
2
A foreign currency ________ option gives the holder the right to ________ a foreign currency whereas a foreign currency ________ option gives the holder the right to ________ an option.
A) call; buy; put; sell
B) call; sell; put; buy
C) put; hold; call; release
D) none of the above
A) call; buy; put; sell
B) call; sell; put; buy
C) put; hold; call; release
D) none of the above
call; buy; put; sell
3
Currency futures contracts have become standard fare and trade readily in the world money centers.
True
4
Peter Simpson thinks that the U.K. pound will cost $1.43/£ in six months. A 6-month currency futures contract is available today at a rate of $1.44/£. If Peter was to speculate in the currency futures market, and his expectations are correct, which of the following strategies would earn him a profit?
A) Sell a pound currency futures contract.
B) Buy a pound currency futures contract.
C) Sell pounds today.
D) Sell pounds in six months.
A) Sell a pound currency futures contract.
B) Buy a pound currency futures contract.
C) Sell pounds today.
D) Sell pounds in six months.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The writer of the option is referred to as the seller, and the buyer of the option is referred to as the holder.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Futures contracts require that the purchaser deposit an initial sum as collateral. This deposit is called a
A) collateralized deposit.
B) marked market sum.
C) margin.
D) settlement.
A) collateralized deposit.
B) marked market sum.
C) margin.
D) settlement.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Jack Hemmings bought a 3-month British pound futures contract for $1.4400/£ only to see the dollar appreciate to a value of $1.4250 at which time he sold the pound futures. If each pound futures contract is for an amount of £62,500, how much money did Jack gain or lose from his speculation with pound futures?
A) $937.50 loss
B) $937.50 gain
C) £937.50 loss
D) £937.50 gain
A) $937.50 loss
B) $937.50 gain
C) £937.50 loss
D) £937.50 gain

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The major difference between currency futures and forward contracts is that futures contracts are standardized for ease of trading on an exchange market whereas forward contracts are specialized and tailored to meet the needs of clients.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
A speculator in the futures market wishing to lock in a price at which they could ________ a foreign currency will ________ a futures contract.
A) buy; sell
B) sell; buy
C) buy; buy
D) none of the above
A) buy; sell
B) sell; buy
C) buy; buy
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which of the following is NOT a contract specification for currency futures trading on an organized exchange?
A) size of the contract
B) maturity date
C) last trading day
D) All of the above are specified.
A) size of the contract
B) maturity date
C) last trading day
D) All of the above are specified.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
An ________ option can be exercised only on its expiration date, whereas an ________ option can be exercised anytime between the date of writing up to and including the exercise date.
A) American; European
B) American; British
C) Asian; American
D) European; American
A) American; European
B) American; British
C) Asian; American
D) European; American

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
A foreign currency ________ gives the purchaser the right, not the obligation, to buy a given amount of foreign exchange at a fixed price per unit for a specified period.
A) future
B) forward
C) option
D) swap
A) future
B) forward
C) option
D) swap

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
About ________ of all futures contracts are settled by physical delivery of foreign exchange between buyer and seller.
A) 0%
B) 5%
C) 50%
D) 95%
A) 0%
B) 5%
C) 50%
D) 95%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
All futures contracts are between the client and the exchange clearing house thus effectively eliminating specific counterparty risk at delivery date.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Financial derivatives are powerful tools that can be used by management for purposes of
A) speculation.
B) hedging.
C) human resource management.
D) A and B above.
A) speculation.
B) hedging.
C) human resource management.
D) A and B above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
A speculator that has ________ a futures contract has taken a ________ position.
A) sold; long
B) purchased; short
C) sold; short
D) purchased; sold
A) sold; long
B) purchased; short
C) sold; short
D) purchased; sold

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The price at which an option can be exercised is called the
A) premium.
B) spot rate.
C) strike price.
D) commission.
A) premium.
B) spot rate.
C) strike price.
D) commission.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
A foreign currency ________ contract calls for the future delivery of a standard amount of foreign exchange at a fixed time, place, and price.
A) futures
B) forward
C) option
D) swap
A) futures
B) forward
C) option
D) swap

