Deck 9: Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/246
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 9: Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy
1
A species of bacteria was cultured in a test tube containing a uniform distribution of glucose but a varying distribution of oxygen.Oxygen was highest near the top of the tube and very low at the bottom.If this bacterial species is incapable of carrying out fermentation or other anaerobic energy-harvesting pathways, which test tube represents the expected growth pattern of the bacterial culture?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)

A
2
In all cells, glucose catabolism begins with
A) glycolysis.
B) fermentation.
C) pyruvate oxidation.
D) the citric acid cycle.
E) chemiosmosis.
A) glycolysis.
B) fermentation.
C) pyruvate oxidation.
D) the citric acid cycle.
E) chemiosmosis.
A
3
Refer to the figure below, which provides information about the series of oxidation-reduction reactions that take place via the respiratory chain in the inner mitochondrial membrane. 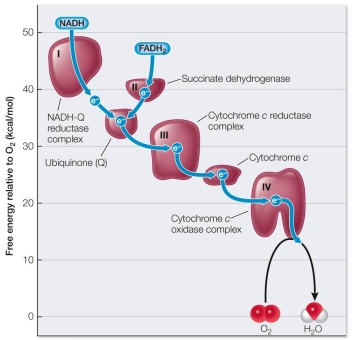 Which statement about the respiratory chain explains the biological importance of the information portrayed in the graph?
Which statement about the respiratory chain explains the biological importance of the information portrayed in the graph?
A) The extensive folding of the inner mitochondrial membrane provides the space needed to accommodate the large number of proteins making up the respiratory chain.
B) Oxygen serves as the final electron acceptor in the respiratory chain, forming water as a result of its acceptance of electrons that have passed down the chain.
C) With each oxidation-reduction step in the respiratory chain, an electron loses free energy that is captured in a form that the cell can use to perform biological work.
D) NADH and FADH2 pass their electrons to different carriers in the respiratory chain.
E) The components of the respiratory chain are physically arranged within the mitochondrial membrane in the order of transfer of electrons down the chain.
 Which statement about the respiratory chain explains the biological importance of the information portrayed in the graph?
Which statement about the respiratory chain explains the biological importance of the information portrayed in the graph?A) The extensive folding of the inner mitochondrial membrane provides the space needed to accommodate the large number of proteins making up the respiratory chain.
B) Oxygen serves as the final electron acceptor in the respiratory chain, forming water as a result of its acceptance of electrons that have passed down the chain.
C) With each oxidation-reduction step in the respiratory chain, an electron loses free energy that is captured in a form that the cell can use to perform biological work.
D) NADH and FADH2 pass their electrons to different carriers in the respiratory chain.
E) The components of the respiratory chain are physically arranged within the mitochondrial membrane in the order of transfer of electrons down the chain.
C
4
The carbon end product of glycolysis is
A) pyruvate.
B) carbon dioxide.
C) ethanol.
D) lactic acid.
E) ATP.
A) pyruvate.
B) carbon dioxide.
C) ethanol.
D) lactic acid.
E) ATP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate is coupled to the reduction of NAD+ to NADH + H+.In this process, NAD+ is a(n)
A) reducing agent.
B) oxidizing agent.
C) vitamin.
D) phosphate ester.
E) phosphorylating agent.
A) reducing agent.
B) oxidizing agent.
C) vitamin.
D) phosphate ester.
E) phosphorylating agent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Refer to the figure below, which shows a series of coupled reactions. 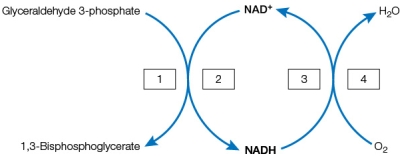 Which terms belong in the numbered boxes?
Which terms belong in the numbered boxes?
A) 1 = reduction; 2 = reduction; 3 = oxidation; 4 = oxidation
B) 1 = oxidation; 2 = oxidation; 3 = reduction; 4 = reduction
C) 1 = reduction; 2 = oxidation; 3 = reduction; 4 = oxidation
D) 1 = oxidation; 2 = reduction; 3 = oxidation; 4 = reduction
E) 1 = oxidation; 2 = reduction; 3 = reduction; 4 = oxidation
 Which terms belong in the numbered boxes?
Which terms belong in the numbered boxes?A) 1 = reduction; 2 = reduction; 3 = oxidation; 4 = oxidation
B) 1 = oxidation; 2 = oxidation; 3 = reduction; 4 = reduction
C) 1 = reduction; 2 = oxidation; 3 = reduction; 4 = oxidation
D) 1 = oxidation; 2 = reduction; 3 = oxidation; 4 = reduction
E) 1 = oxidation; 2 = reduction; 3 = reduction; 4 = oxidation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which statement about metabolic pathways is false?
A) The rate of the pathway can be altered by activating or inhibiting some key enzymes within the pathway.
B) Metabolic pathways are a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
C) Almost all metabolic pathways are anabolic.
D) Many metabolic pathways are similar in all organisms.
E) Many metabolic pathways are compartmentalized in eukaryotes.
A) The rate of the pathway can be altered by activating or inhibiting some key enzymes within the pathway.
B) Metabolic pathways are a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
C) Almost all metabolic pathways are anabolic.
D) Many metabolic pathways are similar in all organisms.
E) Many metabolic pathways are compartmentalized in eukaryotes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
NADH
A) is a key electron carrier in redox reactions.
B) requires O2 to function.
C) is found only in prokaryotes.
D) binds with an acetyl group to form acetyl CoA.
E) detoxifies hydrogen peroxide.
A) is a key electron carrier in redox reactions.
B) requires O2 to function.
C) is found only in prokaryotes.
D) binds with an acetyl group to form acetyl CoA.
E) detoxifies hydrogen peroxide.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Refer to the figure below, which shows an oxidation-reduction reaction that occurs spontaneously. 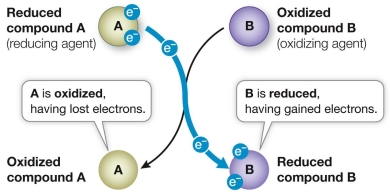 Which statement correctly compares the free energy stored in molecules shown in the figure?
Which statement correctly compares the free energy stored in molecules shown in the figure?
A) The reduced form of B has greater free energy than the reduced form of A.
B) The oxidized form of B has greater free energy than the reduced form of A.
C) The reduced form of A has greater free energy than the oxidized form of A.
D) The oxidized form of B has greater free energy than the reduced form of B.
E) The oxidized form of A has greater free energy than the reduced form of B.
 Which statement correctly compares the free energy stored in molecules shown in the figure?
Which statement correctly compares the free energy stored in molecules shown in the figure?A) The reduced form of B has greater free energy than the reduced form of A.
B) The oxidized form of B has greater free energy than the reduced form of A.
C) The reduced form of A has greater free energy than the oxidized form of A.
D) The oxidized form of B has greater free energy than the reduced form of B.
