Deck 14: Game Theory
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/109
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 14: Game Theory
1
In a two-player simultaneous game,if player A has a dominant strategy and player B does not,player B will
A) employ a mixed strategy.
B) choose his best strategy assuming that player A plays her dominant strategy.
C) not achieve a Nash equilibrium.
D) assume that player A does not choose her dominant strategy.
A) employ a mixed strategy.
B) choose his best strategy assuming that player A plays her dominant strategy.
C) not achieve a Nash equilibrium.
D) assume that player A does not choose her dominant strategy.
choose his best strategy assuming that player A plays her dominant strategy.
2
After analyzing his opponent,a tennis player decides to serve 10% of his serves to the left,50% of his serves to the right,and 40% of his serves at the body of his opponent.This illustrates a
A) deterministic strategy.
B) dominant strategy.
C) mixed strategy.
D) non-game theoretic problem.
A) deterministic strategy.
B) dominant strategy.
C) mixed strategy.
D) non-game theoretic problem.
mixed strategy.
3
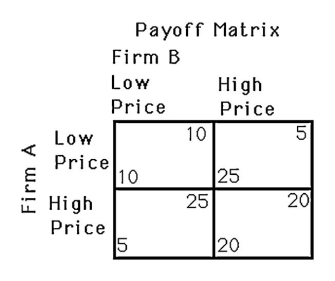
The above figure shows a payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,that must choose between a high-price strategy and a low-price strategy.For firm B,
A) setting a high price is the dominant strategy.
B) setting a low price is the dominant strategy.
C) there is no dominant strategy.
D) doing the opposite of firm A is always the best strategy.
setting a low price is the dominant strategy.
4
A mixed strategy may
A) be part of a Nash equilibrium.
B) be a set of probabilities of selecting each possible action.
C) lead identical firms to choose different actions.
D) All of the above.
A) be part of a Nash equilibrium.
B) be a set of probabilities of selecting each possible action.
C) lead identical firms to choose different actions.
D) All of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
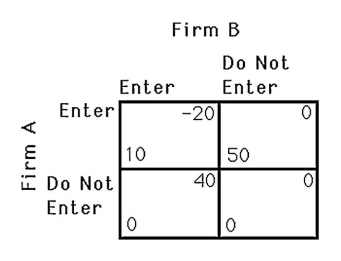
The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,which one of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Firm A does not have a dominant strategy.
B) Firm B does not have a dominant strategy.
C) Neither firm entering is a Nash equilibrium.
D) The outcome of the game is unpredictable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6

The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,what will happen if the government offers a $30 subsidy to airlines that serve this route?
A) Both firms will enter profitably.
B) Firm A will decide not to enter since firm B will.
C) Firm B is still better off not entering.
D) Neither firm will have a dominant strategy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A game in economics is defined as
A) something that is shown on ESPN.
B) competition in which strategic decision making is integral.
C) competition in general.
D) an actual strategy chosen by one or more economic agents.
A) something that is shown on ESPN.
B) competition in which strategic decision making is integral.
C) competition in general.
D) an actual strategy chosen by one or more economic agents.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8

The above figure shows a payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,that must choose between a high-price strategy and a low-price strategy.Both firms setting a high price is not a Nash equilibrium because
A) setting a high price is the dominant strategy for each firm.
B) neither firm can improve its payoff by setting a low price given that the other firm is setting a high price.
C) there is no dominant strategy for either firm.
D) both firms can improve their payoff by setting a low price given that the other firm is setting a high price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9

The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,which one of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Only firm A will enter the market.
B) Only firm B will enter the market.
C) Neither firm entering is a Nash equilibrium.
D) The outcome of the game is unpredictable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10

The above figure shows a payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,that must choose between a high-price strategy and a low-price strategy.The Nash equilibrium in this game
A) does not exist.
B) occurs when both firms set a low price.
C) occurs when both firms set a high price.
D) occurs when firm A sets a high price and firm B sets a low price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11

