Deck 13: Policy Governance and Political Economy
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/28
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: Policy Governance and Political Economy
1
Figure 13.1
Private Choices Regarding How Much of an Activity to Undertake
(a) (b) (c)
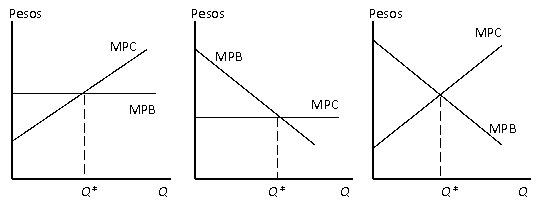
How can we explain the increasing MPC curve in figure 13.1 a?.
A) Increasing marginal returns to labor
B) Increasing marginal returns to production
C) Diminishing marginal returns to production
D) Diminishing marginal returns to consumption
Private Choices Regarding How Much of an Activity to Undertake
(a) (b) (c)

How can we explain the increasing MPC curve in figure 13.1 a?.
A) Increasing marginal returns to labor
B) Increasing marginal returns to production
C) Diminishing marginal returns to production
D) Diminishing marginal returns to consumption
C
2
Policymakers would like to create institutions that provide good governance,that is:
A) They want to divert as many resources as possible toward their policy
B) They want to ensure success of their policy
C) They would like to eliminate agents who rarely offer anything beneficial
D) They would like to guide agents into productive exercise of their discretion
A) They want to divert as many resources as possible toward their policy
B) They want to ensure success of their policy
C) They would like to eliminate agents who rarely offer anything beneficial
D) They would like to guide agents into productive exercise of their discretion
D
3
Government policies have the potential to overcome private market barriers and improve development outcomes; all of the following are reasons why many policies observed in practice fail to achieve their potential except:
A) They are poorly designed
B) Policy makers pursue selfish interests
C) They are poorly implemented
D) They distort private market outcomes
A) They are poorly designed
B) Policy makers pursue selfish interests
C) They are poorly implemented
D) They distort private market outcomes
D
4
Even in the absence of intervention by governments,people make many choices that contribute to development.Which of the following examples will not contribute to development?
A) Household save and invest to build a better future for their children
B) Households specialize and engage in mutually beneficial trade
C) Public good problems give way to free riders in infrastructure projects
D) Households use financial markets to cope with risk and vulnerability
A) Household save and invest to build a better future for their children
B) Households specialize and engage in mutually beneficial trade
C) Public good problems give way to free riders in infrastructure projects
D) Households use financial markets to cope with risk and vulnerability

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
When choosing how much of an activity to undertake,such as how much corn to produce,a private decision-maker assesses the marginal private benefit (MPB)and the marginal private cost (MPC)of each additional unit,and chooses the quantity of activity at which the ____________.
A) MPS just exceed the MPC
B) The MPC just exceed the MPS
C) The MPC and the MPS are equal
D) The private benefits outweigh the private costs
A) MPS just exceed the MPC
B) The MPC just exceed the MPS
C) The MPC and the MPS are equal
D) The private benefits outweigh the private costs

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Public goods are:
A) Rival and non-excludable
B) Rival and excludable
C) Non-rival and non-excludable
D) Non-rival and excludable
A) Rival and non-excludable
B) Rival and excludable
C) Non-rival and non-excludable
D) Non-rival and excludable

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The decision-maker maximizes the activity's net contribution to his ________ by choosing the quantity Q* at which the MPB just _____ the MPC.
A) Net worth; equals
B) Well-being; equals
C) Total surplus; exceeds
D) Consumer surplus; exceeds
A) Net worth; equals
B) Well-being; equals
C) Total surplus; exceeds
D) Consumer surplus; exceeds

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Positive externalities imply _________by others,that private actors cannot appropriate,and result in a tendency for private actors to undertake _______ of the activity.
A) Costs experienced; too much
B) Benefits enjoyed; too much
C) Benefits enjoyed; too little
D) Costs experienced; too little
A) Costs experienced; too much
B) Benefits enjoyed; too much
C) Benefits enjoyed; too little
D) Costs experienced; too little

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Under which of the following market structures do producers take the price as given?
A) Monopoly
B) Oligopoly
C) Perfect competition
D) Monopolistic competition
A) Monopoly
B) Oligopoly
C) Perfect competition
D) Monopolistic competition

