Deck 17: Audit Sampling for Tests of Details of Balances
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/130
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 17: Audit Sampling for Tests of Details of Balances
1
If an auditor desires a greater level of assurance in auditing a balance, the acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance
A) is reduced.
B) is increased.
C) is not changed.
D) may be reduced or increased depending upon other circumstances.
A) is reduced.
B) is increased.
C) is not changed.
D) may be reduced or increased depending upon other circumstances.
A
2
When selecting a sample size for substantive tests of balances which factor, other factors being equal, would result in a larger sample?
A) a decrease in the tolerable misstatement
B) small expected misstatements
C) an increase in the tolerable misstatement
D) an increase in the acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance
A) a decrease in the tolerable misstatement
B) small expected misstatements
C) an increase in the tolerable misstatement
D) an increase in the acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance
A
3
The word below that best explains the relationship between required sample size and the acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance is
A) inverse.
B) direct.
C) proportional.
D) indeterminate.
A) inverse.
B) direct.
C) proportional.
D) indeterminate.
A
4
The auditor's principal objective when using a sample of tests of details of balances is whether the
A) account balance being audited is fairly stated.
B) transactions being audited are free of misstatements.
C) controls being tested are operating effectively.
D) transactions and account balances being audited are fairly stated.
A) account balance being audited is fairly stated.
B) transactions being audited are free of misstatements.
C) controls being tested are operating effectively.
D) transactions and account balances being audited are fairly stated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Tolerable misstatement is used to
A)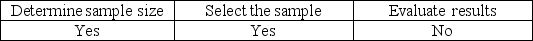
B)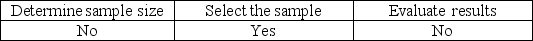
C)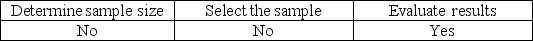
D)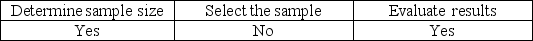
A)
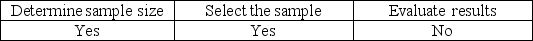
B)
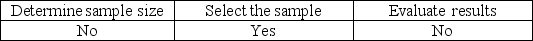
C)
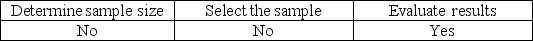
D)
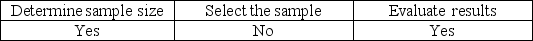

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
In the test of details of balances, the auditor wants to make inferences about the entire population based on a sample.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Tests for rates of occurrence are appropriately used in all but which of the following situations?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
To address sampling risk, auditors can use either nonstatistical or statistical methods for tests of controls, substantive tests of transactions, and test of details of balances.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Auditors perform test of controls and substantive tests of transactions for several reasons. Which of the following is not one of those reasons?
A) for larger public company audits, to conclude the control is operating effectively
B) to reduce assessed control risk and thereby reduce tests of details of balances
C) to determine whether the exception rate in the population is sufficiently low
D) to use rate of occurrence tests in the tests of details of balances
A) for larger public company audits, to conclude the control is operating effectively
B) to reduce assessed control risk and thereby reduce tests of details of balances
C) to determine whether the exception rate in the population is sufficiently low
D) to use rate of occurrence tests in the tests of details of balances

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Auditors generally use rate of occurrence tests in tests of details of balances.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The most important difference among tests of controls, substantive tests of transactions, and tests of details of balances lies in what the auditor wants to measure. Explain what each type of test attempts to measure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
If an auditor concludes that internal controls are likely to be effective, the preliminary assessment of control risk can be reduced, leading to which of the following impacts on the acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance?
A) The acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance will be reduced.
B) The acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance will be increased.
C) The acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance will be eliminated.
D) The acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance will not be impacted.
A) The acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance will be reduced.
B) The acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance will be increased.
