Deck 5: Strategic Planning Regarding Operating Processes
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
الفرضيات:
Cable Television in a smaller city
Cable Television in a smaller city
Cable Television in a smaller city
Cable Television in a smaller city
NFL Football Teams
NFL Football Teams
NFL Football Teams
NFL Football Teams
Soft Drink Companies
Soft Drink Companies
Soft Drink Companies
Soft Drink Companies
Corn farmer in Iowa
Corn farmer in Iowa
Corn farmer in Iowa
Corn farmer in Iowa
الردود:
Monopoly
Pure competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Pure competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Pure competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Pure competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Pure competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Pure competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Pure competition
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Pure competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
الفرضيات:
Electric Utility in a particular region
Electric Utility in a particular region
Electric Utility in a particular region
Electric Utility in a particular region
Automobile Companies
Automobile Companies
Automobile Companies
Automobile Companies
Oil Companies
Oil Companies
Oil Companies
Oil Companies
Wheat farmer in Kansas
Wheat farmer in Kansas
Wheat farmer in Kansas
Wheat farmer in Kansas
الردود:
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Pure competition
Monopoly
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Pure competition
Monopoly
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Pure competition
Monopoly
Monopolistic competition
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Monopoly
Pure competition
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Monopoly
Pure competition
Oligopoly
Pure competition
Monopoly
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Pure competition
Monopoly
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Pure competition
Monopoly
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 5: Strategic Planning Regarding Operating Processes
1
Which of the following is not a factor when using "Target Pricing"?
A)Determining the price based on consumer surveys
B)Determine the markup necessary to get a satisfactory return to stockholders
C)Determining the price of competitors so our price will be lower
D)Determine the target cost and see if product can be produced for that amount.
A)Determining the price based on consumer surveys
B)Determine the markup necessary to get a satisfactory return to stockholders
C)Determining the price of competitors so our price will be lower
D)Determine the target cost and see if product can be produced for that amount.
Determining the price of competitors so our price will be lower
2
Which of the following best describes the competitive environment for Sony high definition TVs?
A)monopolistic competition
B)pure competition
C)free competition
D)monopoly
A)monopolistic competition
B)pure competition
C)free competition
D)monopoly
monopolistic competition
3
The pricing strategy where a company initially sets the price of its product low and then raises it later on in the product's life cycle is called:
A)price skimming
B)target pricing
C)life-cycle pricing
D)penetration pricing
A)price skimming
B)target pricing
C)life-cycle pricing
D)penetration pricing
penetration pricing
4
The type of environment where a large number of sellers produce and distribute virtually identical products and services is referred to as:
A)Monopolistic competition
B)Oligopolistic competition
C)Price competition
D)Pure competition
A)Monopolistic competition
B)Oligopolistic competition
C)Price competition
D)Pure competition

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Which of the following is not one of the perspectives that compose the balanced scorecard approach?
A)financial
B)internal processes
C)learning and growth
D)flexibility and efficiency
A)financial
B)internal processes
C)learning and growth
D)flexibility and efficiency

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
In general,which of the following is true about the pricing of products?
A)When supply increases prices increase
B)When demand decreases prices increase
C)When supply decreases prices increase
D)When demand increases prices increase
A)When supply increases prices increase
B)When demand decreases prices increase
C)When supply decreases prices increase
D)When demand increases prices increase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Mobile phone providers that offer no or low cost phones when customers sign up for service is an example of which pricing strategy?
A)penetration pricing
B)pioneer price
C)life-cycle pricing
D)price skimming
A)penetration pricing
B)pioneer price
C)life-cycle pricing
D)price skimming

