Deck 5: Network Models
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 5: Network Models
1
In transportation problems,shipments between supply points or between demand points are possible.
False
2
The network model representation of the transportation problem has the following advantage relative to the special case of a simple transportation model:
A) it does not require capacity restrictions on the arcs of the network
B) the flows in the network model don't all necessarily have to be from supply locations to demand locations
C) a network model representation is generally easier to formulate and solve
D) All of these options
A) it does not require capacity restrictions on the arcs of the network
B) the flows in the network model don't all necessarily have to be from supply locations to demand locations
C) a network model representation is generally easier to formulate and solve
D) All of these options
B
3
Transshipment points are locations where goods neither originate nor end up,but goods are allowed to enter such points to be shipped out to their eventual destinations.
True
4
The cost of an arc in a shortest path problem is not necessarily equal to the distance of the arc.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
A typical shortest path problem is a special case of the general network flow model.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
In a typical network model representation of the transportation problem,the nodes indicate
A) roads
B) rail lines
C) geographic locations
D) rivers
A) roads
B) rail lines
C) geographic locations
D) rivers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
For all routes with positive flows in an optimized transportation problem,the reduced cost will be:
A) zero
B) how much less shipping costs would have to be for shipments to occur along that route
C) how much more shipping costs would have to be for shipments to occur along that route
D) how much the capacity is along that shipping route
A) zero
B) how much less shipping costs would have to be for shipments to occur along that route
C) how much more shipping costs would have to be for shipments to occur along that route
D) how much the capacity is along that shipping route

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The decision variables in transportation problems are:
A) profits
B) costs
C) flows
D) capacities
A) profits
B) costs
C) flows
D) capacities

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
In a general logistics model that minimizes the cost of network flow,the flow balance constraint for each supply node has the form
A) Flow in ≥ Flow out + Net supply
B) Flow out ≥ Flow in + Net demand
C) Flow in = Flow out
D) Flow out ≤ Flow in + Net supply
E) Flow in ≤ Flow out + Net demand
A) Flow in ≥ Flow out + Net supply
B) Flow out ≥ Flow in + Net demand
C) Flow in = Flow out
D) Flow out ≤ Flow in + Net supply
E) Flow in ≤ Flow out + Net demand

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The objective in transportation problems is typically to:
A) maximize profits
B) maximize revenue
C) minimize costs
D) maximize feasibility
A) maximize profits
B) maximize revenue
C) minimize costs
D) maximize feasibility

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
In an optimized shipping plan,most of the shipments occur on the low-cost routes,but this is not always the case.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of the following is not an example of a condition that a more complex logistics model might include
A) Multiple products
B) Multiple modes of transportation
C) Multiple time periods
D) Multiple objectives
A) Multiple products
B) Multiple modes of transportation
C) Multiple time periods
D) Multiple objectives

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
In transportation problems,the three sets of input numbers that are required are capacities,demands and flows.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The graphical representation of a network in an optimization problem can be an aid in the development of a spreadsheet model.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The flow balance constraint for each transshipment node in a network flow model has the form Flow in = Flow out.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
In an assignment model of machines to jobs,the machines are analogous to which of the following in a transportation problem
A) Suppliers
B) Customers
C) Flows
D) Unit capacities
A) Suppliers
B) Customers
C) Flows
D) Unit capacities

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
It is useful to model network problems by listing all of the arcs and their corresponding flows in one long,comprehensive list.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
In network models of transportation problems,arcs represent the routes for getting a product from one node to another.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
A particularly useful Excel function in the formulation of transportation problems is the:
A) IF function
B) SUMIF function
C) SUMPRODUCT function
D) NPV function
A) IF function
B) SUMIF function
C) SUMPRODUCT function
D) NPV function

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Problems which deal with the direct distribution of products from supply locations to demand locations are called:
A) transportation problems
B) assignment problems
C) network problems
D) transshipment problems
A) transportation problems
B) assignment problems
C) network problems
D) transshipment problems

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
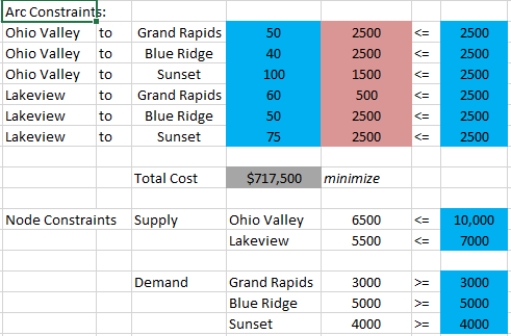
Exhibit 5-1
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month. Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants, Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month), Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month), and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month). The costs of shipping between the respective plants is shown in the table below:
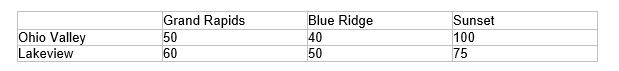
Refer to Exhibit 5-1.Implement the LP model in Solver and obtain the optimal shipping plan.What is the optimized cost
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month. Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants, Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month), Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month), and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month). The costs of shipping between the respective plants is shown in the table below:

Refer to Exhibit 5-1.Implement the LP model in Solver and obtain the optimal shipping plan.What is the optimized cost

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Exhibit 5-3
Steve the auto parts salesman is trying to navigate his way between the rural west Texas towns of Jonestown and Upland. The possible routes for this trip are shown below, along with the mileage along each route.
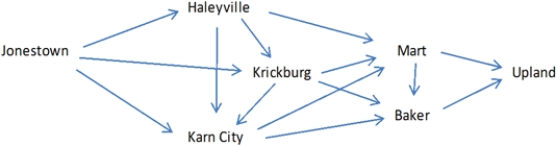
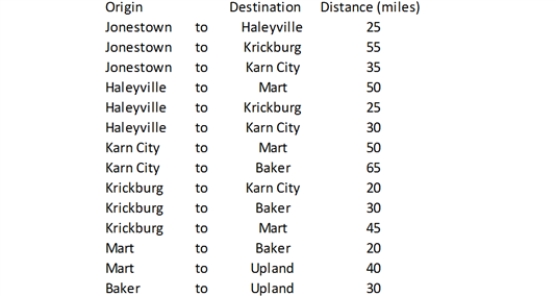
Refer to Exhibit 5-3.Implement the appropriate model in Solver and determine the shortest path for Steve.How many total miles will he travel on his trip
Steve the auto parts salesman is trying to navigate his way between the rural west Texas towns of Jonestown and Upland. The possible routes for this trip are shown below, along with the mileage along each route.


Refer to Exhibit 5-3.Implement the appropriate model in Solver and determine the shortest path for Steve.How many total miles will he travel on his trip

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Exhibit 5-1
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month. Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants, Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month), Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month), and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month). The costs of shipping between the respective plants is shown in the table below:

Refer to Exhibit 5-1.Formulate (write out algebraically)an LP transportation model to help Sinclair minimize its shipping costs.
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month. Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants, Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month), Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month), and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month). The costs of shipping between the respective plants is shown in the table below:

Refer to Exhibit 5-1.Formulate (write out algebraically)an LP transportation model to help Sinclair minimize its shipping costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Exhibit 5-3
Steve the auto parts salesman is trying to navigate his way between the rural west Texas towns of Jonestown and Upland. The possible routes for this trip are shown below, along with the mileage along each route.


Refer to Exhibit 5-3.What general type of LP model can be applied to this problem
What modifications to the general type are required for this problem
Steve the auto parts salesman is trying to navigate his way between the rural west Texas towns of Jonestown and Upland. The possible routes for this trip are shown below, along with the mileage along each route.


Refer to Exhibit 5-3.What general type of LP model can be applied to this problem
What modifications to the general type are required for this problem

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Exhibit 5-2
A small engineering firm employs one civil engineer, two engineering technicians, and one summer intern. The types of projects the firm does includes surveys (typically 7 per month), designs (5 per month), and construction project plans (four per month). The times, in hours, required for each employee to complete teach type of project are shown below. Based on their capabilities and time spent on travel and administrative tasks, the engineer, tech 1, tech 2, and intern can handle 5, 4, 4, and 3 projects per month, respectively.
Refer to Exhibit 5-2.Based on their salaries,the engineer,tech 1,tech 2,and intern earn $90,$65,$65,and $45 per hourly,respectively.Change the firm's objective function to minimize staff costs and find the optimal assignment plan.Does it change from the base case
A small engineering firm employs one civil engineer, two engineering technicians, and one summer intern. The types of projects the firm does includes surveys (typically 7 per month), designs (5 per month), and construction project plans (four per month). The times, in hours, required for each employee to complete teach type of project are shown below. Based on their capabilities and time spent on travel and administrative tasks, the engineer, tech 1, tech 2, and intern can handle 5, 4, 4, and 3 projects per month, respectively.