C) The acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance will be eliminated.
D) The acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance will not be impacted.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Both sampling and nonsampling risks are associated with
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
If acceptable audit risk is increased, acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance should be
A) increased.
B) reduced.
C) unaffected.
D) modified.
A) increased.
B) reduced.
C) unaffected.
D) modified.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Sampling, not nonsampling risks, are important for tests of controls, substantive tests of transaction, and test of details of balances.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
In estimating the population misstatement, the first step in projecting from the sample to the population is to
A) make a point estimate.
B) revise the upper error bound.
C) calculate the precision interval.
D) determine the population mean.
A) make a point estimate.
B) revise the upper error bound.
C) calculate the precision interval.
D) determine the population mean.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The final step in the evaluation of the audit results is the decision to
A) accept the population as fairly stated or to require further action.
B) determine sampling error and calculate the estimated total population error.
C) project the point estimate.
D) determine the error in each sample.
A) accept the population as fairly stated or to require further action.
B) determine sampling error and calculate the estimated total population error.
C) project the point estimate.
D) determine the error in each sample.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which of the following does not have to be considered in determining the initial sample size of a test of details?
A) tolerable misstatement
B) acceptable risk of incorrect rejection
C) estimate of misstatements in the population
D) inherent risk
A) tolerable misstatement
B) acceptable risk of incorrect rejection
C) estimate of misstatements in the population
D) inherent risk

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
What is the purpose of applying stratified sampling to a population?
A)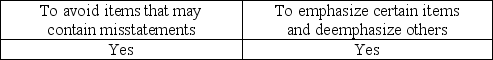
B)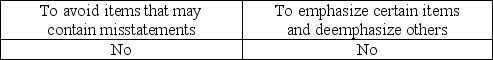
C)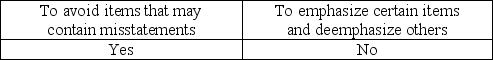
D)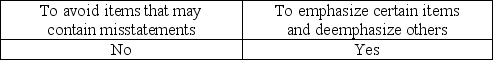
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
When using sampling methods, the auditor is focused on obtaining results in dollar terms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
One of the steps involved in planning the sample for the tests of details of balances is to
A) select the sample.
B) perform the audit procedures.
C) define a misstatement.
D) analyze the misstatements.
A) select the sample.
B) perform the audit procedures.
C) define a misstatement.
D) analyze the misstatements.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
When errors are found in a sample, auditors in practice generally assume
A) that the population errors cannot be determined.
B) that the population errors are larger than the sample errors.
C) that the population errors are smaller than the sample errors.
D) that the actual sample errors are representative of the population errors.
A) that the population errors cannot be determined.
B) that the population errors are larger than the sample errors.
C) that the population errors are smaller than the sample errors.
D) that the actual sample errors are representative of the population errors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
When analyzing misstatements, the auditor will determine
A) the implications of the misstatements on other audit areas.
B) the potential impact on the financial statements.
C) the effect on company operations.
D) all of the above.
A) the implications of the misstatements on other audit areas.
B) the potential impact on the financial statements.
C) the effect on company operations.
D) all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which of the following conditions would lead to a larger sample size?
A) larger tolerable misstatement
B) low inherent risk
C) high control risk
D) smaller account balance
A) larger tolerable misstatement
B) low inherent risk
C) high control risk
D) smaller account balance

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
If no exceptions were found in the substantive tests of transactions,
A) ARIA would stay the same.
B) the sample size would stay the same.
C) ARIA would increase.
D) the sample size would increase.
A) ARIA would stay the same.
B) the sample size would stay the same.
C) ARIA would increase.
D) the sample size would increase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Which of the following would lead to a larger sample size?
A) low inherent risk
B) low control risk
C) larger tolerable misstatement
D) unsatisfactory results in other related substantive procedures
A) low inherent risk
B) low control risk
C) larger tolerable misstatement
D) unsatisfactory results in other related substantive procedures

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
If the population is not considered acceptable, one step the auditor is likely to take is to
A) retest all internal controls.
