Deck 7: Uncertainty Applications and Criticisms
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 7: Uncertainty Applications and Criticisms
1
A decrease in variance makes a gamble _______ attractive.
A) less
B) equally
C) more
A) less
B) equally
C) more
more
2
A method of avoiding risk whereby groups come together to form a pool so as to share a risk if anyone in the group experiences a negative event is known as
A) risk pooling
B) self-insurance
C) Both answers are correct
A) risk pooling
B) self-insurance
C) Both answers are correct
Both answers are correct
3
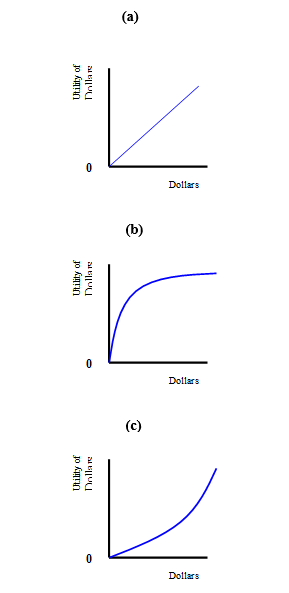
Refer to Exhibit 7-1. Elizabeth is risk preferring; therefore, her utility function most likely looks like Curve (c).
True
4
Risk pooling or self-insurance is a method of avoiding risk whereby groups come together to form a pool so as to share a risk if anyone in the group experiences a negative event.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
A risk-preferring person such as Elizabeth would be willing to sell insurance at a price
A) of zero
B) This question cannot be answered without knowing the exact shapes of the utility functions
C) at which Elizabeth is indifferent between not insuring a Geoffrey and insuring him
A) of zero
B) This question cannot be answered without knowing the exact shapes of the utility functions
C) at which Elizabeth is indifferent between not insuring a Geoffrey and insuring him

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Because of the anomalies pointed out by Kahneman and Tversky, the expected utility theory is not a useful tool to help us organize our thinking about economic decision making under conditions of uncertainty.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
If a risk-averse agent is faced with two gambles, both of which have the same expected monetary return but different variances, the agent will always choose the gamble whose variance is
A) greater
B) smaller
C) equivalent
A) greater
B) smaller
C) equivalent

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Status quo bias is the term given to the fact that people have resistance to changing their current situations even if the new one offered to them is better.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
People are more likely to buy insurance if they are
A) risk averse
B) risk preferring
C) risk neutral
A) risk averse
B) risk preferring
C) risk neutral

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
There ___________________ trading gains to be made in the sale of insurance policies.
A) randomly are or are not
B) are clearly
C) clearly are not
A) randomly are or are not
B) are clearly
C) clearly are not

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The proposition that states that, if a risk-averse agent is faced with two gambles, both of which have the same expected monetary return but different variances, the agent will choose the gamble whose variance is smaller is known as the mean-preserving spread proposition.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Risk pooling can cut the variance of losses while keeping the mean intact. Hence, according to the mean-preserving spread proposition, agents will be _____________ with risk pooling than without it.
A) worse off
B) better off
C) no better or worse off
A) worse off
B) better off
C) no better or worse off

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13

Refer to Exhibit 7-1. Geoffrey is risk averse; therefore, his utility function most likely looks like Curve (a).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The reflection effect predicts that changing the sign on a set of choices will result in people's changing their preferences, even if the final outcomes and the probabilities attached to them are the same.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
People tend to think that low probability events are more likely than they are.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
People are more likely to sell insurance if they are
A) risk averse
B) risk preferring
C) risk neutral
A) risk averse
B) risk preferring
C) risk neutral

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The Linda Problem demonstrates violations of the conjunction law.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The Ellsberg Paradox illustrates ambiguity aversion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
As the population in the risk pool grows larger, the variance in the mean loss approaches
A) positive infinity
B) zero
C) negative infinity
A) positive infinity
B) zero
C) negative infinity

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The profitability of insurance exists because
A) people have identical attitudes toward risk
B) big insurance companies always charge extremely high rates
C) people have different attitudes toward risk
A) people have identical attitudes toward risk
B) big insurance companies always charge extremely high rates
C) people have different attitudes toward risk

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Expected utility theory requires that people
A) assess probabilities in an unbiased manner
B) obey all of the theory's axioms for assigning utilities to outcomes
C) Both answers are correct
A) assess probabilities in an unbiased manner
B) obey all of the theory's axioms for assigning utilities to outcomes
C) Both answers are correct

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Firms will continue to enter the insurance industry as long as
A) uncertainty exists
B) there are profits to be made in selling insurance
C) the population in the risk pool remains very small
A) uncertainty exists
B) there are profits to be made in selling insurance
C) the population in the risk pool remains very small

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
In a survey of university hospital employees, when the insurance causes are broken down to individual cases, people tend to overestimate the probability of each case happening. This is an example of
A) the effect of isolating vivid causes
B) status quo bias
C) the mean-preserving spread proposition
A) the effect of isolating vivid causes
B) status quo bias
C) the mean-preserving spread proposition