The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,which one of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Firm A has a dominant strategy.
B) Firm B has a dominant strategy.
C) Neither firm entering is a Nash equilibrium.
D) The outcome of the game is unpredictable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
When neither player has a dominant strategy,
A) game theory will not provide information.
B) no Nash-Equilibrium exists.
C) at least one Nash-Equilibrium exists.
D) the game cannot be analyzed.
A) game theory will not provide information.
B) no Nash-Equilibrium exists.
C) at least one Nash-Equilibrium exists.
D) the game cannot be analyzed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Which of the following is a simultaneous decision game?
A) Tic-tac-toe
B) Chess
C) Poker
D) Rock-paper-scissors
A) Tic-tac-toe
B) Chess
C) Poker
D) Rock-paper-scissors

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14

The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,and the government imposes a $20 per firm tax on firms that service this route,which of the following maximizes the firms' joint profits?
A) Neither firm services the route.
B) Firm A offers firm B $20 to not enter.
C) Both firms will service this route.
D) Firm B offers firm A $30 to not enter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
In a two-player simultaneous game where neither player has a dominant strategy,
A) there is never a Nash equilibrium.
B) there is only one Nash equilibrium.
C) the actual outcome is unpredictable.
D) the actual outcome will not be a Nash equilibrium.
A) there is never a Nash equilibrium.
B) there is only one Nash equilibrium.
C) the actual outcome is unpredictable.
D) the actual outcome will not be a Nash equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16

The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,which one of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Since firm B has no dominant strategy, its decision is unpredictable.
B) Since firm B's decision is unpredictable, firm A's decision is unpredictable.
C) Neither firm entering is a Nash equilibrium.
D) Firm B will not enter because it knows firm A will.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The game rock-paper-scissors has
A) a mixed strategy equilibrium.
B) a dominant strategy equilibrium.
C) no equilibrium.
D) a pure strategy equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18

The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,how many pure Nash equilibria are there?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) It cannot be determined.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
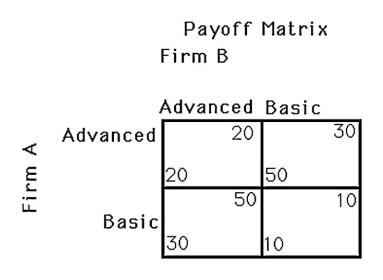
The above figure shows a payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,that must choose between selling basic computers or advanced computers.Firm B's dominant strategy
A) is to make basic computers.
B) is to make advanced computers.
C) is to adopt firm A's strategy.
D) does not exist in this game.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20

The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.If the two airlines must decide simultaneously,what happens if the government imposes a $20 per firm tax on firms that service this route?
A) Neither firm has a dominant strategy.
B) Not entering is a dominant strategy for both firms.
C) Neither firm entering is a Nash equilibrium.
D) Only firm A will enter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
A surprising outcome of the Rock-Paper-Scissors game is that
A) it is a clear example of a first mover advantage.
B) there is no pure-strategy Nash equilibrium.
C) it is best not to play the game.
D) it is a good way to determine who goes first in a sequential move game.
A) it is a clear example of a first mover advantage.
B) there is no pure-strategy Nash equilibrium.
C) it is best not to play the game.
D) it is a good way to determine who goes first in a sequential move game.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
What is the counter-intuitive solution to a mixed strategy?
A) Player A makes Player B indifferent between its strategy choices.
B) Player A makes itself indifferent between its strategy choices.
C) Player A changes the rules of the game.
D) There are no mixed strategies in most games.
A) Player A makes Player B indifferent between its strategy choices.
B) Player A makes itself indifferent between its strategy choices.
C) Player A changes the rules of the game.
D) There are no mixed strategies in most games.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23