B) ask the client to adjust the account balance.
C) test the entire population.
D) decrease inherent risk.
A) retest all internal controls.
B) ask the client to adjust the account balance.
C) test the entire population.
D) decrease inherent risk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
While performing a substantive test of details during an audit, the auditor determined that the sample results supported the conclusion that the recorded account balance was not materially misstated. It was, in fact, materially misstated. This situation illustrates the risk of
A) incorrect rejection.
B) incorrect acceptance.
C) assessing control risk too low.
D) assessing control risk too high.
A) incorrect rejection.
B) incorrect acceptance.
C) assessing control risk too low.
D) assessing control risk too high.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
________ is a method of projecting from the sample to the population to estimate the population misstatement. It assumes that misstatements in the unaudited population are proportional to the misstatements found in the sample.
A) Mean-per-unit estimation
B) Point estimate
C) Monetary unit
D) Basic precision
A) Mean-per-unit estimation
B) Point estimate
C) Monetary unit
D) Basic precision

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
As the amount of misstatements expected in the population approaches tolerable misstatement, the planned sample size will
A) decrease.
B) increase.
C) vary based on characteristics of the population.
D) be unaffected.
A) decrease.
B) increase.
C) vary based on characteristics of the population.
D) be unaffected.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Factors considered by an auditor to determine the possibility that the true population misstatement exceeds a tolerable amount in a nonstatistical sample include all of the following except for
A) the extent to which items in the population have been audited 100%.
B) the difference between the point estimate and acceptable control risk.
C) whether misstatements tend to be offsetting or in only one direction.
D) the amounts of individual misstatements.
A) the extent to which items in the population have been audited 100%.
B) the difference between the point estimate and acceptable control risk.
C) whether misstatements tend to be offsetting or in only one direction.
D) the amounts of individual misstatements.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The risk the auditor is willing to take of accepting a balance as correct when the true misstatement in the balance under audit is greater than the tolerable misstatement is
A) the upper bound.
B) the tolerable risk.
C) the acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance.
D) the lower bound.
A) the upper bound.
B) the tolerable risk.
C) the acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance.
D) the lower bound.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
While performing a substantive test of details during an audit, the auditor determined that the sample results supported the conclusion that the recorded account balance was materially misstated. Which of the following is the least likely auditor reaction to this discovery?
A) perform expanded audit tests in the relevant areas
B) increase detection risk in the relevant areas
C) increase the sample size
D) take no action until tests of other audit areas are completed
A) perform expanded audit tests in the relevant areas
B) increase detection risk in the relevant areas
C) increase the sample size
D) take no action until tests of other audit areas are completed

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
When defining the population and the sampling unit for tests of details of balances,
A) the population is defined as all of the transactions in the journal for the period.
B) the sampling unit must be the same for all balance sheet accounts.
C) if sampling for completeness, the sampling unit will be customers with zero balances.
D) if sampling for completeness, the sampling unit will be the items making up the recorded population.
A) the population is defined as all of the transactions in the journal for the period.
B) the sampling unit must be the same for all balance sheet accounts.
C) if sampling for completeness, the sampling unit will be customers with zero balances.
D) if sampling for completeness, the sampling unit will be the items making up the recorded population.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
If analytical procedures are performed with no indications of likely misstatements, ARIA will ________ and the sample size will ________.
A) remain the same; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; decrease
D) decrease; increase
A) remain the same; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; decrease
D) decrease; increase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
An auditor using nonstatistical sampling cannot formally measure sampling error and therefore must subjectively consider the possibility that the true population misstatement exceeds a tolerable amount. Which of the following factors should be considered by the auditor in making this assessment?