Refer to Exhibit 5-2.Based on their salaries,the engineer,tech 1,tech 2,and intern earn $90,$65,$65,and $45 per hourly,respectively.Change the firm's objective function to minimize staff costs and find the optimal assignment plan.Does it change from the base case

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Exhibit 5-3
Steve the auto parts salesman is trying to navigate his way between the rural west Texas towns of Jonestown and Upland. The possible routes for this trip are shown below, along with the mileage along each route.


Refer to Exhibit 5-3.Suppose the roads leading into and out of Krickburg are unpaved,so Steve would only be able to travel half of his usual 60 mile/hour speed on those routes.Modify the model to account for this condition.Would the shortest path change from the base case solution
Steve the auto parts salesman is trying to navigate his way between the rural west Texas towns of Jonestown and Upland. The possible routes for this trip are shown below, along with the mileage along each route.


Refer to Exhibit 5-3.Suppose the roads leading into and out of Krickburg are unpaved,so Steve would only be able to travel half of his usual 60 mile/hour speed on those routes.Modify the model to account for this condition.Would the shortest path change from the base case solution

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Exhibit 5-1
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month. Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants, Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month), Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month), and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month). The costs of shipping between the respective plants is shown in the table below:

Refer to Exhibit 5-1.Suppose the Lakeview plant was required to run at capacity.How much more would the shipping plan cost Sinclair
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month. Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants, Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month), Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month), and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month). The costs of shipping between the respective plants is shown in the table below:

Refer to Exhibit 5-1.Suppose the Lakeview plant was required to run at capacity.How much more would the shipping plan cost Sinclair

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Exhibit 5-2
A small engineering firm employs one civil engineer, two engineering technicians, and one summer intern. The types of projects the firm does includes surveys (typically 7 per month), designs (5 per month), and construction project plans (four per month). The times, in hours, required for each employee to complete teach type of project are shown below. Based on their capabilities and time spent on travel and administrative tasks, the engineer, tech 1, tech 2, and intern can handle 5, 4, 4, and 3 projects per month, respectively.

Refer to Exhibit 5-2.Implement a LP model in Solver and determine the optimal monthly assignment plan for the firm.What is the total number of hours that will be assigned to projects each month
A small engineering firm employs one civil engineer, two engineering technicians, and one summer intern. The types of projects the firm does includes surveys (typically 7 per month), designs (5 per month), and construction project plans (four per month). The times, in hours, required for each employee to complete teach type of project are shown below. Based on their capabilities and time spent on travel and administrative tasks, the engineer, tech 1, tech 2, and intern can handle 5, 4, 4, and 3 projects per month, respectively.

Refer to Exhibit 5-2.Implement a LP model in Solver and determine the optimal monthly assignment plan for the firm.What is the total number of hours that will be assigned to projects each month

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Exhibit 5-1
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month. Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants, Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month), Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month), and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month). The costs of shipping between the respective plants is shown in the table below:

Refer to Exhibit 5-1.Suppose the shipping capacity between any two plants was limited to 2500 tons per month.Design and implement a network flow version of this model in Solver and obtain the optimal shipping plan.How much more would the shipping plan cost Sinclair in that case
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month. Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants, Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month), Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month), and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month). The costs of shipping between the respective plants is shown in the table below:

Refer to Exhibit 5-1.Suppose the shipping capacity between any two plants was limited to 2500 tons per month.Design and implement a network flow version of this model in Solver and obtain the optimal shipping plan.How much more would the shipping plan cost Sinclair in that case

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Exhibit 5-2
A small engineering firm employs one civil engineer, two engineering technicians, and one summer intern. The types of projects the firm does includes surveys (typically 7 per month), designs (5 per month), and construction project plans (four per month). The times, in hours, required for each employee to complete teach type of project are shown below. Based on their capabilities and time spent on travel and administrative tasks, the engineer, tech 1, tech 2, and intern can handle 5, 4, 4, and 3 projects per month, respectively.

Refer to Exhibit 5-2.Suppose Tech 2 will not be available during the next month.Keeping the same number of design and construction plan projects,how many survey projects would the firm be able to do
What would be the revised assignment plan in that case
A small engineering firm employs one civil engineer, two engineering technicians, and one summer intern. The types of projects the firm does includes surveys (typically 7 per month), designs (5 per month), and construction project plans (four per month). The times, in hours, required for each employee to complete teach type of project are shown below. Based on their capabilities and time spent on travel and administrative tasks, the engineer, tech 1, tech 2, and intern can handle 5, 4, 4, and 3 projects per month, respectively.

Refer to Exhibit 5-2.Suppose Tech 2 will not be available during the next month.Keeping the same number of design and construction plan projects,how many survey projects would the firm be able to do
What would be the revised assignment plan in that case

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