The above figure shows a payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,that must choose between selling basic computers or advanced computers.Which of the following is a Nash equilibrium?
A) Both firms make advanced computers.
B) Both firms make basic computers.
C) Firm A makes basic computers and firm B makes advanced computers.
D) There are no Nash equilibria.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
A strategy is dominant if
A) it yields a greater payoff than any other player receives.
B) it yields a payoff at least as large as that from any other strategy, regardless of the actions of other players.
C) the player cannot gain by changing strategy, assuming that no other player changes strategy.
D) it is part of a Nash equilibrium.
A) it yields a greater payoff than any other player receives.
B) it yields a payoff at least as large as that from any other strategy, regardless of the actions of other players.
C) the player cannot gain by changing strategy, assuming that no other player changes strategy.
D) it is part of a Nash equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Mutually Assured Destruction was a standing policy during the Cold War,in which the United States and the U.S.S.R.maintained and expanded nuclear arsenals beyond practical levels.What could explain such a phenomenon?
A) insane public officials who were bent on world domination
B) a prisoners' dilemma
C) a leader-follower type game
D) tacit collusion
A) insane public officials who were bent on world domination
B) a prisoners' dilemma
C) a leader-follower type game
D) tacit collusion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Which of the following is LEAST likely characterized by mixed strategies?
A) the choice of whether to go to war or not
B) the choice of which pitch to throw in baseball
C) the choice of which play to run in football
D) the choice of where to kick a soccer penalty shot
A) the choice of whether to go to war or not
B) the choice of which pitch to throw in baseball
C) the choice of which play to run in football
D) the choice of where to kick a soccer penalty shot

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The term prisoners' dilemma refers to a game in which
A) there are no Nash equilibria.
B) there are no dominant strategies.
C) the payoff from playing the dominant strategy is the same for each player.
D) the payoff from playing the dominant strategy is not the highest payoff possible.
A) there are no Nash equilibria.
B) there are no dominant strategies.
C) the payoff from playing the dominant strategy is the same for each player.
D) the payoff from playing the dominant strategy is not the highest payoff possible.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28