A)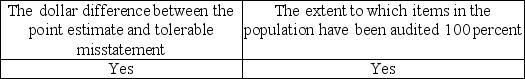
B)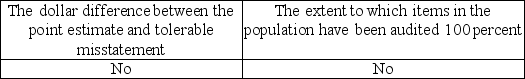
C)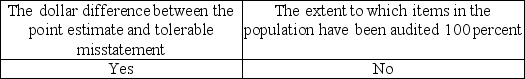
D)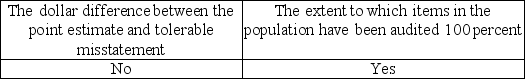
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Which of the following is an accurate statement regarding how the acceptable risk of overreliance (ARO) and the acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance (ARIA) interact to affect evidence accumulation?
A) If internal controls are likely to be effective, preliminary control risk can be increased.
B) A lower control risk requires a lower ARO in testing the controls, which requires a smaller sample size.
C) If controls are found to be effective, control risk can remain low, which permits the auditor to increase ARIA, thereby requiring a smaller sample size in the substantive tests of details of balances.
D) If misstatements are considered unlikely, ARIA will decrease, and the sample size will also decrease.
A) If internal controls are likely to be effective, preliminary control risk can be increased.
B) A lower control risk requires a lower ARO in testing the controls, which requires a smaller sample size.
C) If controls are found to be effective, control risk can remain low, which permits the auditor to increase ARIA, thereby requiring a smaller sample size in the substantive tests of details of balances.
D) If misstatements are considered unlikely, ARIA will decrease, and the sample size will also decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
You are auditing Raji and Company. You discover an item of inventory with an audited value of $5,000 with a recorded amount of $3,000. If this is the only error you discover, the projected misstatement for the sample would be
A) $5,000.
B) $2,000.
C) $3,000.
D) $4,000.
A) $5,000.
B) $2,000.
C) $3,000.
D) $4,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Which of the following needs to be considered when the auditor generalizes from the sample to the population?
A)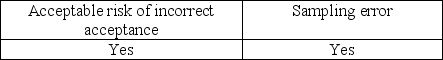
B)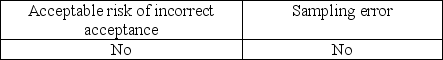
C)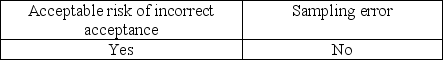
D)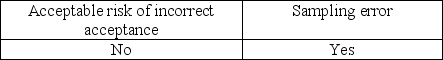
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Which of the following is a correct statement?
A) When internal controls are effective, control risk can be reduced, and therefore the auditor will decrease the ARIA.
B) There is a direct relationship between ARIA and the required sample size.
C) A lower control risk requires a lower ARO in testing the controls.
D) ARO measures the auditor's desired assurance for an account balance.
A) When internal controls are effective, control risk can be reduced, and therefore the auditor will decrease the ARIA.
B) There is a direct relationship between ARIA and the required sample size.
C) A lower control risk requires a lower ARO in testing the controls.