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements regarding currency futures contracts and forward contracts is NOT true?
A) A futures contract is a standardized amount per currency whereas the forward contact is for any size desired.
B) A futures contract is for a fixed maturity whereas the forward contract is for any maturity you like up to one year.
C) Futures contracts trade on organized exchanges whereas forwards take place between individuals and banks with other banks via telecom linkages.
D) All of the above are true.
A) A futures contract is a standardized amount per currency whereas the forward contact is for any size desired.
B) A futures contract is for a fixed maturity whereas the forward contract is for any maturity you like up to one year.
C) Futures contracts trade on organized exchanges whereas forwards take place between individuals and banks with other banks via telecom linkages.
D) All of the above are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
A call option whose exercise price exceeds the spot rate is said to be
A) in-the-money.
B) at-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) over-the-spot.
A) in-the-money.
B) at-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) over-the-spot.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The main advantage(s) of over-the-counter foreign currency options over exchange traded options is(are)
A) expiration dates tailored to the needs of the client.
B) amounts that are tailor made.
C) client desired expiration dates.
D) all of the above.
A) expiration dates tailored to the needs of the client.
B) amounts that are tailor made.
C) client desired expiration dates.
D) all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The most widely used reference rate for standardized quotations, loan agreements, or financial derivative valuations is the
A) Federal Reserve Discount rate.
B) federal funds rate.
C) LIBOR.
D) one-year U.S. Treasury Bill.
A) Federal Reserve Discount rate.
B) federal funds rate.
C) LIBOR.
D) one-year U.S. Treasury Bill.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The ________ of an option is the value if the option were to be exercised immediately. It is the options ________ value.
A) intrinsic value; maximum
B) intrinsic value; minimum
C) time value; maximum
D) time value; minimum
A) intrinsic value; maximum
B) intrinsic value; minimum
C) time value; maximum
D) time value; minimum

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Assume that a call option has an exercise price of $1.50/³. At a spot price of $1.45/³, the call option has
A) a time value of $0.04.
B) a time value of $0.00.
C) an intrinsic value of $0.00.
D) an intrinsic value of -$0.04.
A) a time value of $0.04.
B) a time value of $0.00.
C) an intrinsic value of $0.00.
D) an intrinsic value of -$0.04.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
TABLE 7.1
Use the below mentioned table to answer the following question(s).
April 19, 2010, British Pound Option Prices (cents per pound, 62,500 pound contracts).
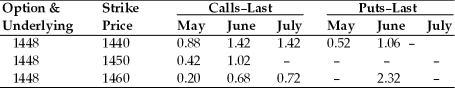
Refer to Table 7.1. The exercise price of ________ giving the purchaser the right to sell pounds in June has a cost per pound of ________ for a total price of ________.
A) 1460; 0.68 cents; $425.00
B) 1440; 1.06 cents; $662.50
C) 1450; 1.02 cents; $637.50
D) 1440; 1.42 cents; $887.50
Use the below mentioned table to answer the following question(s).
April 19, 2010, British Pound Option Prices (cents per pound, 62,500 pound contracts).

Refer to Table 7.1. The exercise price of ________ giving the purchaser the right to sell pounds in June has a cost per pound of ________ for a total price of ________.
A) 1460; 0.68 cents; $425.00
B) 1440; 1.06 cents; $662.50
C) 1450; 1.02 cents; $637.50
D) 1440; 1.42 cents; $887.50

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
What is the reason for an investor to pay for a zero intrinsic value option?
A) there is always a chance that the spot rate will move before expiration putting the option in the money
B) there is always a chance that the strike price for options with different maturities will increase
C) investors are typically not investing in zero intrinsic value options
D) the premiums for zero intrinsic value options are very small
A) there is always a chance that the spot rate will move before expiration putting the option in the money
B) there is always a chance that the strike price for options with different maturities will increase
C) investors are typically not investing in zero intrinsic value options
D) the premiums for zero intrinsic value options are very small

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
TABLE 7.1
Use the below mentioned table to answer the following question(s).
April 19, 2010, British Pound Option Prices (cents per pound, 62,500 pound contracts).

Refer to Table 7.1. The May call option on pounds with a strike price of 1440 means
A) $88/£ per contract.
B) $0.88/£.
C) $0.0088/£.
D) none of the above
Use the below mentioned table to answer the following question(s).
April 19, 2010, British Pound Option Prices (cents per pound, 62,500 pound contracts).

