Deck 13: Game Theory
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/84
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: Game Theory
1
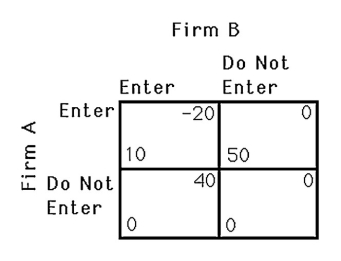
The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,which one of the following statements is true?
A) Only firm A will enter the market.
B) Only firm B will enter the market.
C) Neither firm entering is a Nash equilibrium.
D) The outcome of the game is unpredictable.
A
2

The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,what will happen if the government offers a $30 subsidy to airlines that serve this route?
A) Both firms will enter profitably.
B) Firm A will decide not to enter since firm B will.
C) Firm B is still better off not entering.
D) Neither firm will have a dominant strategy.
A
3
Which of the following games is NOT analyzed with game theory?
A) State Lottery
B) Poker
C) Car Chases
D) Auctions
A) State Lottery
B) Poker
C) Car Chases
D) Auctions
A
4
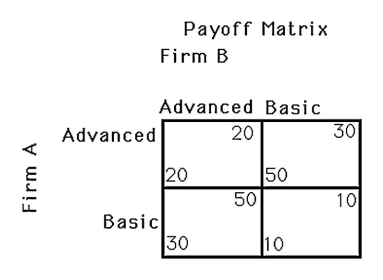
The above figure shows a payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,that must choose between selling basic computers or advanced computers.How many Nash equilibria are there?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
A mixed strategy may
A) be part of a Nash equilibrium.
B) be a set of probabilities of selecting each possible action.
C) lead identical firms to choose different actions.
D) All of the above.
A) be part of a Nash equilibrium.
B) be a set of probabilities of selecting each possible action.
C) lead identical firms to choose different actions.
D) All of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
When neither player has a dominant strategy,
A) game theory will not provide information.
B) no Nash-Equilibrium exists.
C) at least one Nash-Equilibrium exists.
D) the game cannot be analyzed.
A) game theory will not provide information.
B) no Nash-Equilibrium exists.
C) at least one Nash-Equilibrium exists.
D) the game cannot be analyzed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
After analyzing his opponent a tennis player decides to serve 10% of his serves to the left,50% of his serves to the right,and 40% of his serves at the body of his opponent.This illustrates a
A) deterministic strategy.
B) dominant strategy.
C) mixed strategy.
D) non-game theoretic problem.
A) deterministic strategy.
B) dominant strategy.
C) mixed strategy.
D) non-game theoretic problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Game theory shows that
A) sometimes pursuing profit maximization will not yield the highest joint profit.
B) interdependencies between firms have to be taken into account when few firms dominate the market.
C) in an oligopolistic market, firms are likely to collude.
D) All of the above.
A) sometimes pursuing profit maximization will not yield the highest joint profit.
B) interdependencies between firms have to be taken into account when few firms dominate the market.
C) in an oligopolistic market, firms are likely to collude.
D) All of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
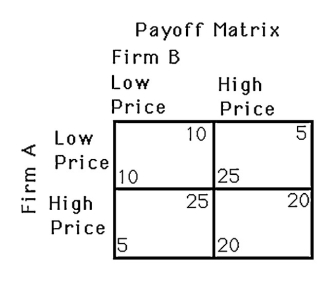
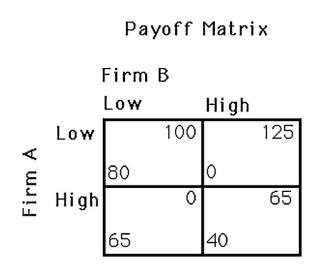
The above figure shows a payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,that must choose between a high-price strategy and a low-price strategy.The Nash equilibrium in this game
A) does not exist.
B) occurs when both firms set a low price.
C) occurs when both firms set a high price.
D) occurs when firm A sets a high price and firm B sets a low price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Chess is an example of a
A) game with perfect information.
B) game with imperfect information.
C) game with incomplete information.
D) static game.
A) game with perfect information.
B) game with imperfect information.
C) game with incomplete information.
D) static game.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
In a two-player simultaneous game,if player A has a dominant strategy and player B does not,player B will
A) employ a mixed strategy.
B) choose his best strategy assuming that player A plays her dominant strategy.
C) not achieve a Nash equilibrium.
D) assume that player A does not choose her dominant strategy.
A) employ a mixed strategy.
B) choose his best strategy assuming that player A plays her dominant strategy.
C) not achieve a Nash equilibrium.
D) assume that player A does not choose her dominant strategy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12