D) ARO measures the auditor's desired assurance for an account balance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The primary factor affecting the auditor's decision about acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance (ARIA) is assessed inherent risk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
An increased sample size will always cause the population to be accepted.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance (ARIA) and sample size are inversely related; that is, as ARIA increases, sample size decreases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The larger the sample size, the more confident the auditor can be that the point estimate is close to the true population value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
If a population is not considered acceptable, and the analysis indicates an individual error is unique or most of the misstatements are of a specific type, it may be appropriate to restrict the additional audit effort to the problem area.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance is directly affected by acceptable audit risk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The auditor may be able to use computer software to test the accuracy of each customer's account balance by taking each customer's beginning balance, adding sales made on account, subtracting payments received, and adding/subtracting other account adjustments to calculate each customer's ending balance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Acceptable audit risk and acceptable risk of incorrect acceptance are inversely related; that is, as AAR increases, ARIA decreases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The auditor must do misstatement analysis to decide whether any modification of the audit risk model is needed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
In stratified sampling, a maximum of four stratum can be used.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
An auditor using nonstatistical sampling cannot formally measure sampling error.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Estimated misstatement in the population and sample size are inversely related; that is, as estimated misstatement increases, sample size decreases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Tolerable misstatement is inversely related to sample size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Auditors may find that the use of data analysis techniques allows them to test the entire population of an account balance for certain audit objectives.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
When using audit sampling for tests of details of balances, the acceptable risk of overreliance must be determined.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
There are 14 steps to audit sampling for tests of details of balances, divided into three sections: plan the sample, select the sample and perform the audit procedures, and evaluate the results. Discuss each of the steps included in the "evaluate the results" section for nonstatistical sampling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
The purpose of stratification is to permit auditors to emphasize certain aspects of a population and deemphasize others.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
ARIA measures the auditor's desired assurance for an account balance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
If the misstatement in a population is larger than tolerable misstatement without considering sampling error, the population will be considered unacceptable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Required sample size increases as the auditor's tolerable misstatement for an account balance or class of transactions decreases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
When using monetary unit sampling, evaluating the likelihood of unrecorded items in the population is
A) unnecessary.
B) impossible.
C) possible but difficult.
D) an automatic outcome of the process.
A) unnecessary.
B) impossible.
C) possible but difficult.
D) an automatic outcome of the process.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Identify each of the seven factors that influence sample size for nonstatistical tests of details of balances, and state whether each factor is directly or inversely related to sample size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Monetary unit sampling is not particularly effective at detecting
A) overstatements.
B) understatements.
C) errors in current assets.
D) errors in noncurrent assets.
A) overstatements.
B) understatements.
C) errors in current assets.
D) errors in noncurrent assets.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
An accounts receivable population contains a total of four customers. The accounts, the amounts, and the cumulative total are shown below. Monetary unit sampling is to be used. 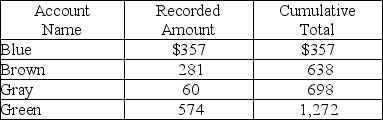 Based on the information above, the population size is
Based on the information above, the population size is
A) 4.
B) 574.
C) 1,272.
D) 2,684.
 Based on the information above, the population size is
Based on the information above, the population size isA) 4.
B) 574.
C) 1,272.
D) 2,684.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
An auditor uses monetary unit sampling with a sampling interval of $20,000 and detects an item with a recorded amount of $10,000 with an audited value of $4,000. The projected misstatement of the sample is
A) $12,000.
B) $6,000.
C) $10,000.
D) $3,000.
A) $12,000.
B) $6,000.
C) $10,000.
D) $3,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
The most commonly used method of statistical sampling for tests of details of balances is
A) attributes sampling.
B) systematic sampling.
C) discovery sampling.
D) monetary unit sampling.
A) attributes sampling.
B) systematic sampling.
C) discovery sampling.
D) monetary unit sampling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Consider the steps in sampling for tests of details and for tests of controls. Explain the differences in applying sampling to these two types of tests.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
The statistical methods used to evaluate monetary unit samples
A) neither exclude nor include units twice.
B) may permit the inclusion of a unit in the sample more than once.
C) do not permit a unit to be included in the sample more than once.
D) ignore the possibility that a unit may be included in a sample more than once.
A) neither exclude nor include units twice.
B) may permit the inclusion of a unit in the sample more than once.
C) do not permit a unit to be included in the sample more than once.
D) ignore the possibility that a unit may be included in a sample more than once.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
The auditor must consider the possibility that the true population misstatement is greater than the amount of misstatement that is tolerable when the auditor is performing
A)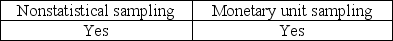
B)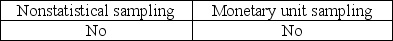
C)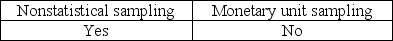
D)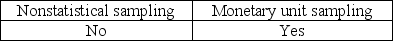
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Which of the following item(s) are needed to determine the sample size using MUS?