Refer to Table 7.1. The May call option on pounds with a strike price of 1440 means
A) $88/£ per contract.
B) $0.88/£.
C) $0.0088/£.
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
As a general statement, it is safe to say that businesses generally use the ________ for foreign currency option contracts, and individuals and financial institutions typically use the ________.
A) exchange markets; over-the-counter
B) over-the-counter; exchange markets
C) private; government sponsored
D) government sponsored; private
A) exchange markets; over-the-counter
B) over-the-counter; exchange markets
C) private; government sponsored
D) government sponsored; private

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
TABLE 7.1
Use the below mentioned table to answer the following question(s).
April 19, 2010, British Pound Option Prices (cents per pound, 62,500 pound contracts).

Refer to Table 7.1. What was the closing price of the British pound on April 18, 2010?
A) $1.448/£
B) £1.448/$
C) $14.48/£
D) None of the above
Use the below mentioned table to answer the following question(s).
April 19, 2010, British Pound Option Prices (cents per pound, 62,500 pound contracts).

Refer to Table 7.1. What was the closing price of the British pound on April 18, 2010?
A) $1.448/£
B) £1.448/$
C) $14.48/£
D) None of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The maximum profit that a writer of a call can make is
A) unlimited if the option is in the money.
B) unlimited if the option is out of the money.
C) limited to the received premium.
D) none of the above
A) unlimited if the option is in the money.
B) unlimited if the option is out of the money.
C) limited to the received premium.
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Other things equal, the price of an option goes up as the volatility of the option decreases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Which of the following is NOT a factor in determining the price of a currency option?
A) the present spot rate
B) the time to maturity
C) the standard deviation of the daily spot price movement
D) All of the above are factors in determining the premium price.
A) the present spot rate
B) the time to maturity
C) the standard deviation of the daily spot price movement
D) All of the above are factors in determining the premium price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Foreign currency options are available both over-the-counter and on organized exchanges.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The time value is asymmetric in value as you move away from the strike price. (i.e., the time value at two cents above the strike price is not necessarily the same as the time value two cents below the strike price.)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Company's treasurer decides to go long on a currency put option to
A) gain potential unlimited profit if the spot price is less than the strike price.
B) limit potential loss to a maximum equivalent of the strike price.
C) limit potential loss to the premium equivalent.
D) because it has a gut feeling that the underlying asset currency will appreciate.
A) gain potential unlimited profit if the spot price is less than the strike price.
B) limit potential loss to a maximum equivalent of the strike price.
C) limit potential loss to the premium equivalent.
D) because it has a gut feeling that the underlying asset currency will appreciate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
A call option whose exercise price is less than the spot rate is said to be
A) in-the-money.
B) at-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) under-the-spot.
A) in-the-money.
B) at-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) under-the-spot.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
An option whose exercise price is equal to the spot rate is said to be
A) in-the-money.
B) at-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) on-the-spot.
A) in-the-money.
B) at-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) on-the-spot.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The value of a European style call option is the sum of two components, the
A) present value plus the intrinsic value.
B) time value plus the present value.
C) intrinsic value plus the time value.
D) the intrinsic value plus the standard deviation.
A) present value plus the intrinsic value.
B) time value plus the present value.
C) intrinsic value plus the time value.
D) the intrinsic value plus the standard deviation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
The single largest interest rate risk of a firm is
A) interest sensitive securities.
B) debt service.
C) dividend payments.
D) accounts payable.
A) interest sensitive securities.
B) debt service.
C) dividend payments.
D) accounts payable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
All exchange-traded options are settled through a clearing house but over-the-counter options are not and are thus subject to greater ________ risk.
A) exchange rate
B) country
C) counterparty
D) none of the above
A) exchange rate
B) country
C) counterparty
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Interest rate risks that a non-financial MNE faces can affect
A) the periodical levels of debt service.
B) the outstanding principal debt recognized as long term liability.
C) the outstanding amount of short term government securities recognized as an asset.
D) all of the above
A) the periodical levels of debt service.
B) the outstanding principal debt recognized as long term liability.
C) the outstanding amount of short term government securities recognized as an asset.
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
For the following problem(s), consider these debt strategies being considered by a corporate borrower. Each is intended to provide $1,000,000 in financing for a three-year period.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. After the fact, under which set of circumstances would you prefer strategy #3? (Assume your firm is borrowing money.)
A) Your credit rating stayed the same and interest rates went up.
B) Your credit rating stayed the same and interest rates went down.
C) Your credit rating improved and interest rates went down.
D) Not enough information to make a judgment.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. After the fact, under which set of circumstances would you prefer strategy #3? (Assume your firm is borrowing money.)
A) Your credit rating stayed the same and interest rates went up.
B) Your credit rating stayed the same and interest rates went down.
C) Your credit rating improved and interest rates went down.
D) Not enough information to make a judgment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Which of the following would be considered an example of a currency swap?
A) exchanging a dollar interest obligation for a British pound obligation
B) exchanging a eurodollar interest obligation for a dollar obligation
C) exchanging a eurodollar interest obligation for a British pound obligation
D) All of the above are example of a currency swap.
A) exchanging a dollar interest obligation for a British pound obligation
B) exchanging a eurodollar interest obligation for a dollar obligation
C) exchanging a eurodollar interest obligation for a British pound obligation
D) All of the above are example of a currency swap.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
For the following problem(s), consider these debt strategies being considered by a corporate borrower. Each is intended to provide $1,000,000 in financing for a three-year period.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. Which strategy (strategies) will eliminate credit risk?
A) Strategy #1
B) Strategy #2
C) Strategy #3
D) Strategy #1 and #2
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. Which strategy (strategies) will eliminate credit risk?
A) Strategy #1
B) Strategy #2
C) Strategy #3
D) Strategy #1 and #2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
TABLE 7.2
Use the information for Polaris Corporation to answer the following question(s).
Polaris is taking out a $5,000,000 two-year loan at a variable rate of LIBOR plus 1.00%. The LIBOR rate will be reset each year at an agreed upon date. The current LIBOR rate is 4.00% per year. The loan has an upfront fee of 2.00%
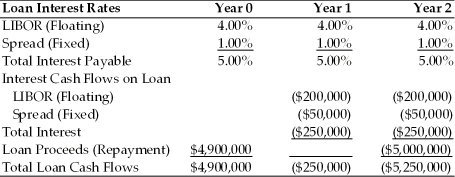
Refer to Table 7.2. What is the all-in-cost (i.e., the internal rate of return) of the Polaris loan including the LIBOR rate, fixed spread and upfront fee?
A) 4.00%
B) 5.00%
C) 5.53%
D) 6.09%
Use the information for Polaris Corporation to answer the following question(s).
Polaris is taking out a $5,000,000 two-year loan at a variable rate of LIBOR plus 1.00%. The LIBOR rate will be reset each year at an agreed upon date. The current LIBOR rate is 4.00% per year. The loan has an upfront fee of 2.00%