E) The oxidized form of A has greater free energy than the reduced form of B.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Glycolysis converts glucose to pyruvate with the formation of ATP and NADH.This process requires
A) O2, ATP, and a series of reactions.
B) CO2, five enzyme-catalyzed reactions, and glucose to begin the series of reactions.
C) pyruvic acid, O2, and enzymes to oxidize glucose inside the mitochondria.
D) the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex to catalyze the reactions.
E) ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions, with each reaction dependent on the products of the previous reaction.
A) O2, ATP, and a series of reactions.
B) CO2, five enzyme-catalyzed reactions, and glucose to begin the series of reactions.
C) pyruvic acid, O2, and enzymes to oxidize glucose inside the mitochondria.
D) the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex to catalyze the reactions.
E) ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions, with each reaction dependent on the products of the previous reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Refer to the figure below, illustrating how two redox reactions are coupled in an energy-harvesting pathway in a cell. 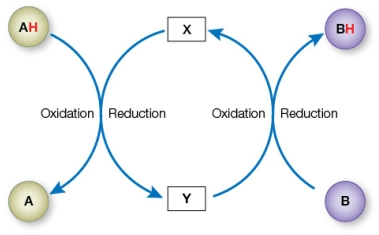 Which molecules could serve as compounds X and Y, respectively?
Which molecules could serve as compounds X and Y, respectively?
A) ADP and ATP
B) ATP and ADP
C) FADH2 and FAD
D) NAD+ and NADH
E) NADH and NAD+
 Which molecules could serve as compounds X and Y, respectively?
Which molecules could serve as compounds X and Y, respectively?A) ADP and ATP
B) ATP and ADP
C) FADH2 and FAD
D) NAD+ and NADH
E) NADH and NAD+

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Refer to the figure below. 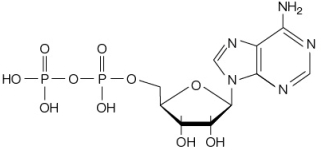 How is this molecule involved in the cellular harvesting of energy from glucose oxidation?
How is this molecule involved in the cellular harvesting of energy from glucose oxidation?
A) During the oxidation of glucose in a cell, this molecule is hydrolyzed to release the chemical energy in its phosphate bonds.
B) Electrons are removed from glucose and transferred to this molecule as a means of harvesting energy from glucose's chemical bonds.
C) This molecule transfers electrons to glucose in one step of the cellular glucose oxidation pathway.
D) Energy released during the cellular oxidation of glucose is used to add a phosphate to this molecule.
E) Oxygen accepts electrons from this molecule as the final step in the cellular oxidation of glucose.
 How is this molecule involved in the cellular harvesting of energy from glucose oxidation?
How is this molecule involved in the cellular harvesting of energy from glucose oxidation?A) During the oxidation of glucose in a cell, this molecule is hydrolyzed to release the chemical energy in its phosphate bonds.
B) Electrons are removed from glucose and transferred to this molecule as a means of harvesting energy from glucose's chemical bonds.
C) This molecule transfers electrons to glucose in one step of the cellular glucose oxidation pathway.
D) Energy released during the cellular oxidation of glucose is used to add a phosphate to this molecule.
E) Oxygen accepts electrons from this molecule as the final step in the cellular oxidation of glucose.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Refer to the reaction below.
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) + NAD+ + H+ + Pi 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) + NADH
In this redox reaction, _______ is oxidized and _______ is reduced.
A) G3P; NAD+
B) BPG; NADH + H+
C) G3P; NADH + H+
D) NAD+; NADH + H+
E) NAD+; G3P
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) + NAD+ + H+ + Pi 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) + NADH
In this redox reaction, _______ is oxidized and _______ is reduced.
A) G3P; NAD+
B) BPG; NADH + H+
C) G3P; NADH + H+
D) NAD+; NADH + H+
E) NAD+; G3P

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Refer to the figure below, showing the exergonic reaction that links glycolysis to the citric acid cycle. 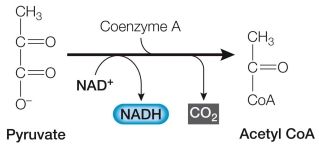 Which statement about the molecules participating in this cellular reaction is correct?
Which statement about the molecules participating in this cellular reaction is correct?
A) Pyruvate has higher stored free energy than acetyl CoA, and NAD+ has the same stored free energy as NADH.
B) Acetyl CoA has higher stored free energy than pyruvate, and NAD+ has higher stored free energy than NADH.
C) Pyruvate has higher stored free energy than acetyl CoA, and NAD+ has higher stored free energy than NADH.
D) Acetyl CoA has higher stored free energy than pyruvate, and NADH has higher stored free energy than NAD+.
E) Pyruvate has higher stored free energy than acetyl CoA, and NADH has higher stored free energy than NAD+.
 Which statement about the molecules participating in this cellular reaction is correct?
Which statement about the molecules participating in this cellular reaction is correct?A) Pyruvate has higher stored free energy than acetyl CoA, and NAD+ has the same stored free energy as NADH.
B) Acetyl CoA has higher stored free energy than pyruvate, and NAD+ has higher stored free energy than NADH.
C) Pyruvate has higher stored free energy than acetyl CoA, and NAD+ has higher stored free energy than NADH.
D) Acetyl CoA has higher stored free energy than pyruvate, and NADH has higher stored free energy than NAD+.
E) Pyruvate has higher stored free energy than acetyl CoA, and NADH has higher stored free energy than NAD+.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements can be used as evidence that living cells follow the same basic principles of chemistry that nonliving systems follow?
A) Cells use three catabolic processes to harvest energy in the chemical bonds of glucose: glycolysis, cellular respiration, and fermentation.
B) Anaerobic oxidation of glucose is incomplete, since oxidation does not proceed completely to carbon dioxide and water, but stops at an intermediate end product.
C) Each step in the oxidation of glucose in a cell is catalyzed by a different enzyme.
D) One mole of glucose burned in a dish releases 686 kcal of heat energy, while a group of cells oxidizing the same quantity of glucose releases the same quantity of energy in a different form.
E) In a cell, different steps in the complete oxidation of glucose are carried out in different cellular compartments.
A) Cells use three catabolic processes to harvest energy in the chemical bonds of glucose: glycolysis, cellular respiration, and fermentation.
B) Anaerobic oxidation of glucose is incomplete, since oxidation does not proceed completely to carbon dioxide and water, but stops at an intermediate end product.
C) Each step in the oxidation of glucose in a cell is catalyzed by a different enzyme.
D) One mole of glucose burned in a dish releases 686 kcal of heat energy, while a group of cells oxidizing the same quantity of glucose releases the same quantity of energy in a different form.
E) In a cell, different steps in the complete oxidation of glucose are carried out in different cellular compartments.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Which process converts glucose to pyruvate, generating a small amount of ATP but no CO2?
A) Pyruvate oxidation
B) Glycolysis
C) The citric acid cycle
D) The respiratory chain
E) Gluconeogenesis
A) Pyruvate oxidation
B) Glycolysis
C) The citric acid cycle
D) The respiratory chain
E) Gluconeogenesis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which statement about metabolic pathways is true?