A)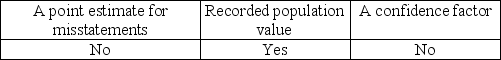
B)
C)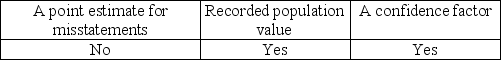
D)
A)
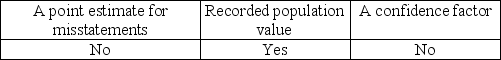
B)

C)
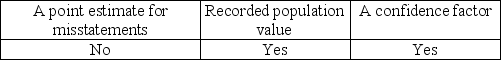
D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
When the sample selection is done using probability proportional to size sample selection (PPS),
A) the actual number of units selected for testing may be more than the computed sample size.
B) the auditor must use systematic selection, rather than random selection of dollars.
C) population items with a zero recorded balance have no chance of being selected.
D) negative balances must be treated as positive balances.
A) the actual number of units selected for testing may be more than the computed sample size.
B) the auditor must use systematic selection, rather than random selection of dollars.
C) population items with a zero recorded balance have no chance of being selected.
D) negative balances must be treated as positive balances.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
PPS samples can be obtained in an efficient manner using all but which of the following?
A) hand selection by the auditor
B) computer software
C) random number tables
D) systematic sampling techniques
A) hand selection by the auditor
B) computer software
C) random number tables
D) systematic sampling techniques

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
An auditor is confirming a population of accounts receivable for monetary correctness. The population totals $2,000,000 and a sample of 200 confirmations is obtained. Upon audit, no misstatements are uncovered in the sample. Assuming an ARIA of 10%, the confidence factor would be 2.31. Applied to a sampling interval of $10,000, the upper misstatement bound is calculated as
A) $462.
B) $4,329.
C) $23,100.
D) $865,801.
A) $462.
B) $4,329.
C) $23,100.
D) $865,801.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Which balance-related audit objective cannot be assessed using monetary unit sampling?
A) accuracy
B) completeness
C) existence
D) All of the above can be assessed using monetary unit sampling.
A) accuracy
B) completeness
C) existence
D) All of the above can be assessed using monetary unit sampling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
In monetary unit sampling, a sampling interval of 900 means that
A) every 900th item will be selected.
B) every 900th dollar in the account will be sampled.
C) expected misstatement is 900.
D) tolerable misstatement is 900.
A) every 900th item will be selected.
B) every 900th dollar in the account will be sampled.
C) expected misstatement is 900.
D) tolerable misstatement is 900.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
When using nonstatistical sampling, the auditor must subjectively consider whether the true population misstatement exceeds a tolerable amount. This is done by considering five factors. One factor is the difference between the point estimate and tolerable misstatement. State the other four factors the auditor must consider.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
There are 14 steps to audit sampling for tests of details of balances, divided into three sections: plan the sample, select the sample and perform the audit procedures, and evaluate the results. Discuss 5 of the 9 steps included in the "plan the sample" section for nonstatistical sampling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
When using monetary unit sampling, the recorded dollar population is a definition of all the items in the
A) population.
B) population which the auditor has included in the sample.
C) population which contain errors.
D) sample which contain errors.
A) population.
B) population which the auditor has included in the sample.
C) population which contain errors.
D) sample which contain errors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
An estimate of the largest likely overstatement in a population at a given ARIA, using monetary unit sampling is the
A) point estimates.
B) precision intervals.
C) confidence intervals.
D) misstatement bound.
A) point estimates.
B) precision intervals.
C) confidence intervals.
D) misstatement bound.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Discuss each of the six possible courses of action the auditor can take when he or she has concluded that the population is misstated by more than a tolerable amount.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 130 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