The above figure shows a payoff matrix for two firms,A and B,that must choose between selling basic computers or advanced computers.How many Nash equilibria are there?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
If the payoff to the United States to pursuing nuclear weapons is 100 if the USSR does not pursue nuclear weapons and 50 if they do,and the payoff to the USSR to pursuing nuclear weapons is 80 if the USA doesn't pursue nuclear weapons and 30 if they do,what is the non-cooperative equilibrium?
A) The USA pursues nuclear weapons, the USSR does not.
B) The USA pursues nuclear weapons, the USSR pursues nuclear weapons.
C) The USA does not pursue nuclear weapons, the USSR does not pursue nuclear weapons.
D) The USA does not pursue nuclear weapons, the USSR does pursue nuclear weapons.
A) The USA pursues nuclear weapons, the USSR does not.
B) The USA pursues nuclear weapons, the USSR pursues nuclear weapons.
C) The USA does not pursue nuclear weapons, the USSR does not pursue nuclear weapons.
D) The USA does not pursue nuclear weapons, the USSR does pursue nuclear weapons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
What is the primary difference between a mixed strategy and a pure strategy?
A) Pure strategies are always dominated strategies.
B) Mixed strategies call for randomizing over possible actions, pure strategies do not.
C) Pure strategies are much more common than mixed strategies.
D) Mixed strategies are not optimal whereas pure strategies are.
A) Pure strategies are always dominated strategies.
B) Mixed strategies call for randomizing over possible actions, pure strategies do not.
C) Pure strategies are much more common than mixed strategies.
D) Mixed strategies are not optimal whereas pure strategies are.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
A Nash equilibrium occurs when
A) players choose their best strategy given the strategies chosen by others.
B) the efficient allocation of resources is achieved by setting marginal revenue equal to marginal cost.
C) a monopolist is forced to produce the efficient level of output.
D) oligopolists cooperate with each other.
A) players choose their best strategy given the strategies chosen by others.
B) the efficient allocation of resources is achieved by setting marginal revenue equal to marginal cost.
C) a monopolist is forced to produce the efficient level of output.
D) oligopolists cooperate with each other.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Collusion is more likely to occur when
A) there is fear of punishment for not colluding.
B) there is a known finite time horizon.
C) there are large gains to be made by cheating on an agreement.
D) the game lasts only one period.
A) there is fear of punishment for not colluding.
B) there is a known finite time horizon.
C) there are large gains to be made by cheating on an agreement.
D) the game lasts only one period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
A player can choose among three strategies: T,M,and B.Nevertheless,strategy B is dominated by strategy T.This means that
A) strategy T is always played.
B) strategy B is never played.
C) strategy B will be part of a Nash equilibrium.
D) strategy M is never played.
A) strategy T is always played.
B) strategy B is never played.
C) strategy B will be part of a Nash equilibrium.
D) strategy M is never played.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
In a non-cooperative,imperfect information,simultaneous-choice,one-period game,a Nash equilibrium
A) will never exist.
B) will always include dominant strategies.
C) will always result in both players taking the same action.
D) may not maximize the sum of the firms' profits.
A) will never exist.
B) will always include dominant strategies.
C) will always result in both players taking the same action.
D) may not maximize the sum of the firms' profits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Which of the following is NOT part of solving a game?
A) Write down all possible combinations of strategies.
B) Write down all possible payoffs and eliminate dominated strategies.
C) Solve for any Nash Equilibrium.
D) None of the above.
A) Write down all possible combinations of strategies.
B) Write down all possible payoffs and eliminate dominated strategies.
C) Solve for any Nash Equilibrium.
D) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
A dominated strategy
A) may be part of a Nash equilibrium.
B) is never played.
C) can be a best response.
D) is always part of a mixed-strategy Nash equilibrium.
A) may be part of a Nash equilibrium.
B) is never played.
C) can be a best response.
D) is always part of a mixed-strategy Nash equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
In the 1980s,the USA and the USSR negotiated a reduction in nuclear arms; this is an example of a
A) non-cooperative equilibrium.
B) cooperative outcome that may not be a Nash equilibrium.
C) cooperative outcome that was a Nash equilibrium.
D) sub-game perfect equilibrium.
A) non-cooperative equilibrium.
B) cooperative outcome that may not be a Nash equilibrium.
C) cooperative outcome that was a Nash equilibrium.
D) sub-game perfect equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
If a strategy is a best response,then
A) it will never be played.
B) it will never be part of a Nash equilibrium.
C) A and B are correct.
D) it could be part of a Nash equilibrium.
A) it will never be played.
B) it will never be part of a Nash equilibrium.
C) A and B are correct.
D) it could be part of a Nash equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Which of the following constitutes a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium of the Odds and Evens game?
A) Play Even and Odd with 50% probability each.
B) Play Even with 75% probability and Odd with 25% probability.
C) Always play Even.
D) This game has no mixed strategy Nash equilibrium.
A) Play Even and Odd with 50% probability each.
B) Play Even with 75% probability and Odd with 25% probability.
C) Always play Even.
D) This game has no mixed strategy Nash equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
A single-period duopoly firm can choose output level A or B.The firm decides it will produce level A regardless of what the other firm produces.This decision may occur because
A) producing the output level A is a dominant strategy.
B) this firm has simply decided to always produce at level A.
C) Both A and B are possible.
D) None of the above.
A) producing the output level A is a dominant strategy.
B) this firm has simply decided to always produce at level A.
C) Both A and B are possible.
D) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
If only one firm operates in a market,and a potential entrant is blockaded from entering the market,then the incumbent firm must
A) have acted to prevent entry.
B) be pricing where price equals marginal cost.
C) be a natural monopoly.
D) be the Stackelberg leader.
A) have acted to prevent entry.
B) be pricing where price equals marginal cost.
C) be a natural monopoly.
D) be the Stackelberg leader.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
14.3 Sequential Dynamic Games 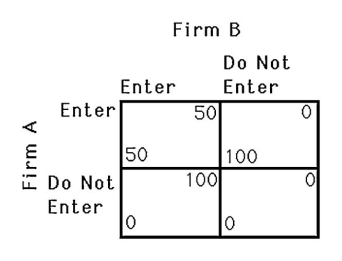
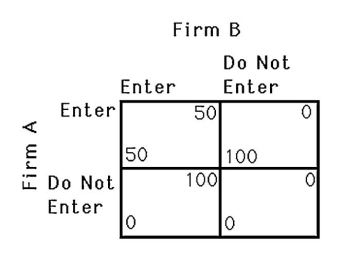
The above figure shows the payoff to two gasoline stations,A and B,deciding to operate in an isolated town.Suppose a $30 fee is required to enter the market.If firm A chooses its strategy first,then
A) firm A will not enter.
B) neither firm will enter.
C) both firms will enter.
D) firm A will enter and firm B will not.