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
When consumption by one person does not reduce the potential for consumption by others good is said to be ___________.
A) Rival
B) Non-rival
C) Excludable
D) Non-excludable
A) Rival
B) Non-rival
C) Excludable
D) Non-excludable

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Figure 13.2
Private and Socially Ideal Choices when
Marginal Social Benefit Exceeds Marginal Private Benefit
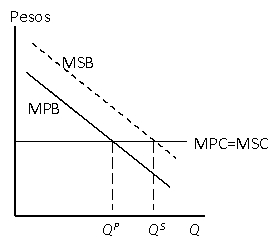
According to figure 13.2 if the market is unregulated:
A) The private decision-maker only considers his marginal private benefit and the quantity consumed will be QP
B) The private decision-maker only considers his marginal private benefit and the quantity consumed will be Qs
C) The social decision-maker considers the marginal social benefit and the quantity consumed will be QP
D) The private decision-maker considers his marginal social benefit and the quantity consumed will be QP
Private and Socially Ideal Choices when
Marginal Social Benefit Exceeds Marginal Private Benefit

According to figure 13.2 if the market is unregulated:
A) The private decision-maker only considers his marginal private benefit and the quantity consumed will be QP
B) The private decision-maker only considers his marginal private benefit and the quantity consumed will be Qs
C) The social decision-maker considers the marginal social benefit and the quantity consumed will be QP
D) The private decision-maker considers his marginal social benefit and the quantity consumed will be QP

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The benefits a private decision-maker can appropriate are the:
A) Efficient amount of benefits a policy can bring
B) Benefits at the socially optimal quantity
C) Benefits he can claim for himself and dispose of as he wishes.
D) Benefits a social planner assigns to a participant in a program
A) Efficient amount of benefits a policy can bring
B) Benefits at the socially optimal quantity
C) Benefits he can claim for himself and dispose of as he wishes.
D) Benefits a social planner assigns to a participant in a program

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A rationale for intervention is a reason why ______________,guided only by markets and private institutions,might make ____________ choices.This means that,compared to some societal ideal,they choose to __________________ of some activity.
A) Private actors; socially suboptimal; do either too little or too much
B) Public actors; socially optimal; do too much
C) Private actors; privately suboptimal; do too little
D) Public actors; socially suboptimal; do too little
A) Private actors; socially suboptimal; do either too little or too much
B) Public actors; socially optimal; do too much
C) Private actors; privately suboptimal; do too little
D) Public actors; socially suboptimal; do too little

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Negative externalities imply _________by others,that private actors do not bear,and result in a tendency for private actors to undertake _______ of the activity.
A) Costs experienced; too much
B) Benefits enjoyed; too much
C) Benefits enjoyed; too little
D) Costs experienced; too little
A) Costs experienced; too much
B) Benefits enjoyed; too much
C) Benefits enjoyed; too little
D) Costs experienced; too little

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The marginal social cost (MSC)is:
A) The private cost of producing one more unit
B) The benefit from producing one more unit
C) Total cost to society from producing one more unit
D) The reduction in the decision makers living standards when one more unit is produced
A) The private cost of producing one more unit
B) The benefit from producing one more unit
C) Total cost to society from producing one more unit
D) The reduction in the decision makers living standards when one more unit is produced

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Figure 13.1
Private Choices Regarding How Much of an Activity to Undertake
(a) (b) (c)

According to figure 13.1 which of the figures depict a household that face perfectly competitive markets to that the Marginal private benefit is just the price.
A) Figure a
B) Figures a and b
C) Figures b and c
D) Figure c
Private Choices Regarding How Much of an Activity to Undertake
(a) (b) (c)

According to figure 13.1 which of the figures depict a household that face perfectly competitive markets to that the Marginal private benefit is just the price.
A) Figure a
B) Figures a and b
C) Figures b and c
D) Figure c