The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,which one of the following statements is true?
A) Firm A has a dominant strategy.
B) Firm B has a dominant strategy.
C) Neither firm entering is a Nash equilibrium.
D) The outcome of the game is unpredictable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13

The above figure shows a payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,that must choose between selling basic computers or advanced computers.Firm B's dominant strategy
A) is to make basic computers.
B) is to make advanced computers.
C) is to adopt firm A's strategy.
D) does not exist in this game.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
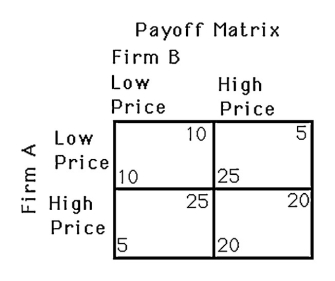
The above figure shows a payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,that must choose between a high-price strategy and a low-price strategy.For firm B,
A) setting a high price is the dominant strategy.
B) setting a low price is the dominant strategy.
C) there is no dominant strategy.
D) doing the opposite of firm A is always the best strategy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15

The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,which one of the following statements is true?
A) Firm A does not have a dominant strategy.
B) Firm B does not have a dominant strategy.
C) Neither firm entering is a Nash equilibrium.
D) The outcome of the game is unpredictable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
What aspects of a game are specified by "the rules of the game"?
A) timing of players' moves
B) payoffs
C) information available to each player
D) All of the above
A) timing of players' moves
B) payoffs
C) information available to each player
D) All of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
For an oligopolistic firm,which of the following can be identified as a strategy?
A) Produce 10,000 units regardless of what the rivals do.
B) Advertise if the rival advertises, do not advertise if the rival does not advertise.
C) Raise the price if the rival raises the price, keep the current price if the rival lowers its price.
D) All of above
A) Produce 10,000 units regardless of what the rivals do.
B) Advertise if the rival advertises, do not advertise if the rival does not advertise.
C) Raise the price if the rival raises the price, keep the current price if the rival lowers its price.
D) All of above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The "Normal-Form" of a game is a description including
A) the players.
B) the strategies possible.
C) the payoffs.
D) All of the above
A) the players.
B) the strategies possible.
C) the payoffs.
D) All of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19

The above figure shows a payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,that must choose between a high-price strategy and a low-price strategy.For firm A,
A) setting a low price is the dominant strategy.
B) setting a high price is the dominant strategy.
C) setting a high price when firm B sets a high price, and setting a low price when firm B sets a low price is the dominant strategy.
D) setting a high price when firm B sets a low price, and setting a low price when firm B sets a high price is the dominant strategy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20

The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,which one of the following statements is true?
A) Since firm B has no dominant strategy, its decision is unpredictable.
B) Since firm B's decision is unpredictable, firm A's decision is unpredictable.
C) Neither firm entering is a Nash equilibrium.
D) Firm B will not enter because it knows firm A will.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
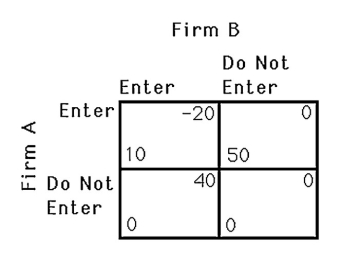
The above figure shows the payoffs to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.Is there a Nash equilibrium? What is it? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22