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
People tend to
A) make a distinction between events that are certain and those that are close to, but are not certain
B) think that low probability events are less likely than they are
C) overplay or overweigh events that are close to, but are not certain
A) make a distinction between events that are certain and those that are close to, but are not certain
B) think that low probability events are less likely than they are
C) overplay or overweigh events that are close to, but are not certain

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Researchers who study the application of neuroscience to economics are known as
A) brain surgeons
B) mad monkey doctors
C) neuroeconomists
A) brain surgeons
B) mad monkey doctors
C) neuroeconomists

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
While the marginal utility of increments from the status quo is considered to be _____________, the marginal utility of decrements below the status quo is _____________.
A) decreasing, increasing
B) increasing, decreasing
C) decreasing, constant
A) decreasing, increasing
B) increasing, decreasing
C) decreasing, constant

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Explain how a risk-averse buyer of insurance obeys the mean-preserving spread proposition.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
As a society's agents face the uncertainties in their lives and try to come to terms with these uncertainties,
A) insurance and an insurance industry will emerge
B) the agents will give up hope of success
C) gambling will strenghten as a social disease
A) insurance and an insurance industry will emerge
B) the agents will give up hope of success
C) gambling will strenghten as a social disease

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
This is gamble 1: do you prefer a sure win of $5 or a 75% chance to win $8? This is gamble 2: in the first stage, you have an 80% chance to end the game with no prize and a 20% chance to move to the second stage. Before completing the first stage, you must select one of the following second-stage choices: do you prefer a sure win of $5 or a 75% chance to win $8? This is gamble 3: do you prefer a 20% chance to win $5 or a 15% chance to win $8? Which two of the preceding gambles are identical?
A) gamble 1 and 2
B) gamble 2 and 3
C) gamble 1 and 3
A) gamble 1 and 2
B) gamble 2 and 3
C) gamble 1 and 3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Why use the expected utility theory?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Tina Sierra investigated a fight outside a college classroom. At this college, 75 percent of the students are female and 25 percent are male. Bob, a witness, testified that a male started the fight. After testing, Tina determined that Bob correctly identifies a person's gender 90 percent of the time. Tina concluded that there was a 90 percent chance that a male started the fight. Her mistake is a(n)
A) use of nonlinear probability weights
B) violation of base rates
C) framing error
A) use of nonlinear probability weights
B) violation of base rates
C) framing error

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The Ellsberg Paradox is an example of
A) violations of the conjunction law
B) ambiguity aversion
C) violation of base rates
A) violations of the conjunction law
B) ambiguity aversion
C) violation of base rates

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
When people use ____________ probability weights, people assign too _________ weight to very low probabilities and too _________ to high probabilities.
A) nonlinear, little, much
B) nonlinear, much, little
C) linear, much, little
A) nonlinear, little, much
B) nonlinear, much, little
C) linear, much, little

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Describe the difference between linear and nonlinear probability weights.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Kahneman and Tversky suggest that the way people go about assigning values to utilities of prizes is by
A) defiining for themselves a status quo outcome only
B) judging all outcomes other than the status quo as either gains or losses from the status quo only
C) defiining for themselves a status quo outcome and judging all outcomes other than the status quo as either gains or losses from the status quo
A) defiining for themselves a status quo outcome only
B) judging all outcomes other than the status quo as either gains or losses from the status quo only
C) defiining for themselves a status quo outcome and judging all outcomes other than the status quo as either gains or losses from the status quo

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
This is gamble 1: do you prefer a sure win of $5 or a 75% chance to win $8? This is gamble 2: in the first stage, you have an 80% chance to end the game with no prize and a 20% chance to move to the second stage. Before completing the first stage, you must select one of the following second-stage choices: do you prefer a sure win of $5 or a 75% chance to win $8? This is gamble 3: do you prefer a 20% chance to win $5 or a 15% chance to win $8? Because of framing, which two of the gambles do people tend to treat incorrectly as identical?
A) gamble 1 and 2
B) gamble 2 and 3
C) gamble 1 and 3
A) gamble 1 and 2
B) gamble 2 and 3
C) gamble 1 and 3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
What is Linda's problem?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The Linda Problem is an example of
A) violations of the conjunction law
B) ambiguity aversion
C) violation of base rates
A) violations of the conjunction law
B) ambiguity aversion
C) violation of base rates

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Describe the trading gains to be made in the sale of insurance policies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Kahneman and Tversky concluded that people
A) maximize their expected utility by multiplying it by probabilities
B) use probability weights in place of raw probabilities
C) process probabilities in an unbiased and unemotional manner
A) maximize their expected utility by multiplying it by probabilities
B) use probability weights in place of raw probabilities
C) process probabilities in an unbiased and unemotional manner

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