A) Complex chemical transformations in the cell occur in a single reaction.
B) Each reaction of the pathway requires O2.
C) In eukaryotes, the pathways exist in the cytoplasm.
D) The pathways vary from organism to organism.
E) Each pathway is regulated by specific enzymes.
A) Complex chemical transformations in the cell occur in a single reaction.
B) Each reaction of the pathway requires O2.
C) In eukaryotes, the pathways exist in the cytoplasm.
D) The pathways vary from organism to organism.
E) Each pathway is regulated by specific enzymes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
When a molecule loses hydrogen atoms (as opposed to hydrogen ions), it becomes
A) reduced.
B) oxidized.
C) redoxed.
D) hydrogenated.
E) hydrolyzed.
A) reduced.
B) oxidized.
C) redoxed.
D) hydrogenated.
E) hydrolyzed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The end result of glycolysis includes the formation of many molecules, including the
A) formation of 38 molecules of ATP.
B) reduction of 8 molecules of NAD+ to NADH.
C) formation of 2 molecules of pyruvate.
D) conversion of 1 molecule of glucose to lactic acid.
E) production of carbon dioxide.
A) formation of 38 molecules of ATP.
B) reduction of 8 molecules of NAD+ to NADH.
C) formation of 2 molecules of pyruvate.
D) conversion of 1 molecule of glucose to lactic acid.
E) production of carbon dioxide.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Refer to the equation below, summarizing a step in lactic acid fermentation. Pyruvate + NADH + H+ lactate + NAD+
In this reaction, which compound is oxidized and which is reduced?
A) Pyruvate is oxidized and lactate is reduced.
B) NADH is oxidized and lactate is reduced.
C) Pyruvate is reduced and NADH is oxidized.
D) NAD+ is reduced and pyruvate is oxidized.
E) Lactate is oxidized and NADH is reduced.
In this reaction, which compound is oxidized and which is reduced?
A) Pyruvate is oxidized and lactate is reduced.
B) NADH is oxidized and lactate is reduced.
C) Pyruvate is reduced and NADH is oxidized.
D) NAD+ is reduced and pyruvate is oxidized.
E) Lactate is oxidized and NADH is reduced.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The following reaction summarizes the overall chemical change that takes place as the result of electrons transferred along the respiratory chain. 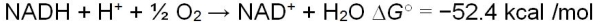 The formation of ATP from ADP and Pi requires the input of 7.3 kcal/mol.The respiratory chain can efficiently convert the majority of the free energy released from electrons to the chemical energy of phosphate bonds in ATP molecules, without a lot of wasted energy given off as heat.Which characteristic of the respiratory chain explains how this is possible?
The formation of ATP from ADP and Pi requires the input of 7.3 kcal/mol.The respiratory chain can efficiently convert the majority of the free energy released from electrons to the chemical energy of phosphate bonds in ATP molecules, without a lot of wasted energy given off as heat.Which characteristic of the respiratory chain explains how this is possible?
A) The number of components in the respiratory chain
B) The sizes of the components of the respiratory chain
C) The protein nature of many of the components in the respiratory chain
D) The location of the components in the inner mitochondrial membrane
E) The identity of the final electron acceptor at the end of the respiratory chain
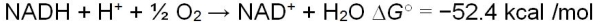 The formation of ATP from ADP and Pi requires the input of 7.3 kcal/mol.The respiratory chain can efficiently convert the majority of the free energy released from electrons to the chemical energy of phosphate bonds in ATP molecules, without a lot of wasted energy given off as heat.Which characteristic of the respiratory chain explains how this is possible?
The formation of ATP from ADP and Pi requires the input of 7.3 kcal/mol.The respiratory chain can efficiently convert the majority of the free energy released from electrons to the chemical energy of phosphate bonds in ATP molecules, without a lot of wasted energy given off as heat.Which characteristic of the respiratory chain explains how this is possible?A) The number of components in the respiratory chain
B) The sizes of the components of the respiratory chain
C) The protein nature of many of the components in the respiratory chain
D) The location of the components in the inner mitochondrial membrane
E) The identity of the final electron acceptor at the end of the respiratory chain

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Some aerobic bacterial species have respiratory chains with fewer components than those in mammalian respiratory chains.Which other characteristic would you expect to differ between these bacteria and mammalian cells?
A) The mechanism of ATP synthase in forming ATP
B) The production of a hydrogen ion gradient across a membrane
C) The arrangement of respiratory proteins in a series to facilitate electron transfer
D) The quantity of ATP synthesized per electron passed down the respiratory chain
E) The free energy change associated with the oxidation of NADH to NAD+ by oxygen
A) The mechanism of ATP synthase in forming ATP
B) The production of a hydrogen ion gradient across a membrane
C) The arrangement of respiratory proteins in a series to facilitate electron transfer
D) The quantity of ATP synthesized per electron passed down the respiratory chain
E) The free energy change associated with the oxidation of NADH to NAD+ by oxygen

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Which pathways are found in the mitochondrial matrix?
A) Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
B) Glycolysis and fermentation
C) Pyruvate oxidation and the respiratory chain
D) Pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle
E) Pyruvate oxidation and fermentation
A) Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
B) Glycolysis and fermentation
C) Pyruvate oxidation and the respiratory chain
D) Pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle
E) Pyruvate oxidation and fermentation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Pyruvate oxidation generates
A) acetyl CoA and carbon dioxide.
B) lactic acid and NADH.
C) ethanol and carbon dioxide.
D) citrate and ATP.
E) amino acids and ATP.
A) acetyl CoA and carbon dioxide.
B) lactic acid and NADH.
C) ethanol and carbon dioxide.
D) citrate and ATP.
E) amino acids and ATP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which event is not a part of oxidative phosphorylation?
A) Consumption of O2
B) Formation of ATP
C) Formation of H2O
D) Formation of carbon dioxide
E) Donation of electrons from FADH2
A) Consumption of O2
B) Formation of ATP
C) Formation of H2O
D) Formation of carbon dioxide
E) Donation of electrons from FADH2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Refer to the table below, which summarizes similarities and differences between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle in animal cells. 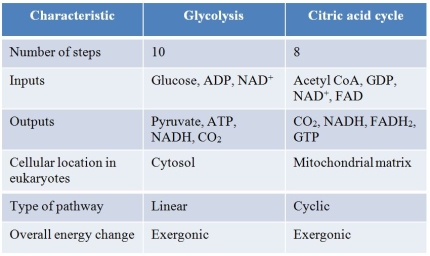 A student prepared this table as an aid to her study of these metabolic processes.Which statement best evaluates the accuracy of the student's work?
A student prepared this table as an aid to her study of these metabolic processes.Which statement best evaluates the accuracy of the student's work?
A) The table is accurate as written.
B) The inputs are not accurate for either glycolysis or the citric acid cycle.
C) The outputs are not accurate for glycolysis.
D) The type of pathway listed for glycolysis is not accurate.
