Deck 10: Introduction to Simulation Modeling
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 10: Introduction to Simulation Modeling
1
A correlation matrix must always have 1's along its diagonal (because a variable is always perfectly correlated with itself) and numbers between −1 and +1 elsewhere.
True
2
Excel's standard functions, along with the RAND function, can be used to generate random numbers from many different types of probability distributions.
True
3
The RAND() function in excel models which of the following probability distributions?
A)Normal(0,1)
B)Uniform(0,1)
C)Normal(−1,1)
D)Uniform(−1,1).
A)Normal(0,1)
B)Uniform(0,1)
C)Normal(−1,1)
D)Uniform(−1,1).
B
4
A correlation matrix must always be symmetric, so that the correlations above the diagonal are a mirror image of those below it.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
One of the primary advantages of simulation models that they enable managers to answer what-if questions about changes in systems without actually changing the systems themselves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Correlation between two random input variables may change the mean of an output, but it will not affect the variability and shape of an output distribution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
If x is a random number between 0 and 1, then we can use x to simulate a variable that is uniformly distributed between 100 and 200 using the formula:
A)100 + x
B)200 − x
C)100 + 100x
D)200x
A)100 + x
B)200 − x
C)100 + 100x
D)200x

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The primary difference between simulation models and other types of spreadsheet models is that simulation models contain ____:
A)deterministic inputs
B)random numbers
C)output cells
D)constraints
A)deterministic inputs
B)random numbers
C)output cells
D)constraints

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Discrete distributions are sometimes used in place of continuous distributions:
A)because they are more accurate
B)because they are more simple
C)when we don't know the mean and variance of the distribution
D)when we need to generate a histogram
A)because they are more accurate
B)because they are more simple
C)when we don't know the mean and variance of the distribution
D)when we need to generate a histogram

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which of the following is not one of the important distinctions of probability distributions?
A)Discrete versus continuous
B)Symmetric versus skewed
C)Bounded versus unbounded
D)Positive versus negative
A)Discrete versus continuous
B)Symmetric versus skewed
C)Bounded versus unbounded
D)Positive versus negative

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
It is usually fairly straightforward to predict the shape of the output distribution from the shape(s) of the input distribution(s).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
When the value of a decision variable has been optimized by running several simulations, attitude toward risk should no longer be relevant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
RISKSIMTABLE is an @RISK function for running several simulations simultaneously, one for each setting of an input or decision variable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A distribution for modeling the time it takes to serve a customer at a bank is probably:
A)symmetric
B)left skewed
C)right skewed
D)uniform
A)symmetric
B)left skewed
C)right skewed
D)uniform

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
When n is reasonably large and p isn't too close to 0 or 1, the binomial distribution can be well approximated by which of the following distributions?
A)Uniform distribution
B)Normal distribution
C)Triangular distribution
D)None of these options
A)Uniform distribution
B)Normal distribution
C)Triangular distribution
D)None of these options

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements is true regarding the Triangular distribution?
A)It is a discrete distribution with a minimum, maximum and most likely value
B)It is more flexible and intuitive than the normal distribution
C)It is a symmetric distribution
D)All of these options
A)It is a discrete distribution with a minimum, maximum and most likely value
B)It is more flexible and intuitive than the normal distribution
C)It is a symmetric distribution
D)All of these options

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
A common guideline for constructing a 95% confidence interval is to place upper and lower bounds one standard error on either side of the mean.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements is true regarding the Normal distribution?
A)It is always the appropriate distribution in simulation modeling
B)It does not permit negative values
C)There is a 95% chance that values will be within ± 2 standard deviations of the mean
D)All of these options
A)It is always the appropriate distribution in simulation modeling
B)It does not permit negative values
C)There is a 95% chance that values will be within ± 2 standard deviations of the mean
D)All of these options