The above figure shows the payoff to two gasoline stations,A and B,deciding to operate in an isolated town.Suppose a $30 fee is required to enter the market.If firm A chooses its strategy first,then
A) firm A will not enter.
B) neither firm will enter.
C) both firms will enter.
D) firm A will enter and firm B will not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
In a repeated game,cooperation can be enforced by the use of a trigger strategy that
A) leads to a higher payoff of the cheated upon player.
B) reduces the payoff of the player that reneged the agreement.
C) rewards the player that reneged the agreement.
D) is a dominant strategy.
A) leads to a higher payoff of the cheated upon player.
B) reduces the payoff of the player that reneged the agreement.
C) rewards the player that reneged the agreement.
D) is a dominant strategy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
A trigger strategy
A) is always a dominant strategy.
B) is used to punish the player that reneges on agreements.
C) is used to reward the player that never reneges on agreements.
D) is a best response whenever all players cooperate.
A) is always a dominant strategy.
B) is used to punish the player that reneges on agreements.
C) is used to reward the player that never reneges on agreements.
D) is a best response whenever all players cooperate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
14.3 Sequential Dynamic Games 
The above figure shows the payoff to two gasoline stations,A and B,deciding to operate in an isolated town.Suppose a $60 fee is required to enter the market.If firm A chooses its strategy first,then
A) firm A will not enter.
B) neither firm will enter.
C) both firms will enter.
D) firm A will enter and firm B will not.

The above figure shows the payoff to two gasoline stations,A and B,deciding to operate in an isolated town.Suppose a $60 fee is required to enter the market.If firm A chooses its strategy first,then
A) firm A will not enter.
B) neither firm will enter.
C) both firms will enter.
D) firm A will enter and firm B will not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
A player can choose among three strategies: L,C,and R.Strategy C is never a best response to the other player strategies.This means that
A) strategy C is always played.
B) strategy C is never played.
C) strategy C will be part of a Nash equilibrium.
D) strategies L and R are never played.
A) strategy C is always played.
B) strategy C is never played.
C) strategy C will be part of a Nash equilibrium.
D) strategies L and R are never played.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Why is collusion more likely in a repeated game?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Repeated games are conducive to
A) explicit cooperation.
B) tacit cooperation.
C) corruption.
D) failing to have a Nash equilibrium.
A) explicit cooperation.
B) tacit cooperation.
C) corruption.
D) failing to have a Nash equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
If neither firm has a dominant strategy,a Nash equilibrium cannot exist.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
One interesting feature of a prisoner's dilemma game is that
A) non-cooperative behavior leads to lower payoffs than cooperative behavior.
B) it was only valid before the industrial revolution.
C) individuals behave irrationally when they behave non-cooperatively.
D) cooperative behavior leads to lower payoffs than non-cooperative behavior.
A) non-cooperative behavior leads to lower payoffs than cooperative behavior.
B) it was only valid before the industrial revolution.
C) individuals behave irrationally when they behave non-cooperatively.
D) cooperative behavior leads to lower payoffs than non-cooperative behavior.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
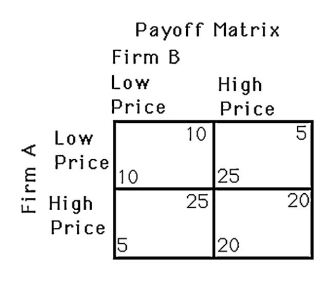
The above figure shows the payoff for two firms,A and B,that must each choose to sell either at a high or low price.Determine the dominant strategies for each firm (if any)and the Nash equilibria (if any).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
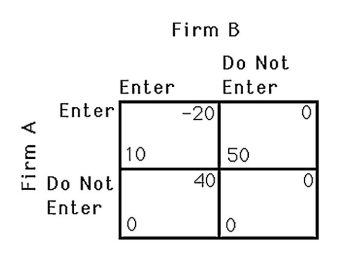
The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.What is Firm A's best response if Firm B decides to enter?
A) Firm A does not have a best response strategy.
B) Firm A chooses to enter.
C) Firm A chooses do not enter.
D) Both enter and do not enter are best responses for firm A.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
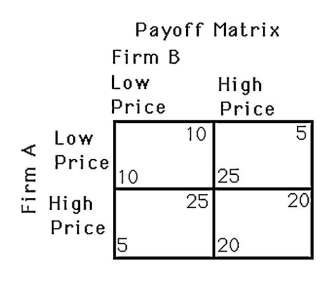
The above figure shows the payoff to two firms,A and B,of releasing two versions of a new product.What is Firm A's best response if Firm B decides to release the high price version?
A) Firm A does not have a best response strategy.
B) Firm A chooses the low price version.
C) Firm A chooses the high price version.
D) Both low price and high price versions are best responses for firm A.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
One way to ensure cooperation in an infinitely repeated simultaneous game is
A) to always play the dominant strategy.
B) to punish the player that reneges on agreements.
C) to never punish any player.
D) to always punish all players.
A) to always play the dominant strategy.
B) to punish the player that reneges on agreements.
C) to never punish any player.
D) to always punish all players.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Suppose two firms,A and B,are simultaneously considering entry into a new market.If neither enters,both earn zero.If both enter,they both lose 100.If one firm enters,it gains 50 while the other earns zero.Set up the payoff matrix for this game and determine if any Nash equilibria exist.Can you predict the outcome? What if firm A gets to decide first?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
In a simultaneous game where both players prefer doing the opposite of what the opponent does,a Nash equilibrium does not exist.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Which of the following is a dynamic game?
A) rock-paper-scissors
B) flipping pennies
C) chess
D) the card game "war"
A) rock-paper-scissors
B) flipping pennies
C) chess
D) the card game "war"