E) The overall energy change is not accurately described for the citric acid cycle.
 A student prepared this table as an aid to her study of these metabolic processes.Which statement best evaluates the accuracy of the student's work?
A student prepared this table as an aid to her study of these metabolic processes.Which statement best evaluates the accuracy of the student's work?A) The table is accurate as written.
B) The inputs are not accurate for either glycolysis or the citric acid cycle.
C) The outputs are not accurate for glycolysis.
D) The type of pathway listed for glycolysis is not accurate.
E) The overall energy change is not accurately described for the citric acid cycle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Aerobic organisms exchange air containing O2 with air containing less O2 and more CO2.The CO2 comes from
A) hydrocarbons and the air.
B) the citric acid cycle.
C) glycolysis.
D) waste products.
E) oxidative phosphorylation.
A) hydrocarbons and the air.
B) the citric acid cycle.
C) glycolysis.
D) waste products.
E) oxidative phosphorylation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
More free energy is harvested during the citric acid cycle than during glycolysis, but only 1 mole of ATP is produced for each mole of acetyl CoA that enters the cycle.Most of the remaining free energy released during the citric acid cycle is
A) used to synthesize GTP.
B) used to reduce electron carriers.
C) lost as heat.
D) used to reduce pyruvate.
E) converted to kinetic energy.
A) used to synthesize GTP.
B) used to reduce electron carriers.
C) lost as heat.
D) used to reduce pyruvate.
E) converted to kinetic energy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
In the first reaction of glycolysis, glucose receives a phosphate group from ATP.This reaction is
A) respiration.
B) a redox reaction.
C) exergonic.
D) endergonic.
E) fermentation.
A) respiration.
B) a redox reaction.
C) exergonic.
D) endergonic.
E) fermentation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
In steps 6 through 10 of glycolysis, the conversion of 1 mole of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to pyruvate yields 2 moles of ATP.But the oxidation of glucose to pyruvate produces a total of 4 moles of ATP.Where do the remaining 2 moles of ATP come from?
A) One mole of glucose yields 2 moles of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
B) Two moles of ATP are used during the conversion of glucose to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
C) Glycolysis produces 2 moles of NADH.
D) Fermentation of pyruvate to lactic acid yields 2 moles of ATP.
E) Fermentation of pyruvate to lactic acid yields 2 moles of NAD+.
A) One mole of glucose yields 2 moles of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
B) Two moles of ATP are used during the conversion of glucose to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
C) Glycolysis produces 2 moles of NADH.
D) Fermentation of pyruvate to lactic acid yields 2 moles of ATP.
E) Fermentation of pyruvate to lactic acid yields 2 moles of NAD+.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
In the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, hydrogen atoms are transferred to NAD+.The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA is an example of a(n)
A) endergonic reaction.
B) allosteric reaction.
C) metabolic pathway.
D) reduction reaction.
E) redox reaction.
A) endergonic reaction.
B) allosteric reaction.
C) metabolic pathway.
D) reduction reaction.
E) redox reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The first and third reactions of the glycolytic pathway result in consumption of ATP.These are examples of
A) endergonic reactions.
B) allosteric reactions.
C) metabolic pathways.
D) oxidation reactions.
E) redox reactions.
A) endergonic reactions.
B) allosteric reactions.
C) metabolic pathways.
D) oxidation reactions.
E) redox reactions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
During the energy-investing portion of glycolysis, the phosphates from ATP molecules are
A) added to carbon atoms to form fructose 1,6-bisphosphate.
B) added to carbon atoms to form 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
C) wasted as an energy investment in glucose.
D) used to make pyruvate from glucose.
E) used to make lactate from glucose.
A) added to carbon atoms to form fructose 1,6-bisphosphate.
B) added to carbon atoms to form 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
C) wasted as an energy investment in glucose.
D) used to make pyruvate from glucose.
E) used to make lactate from glucose.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The oxidation of acetyl CoA to CO2 occurs via
A) fermentation.
B) the citric acid cycle.
C) glycolysis.
D) oxidative phosphorylation.
E) the respiratory chain.
A) fermentation.
B) the citric acid cycle.
C) glycolysis.
D) oxidative phosphorylation.
E) the respiratory chain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Absence of _______ would disrupt the citric acid cycle but not glycolysis.
A) ADP
B) NAD+
C) FAD
D) CO2
E) ATP
A) ADP
B) NAD+
C) FAD
D) CO2
E) ATP

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which product of glycolysis is transported across the mitochondrial membrane, where it is converted to the molecule that enters the citric acid cycle?
A) Glucose
B) Pyruvate
C) Acetyl CoA
D) NADH + H+
E) ATP synthase
A) Glucose
B) Pyruvate
C) Acetyl CoA
D) NADH + H+
E) ATP synthase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
For glycolysis to continue, cells require
A) a respiratory chain.
B) O2.
C) mitochondria.
D) chloroplasts.
E) NAD+.
A) a respiratory chain.
B) O2.
C) mitochondria.
D) chloroplasts.
E) NAD+.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, a multienzyme complex in the citric acid cycle, is located in the
A) thylakoids.
B) cytoplasm.
C) chloroplasts.
D) mitochondrial matrix.
E) cell membrane.
A) thylakoids.
B) cytoplasm.
C) chloroplasts.
D) mitochondrial matrix.
E) cell membrane.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Overall, four molecules of ATP are produced during glycolysis.However, at the end of glycolysis there are two ATP molecules, two pyruvate molecules, and two NADH molecules present.The ATP numbers do not match because
A) glucose metabolism is inefficient.
B) glucose phosphate is formed from fructose phosphate.
C) glucose is degraded to CO2.
D) two ATP are invested in the process of glycolysis.
E) two ATP are used to produce NADH.
A) glucose metabolism is inefficient.
B) glucose phosphate is formed from fructose phosphate.
C) glucose is degraded to CO2.
D) two ATP are invested in the process of glycolysis.
E) two ATP are used to produce NADH.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The citric acid cycle produces
A) ethanol.
B) pyruvate.
C) H2O.
D) lactic acid.
E) NADH and FADH2.
A) ethanol.
B) pyruvate.
C) H2O.
D) lactic acid.
E) NADH and FADH2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Rotenone is a potent inhibitor of mitochondrial complex I.If you were to treat isolated mitochondria with rotenone, what would happen to ATP production by oxidative phosphorylation?
A) ATP production would decrease, and electron transport would increase.
B) ATP production would increase, and electron transport would decrease.
C) ATP production and electron transport would decrease.
D) ATP production and electron transport would increase.
E) ATP production would become uncoupled from electron transport.
A) ATP production would decrease, and electron transport would increase.
B) ATP production would increase, and electron transport would decrease.
C) ATP production and electron transport would decrease.
D) ATP production and electron transport would increase.
E) ATP production would become uncoupled from electron transport.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Arsenate is used by phosphate-requiring enzymes as an alternative substrate to phosphate.Arsenate poisoning would have the greatest effect on cellular respiration by inhibiting which enzyme?