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The four primary influences on selling price are:
A)product,variable costs,fixed costs,and mixed costs
B)customers,competition,legal and social issues,and costs
C)competition,variable costs,fixed costs,and mixed costs
D)legal constraints,government regulations,costs and customers
A)product,variable costs,fixed costs,and mixed costs
B)customers,competition,legal and social issues,and costs
C)competition,variable costs,fixed costs,and mixed costs
D)legal constraints,government regulations,costs and customers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
If a product has a cost of the $250 and a selling price of $450,what is the products markup percentage?
A)200%
B)80%
C)44.4%
D)Not enough information to calculate
A)200%
B)80%
C)44.4%
D)Not enough information to calculate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which of the following best describes the competitive environment for Microsoft Windows?
A)monopolistic competition
B)pure competition
C)oligopoly
D)monopoly
A)monopolistic competition
B)pure competition
C)oligopoly
D)monopoly

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Life-cycle pricing:
A)attempts to establish a price that can be maintained throughout the life of the product
B)sets the price high to begin with and then lowers it later on in the life of the product
C)sets the price low to begin with and then raises it later on in the life of the product
D)is the same as target pricing
A)attempts to establish a price that can be maintained throughout the life of the product
B)sets the price high to begin with and then lowers it later on in the life of the product
C)sets the price low to begin with and then raises it later on in the life of the product
D)is the same as target pricing

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Model bakers have developed a snack cake that it wants to compete with Hostess Twinkies and has set their introductory price 10 cents below the price of a Twinkie.This
Is an example of which of the following?
A)Penetrating pricing
B)Skimming pricing
C)Life-cycle pricing
D)Competitive cycle pricing
Is an example of which of the following?
A)Penetrating pricing
B)Skimming pricing
C)Life-cycle pricing
D)Competitive cycle pricing

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
If a product has a cost of $160 and a markup percentage of 60 % what is the selling margin of the product?
A)$256
B)$160
C)$96
D)Not enough information to calculate
A)$256
B)$160
C)$96
D)Not enough information to calculate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which of the following business are considered part of monopolistic competition?
A)Power Company
B)Athletic Shoe Company
C)Oil Company
D)Fruit Farmer
A)Power Company
B)Athletic Shoe Company
C)Oil Company
D)Fruit Farmer

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
When the iPhon was introduced its price was set by which of the following?
A)Bonus pricing
B)Life-cycle pricing
C)Penetrating pricing
D)Skimming pricing
A)Bonus pricing
B)Life-cycle pricing
C)Penetrating pricing
D)Skimming pricing

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Which of the following describes the practice of selling a product in other countries for a price less than the company's cost?
A)Dumping
B)Predatory Pricing
C)Price Skimming
D)Penetrating Pricing
A)Dumping
B)Predatory Pricing
C)Price Skimming
D)Penetrating Pricing

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which of the following business is considered part of an oligopoly?
A)Automobile Manufacturers
B)Oil Companies
C)Wheat farmer
D)Insurance Companies
A)Automobile Manufacturers
B)Oil Companies
C)Wheat farmer
D)Insurance Companies

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Panascope manufactures high-definition TVs (HDTVs).It costs Panascope $1,500 to produce one HDTV.Panascope,planning to "make hay while the sun shines" has priced its HDTVs at $12,000.This is an example of which pricing strategy?
A)penetration pricing
B)life-cycle pricing
C)price skimming
D)pioneer price
A)penetration pricing
B)life-cycle pricing
C)price skimming
D)pioneer price

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The seller of a product is a price taker in which of the following environment?
A)Monopolistic competition
B)Pure Competition
C)Monopoly
D)Oligopoly
A)Monopolistic competition
B)Pure Competition
C)Monopoly
D)Oligopoly

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not involved in Pure Competition
A)Cotton farmer in Texas
B)National Basketball Association franchise
C)Starbucks
D)Macy's
A)Cotton farmer in Texas
B)National Basketball Association franchise
C)Starbucks
D)Macy's