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
When the social decision-maker perceives benefits to each unit of an activity that the private decision-maker does not (in addition to the benefits the private decision-maker perceives),the __________________.
A) The marginal social benefit (MSB) lies above the marginal private benefit (MPB)
B) The marginal private cost (MPC) lies above the marginal social cost
C) The marginal private benefit (MPB) lies above the marginal social benefit (MSB)
D) The marginal private benefit (MPB) lies above the marginal private cost (MPC)
A) The marginal social benefit (MSB) lies above the marginal private benefit (MPB)
B) The marginal private cost (MPC) lies above the marginal social cost
C) The marginal private benefit (MPB) lies above the marginal social benefit (MSB)
D) The marginal private benefit (MPB) lies above the marginal private cost (MPC)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
When choosing whether or not to undertake a _________________,such as adopting a new technology or vaccinating a child,a private decision-maker chooses to undertake the activity if he is aware of the opportunity and if he judges that the ______________ outweigh the _________.
A) Non-discrete activity; private benefits; private costs
B) Non-discrete activity; marginal social benefits; marginal social costs
C) Discrete activity; private benefits; private costs
D) Discrete activity; marginal private benefits; marginal private costs
A) Non-discrete activity; private benefits; private costs
B) Non-discrete activity; marginal social benefits; marginal social costs
C) Discrete activity; private benefits; private costs
D) Discrete activity; marginal private benefits; marginal private costs

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Common property resources are:
A) Non-rival and non-excludable
B) Rival and non-excludable
C) Rival and excludable
D) Non-rival and excludable
A) Non-rival and non-excludable
B) Rival and non-excludable
C) Rival and excludable
D) Non-rival and excludable

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Figure 13.2
Private and Socially Ideal Choices when
Marginal Social Benefit Exceeds Marginal Private Benefit

According to figure 13.2:
A) The private decision-maker perceives benefits to each unit of an activity that the social decision-maker does not
B) The private decision-maker perceives costs to each unit of an activity that the social decision-maker does not
C) The social decision-maker perceives costs to each unit of an activity that the private decision maker does not
D) The social decision-maker perceives benefits to each unit of an activity that the private decision-maker does not
Private and Socially Ideal Choices when
Marginal Social Benefit Exceeds Marginal Private Benefit

According to figure 13.2:
A) The private decision-maker perceives benefits to each unit of an activity that the social decision-maker does not
B) The private decision-maker perceives costs to each unit of an activity that the social decision-maker does not
C) The social decision-maker perceives costs to each unit of an activity that the private decision maker does not
D) The social decision-maker perceives benefits to each unit of an activity that the private decision-maker does not

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Why is the consolidation of power likely to reduce development outcomes?
A) There is a strong temptation to pursue person interests
B) It requires strong character to avoid corruption
C) Healthy political institutions find a way to constrain the policymakers' use of consolidated power
D) All of the above
A) There is a strong temptation to pursue person interests
B) It requires strong character to avoid corruption
C) Healthy political institutions find a way to constrain the policymakers' use of consolidated power
D) All of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
How can foreign aid do more harm than good,from a development standpoint?
A) When it adds to corruption
B) When the majority of the aid does not reach its target population
C) By financing investment in the wrong types areas.
D) By weakening society's capacity to hold policy makers accountable
A) When it adds to corruption
B) When the majority of the aid does not reach its target population
C) By financing investment in the wrong types areas.
D) By weakening society's capacity to hold policy makers accountable

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Under demand-side financing arrangements,the government provides citizens with financial means to ______ services or goods (e.g.education services or food)_________,rather than providing the services or goods ______.?
A) Sell; to competitive private buyers; directly
B) Sell; to government buyers; indirectly
C) Purchase; from competitive private sellers; directly
D) Purchase; from government suppliers; indirectly
A) Sell; to competitive private buyers; directly
B) Sell; to government buyers; indirectly
C) Purchase; from competitive private sellers; directly
D) Purchase; from government suppliers; indirectly

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
How might private institutions succeed in providing public goods where markets fail? Is this likely to succeed?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
How can agents be held accountable for their choices and under what conditions will various schemes work to ensure feasible accountability?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Good policy implementation choices require varying combinations of what five key "inputs"?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
How can an agent be held accountable for their choices?
A) By hiring agents under a performance contract with superiors to monitor performance
B) By hiring agents under a performance contract with only self-supervision to monitor performance
C) Through competition when clients have no say in their agents choices
D) All of the above
A) By hiring agents under a performance contract with superiors to monitor performance
B) By hiring agents under a performance contract with only self-supervision to monitor performance
C) Through competition when clients have no say in their agents choices
D) All of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Interest groups derive their ________ from their economic power and from the ________of their organization?
A) Political power; efficiency
B) Political power; effectiveness
C) Political institutions; efficiency
D) Political institutions; effectiveness
A) Political power; efficiency
B) Political power; effectiveness
C) Political institutions; efficiency
D) Political institutions; effectiveness

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