A) ATP synthase
B) NADH dehydrogenase
C) Phosphofructokinase
D) Pyruvate decarboxylase
E) Citrate synthase
A) ATP synthase
B) NADH dehydrogenase
C) Phosphofructokinase
D) Pyruvate decarboxylase
E) Citrate synthase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Which analogy best describes the mechanism of ATP synthase?
A) A ball bouncing down a stairway bumps into a cart and causes it to roll forward.
B) Water flowing across a waterwheel makes the wheel turn, which causes a milling grindstone to turn.
C) A rubber band stores more and more potential energy as it is continually twisted in one direction.
D) A snowball pushed down a hill becomes larger and larger as it picks up snow as it rolls.
E) A bucket of water positioned on top of a half-opened door spills its load as the door is pushed open.
A) A ball bouncing down a stairway bumps into a cart and causes it to roll forward.
B) Water flowing across a waterwheel makes the wheel turn, which causes a milling grindstone to turn.
C) A rubber band stores more and more potential energy as it is continually twisted in one direction.
D) A snowball pushed down a hill becomes larger and larger as it picks up snow as it rolls.
E) A bucket of water positioned on top of a half-opened door spills its load as the door is pushed open.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The chemiosmotic generation of ATP is driven by
A) osmotic movement of H2O into an area of high solute concentration.
B) the addition of protons to ADP and phosphate via enzymes.
C) oxidative phosphorylation.
D) the proton-motive force.
E) isocitrate dehydrogenase.
A) osmotic movement of H2O into an area of high solute concentration.
B) the addition of protons to ADP and phosphate via enzymes.
C) oxidative phosphorylation.
D) the proton-motive force.
E) isocitrate dehydrogenase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Refer to the table below, showing data collected from experiments using purified soybean mitochondria incubated in buffer containing compound X, compound Y, or no additions.Three different assays were performed on each group of mitochondria to determine the rate of oxygen uptake, ATP synthesis, and formation of a hydrogen ion gradient.The results are expressed as a percentage relative to the control group. 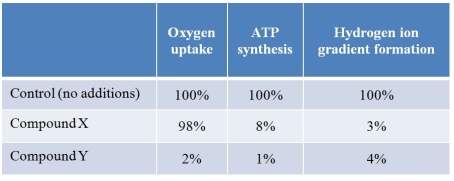 Which conclusion is consistent with these results?
Which conclusion is consistent with these results?
A) Compound X and compound Y inhibit different proteins in the respiratory chain.
B) Compound X and compound Y both uncouple electron transport from ATP synthesis.
C) Compound X uncouples electron transport from ATP synthesis, and compound Y inhibits a protein in the respiratory chain.
D) Compound X inhibits a protein in the respiratory chain, and compound Y uncouples electron transport from ATP synthesis.
E) Compound X prevents oxygen from functioning as the final electron acceptor, and compound Y inhibits a protein in the respiratory chain.
 Which conclusion is consistent with these results?
Which conclusion is consistent with these results?A) Compound X and compound Y inhibit different proteins in the respiratory chain.
B) Compound X and compound Y both uncouple electron transport from ATP synthesis.
C) Compound X uncouples electron transport from ATP synthesis, and compound Y inhibits a protein in the respiratory chain.
D) Compound X inhibits a protein in the respiratory chain, and compound Y uncouples electron transport from ATP synthesis.
E) Compound X prevents oxygen from functioning as the final electron acceptor, and compound Y inhibits a protein in the respiratory chain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Which statement about the respiratory electron transport chain is true?
A) Electrons are received from NADH only.
B) Electrons are passed from donor to recipient carrier molecules in a series of oxidation-reduction reactions.
C) The terminal electron acceptor is usually H2O.
D) Most of the respiratory proteins are in the cytosol.
E) Energy must be added to move electrons from one electron carrier to the next.
A) Electrons are received from NADH only.
B) Electrons are passed from donor to recipient carrier molecules in a series of oxidation-reduction reactions.
C) The terminal electron acceptor is usually H2O.
D) Most of the respiratory proteins are in the cytosol.
E) Energy must be added to move electrons from one electron carrier to the next.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Refer to the diagram below, showing electron transport and ATP synthesis.When pure reduced cytochrome c is added to isolated mitochondria in a solution containing ADP, Pi, O2, and antimycin A (a mitochondria complex II inhibitor), the cytochrome c becomes oxidized and ATP is formed. 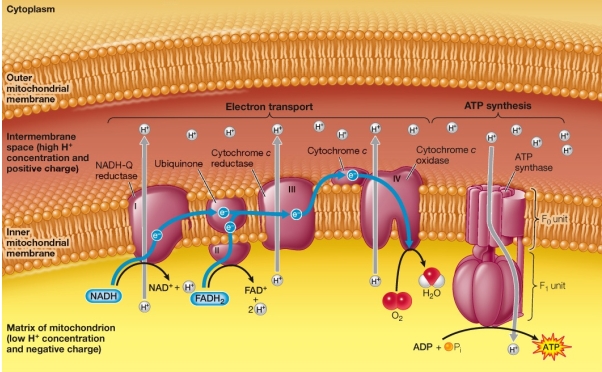 Which sequence represents the probable flow of electrons in this system?
Which sequence represents the probable flow of electrons in this system?
A) NADH-Q reductase cytochrome c complex IV O2
B) Cytochrome c O2 complex IV
C) Complex IV cytochrome c O2
D) Cytochrome c complex IV 0 O2
E) Cytochrome c NADH-Q reductase complex IV O2
 Which sequence represents the probable flow of electrons in this system?
Which sequence represents the probable flow of electrons in this system?A) NADH-Q reductase cytochrome c complex IV O2
B) Cytochrome c O2 complex IV
C) Complex IV cytochrome c O2
D) Cytochrome c complex IV 0 O2
E) Cytochrome c NADH-Q reductase complex IV O2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Oxygen is used by
A) glycolysis.
B) the citric acid cycle.
C) the respiratory electron transport chain.
D) substrate-level phosphorylation.
E) ATP synthase.
A) glycolysis.
B) the citric acid cycle.
C) the respiratory electron transport chain.
D) substrate-level phosphorylation.
E) ATP synthase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The drug 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP) destroys the proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane.What would be the effect of incubating isolated mitochondria in a solution of DNP?
A) O2 would no longer be reduced to H2O.
B) ATP synthesis would decline.
C) Mitochondria would show a burst of increased ATP synthesis.
D) Glycolysis would stop.
E) Mitochondria would switch from glycolysis to fermentation.
A) O2 would no longer be reduced to H2O.
B) ATP synthesis would decline.
C) Mitochondria would show a burst of increased ATP synthesis.
D) Glycolysis would stop.
E) Mitochondria would switch from glycolysis to fermentation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The respiratory electron transport chain
A) is located in the mitochondrial matrix.
B) includes only peripheral membrane proteins.
C) always produces ATP.
D) oxidizes reduced coenzymes.
E) operates simultaneously with fermentation.