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Which of the following is not a factor in the EOQ inventory model?
A)Annual demand for the inventory in units
B)Cost to place one additional order
C)Cost to carry one additional unit in inventory
D)All of the following are factors in the EOQ model.
A)Annual demand for the inventory in units
B)Cost to place one additional order
C)Cost to carry one additional unit in inventory
D)All of the following are factors in the EOQ model.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Which of the following is not withheld from the employee's check?
A)Federal Unemployment Tax
B)Federal Income Tax
C)Social Security
D)Union dues
A)Federal Unemployment Tax
B)Federal Income Tax
C)Social Security
D)Union dues

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
A compensation method whereby employees are paid according to the amount they sell in a given time-period is known as:
A)commission-based compensation
B)piece-rate compensation
C)deferred compensation
D)bonus compensation
A)commission-based compensation
B)piece-rate compensation
C)deferred compensation
D)bonus compensation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which of the following is not a key feature of a JIT inventory system?
A)Quality and reliable suppliers
B)Adequate safety stock
C)Well-trained employees
D)Customer demand pulls the system
A)Quality and reliable suppliers
B)Adequate safety stock
C)Well-trained employees
D)Customer demand pulls the system

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which of the following is not withheld from the employee's check?
A)Union Dues
B)Federal Income Tax
C)Social Security
D)All of the above are withheld
A)Union Dues
B)Federal Income Tax
C)Social Security
D)All of the above are withheld

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
A compensation method under which a company pays employees according to the number of items they produce during a given time-period is known as:
A)piece-rate pay
B)deferred pay
C)contract pay
D)bonus pay
A)piece-rate pay
B)deferred pay
C)contract pay
D)bonus pay

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Which of the following is a feature of a JIT inventory system?
A)Sufficient inventory on hand to meet unexpected demand.
B)Plan to sell slightly defective products to meet demand of bargain hunting
Consumers.
C)Amount of production based on pull of consumer demand.
D)Plan to keep assembly line moving at all cost.
A)Sufficient inventory on hand to meet unexpected demand.
B)Plan to sell slightly defective products to meet demand of bargain hunting
Consumers.
C)Amount of production based on pull of consumer demand.
D)Plan to keep assembly line moving at all cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which of the following statements is false?
A)JIT is a pull system.
B)JIT is a short-run model.
C)The JIT philosophy is based on continuous improvement.
D)JIT requires a company to have strong relationships with its suppliers.
A)JIT is a pull system.
B)JIT is a short-run model.
C)The JIT philosophy is based on continuous improvement.
D)JIT requires a company to have strong relationships with its suppliers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
How are defective products identified in a JIT inventory system?
A)Defective inventory is stacked in a particular location.
B)Defective inventory is color coded
C)Defective inventory marked down for consumers
D)The production line is stopped and only started when the problem causing the defective product is identified.
A)Defective inventory is stacked in a particular location.
B)Defective inventory is color coded
C)Defective inventory marked down for consumers
D)The production line is stopped and only started when the problem causing the defective product is identified.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which of the following companies would not be a good candidate for a JIT system?
A)Ford Motor Company
B)The GAP
C)A company that manufactures yachts
D)Dell computers
A)Ford Motor Company
B)The GAP
C)A company that manufactures yachts
D)Dell computers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Which of the following is withheld from an employee's pay and also paid by the employer?
A)Income tax
B)Union dues
C)Vacation Pay
D)Social Security
A)Income tax
B)Union dues
C)Vacation Pay
D)Social Security

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements is false?
A)JIT is a pull system.
B)The JIT philosophy is based on continuous improvement.
C)JIT requires a company to have strong relationships with its suppliers.
D)All of the above are true.
A)JIT is a pull system.
B)The JIT philosophy is based on continuous improvement.
C)JIT requires a company to have strong relationships with its suppliers.
D)All of the above are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Which of the following is not a factor in the EOQ inventory model?
A)Annual demand for the inventory in units
B)Cost of the inventory item
C)Cost to place one additional order
D)Cost to carry one additional unit in inventory
A)Annual demand for the inventory in units
B)Cost of the inventory item
C)Cost to place one additional order
D)Cost to carry one additional unit in inventory