Refer to Table 7.2. What is the all-in-cost (i.e., the internal rate of return) of the Polaris loan including the LIBOR rate, fixed spread and upfront fee?
A) 4.00%
B) 5.00%
C) 5.53%
D) 6.09%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
For the following problem(s), consider these debt strategies being considered by a corporate borrower. Each is intended to provide $1,000,000 in financing for a three-year period.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. Choosing strategy #1 will
A) guarantee the lowest average annual rate over the next three years.
B) eliminate credit risk but retain repricing risk.
C) maintain the possibility of lower interest costs, but maximizes the combined credit and repricing risks.
D) preclude the possibility of sharing in lower interest rates over the three-year period.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. Choosing strategy #1 will
A) guarantee the lowest average annual rate over the next three years.
B) eliminate credit risk but retain repricing risk.
C) maintain the possibility of lower interest costs, but maximizes the combined credit and repricing risks.
D) preclude the possibility of sharing in lower interest rates over the three-year period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
For the following problem(s), consider these debt strategies being considered by a corporate borrower. Each is intended to provide $1,000,000 in financing for a three-year period.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. The risk of strategy #1 is that interest rates might go down or that your credit rating might improve. What is the risk of strategy #3? (Assume your firm is borrowing money.)
A) Interest rates might go down or your credit rating might improve.
B) Interest rates might go up or your credit rating might improve.
C) Interest rates might go up or your credit rating might get worse.
D) none of the above.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. The risk of strategy #1 is that interest rates might go down or that your credit rating might improve. What is the risk of strategy #3? (Assume your firm is borrowing money.)
A) Interest rates might go down or your credit rating might improve.
B) Interest rates might go up or your credit rating might improve.
C) Interest rates might go up or your credit rating might get worse.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
For the following problem(s), consider these debt strategies being considered by a corporate borrower. Each is intended to provide $1,000,000 in financing for a three-year period.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. After the fact, under which set of circumstances would you prefer strategy #2? (Assume your firm is borrowing money.)
A) Your credit rating stayed the same and interest rates went up.
B) Your credit rating stayed the same and interest rates went down.
C) Your credit rating improved and interest rates went down.
D) Not enough information to make a judgment.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. After the fact, under which set of circumstances would you prefer strategy #2? (Assume your firm is borrowing money.)
A) Your credit rating stayed the same and interest rates went up.
B) Your credit rating stayed the same and interest rates went down.
C) Your credit rating improved and interest rates went down.
D) Not enough information to make a judgment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
TABLE 7.2
Use the information for Polaris Corporation to answer the following question(s).
Polaris is taking out a $5,000,000 two-year loan at a variable rate of LIBOR plus 1.00%. The LIBOR rate will be reset each year at an agreed upon date. The current LIBOR rate is 4.00% per year. The loan has an upfront fee of 2.00%