The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,what will happen if the government offers a $30 subsidy to airlines that serve this route?
A) The Nash equilibrium remains the same.
B) Only firm A will have a dominant strategy.
C) Both firms will choose to enter the market.
D) Joint profts will be maximized.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The above figure shows the payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,selecting an advertising budget.The firms must choose between a high advertising budget and a low advertising budget.Firm A's dominant strategy
A) does not exist.
B) is to do the opposite of firm B.
C) is to select a high advertising budget.
D) is to select a low advertising budget.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24

The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,how many Nash equilibria are there?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) It cannot be determined.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25

The above figure shows the payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,selecting an advertising budget.The firms must choose between a high advertising budget and a low advertising budget.A Nash equilibrium
A) occurs when both firms select a high advertising budget.
B) exists at any of the four possible strategy combinations because there is never an incentive to change strategy.
C) is for both firms to choose the low advertising budget because this yields the highest joint profit.
D) does not exist because firm A does not have a dominant strategy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
A single-period duopoly firm can choose output level A or B.The firm decides it will produce level A regardless of what the other firm produces.This decision may occur because
A) producing the output level A is a dominant strategy.
B) this firm has simply decided to always produce at level A.
C) Both A and B are possible.
D) None of the above.
A) producing the output level A is a dominant strategy.
B) this firm has simply decided to always produce at level A.
C) Both A and B are possible.
D) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
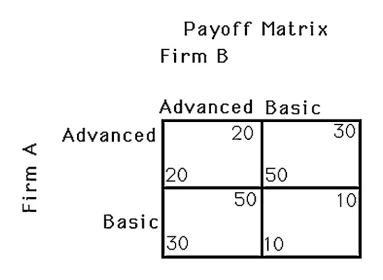
The above figure shows the payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,choosing to produce a basic computer or an advanced computer.The joint profits
A) will be maximized at a Nash equilibrium.
B) will be maximized when both firms take different actions.
C) will be maximized when both firms take the same actions.
D) Both A and B.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28

The above figure shows the payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,choosing to produce a basic computer or an advanced computer.Now the payoff of the firm who produces a basic computer falls to 10 if the other firm chooses to produce an advanced computer.Then the joint profits
A) will be maximized at a Nash equilibrium.
B) will be maximized when both firms take different actions.
C) will be maximized when both firms choose to produce advanced computers.
D) will be maximized when both firms choose to produce basic computers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29

The above figure shows the payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,choosing to produce a basic computer or an advanced computer.Which of the following is a Nash equilibrium?
A) Firm A produces an advanced computer, and firm B produces a basic computer.
B) Both firms produce advanced computers.
C) Both firms produce basic computers.
D) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30

The above figure shows the payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,choosing to produce a basic computer or an advanced computer.How many pure-strategy Nash equilibria are in this game?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
In a non-cooperative,imperfect information,simultaneous-choice,one-period game,a Nash equilibrium
A) will never exist.
B) will always include dominant strategies.
C) will always result in both players taking the same action.
D) may not maximize the sum of the firms' profits.
A) will never exist.
B) will always include dominant strategies.
C) will always result in both players taking the same action.
D) may not maximize the sum of the firms' profits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32

The above figure shows the payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,choosing to produce a basic computer or an advanced computer.Now the payoff of the firm who produces a basic computer falls to 10 if the other firm chooses to produce an advanced computer.Then
A) both firms will have dominant strategies.
B) Nash equilibria will not change.
C) joint profits will be maximized at the Nash equilibrium.
D) Firm A and firm B will choose different actions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33

The above figure shows the payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,choosing to produce a basic computer or an advanced computer.The mixed-strategy Nash equilibrium is
A) Firm A produces an advanced computer with 80% chance, firm B produces an advanced computer with 20% chance.
B) Both firms produce advanced computers with 50% chance.
C) Firm A produces an advanced computer with 60% chance, firm B produces an advanced computer with 40% chance.
D) Both firms produce advanced computer with 80% chance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34