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The three parameters required to specify a triangular distribution are the minimum, mean and maximum.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
If a model contains uncertain outputs, it can be very misleading to build a deterministic model by using the means of the inputs to predict an output. This is called the:
A)Law of Large Numbers.
B)Flaw of Averages
C)Law of Inevitable Disappointment
D)Central Limit Theorem
A)Law of Large Numbers.
B)Flaw of Averages
C)Law of Inevitable Disappointment
D)Central Limit Theorem

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Exhibit 10-2A large apparel company wants to determine the profitability of one of its most popular products, a particular type of jacket. Demand is uncertain, due to economic conditions, competition, weather and other factors, and the following probability distributions have been estimated for each of the company's three regions:
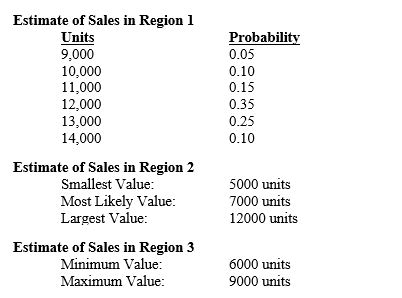
Refer to Exhibit 10-2. What is the probability that the apparel company will exceed a profit at least $0.5M from the jacket line?

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. What is the probability that the apparel company will exceed a profit at least $0.5M from the jacket line?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Exhibit 10-2A large apparel company wants to determine the profitability of one of its most popular products, a particular type of jacket. Demand is uncertain, due to economic conditions, competition, weather and other factors, and the following probability distributions have been estimated for each of the company's three regions:

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. Finally, suppose the apparel company receives an uncertain fraction of the total retail revenue from its retailers, modeled as a Triangular(0.70,0.75,0.80) distribution, and then must subtract production and operations costs, which are modeled as a Lognormal distribution with mean of $1,000,000 and standard deviation of $300,000. In that case, what is the expected net profit from the jacket line?

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. Finally, suppose the apparel company receives an uncertain fraction of the total retail revenue from its retailers, modeled as a Triangular(0.70,0.75,0.80) distribution, and then must subtract production and operations costs, which are modeled as a Lognormal distribution with mean of $1,000,000 and standard deviation of $300,000. In that case, what is the expected net profit from the jacket line?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Exhibit 10-1A company is in the planning phase of constructing a new production facility. It wants to build a simulation model for the economics of the facility, and one key uncertain input is the construction cost. For each of the scenarios in the questions below, choose an "appropriate" distribution, together with its parameters, and explain your choice.
Refer to Exhibit 10-1. Company management currently has no idea what the distribution of the construction cost is. All they can state is that "we think it will be somewhere between $5,000,000 and $8,000,000."
Refer to Exhibit 10-1. Company management currently has no idea what the distribution of the construction cost is. All they can state is that "we think it will be somewhere between $5,000,000 and $8,000,000."

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Exhibit 10-2A large apparel company wants to determine the profitability of one of its most popular products, a particular type of jacket. Demand is uncertain, due to economic conditions, competition, weather and other factors, and the following probability distributions have been estimated for each of the company's three regions:

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. Total sales is a product of three different types of input distributions. What does the output distribution look like? What is the standard deviation of the total sales? What are the 5th and 95th percentiles of this distribution?