A) is located in the mitochondrial matrix.
B) includes only peripheral membrane proteins.
C) always produces ATP.
D) oxidizes reduced coenzymes.
E) operates simultaneously with fermentation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Electron transport within NADH-Q reductase, cytochrome reductase, and cytochrome oxidase can be coupled to proton transport from the mitochondrial matrix to the space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes.This is because those protein complexes
A) are in the mitochondrial matrix.
B) span the inner mitochondrial membrane.
C) are in the space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes.
D) remain in the cytoplasm.
E) loosely attach to the inner mitochondrial membrane.
A) are in the mitochondrial matrix.
B) span the inner mitochondrial membrane.
C) are in the space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes.
D) remain in the cytoplasm.
E) loosely attach to the inner mitochondrial membrane.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
ATP is produced by which enzymatic complex?
A) NADH-Q
B) Ubiquinone (Q)
C) ATP synthase
D) Succinate dehydrogenase
E) Cytochrome c reductase
A) NADH-Q
B) Ubiquinone (Q)
C) ATP synthase
D) Succinate dehydrogenase
E) Cytochrome c reductase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Some microbes use non-O2 electron acceptors to complete the electron transport chain.An example of an organism that carries out this type of electron transport is a soil bacterium that takes in nitrate (NO3−) and releases nitrogen gas (N2).The nitrate functions as a(n)
A) energy source.
B) electron acceptor.
C) source of electrons.
D) fuel molecule.
E) respiratory chain component.
A) energy source.
B) electron acceptor.
C) source of electrons.
D) fuel molecule.
E) respiratory chain component.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Overall, the _______ within each complex of the respiratory chain decreases as electrons move from the first to the last complex.
A) number of proteins
B) efficiency of electron transfer
C) level of entropy
D) standard free energy
E) degree of oxidation
A) number of proteins
B) efficiency of electron transfer
C) level of entropy
D) standard free energy
E) degree of oxidation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The electron transport chain contains four large protein complexes (I, II, III, and IV) plus cytochrome c and ubiquinone.One function of these components is to
A) sequester electrons.
B) ensure the production of H2O from O2.
C) regulate the passage of protons through the chain.
D) synthesize ATP.
E) transport protons across the membrane.
A) sequester electrons.
B) ensure the production of H2O from O2.
C) regulate the passage of protons through the chain.
D) synthesize ATP.
E) transport protons across the membrane.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
According to the chemiosmotic theory, the energy for the synthesis of ATP during the flow of electrons down the respiratory chain is provided directly by the
A) hydrolysis of GTP.
B) reduction of NAD+.
C) hydrolysis of ATP.
D) reduction of FAD.
E) diffusion of protons.
A) hydrolysis of GTP.
B) reduction of NAD+.
C) hydrolysis of ATP.
D) reduction of FAD.
E) diffusion of protons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
During cellular respiration, H2O is produced as a result of the
A) combining of CO2 with protons.
B) conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA.
C) degradation of glucose to pyruvate.
D) reduction of O2 at the end of the electron transport chain.
E) chemiosmosis process.
A) combining of CO2 with protons.
B) conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA.
C) degradation of glucose to pyruvate.
D) reduction of O2 at the end of the electron transport chain.
E) chemiosmosis process.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Increasing the body's brown fat could be a weight loss method because brown fat mitochondria waste energy instead of creating usable energy.What is the mechanism for this waste in brown fat?
A) UCP1 in brown fat uncouples the electron transport chain from ATP synthesis.
B) Brown fat bypasses the process of glycolysis.
C) Brown fat is less efficient than white fat and causes shivering.
D) Hydrogen ions leak across the cell's plasma membrane in white fat.
E) Cytochrome reductase activity decreases in brown fat in response to respiration.
A) UCP1 in brown fat uncouples the electron transport chain from ATP synthesis.
B) Brown fat bypasses the process of glycolysis.
C) Brown fat is less efficient than white fat and causes shivering.
D) Hydrogen ions leak across the cell's plasma membrane in white fat.
E) Cytochrome reductase activity decreases in brown fat in response to respiration.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
In the absence of O2, cells capable of fermentation
A) accumulate glucose.
B) no longer produce ATP.
C) accumulate pyruvate.
D) can oxidize FAD.
E) can oxidize NADH to produce NAD+.
A) accumulate glucose.
B) no longer produce ATP.
C) accumulate pyruvate.
D) can oxidize FAD.
E) can oxidize NADH to produce NAD+.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The oxidizing agent at the end of the electron transport chain is
A) O2.
B) NAD+.
C) ATP.
D) FAD.
E) ubiquinone.
A) O2.
B) NAD+.
C) ATP.
D) FAD.
E) ubiquinone.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Refer to the table below. 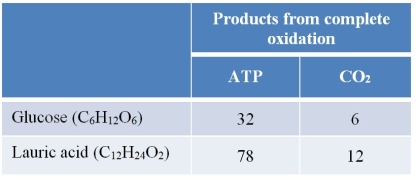 The table summarizes the products (in moles) of the complete oxidation of 1 mole of glucose and the complete oxidation of 1 mole of lauric acid, a fatty acid.Use this information to determine how energy production will compare when an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide is produced from oxidation events involving these two molecules.
The table summarizes the products (in moles) of the complete oxidation of 1 mole of glucose and the complete oxidation of 1 mole of lauric acid, a fatty acid.Use this information to determine how energy production will compare when an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide is produced from oxidation events involving these two molecules.
A) The energy production will be equal for equal quantities of CO2 production by these two molecules.
B) The energy production by lauric acid oxidation will be greater by 10 ATP when the two molecules are fully oxidized to produce equal quantities of CO2.
C) The energy production by glucose oxidation will be greater by 10 ATP when the two molecules are fully oxidized to produce equal quantities of CO2.
D) The energy production by lauric acid oxidation will be greater by 14 ATP when the two molecules are fully oxidized to produce equal quantities of CO2.
E) The energy production by glucose oxidation will be greater by 14 ATP when the two molecules are fully oxidized to produce equal quantities of CO2.
 The table summarizes the products (in moles) of the complete oxidation of 1 mole of glucose and the complete oxidation of 1 mole of lauric acid, a fatty acid.Use this information to determine how energy production will compare when an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide is produced from oxidation events involving these two molecules.
The table summarizes the products (in moles) of the complete oxidation of 1 mole of glucose and the complete oxidation of 1 mole of lauric acid, a fatty acid.Use this information to determine how energy production will compare when an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide is produced from oxidation events involving these two molecules.A) The energy production will be equal for equal quantities of CO2 production by these two molecules.
B) The energy production by lauric acid oxidation will be greater by 10 ATP when the two molecules are fully oxidized to produce equal quantities of CO2.
C) The energy production by glucose oxidation will be greater by 10 ATP when the two molecules are fully oxidized to produce equal quantities of CO2.
D) The energy production by lauric acid oxidation will be greater by 14 ATP when the two molecules are fully oxidized to produce equal quantities of CO2.