The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,and the government imposes a $20 per firm tax on firms that service this route,which of the following maximizes the firms' joint profits?
A) Neither firm services the route.
B) Firm A offers firm B $20 to not enter.
C) Both firms will service this route.
D) Firm B offers firm A $30 to not enter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35

The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,what happens if the government imposes a $20 per firm tax on firms that service this route?
A) Neither firm has a dominant strategy.
B) Not entering is a dominant strategy for both firms.
C) Neither firm entering is a Nash equilibrium.
D) Only firm A will enter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36

The above figure shows the payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,selecting an advertising budget.The firms must choose between a high advertising budget and a low advertising budget.Firm B's dominant strategy
A) does not exist.
B) is to copy firm A.
C) is to select a high advertising budget.
D) is to select a low advertising budget.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37

The above figure shows the payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,choosing to produce a basic computer or an advanced computer.The dominant strategy for firm A is
A) producing an advanced computer.
B) producing a basic computer.
C) copy firm B's action.
D) Firm A does not have a dominant strategy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Collusion is more likely to occur when
A) there is fear of punishment for not colluding.
B) there is a known finite time horizon.
C) there are large gains to be made by cheating on an agreement.
D) the game lasts only one period.
A) there is fear of punishment for not colluding.
B) there is a known finite time horizon.
C) there are large gains to be made by cheating on an agreement.
D) the game lasts only one period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39

The above figure shows the payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,selecting an advertising budget.The firms must choose between a high advertising budget and a low advertising budget.A Nash equilibrium is that
A) firm A selects a high advertising budget and firm B selects a low advertising budget.
B) firm A selects a low advertising budget and firm B selects a high advertising budget.
C) both firms select a high advertising budget.
D) both firms select a low advertising budget.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
In a simultaneous game where both players prefer doing the opposite of what the opponent does,a Nash equilibrium does not exist.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
13.2 Dynamic Games
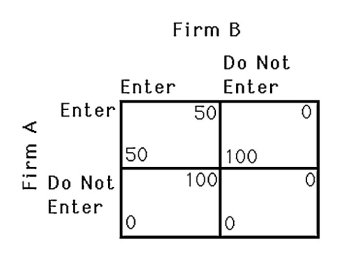
The above figure shows the payoff to two gasoline stations,A and B,deciding to operate in an isolated town.If firm A chooses its strategy first,then
A) firm A will not enter.
B) firm B's entry is blockaded.
C) both firms will enter.
D) firm A will enter and firm B will not.

The above figure shows the payoff to two gasoline stations,A and B,deciding to operate in an isolated town.If firm A chooses its strategy first,then
A) firm A will not enter.
B) firm B's entry is blockaded.
C) both firms will enter.
D) firm A will enter and firm B will not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
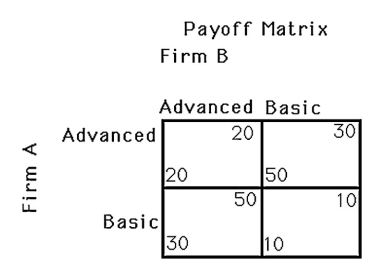
The above figure shows the payoff for two firms,A and B,that must each choose to produce either an advanced computer or a basic computer.Determine the dominant strategies for each firm (if any)and the Nash equilibria (if any).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Explain why to some game theorists,the idea of mixed strategies is appealing,and to others it is implausible.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
An incumbent's threat to retaliate after a potential competitor enters the market will be taken seriously by potential competitors if
A) the incumbent can still earn a profit after carrying out the threat.
B) the incumbent earns greater profit carrying out the threat than by accommodating entry.
C) the potential entrant cannot earn a profit if the threat is carried out.
D) the potential entrant's profit exceeds the incumbent's if the threat is carried out.
A) the incumbent can still earn a profit after carrying out the threat.
B) the incumbent earns greater profit carrying out the threat than by accommodating entry.
C) the potential entrant cannot earn a profit if the threat is carried out.
D) the potential entrant's profit exceeds the incumbent's if the threat is carried out.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Suppose two firms,A and B,are simultaneously considering entry into a new market.If neither enters,both earn zero.If both enter,they both lose 100.If one firm enters,it gains 50 while the other earns zero.Set up the payoff matrix for this game and determine if any Nash equilibria exist.Can you predict the outcome? What if firm A gets to decide first?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
If a player has a dominant strategy in a simultaneous-move game,then she is sure to get her best outcome.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
If neither firm has a dominant strategy,a Nash equilibrium cannot exist.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
13.2 Dynamic Games