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. Total sales is a product of three different types of input distributions. What does the output distribution look like? What is the standard deviation of the total sales? What are the 5th and 95th percentiles of this distribution?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Exhibit 10-1A company is in the planning phase of constructing a new production facility. It wants to build a simulation model for the economics of the facility, and one key uncertain input is the construction cost. For each of the scenarios in the questions below, choose an "appropriate" distribution, together with its parameters, and explain your choice.
Refer to Exhibit 10-1. Engineering also believes the construction time will be from 5 to 9 months. However, they believe that 7 months is twice as likely as either 6 months or 8 months and that either of these latter possibilities is three times as likely as either 5 months or 9 months.
Refer to Exhibit 10-1. Engineering also believes the construction time will be from 5 to 9 months. However, they believe that 7 months is twice as likely as either 6 months or 8 months and that either of these latter possibilities is three times as likely as either 5 months or 9 months.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Exhibit 10-1A company is in the planning phase of constructing a new production facility. It wants to build a simulation model for the economics of the facility, and one key uncertain input is the construction cost. For each of the scenarios in the questions below, choose an "appropriate" distribution, together with its parameters, and explain your choice.
If you add n lognormally distributed random numbers, the mean of the distribution for the sum is the sum of the individual means, and the variance of the distribution of the sum is the individual variances. This result is difficult to prove mathematically, but it is easy to demonstrate with simulation. To do so, run a simulation where you add three lognormally distributed random numbers, with means of 300, 700 and 100, and standard deviations of 20, 50, and 30, respectively. Your single output variable should be the sum of these three numbers. Verify with @RISK that the distribution of this output has a mean of 1,000 and standard deviation .
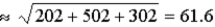
If you add n lognormally distributed random numbers, the mean of the distribution for the sum is the sum of the individual means, and the variance of the distribution of the sum is the individual variances. This result is difficult to prove mathematically, but it is easy to demonstrate with simulation. To do so, run a simulation where you add three lognormally distributed random numbers, with means of 300, 700 and 100, and standard deviations of 20, 50, and 30, respectively. Your single output variable should be the sum of these three numbers. Verify with @RISK that the distribution of this output has a mean of 1,000 and standard deviation .
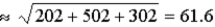

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Exhibit 10-1A company is in the planning phase of constructing a new production facility. It wants to build a simulation model for the economics of the facility, and one key uncertain input is the construction cost. For each of the scenarios in the questions below, choose an "appropriate" distribution, together with its parameters, and explain your choice.
Refer to Exhibit 10-1. A little later on, management still believes the upper and lower bounds for the costs are $5M and $8M, but now they can also state that "we believe the most likely value is about $6.5M."
Refer to Exhibit 10-1. A little later on, management still believes the upper and lower bounds for the costs are $5M and $8M, but now they can also state that "we believe the most likely value is about $6.5M."

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Exhibit 10-1A company is in the planning phase of constructing a new production facility. It wants to build a simulation model for the economics of the facility, and one key uncertain input is the construction cost. For each of the scenarios in the questions below, choose an "appropriate" distribution, together with its parameters, and explain your choice.
Refer to Exhibit 10-1. Management believes the facility construction time will be somewhere from 5 to 9 months. They believe the probabilities of the extremes (5 and 9 months) are both 10%, and the probabilities will vary linearly from those endpoints to a most likely value at 7 months.
Refer to Exhibit 10-1. Management believes the facility construction time will be somewhere from 5 to 9 months. They believe the probabilities of the extremes (5 and 9 months) are both 10%, and the probabilities will vary linearly from those endpoints to a most likely value at 7 months.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Exhibit 10-2A large apparel company wants to determine the profitability of one of its most popular products, a particular type of jacket. Demand is uncertain, due to economic conditions, competition, weather and other factors, and the following probability distributions have been estimated for each of the company's three regions:

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. Use @RISK distributions to generate the three random variables for regional sales and derive a distribution for the total sales. What is the expected total sales?

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. Use @RISK distributions to generate the three random variables for regional sales and derive a distribution for the total sales. What is the expected total sales?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Exhibit 10-2A large apparel company wants to determine the profitability of one of its most popular products, a particular type of jacket. Demand is uncertain, due to economic conditions, competition, weather and other factors, and the following probability distributions have been estimated for each of the company's three regions:

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. Suppose the jacket sales price also varies, depending on the individual retailers and their pricing strategies. Assume that sales price is normally distributed with a mean of $65 per unit and a standard deviation of $10. How much revenue will the jacket line produce (ignore discounting)?

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. Suppose the jacket sales price also varies, depending on the individual retailers and their pricing strategies. Assume that sales price is normally distributed with a mean of $65 per unit and a standard deviation of $10. How much revenue will the jacket line produce (ignore discounting)?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