E) The energy production by glucose oxidation will be greater by 14 ATP when the two molecules are fully oxidized to produce equal quantities of CO2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Key events in the rise of multicellularity in living organisms included the increase in _______ in/on Earth's _______ as a result of photosynthesis, and the evolution of _______ that enabled organisms to use _______.
A) dry land; surface; lungs; oxygen
B) water; oceans; gills; oxygen
C) oxygen; atmosphere; cellular respiration; oxygen
D) carbon dioxide; atmosphere; photosynthesis; carbon dioxide
E) prey; ecosystems; primitive brains; fermentation
A) dry land; surface; lungs; oxygen
B) water; oceans; gills; oxygen
C) oxygen; atmosphere; cellular respiration; oxygen
D) carbon dioxide; atmosphere; photosynthesis; carbon dioxide
E) prey; ecosystems; primitive brains; fermentation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Bacteria that are shifted from an oxygen-rich environment to an anaerobic environment can continue to grow rapidly only if they
A) increase the rate of the citric acid cycle.
B) produce more ATP per mole of glucose during glycolysis.
C) produce ATP during the oxidation of NADH.
D) increase the rate of transport of electrons down the respiratory chain.
E) increase the rate of the glycolytic reactions.
A) increase the rate of the citric acid cycle.
B) produce more ATP per mole of glucose during glycolysis.
C) produce ATP during the oxidation of NADH.
D) increase the rate of transport of electrons down the respiratory chain.
E) increase the rate of the glycolytic reactions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Refer to the table below.  A student created this table as a study guide for learning the similarities and differences between lactic acid and alcoholic fermentation.Which statement best evaluates the accuracy of the student's efforts?
A student created this table as a study guide for learning the similarities and differences between lactic acid and alcoholic fermentation.Which statement best evaluates the accuracy of the student's efforts?
A) The table is accurate as written.
B) Lactic acid fermentation has different inputs than alcoholic fermentation.
C) NADH is a net output for both types of fermentation and should be listed.
D) Alcoholic fermentation results in less ATP production than lactic acid fermentation.
E) Both types of fermentation differ by two steps.
 A student created this table as a study guide for learning the similarities and differences between lactic acid and alcoholic fermentation.Which statement best evaluates the accuracy of the student's efforts?
A student created this table as a study guide for learning the similarities and differences between lactic acid and alcoholic fermentation.Which statement best evaluates the accuracy of the student's efforts?A) The table is accurate as written.
B) Lactic acid fermentation has different inputs than alcoholic fermentation.
C) NADH is a net output for both types of fermentation and should be listed.
D) Alcoholic fermentation results in less ATP production than lactic acid fermentation.
E) Both types of fermentation differ by two steps.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Most ATP produced in aerobic organisms is made
A) by glycolysis.
B) in the citric acid cycle.
C) using ATP synthase.
D) from photosynthesis.
E) by burning fat.
A) by glycolysis.
B) in the citric acid cycle.
C) using ATP synthase.
D) from photosynthesis.
E) by burning fat.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
The fermentation process in vertebrate muscle cells produces
A) lactic acid.
B) 12 moles of ATP.
C) pyruvic acid.
D) an excessive amount of energy.
E) ethanol.
A) lactic acid.
B) 12 moles of ATP.
C) pyruvic acid.
D) an excessive amount of energy.
E) ethanol.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Substrate-level phosphorylation is used to produce ATP in the absence of O2.This process depends on _______ to regenerate NAD+.
A) glycolysis
B) fermentation
C) chemiosmosis
D) proteolysis
E) pyruvate oxidation
A) glycolysis
B) fermentation
C) chemiosmosis
D) proteolysis
E) pyruvate oxidation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
The reduction of pyruvate to lactic acid during fermentation allows glycolysis to continue in the absence of O2 because this reaction
A) produces H2O.
B) is a kinase reaction.
C) is coupled to the oxidation of NADH to NAD+.
D) is coupled to the formation of ATP.
E) is coupled to the reduction of NAD+ to NADH.
A) produces H2O.
B) is a kinase reaction.
C) is coupled to the oxidation of NADH to NAD+.
D) is coupled to the formation of ATP.
E) is coupled to the reduction of NAD+ to NADH.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
The component of aerobic respiration that produces the most ATP per mole of glucose is
A) the electron transport chain.
B) the citric acid cycle.
C) glycolysis.
D) lactic acid fermentation.
E) alcoholic fermentation.
A) the electron transport chain.
B) the citric acid cycle.
C) glycolysis.
D) lactic acid fermentation.
E) alcoholic fermentation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Which path could a carbon atom follow if it began in an amino acid in a protein in some tuna that was eaten by a cat and eventually ended up in a lipid in the cell membrane of one of the cat's muscle cells?
A) Amino acid citric acid cycle acetyl CoA fatty acid triglyceride cell membrane
B) Amino acid acetyl CoA citric acid cycle pyruvate oxidation cell membrane
C) Amino acid pyruvate oxidation gluconeogenesis glucose glycerol triglyceride cell membrane
D) Amino acid electron transport citric acid cycle acetyl CoA lipid cell membrane
E) Amino acid citric acid cycle acetyl CoA pyruvate glycolysis glycerol triglyceride cell membrane
A) Amino acid citric acid cycle acetyl CoA fatty acid triglyceride cell membrane
B) Amino acid acetyl CoA citric acid cycle pyruvate oxidation cell membrane
C) Amino acid pyruvate oxidation gluconeogenesis glucose glycerol triglyceride cell membrane
D) Amino acid electron transport citric acid cycle acetyl CoA lipid cell membrane
E) Amino acid citric acid cycle acetyl CoA pyruvate glycolysis glycerol triglyceride cell membrane

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
The formation of ethanol from pyruvate is an example of
A) an irreversible reaction.
B) a fermentation process that takes place in the absence of O2.
C) the production of extra energy from glycolysis.
D) cellular respiration.
E) a high-energy-yielding process.
A) an irreversible reaction.
B) a fermentation process that takes place in the absence of O2.
C) the production of extra energy from glycolysis.
D) cellular respiration.
E) a high-energy-yielding process.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Regardless of the electron or hydrogen acceptor employed, fermentation always produces
A) AMP.
B) DNA.
C) Pi.
D) NAD+.
E) CO2.
A) AMP.
B) DNA.
C) Pi.
D) NAD+.
E) CO2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Before starch can be used for respiratory ATP production, it must be hydrolyzed to
A) pyruvate.
B) fatty acids.
C) amino acids.
D) glucose.
E) oxaloacetate.
A) pyruvate.
B) fatty acids.
C) amino acids.
D) glucose.
E) oxaloacetate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
How many moles of high-energy phosphates are generated in converting 1 mole of glucose to lactate?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 36
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 36

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
When the supply of acetyl CoA being produced exceeds the demands of the citric acid cycle, some of the acetyl CoA is diverted to the synthesis of
A) pyruvate.
B) NAD.
C) proteins.
D) fatty acids.
E) lactic acid.
A) pyruvate.