The above figure shows the payoff to two gasoline stations,A and B,deciding to operate in an isolated town.Suppose a $30 fee is required to enter the market.If firm A chooses its strategy first,then
A) firm A will not enter.
B) neither firm will enter.
C) both firms will enter.
D) firm A will enter and firm B will not.

The above figure shows the payoff to two gasoline stations,A and B,deciding to operate in an isolated town.Suppose a $30 fee is required to enter the market.If firm A chooses its strategy first,then
A) firm A will not enter.
B) neither firm will enter.
C) both firms will enter.
D) firm A will enter and firm B will not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
All Nash equilibria consist of Dominant Strategies

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Why is collusion more likely in a repeated game?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Consider the following game:
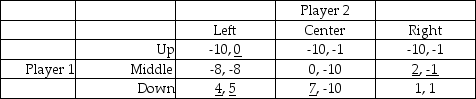
a.Does either player have a dominant strategy? Explain.
b.Use the process of iterated elimination of dominated strategies to reduce the possible outcomes for the game.
c.Find all pure Nash Equilibrium(s).

a.Does either player have a dominant strategy? Explain.
b.Use the process of iterated elimination of dominated strategies to reduce the possible outcomes for the game.
c.Find all pure Nash Equilibrium(s).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
13.2 Dynamic Games

The above figure shows the payoff to two gasoline stations,A and B,deciding to operate in an isolated town.Suppose a $60 fee is required to enter the market.If firm A chooses its strategy first,then
A) firm A will not enter.
B) neither firm will enter.
C) both firms will enter.
D) firm A will enter and firm B will not.

The above figure shows the payoff to two gasoline stations,A and B,deciding to operate in an isolated town.Suppose a $60 fee is required to enter the market.If firm A chooses its strategy first,then
A) firm A will not enter.
B) neither firm will enter.
C) both firms will enter.
D) firm A will enter and firm B will not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The following is a simplified duopoly model of competition between two firms.Firms simultaneously choose the quantity of outputs to produce,and then profits are realized.Each firm is restricted to producing 25,35,50 or 100 units of output.The details of how the payoffs are derived are unimportant because payoffs are all given in the table below.
Firm 2

Find the Nash equilibrium(s)in the game.
Firm 2

Find the Nash equilibrium(s)in the game.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
All normal-form games have at least one dominant strategy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
If each player has a dominant strategy,then those strategies make up the Nash equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
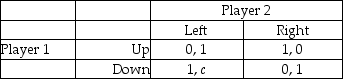
a.Suppose c = 0.Find any (pure strategy)Nash Equilibrium.
b.Suppose c = 2.Find any (pure strategy)Nash Equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Consider two agents simultaneously deciding whether to contribute to a public good - the good is said to be public because,if it is made available,an agent who free-rides by paying nothing gets just as much pleasure from its enjoyment as an agent who paid for it.If at least one agent contributes to the construction of the public good,both agents will enjoy a payoff of four from the public good.To ensure the public good is constructed,player one must pay c₁ or player two must pay c₂.Assume that c₁ < 4 and c₂ < 4.If neither contributes,the good is not constructed and neither player gets enjoyment from the project.If one or both players contribute,then the good is constructed and each player enjoys a payoff of four minus the contribution cost if that player has contributed.The grid below shows this:

Assume that the costs are common knowledge to both players.
a.Find any pure-strategy Nash Equilibrium(s)to the game.
b.Find the Mixed Strategy Nash Equilibrium - the probabilities you find will be functions of the cost parameters.
c.If c₁ = c₂ = 1,write out the mixed strategy NE and find the probability that the public good is provided?
d.If c₁ = c₂ = 3,write out the mixed strategy NE and find the probability that the public good is provided?