Refer to Table 7.2. What portion of the cost of the loan is at risk of changing?
A) the LIBOR rate
B) the spread
C) the upfront fee
D) all of the above
Use the information for Polaris Corporation to answer the following question(s).
Polaris is taking out a $5,000,000 two-year loan at a variable rate of LIBOR plus 1.00%. The LIBOR rate will be reset each year at an agreed upon date. The current LIBOR rate is 4.00% per year. The loan has an upfront fee of 2.00%

Refer to Table 7.2. What portion of the cost of the loan is at risk of changing?
A) the LIBOR rate
B) the spread
C) the upfront fee
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
TABLE 7.2
Use the information for Polaris Corporation to answer the following question(s).
Polaris is taking out a $5,000,000 two-year loan at a variable rate of LIBOR plus 1.00%. The LIBOR rate will be reset each year at an agreed upon date. The current LIBOR rate is 4.00% per year. The loan has an upfront fee of 2.00%

Refer to Table 7.2. If the LIBOR rate falls to 3.00% after the first year what will be the all-in-cost (i.e. the internal rate of return) for Polaris for the entire loan?
A) 4.00%
B) 4.50%
C) 5.25%
D) 5.60%
Use the information for Polaris Corporation to answer the following question(s).
Polaris is taking out a $5,000,000 two-year loan at a variable rate of LIBOR plus 1.00%. The LIBOR rate will be reset each year at an agreed upon date. The current LIBOR rate is 4.00% per year. The loan has an upfront fee of 2.00%

Refer to Table 7.2. If the LIBOR rate falls to 3.00% after the first year what will be the all-in-cost (i.e. the internal rate of return) for Polaris for the entire loan?
A) 4.00%
B) 4.50%
C) 5.25%
D) 5.60%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
________ is the possibility that the borrower's creditworthiness is reclassified by the lender at the time of renewing credit. ________ is the risk of changes in interest rates charged at the time a financial contract rate is set.
A) Credit risk; Interest rate risk
B) Repricing risk; Credit risk
C) Interest rate risk; Credit risk
D) Credit risk; Repricing risk
A) Credit risk; Interest rate risk
B) Repricing risk; Credit risk
C) Interest rate risk; Credit risk
D) Credit risk; Repricing risk