B) NAD.
C) proteins.
D) fatty acids.
E) lactic acid.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Refer to the table below. 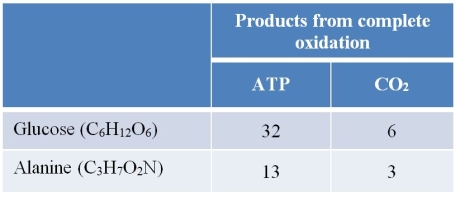 The complete oxidation of 1 mole of glucose and the complete oxidation of 1 mole of alanine give the same products in different quantities, as shown in the table.Given this information, it can be stated that
The complete oxidation of 1 mole of glucose and the complete oxidation of 1 mole of alanine give the same products in different quantities, as shown in the table.Given this information, it can be stated that
A) alanine produces 6 more ATP per carbon oxidized than glucose.
B) glucose produces 4 more ATP per carbon oxidized than alanine.
C) alanine produces 2 more ATP per carbon oxidized than glucose.
D) glucose produces 1 more ATP per carbon oxidized than alanine.
E) alanine produces approximately the same ATP per carbon oxidized as glucose.
 The complete oxidation of 1 mole of glucose and the complete oxidation of 1 mole of alanine give the same products in different quantities, as shown in the table.Given this information, it can be stated that
The complete oxidation of 1 mole of glucose and the complete oxidation of 1 mole of alanine give the same products in different quantities, as shown in the table.Given this information, it can be stated thatA) alanine produces 6 more ATP per carbon oxidized than glucose.
B) glucose produces 4 more ATP per carbon oxidized than alanine.
C) alanine produces 2 more ATP per carbon oxidized than glucose.
D) glucose produces 1 more ATP per carbon oxidized than alanine.
E) alanine produces approximately the same ATP per carbon oxidized as glucose.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Refer to the table below, showing ATP yield from cellular respiration in two different microorganisms.Yield is defined as the net number of molecules of ATP formed for every glucose molecule oxidized. 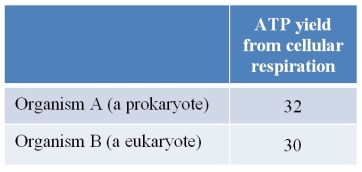 Which statement provides a possible explanation for why the yields differ?
Which statement provides a possible explanation for why the yields differ?
A) There is more opportunity for ATP to hydrolyze spontaneously before it can be used in the eukaryotic cell than in the prokaryotic cell.
B) The prokaryote has fewer respiratory proteins in its electron transport chain than the eukaryote.
C) NADH produced via glycolysis must be shuttled across the mitochondrial membrane in the eukaryote but not in the prokaryote.
D) Some ATP is used in the beginning steps of glycolysis in the eukaryote but not in the prokaryote.
E) The prokaryote has the capability of switching from aerobic to anaerobic respiration whereas the eukaryote does not.
 Which statement provides a possible explanation for why the yields differ?
Which statement provides a possible explanation for why the yields differ?A) There is more opportunity for ATP to hydrolyze spontaneously before it can be used in the eukaryotic cell than in the prokaryotic cell.
B) The prokaryote has fewer respiratory proteins in its electron transport chain than the eukaryote.
C) NADH produced via glycolysis must be shuttled across the mitochondrial membrane in the eukaryote but not in the prokaryote.
D) Some ATP is used in the beginning steps of glycolysis in the eukaryote but not in the prokaryote.
E) The prokaryote has the capability of switching from aerobic to anaerobic respiration whereas the eukaryote does not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Refer to the graph below, showing changes in the source of blood glucose as a person goes from a state of active food intake to a state of starvation. 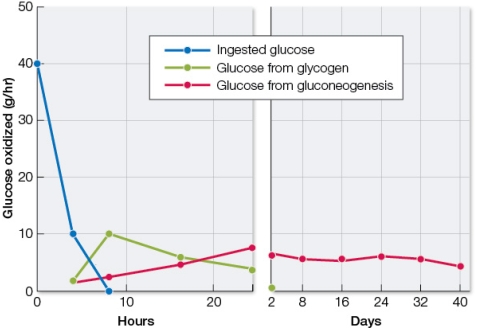 The person's blood glucose levels remain very stable; only the source of glucose changes.Liver cells play an active role in maintaining the stable levels of blood glucose.Which changes in liver cell metabolism could account for the data shown?
The person's blood glucose levels remain very stable; only the source of glucose changes.Liver cells play an active role in maintaining the stable levels of blood glucose.Which changes in liver cell metabolism could account for the data shown?
A) At 1 hour after eating, liver cells inhibit phosphofructokinase and activate enzymes involved in glycogen breakdown.
B) At 4 hours after eating, liver cells activate enzymes involved in glycogen breakdown as well as enzymes involved in the breakdown of proteins and lipids.
C) At 10 hours after eating, liver cells activate fatty acid synthase and inhibit enzymes involved in the breakdown of proteins and lipids.
D) At 2 days into starvation, liver cells activate phosphofructokinase and inhibit enzymes involved in glycogen breakdown.
E) At 16 days into starvation, liver cells activate phosphofructokinase and inhibit enzymes involved in the breakdown of proteins and lipids.
 The person's blood glucose levels remain very stable; only the source of glucose changes.Liver cells play an active role in maintaining the stable levels of blood glucose.Which changes in liver cell metabolism could account for the data shown?
The person's blood glucose levels remain very stable; only the source of glucose changes.Liver cells play an active role in maintaining the stable levels of blood glucose.Which changes in liver cell metabolism could account for the data shown?A) At 1 hour after eating, liver cells inhibit phosphofructokinase and activate enzymes involved in glycogen breakdown.
B) At 4 hours after eating, liver cells activate enzymes involved in glycogen breakdown as well as enzymes involved in the breakdown of proteins and lipids.
C) At 10 hours after eating, liver cells activate fatty acid synthase and inhibit enzymes involved in the breakdown of proteins and lipids.
D) At 2 days into starvation, liver cells activate phosphofructokinase and inhibit enzymes involved in glycogen breakdown.
E) At 16 days into starvation, liver cells activate phosphofructokinase and inhibit enzymes involved in the breakdown of proteins and lipids.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Which process occurs when O2 is unavailable to a cell?
A) Pyruvate oxidation
B) The citric acid cycle
C) Fermentation
D) Formation of H2O by the electron transport chain
E) Oxidative phosphorylation
A) Pyruvate oxidation
B) The citric acid cycle
C) Fermentation
D) Formation of H2O by the electron transport chain
E) Oxidative phosphorylation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
In lactate fermentation, NAD+ is produced during the
A) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA.
B) reduction of pyruvate to lactic acid.
C) reduction of acetaldehyde to ethanol.
D) hydrolysis of ATP to ADP.
E) oxidation of glucose.
A) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA.
B) reduction of pyruvate to lactic acid.
C) reduction of acetaldehyde to ethanol.
D) hydrolysis of ATP to ADP.
E) oxidation of glucose.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 246 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