Assume that the costs are common knowledge to both players.
a.Find any pure-strategy Nash Equilibrium(s)to the game.
b.Find the Mixed Strategy Nash Equilibrium - the probabilities you find will be functions of the cost parameters.
c.If c₁ = c₂ = 1,write out the mixed strategy NE and find the probability that the public good is provided?
d.If c₁ = c₂ = 3,write out the mixed strategy NE and find the probability that the public good is provided?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
If only one firm operates in a market,and a potential entrant is blockaded from entering the market,then the incumbent firm must
A) have acted to prevent entry.
B) be pricing where price equals marginal cost.
C) be a natural monopoly.
D) be the Stackelberg leader.
A) have acted to prevent entry.
B) be pricing where price equals marginal cost.
C) be a natural monopoly.
D) be the Stackelberg leader.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
A Nash equilibrium will always provide both players with their highest payoffs possible.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
With regard to preventing entry,if identical firms act simultaneously,
A) they cannot credibly threaten each other.
B) they will all incur losses.
C) only one firm will enter the market.
D) none of them will enter the market.
A) they cannot credibly threaten each other.
B) they will all incur losses.
C) only one firm will enter the market.
D) none of them will enter the market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Consider the game below:
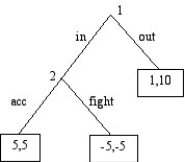
a.Use backward induction to find the subgame perfect Nash equilibrium to the game.
b.Model the game with a strategic grid.Find all Nash Equilibrium to the normal-form game.Why is your answer different than in (a)?

a.Use backward induction to find the subgame perfect Nash equilibrium to the game.
b.Model the game with a strategic grid.Find all Nash Equilibrium to the normal-form game.Why is your answer different than in (a)?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
A private auction is an auction in which
A) individuals know their own value of the good and everyone else's valuation, too.
B) individuals have their own valuation of the good but don't know everyone else's.
C) many auctions are auctioned off at the same time.
D) only one good is auctioned off.
A) individuals know their own value of the good and everyone else's valuation, too.
B) individuals have their own valuation of the good but don't know everyone else's.
C) many auctions are auctioned off at the same time.
D) only one good is auctioned off.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
A sale in which property or a service is sold to the highest bidder is called a(n)
A) auction.
B) bidder sale.
C) competitive market.
D) Austrian bundle.
A) auction.
B) bidder sale.
C) competitive market.
D) Austrian bundle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The individual with the highest valuation of the good will win in which of the following auctions?
A) English Auction
B) Dutch Auction
C) Sealed Bid Auction
D) All of the above.
A) English Auction
B) Dutch Auction
C) Sealed Bid Auction
D) All of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Suppose market demand is p = 10 - Q.Firms incur no cost of production.If firm A is the incumbent,can it deter the entry of its rival,firm B?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
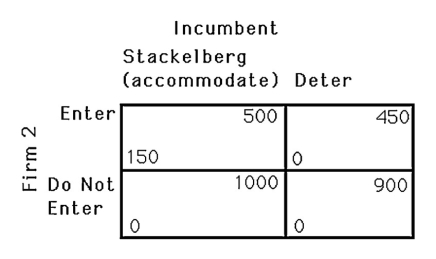
The above figure shows the payoffs to two firms deciding to open a gasoline station in an isolated town.If firm A decides first,what will happen? If there is a $60 fee to enter this market,what will happen?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Fixed costs of entry create an advantage for potential entrants since incumbents have already made these expenditures while potential entrants can avoid these costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
The Internet auction site eBay is an example of a(n)
A) Sealed Bid Auction.
B) Second-Price Auction.
C) English Auction.
D) both A and B.
A) Sealed Bid Auction.
B) Second-Price Auction.
C) English Auction.
D) both A and B.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
The result that different auction styles in which the good goes to the winner with the highest valuation of the good generate the same amount of revenue is called
A) Revenue Equivalence Theorem.
B) Marginal Revenue Theory.
C) Auction Revenue Theory.
D) First Bid Revenue Theorem.
A) Revenue Equivalence Theorem.
B) Marginal Revenue Theory.
C) Auction Revenue Theory.
D) First Bid Revenue Theorem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
How can a firm be made better off by limiting its options?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71