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
West Coast Creamery's economic order quantity is 300 units.Demand for the year is 41,975 units.There are seven days between the time an order is placed and the day it is received.West Coast operates 365 days per year.The reorder point is:
A)268 units
B)805 units
C)2,683 units
D)2,905 units
A)268 units
B)805 units
C)2,683 units
D)2,905 units

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Which of the following describes the practice of setting the price of a product at less than cost to take over a market and then to raise the price?
A)Dumping
B)Price Skimming
C)Penetrating Pricing
D)Predatory Pricing
A)Dumping
B)Price Skimming
C)Penetrating Pricing
D)Predatory Pricing

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Capital Industries' president receives a bonus equal to 6% of net income.This bonus is included in the determination of net income.If the company's income before bonus was $3,800,000,the amount of the bonus is:
A)$215,094
B)$228,000
C)$242,553
D)cannot be determined from the information given
A)$215,094
B)$228,000
C)$242,553
D)cannot be determined from the information given

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Lockwood International's president receives a bonus equal to 7% of net income.This bonus is included in the determination of net income.If the company's income before the bonus was $4,500,000,the amount of the bonus is:
A)$294,393
B)$315,000
C)$338,710
D)cannot be determined from the information given
A)$294,393
B)$315,000
C)$338,710
D)cannot be determined from the information given

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A reorder point in a Kanban system is identified by a:
A)A card
B)A color coded inventory item
C)A predetermined date
D)A pokemon
A)A card
B)A color coded inventory item
C)A predetermined date
D)A pokemon

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Safety stock is kept in order to:
A)Guard against defective products.
B)Prevent losses created by a stockout
C)Prevent people from being injured by dangerous inventory
D)Help identify the reorder point
A)Guard against defective products.
B)Prevent losses created by a stockout
C)Prevent people from being injured by dangerous inventory
D)Help identify the reorder point

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Lead time in an inventory system is:
A)The time it takes to sell inventory
B)The time it takes to move raw materials inventory from the warehouse to the manufacturing facility
C)The time between placing an order for inventory and the when the inventory is received
D)The time it takes to manufacture a product plus the time it takes to ship the product to the customer.
A)The time it takes to sell inventory
B)The time it takes to move raw materials inventory from the warehouse to the manufacturing facility
C)The time between placing an order for inventory and the when the inventory is received
D)The time it takes to manufacture a product plus the time it takes to ship the product to the customer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
What is the distinction between penetrating and predatory pricing?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Which of the following companies would be a good candidate for a JIT system?
A)Grocery Store
B)Macys
C)Construction company
D)Sporting Goods Store
A)Grocery Store
B)Macys
C)Construction company
D)Sporting Goods Store