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
A/an ________ is a contract to lock in today interest rates over a given period of time.
A) forward rate agreement
B) interest rate future
C) interest rate swap
D) none of the above
A) forward rate agreement
B) interest rate future
C) interest rate swap
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
An agreement to swap a fixed interest payment for a floating interest payment would be considered a/an
A) currency swap.
B) forward swap.
C) interest rate swap.
D) none of the above
A) currency swap.
B) forward swap.
C) interest rate swap.
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
For the following problem(s), consider these debt strategies being considered by a corporate borrower. Each is intended to provide $1,000,000 in financing for a three-year period.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. Choosing strategy #2 will
A) guarantee the lowest average annual rate over the next three years.
B) eliminate credit risk but retain repricing risk.
C) maintain the possibility of lower interest costs, but maximizes the combined credit and repricing risks.
D) preclude the possibility of sharing in lower interest rates over the three-year period.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. Choosing strategy #2 will
A) guarantee the lowest average annual rate over the next three years.
B) eliminate credit risk but retain repricing risk.
C) maintain the possibility of lower interest costs, but maximizes the combined credit and repricing risks.
D) preclude the possibility of sharing in lower interest rates over the three-year period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
For the following problem(s), consider these debt strategies being considered by a corporate borrower. Each is intended to provide $1,000,000 in financing for a three-year period.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. Choosing strategy #3 will
A) guarantee the lowest average annual rate over the next three years.
B) eliminate credit risk but retain repricing risk.
C) maintain the possibility of lower interest costs, but maximizes the combined credit and repricing risks.
D) preclude the possibility of sharing in lower interest rates over the three-year period.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. Choosing strategy #3 will
A) guarantee the lowest average annual rate over the next three years.
B) eliminate credit risk but retain repricing risk.
C) maintain the possibility of lower interest costs, but maximizes the combined credit and repricing risks.
D) preclude the possibility of sharing in lower interest rates over the three-year period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
An agreement to exchange interest payments based on a fixed payment for those based on a variable rate (or vice versa) is known as a/an
A) forward rate agreement.
B) interest rate future.
C) interest rate swap.
D) none of the above
A) forward rate agreement.
B) interest rate future.
C) interest rate swap.
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
For the following problem(s), consider these debt strategies being considered by a corporate borrower. Each is intended to provide $1,000,000 in financing for a three-year period.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. After the fact, under which set of circumstances would you prefer strategy #1? (Assume your firm is borrowing money.)
A) Your credit rating stayed the same and interest rates went up.
B) Your credit rating stayed the same and interest rates went down.
C) Your credit rating improved and interest rates went down.
D) Not enough information to make a judgment.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. After the fact, under which set of circumstances would you prefer strategy #1? (Assume your firm is borrowing money.)
A) Your credit rating stayed the same and interest rates went up.
B) Your credit rating stayed the same and interest rates went down.
C) Your credit rating improved and interest rates went down.
D) Not enough information to make a judgment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
For the following problem(s), consider these debt strategies being considered by a corporate borrower. Each is intended to provide $1,000,000 in financing for a three-year period.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. If your firm felt very confident that interest rates would fall or, at worst, remain at current levels, and were very confident about the firm's credit rating for the next 10 years, which strategy (strategies) would you likely choose? (Assume your firm is borrowing money.)
A) Strategy #3
B) Strategy #2
C) Strategy #1
D) Strategy #1, #2, or #3, you are indifferent among the choices.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. If your firm felt very confident that interest rates would fall or, at worst, remain at current levels, and were very confident about the firm's credit rating for the next 10 years, which strategy (strategies) would you likely choose? (Assume your firm is borrowing money.)
A) Strategy #3
B) Strategy #2
C) Strategy #1
D) Strategy #1, #2, or #3, you are indifferent among the choices.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
For the following problem(s), consider these debt strategies being considered by a corporate borrower. Each is intended to provide $1,000,000 in financing for a three-year period.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. The risk of strategy #1 is that interest rates might go down or that your credit rating might improve. The risk of strategy #2 is (Assume your firm is borrowing money.)
A) that interest rates might go down or that your credit rating might improve.
B) that interest rates might go up or that your credit rating might improve.
C) that interest rates might go up or that your credit rating might get worse.
D) none of the above.
• Strategy #1: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a fixed rate of interest of 7%.
• Strategy #2: Borrow $1,000,000 for three years at a floating rate of LIBOR + 2%, to be reset annually. The current LIBOR rate is 3.50%
• Strategy #3: Borrow $1,000,000 for one year at a fixed rate, and then renew the credit annually. The current one-year rate is 5%.
Refer to Instruction 7.1. The risk of strategy #1 is that interest rates might go down or that your credit rating might improve. The risk of strategy #2 is (Assume your firm is borrowing money.)
A) that interest rates might go down or that your credit rating might improve.
B) that interest rates might go up or that your credit rating might improve.
C) that interest rates might go up or that your credit rating might get worse.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
TABLE 7.2
Use the information for Polaris Corporation to answer the following question(s).
Polaris is taking out a $5,000,000 two-year loan at a variable rate of LIBOR plus 1.00%. The LIBOR rate will be reset each year at an agreed upon date. The current LIBOR rate is 4.00% per year. The loan has an upfront fee of 2.00%