The above figure shows the payoff matrix facing an incumbent firm.Assuming a fixed cost of entry,will the incumbent deter entry? Why?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
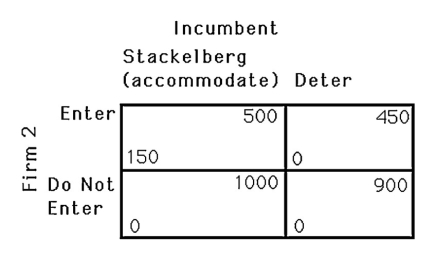
The above figure shows the payoff matrix facing an incumbent firm and a potential entrant.Assuming a fixed cost of entry,the incumbent will deter entry because
A) it is more profitable than accommodating entry.
B) it increases consumer surplus.
C) the potential entrant winds up with zero profit.
D) the incumbent would earn zero profit if it accommodated entry.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73

The above figure shows the payoff matrix facing an incumbent firm and a potential entrant.The potential entrant cannot earn a profit if the incumbent
A) chooses the Cournot level of output.
B) chooses the Stackelberg leader level of output.
C) shuts down.
D) deters entry.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Consider the following sequential move game:
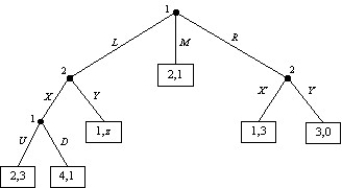
A)If z=0,find any subgame perfect NE.
B)For what values of z will M occur in the subgame perfect equilibrium?

A)If z=0,find any subgame perfect NE.
B)For what values of z will M occur in the subgame perfect equilibrium?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
An auction in which the price announced by the auctioneer DESCENDS is called a
A) Dutch Auction.
B) English Auction.
C) Sealed Bid Auction.
D) Descending Option Auction.
A) Dutch Auction.
B) English Auction.
C) Sealed Bid Auction.
D) Descending Option Auction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Suppose market demand is p = 10 - Q.Firms have a fixed cost of five and no marginal cost.If firm A is the incumbent,can it deter the entry of its rival,firm B?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77

The above figure shows the payoff matrix facing an incumbent firm and a potential entrant.Assuming a fixed cost of entry,the outcome will be that the incumbent
A) deters entry.
B) chooses the Stackelberg leader level of output but the potential entrant does not enter anyway.
C) chooses the Stackelberg leader level of output and the potential entrant enters.
D) deters entry and earns zero profit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78

The above figure shows the payoff matrix facing an incumbent firm and a potential entrant.If the fixed cost of entry were to increase,which of the following would occur?
A) The incumbent chooses the Cournot level of output.
B) The incumbent shuts down.
C) The entry-deterring level of output rises.
D) The entry-deterring level of output falls.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
An incumbent announces it will significantly increase output in the next period,but only has contracts for the amount produced this period.The announcement is a
A) credible threat.
B) non-credible threat.
C) commitment.
D) mixed strategy.
A) credible threat.
B) non-credible threat.
C) commitment.
D) mixed strategy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Two identical firms are considering entering a new market that currently has no suppliers.The demand is large enough for both firms to make a positive profit.There are no fixed costs to enter.Explain how a simultaneous decision to enter on the part of the two firms will lead to a different outcome than a sequential entry decision.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