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
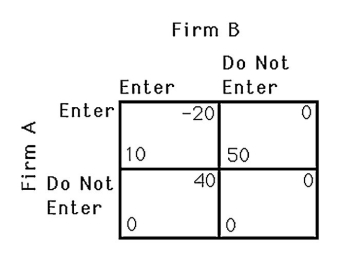
The above figure shows the payoffs to two airlines,A and B,of serving a particular route.Is there a Nash equilibrium? What is it? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
14.3 Sequential Dynamic Games 
The above figure shows the payoff to two gasoline stations,A and B,deciding to operate in an isolated town.If firm A chooses its strategy first,then
A) firm A will not enter.
B) firm B's entry is blockaded.
C) both firms will enter.
D) firm A will enter and firm B will not.

The above figure shows the payoff to two gasoline stations,A and B,deciding to operate in an isolated town.If firm A chooses its strategy first,then
A) firm A will not enter.
B) firm B's entry is blockaded.
C) both firms will enter.
D) firm A will enter and firm B will not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Two identical firms are considering entering a new market that currently has no suppliers.The demand is large enough for both firms to make a positive profit.There are no fixed costs to enter.Explain how a simultaneous decision to enter on the part of the two firms will lead to a different outcome than a sequential entry decision.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
With regard to preventing entry,if identical firms act simultaneously,
A) they cannot credibly threaten each other.
B) they will all incur losses.
C) only one firm will enter the market.
D) none of them will enter the market.
A) they cannot credibly threaten each other.
B) they will all incur losses.
C) only one firm will enter the market.
D) none of them will enter the market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
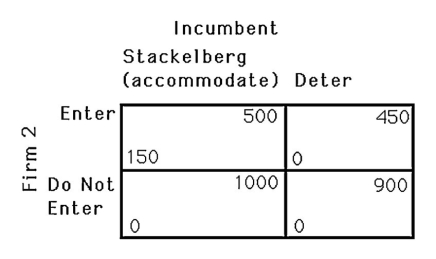
The above figure shows the payoff matrix facing an incumbent firm and a potential entrant.The potential entrant cannot earn a profit if the incumbent
A) chooses the Cournot level of output.
B) chooses the Stackelberg leader level of output.
C) shuts down.
D) deters entry.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
The ability to deter entry requires
A) a credible threat that if entry occurs the firm is willing to produce more than they would otherwise.
B) a credible threat that if entry occurs the firm will not produce more than they would otherwise.
C) a good lawyer.
D) a clever accounting department.
A) a credible threat that if entry occurs the firm is willing to produce more than they would otherwise.
B) a credible threat that if entry occurs the firm will not produce more than they would otherwise.
C) a good lawyer.
D) a clever accounting department.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
If a Cournot duopolist announced that it will double its output,the other firm does not view the announcement as credible because
A) the announcing firm's profits will fall if it carries out the threat.
B) the other firm's profits will fall if the announcing firm carries out the threat.
C) the other firm's profits will rise if the announcing firm carries out the threat.
D) the other firm will double output also.
A) the announcing firm's profits will fall if it carries out the threat.
B) the other firm's profits will fall if the announcing firm carries out the threat.
C) the other firm's profits will rise if the announcing firm carries out the threat.
D) the other firm will double output also.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Deterring entry might require a firm to
A) price their product closer to the competitive price than to the monopoly price.
B) price their product closer to the monopoly price than to the competitive price.
C) drop output almost to zero to show the consumers "who's boss."
D) drop price almost to zero to get price below marginal cost.
A) price their product closer to the competitive price than to the monopoly price.
B) price their product closer to the monopoly price than to the competitive price.
C) drop output almost to zero to show the consumers "who's boss."
D) drop price almost to zero to get price below marginal cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Assume an industry,currently dominated by one firm,experiences a large decline in fixed costs.This will