Refer to Table 7.2. If the LIBOR rate jumps to 5.00% after the first year what will be the all-in-cost (i.e. the internal rate of return) for Polaris for the entire loan?
A) 5.25%
B) 5.50%
C) 6.09%
D) 6.58%
Use the information for Polaris Corporation to answer the following question(s).
Polaris is taking out a $5,000,000 two-year loan at a variable rate of LIBOR plus 1.00%. The LIBOR rate will be reset each year at an agreed upon date. The current LIBOR rate is 4.00% per year. The loan has an upfront fee of 2.00%

Refer to Table 7.2. If the LIBOR rate jumps to 5.00% after the first year what will be the all-in-cost (i.e. the internal rate of return) for Polaris for the entire loan?
A) 5.25%
B) 5.50%
C) 6.09%
D) 6.58%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Compare and contrast foreign currency options and futures. Identify situations when you may prefer one vs. the other when speculating on foreign exchange.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Which of the following would an MNE NOT want to do?
A) Pay a very low fixed rate of interest in the long term.
B) Swap into a foreign currency payment that is falling in value.
C) Swap into a floating interest rate receivable just prior to interest rates going up.
D) Swap into a fixed interest rate receivable just prior to interest rates going up.
A) Pay a very low fixed rate of interest in the long term.
B) Swap into a foreign currency payment that is falling in value.
C) Swap into a floating interest rate receivable just prior to interest rates going up.
D) Swap into a fixed interest rate receivable just prior to interest rates going up.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
A firm with variable-rate debt that expects interest rates to rise may engage in a swap agreement to
A) pay fixed-rate interest and receive floating rate interest.
B) pay floating rate and receive fixed rate.
C) pay fixed rate and receive fixed rate.
D) pay floating rate and receive floating rate.
A) pay fixed-rate interest and receive floating rate interest.
B) pay floating rate and receive fixed rate.
C) pay fixed rate and receive fixed rate.
D) pay floating rate and receive floating rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
A firm with fixed-rate debt that expects interest rates to fall may engage in a swap agreement to
A) pay fixed-rate interest and receive floating rate interest.
B) pay floating rate and receive fixed rate.
C) pay fixed rate and receive fixed rate.
D) pay floating rate and receive floating rate.
A) pay fixed-rate interest and receive floating rate interest.
B) pay floating rate and receive fixed rate.
C) pay fixed rate and receive fixed rate.
D) pay floating rate and receive floating rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
In option valuation, total value is equal to the intrinsic value plus the time value of the option. Define the latter two terms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Polaris Inc. has a significant amount of bonds outstanding denominated in yen because of the attractive variable rate available to the firm in yen when the loan was made. However, Polaris does not have significant receivables in yen. Options available to Polaris to consider the risk of such a loan include which one of the following?
A) doing nothing to offset the need for yen
B) developing a currency swap of paying dollars and receiving yen
C) developing an interest rate swap of receiving a variable rate while paying a fixed rate
D) Polaris may engage in any of the strategies to a varying degree of effectiveness.
A) doing nothing to offset the need for yen
B) developing a currency swap of paying dollars and receiving yen
C) developing an interest rate swap of receiving a variable rate while paying a fixed rate
D) Polaris may engage in any of the strategies to a varying degree of effectiveness.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
How does counterparty risk influence a firm's decision to trade exchange-traded derivatives rather than over-the-counter derivatives?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Why are foreign currency futures contracts more popular with individuals and banks while foreign currency forwards are more popular with businesses?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
A preferred interest rate swap strategy for a firm with variable-rate debt and that expects rates to go up is to
A) receive floating rate and pay fixed rate.
B) pay floating and receive fixed.
C) pay floating and pay fixed.
D) none of the above.
A) receive floating rate and pay fixed rate.
B) pay floating and receive fixed.
C) pay floating and pay fixed.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Your firm is faced with paying a variable rate debt obligation with the expectation that interest rates are likely to go up. Identify two strategies using interest rate futures and interest rate swaps that could reduce the risk to the firm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