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Malsom Corp's monthly payroll is $100,000.If the FICA rate is 7.65% ,income tax is
withheld at a 15% rate,the State Unemployment (SUT
A)rate is 2.8% and the Federal
Unemployment (FUT
A)tax rate is .8%,how much is withheld from the workers' wages
and how much does Malsom have to pay in payroll taxes?
withheld at a 15% rate,the State Unemployment (SUT
A)rate is 2.8% and the Federal
Unemployment (FUT
A)tax rate is .8%,how much is withheld from the workers' wages
and how much does Malsom have to pay in payroll taxes?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Match between columns
الفرضيات:
Cable Television in a smaller city
Cable Television in a smaller city
Cable Television in a smaller city
Cable Television in a smaller city
NFL Football Teams
NFL Football Teams
NFL Football Teams
NFL Football Teams
Soft Drink Companies
Soft Drink Companies
Soft Drink Companies
Soft Drink Companies
Corn farmer in Iowa
Corn farmer in Iowa
Corn farmer in Iowa
Corn farmer in Iowa
الردود:
Monopoly
Pure competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Pure competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Pure competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Pure competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Pure competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Pure competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Pure competition
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Pure competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Barton Corporation generated the following income:
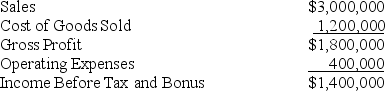 Jackson Barton,the president of Barton Corporation,wants to establish a bonus system.If the tax rate is 30%,what is President Barton's bonus under each of the three options below.
Jackson Barton,the president of Barton Corporation,wants to establish a bonus system.If the tax rate is 30%,what is President Barton's bonus under each of the three options below.
A.Bonus based on Income before Bonus and Taxes using a bonus rate of 6%.
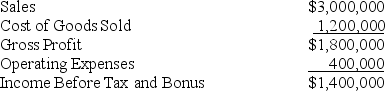 Jackson Barton,the president of Barton Corporation,wants to establish a bonus system.If the tax rate is 30%,what is President Barton's bonus under each of the three options below.
Jackson Barton,the president of Barton Corporation,wants to establish a bonus system.If the tax rate is 30%,what is President Barton's bonus under each of the three options below. A.Bonus based on Income before Bonus and Taxes using a bonus rate of 6%.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Match between columns
الفرضيات:
Electric Utility in a particular region
Electric Utility in a particular region
Electric Utility in a particular region
Electric Utility in a particular region
Automobile Companies
Automobile Companies
Automobile Companies
Automobile Companies
Oil Companies
Oil Companies
Oil Companies
Oil Companies
Wheat farmer in Kansas
Wheat farmer in Kansas
Wheat farmer in Kansas
Wheat farmer in Kansas
الردود:
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Pure competition
Monopoly
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Pure competition
Monopoly
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Pure competition
Monopoly
Monopolistic competition
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Monopoly
Pure competition
Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition
Monopoly
Pure competition
Oligopoly
Pure competition
Monopoly
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Pure competition
Monopoly
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Pure competition
Monopoly

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Duracraft Industries' president receives a bonus equal to 5% of income before taxes.This bonus is included in the determination of income before taxes.Assuming the company's income before consideration of the bonus and taxes was $28,350,000,determine the amount of the president's bonus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Zeigler Corp's monthly payroll is $200,000.If the FICA rate is 7.65% ,income tax is
withheld at a 15% rate,the State Unemployment (SUT
A)rate is 2.8% and the Federal
Unemployment (FUT
A)tax rate is .8%,how much is withheld from the workers' wages
and how much does Malsom have to pay in payroll taxes?
withheld at a 15% rate,the State Unemployment (SUT
A)rate is 2.8% and the Federal
Unemployment (FUT
A)tax rate is .8%,how much is withheld from the workers' wages
and how much does Malsom have to pay in payroll taxes?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
It is said that one of the benefits of the Just-In-Time (JIT)system is that it can't hide defective products.What does this mean?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Julia B Enterprises generated the following income:
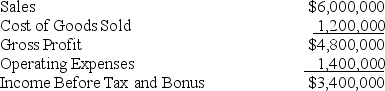 Julia Barton,the president of Julia B Enterprises,wants to establish a bonus system.If the tax rate is 30%,what is President Barton's bonus under each of the three options below.
Julia Barton,the president of Julia B Enterprises,wants to establish a bonus system.If the tax rate is 30%,what is President Barton's bonus under each of the three options below.
A.Bonus based on Income before Bonus and Taxes using a bonus rate of 6%.
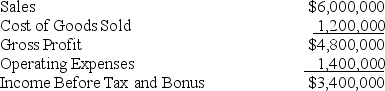 Julia Barton,the president of Julia B Enterprises,wants to establish a bonus system.If the tax rate is 30%,what is President Barton's bonus under each of the three options below.
Julia Barton,the president of Julia B Enterprises,wants to establish a bonus system.If the tax rate is 30%,what is President Barton's bonus under each of the three options below. A.Bonus based on Income before Bonus and Taxes using a bonus rate of 6%.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