A) make entry of other firms more likely.
B) make entry of other firms less likely.
C) serve as higher barrier to entry.
D) induce the incumbent firm to exit the industry.
A) make entry of other firms more likely.
B) make entry of other firms less likely.
C) serve as higher barrier to entry.
D) induce the incumbent firm to exit the industry.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Before entering,fixed cost associated with the industry in question are sunk costs for
A) the incumbent firm.
B) the outside firm.
C) both firms.
D) neither firm.
A) the incumbent firm.
B) the outside firm.
C) both firms.
D) neither firm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
An incumbent announces it will significantly increase output in the next period,but only has contracts for the amount produced this period.The announcement is a
A) credible threat.
B) non-credible threat.
C) commitment.
D) mixed strategy.
A) credible threat.
B) non-credible threat.
C) commitment.
D) mixed strategy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
One firm previously operated as a monopoly.Now,one potential entrant exists.Consumers would prefer
A) entry, and the firms to split the output equally.
B) no entry, and for the incumbent to produce the Stackelberg leader level of output.
C) entry, and for the incumbent to produce the Stackelberg leader level of output.
D) no entry, and the monopoly to continue.
A) entry, and the firms to split the output equally.
B) no entry, and for the incumbent to produce the Stackelberg leader level of output.
C) entry, and for the incumbent to produce the Stackelberg leader level of output.
D) no entry, and the monopoly to continue.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70

The above figure shows the payoff matrix facing an incumbent firm and a potential entrant.Assuming a fixed cost of entry,the incumbent will deter entry because
A) it is more profitable than accommodating entry.
B) it increases consumer surplus.
C) the potential entrant winds up with zero profit.
D) the incumbent would earn zero profit if it accommodated entry.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Incumbents are unaffected by fixed costs of entry while potential entrants are affected by them because
A) for potential entrants the cost is avoidable, while for the incumbent, it is not.
B) fixed costs will be greater for the potential entrant than for the incumbent.
C) fixed costs are zero for the incumbent.
D) incumbents will act to prevent entry at all costs.
A) for potential entrants the cost is avoidable, while for the incumbent, it is not.
B) fixed costs will be greater for the potential entrant than for the incumbent.
C) fixed costs are zero for the incumbent.
D) incumbents will act to prevent entry at all costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72

The above figure shows the payoff matrix facing an incumbent firm and a potential entrant.If the fixed cost of entry were to increase,which of the following would occur?
A) The incumbent chooses the Cournot level of output.
B) The incumbent shuts down.
C) The entry-deterring level of output rises.
D) The entry-deterring level of output falls.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
If an incumbent cannot commit and faces an identical potential entrant with relatively high fixed costs that are below the level where entry is blockaded,the incumbent will
A) produce the Cournot duopolist level of output.
B) produce the Stackelberg leader level of output.
C) set price equal to marginal cost.
D) produce a level of output that is greater than the Stackelberg leader level of output.
A) produce the Cournot duopolist level of output.
B) produce the Stackelberg leader level of output.
C) set price equal to marginal cost.
D) produce a level of output that is greater than the Stackelberg leader level of output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
In the Stackelberg model,the leader has a first-mover advantage because it
A) has lower costs than the follower.
B) commits to producing a larger quantity.
C) reacts to the follower's decision.
D) differentiates its output.
A) has lower costs than the follower.
B) commits to producing a larger quantity.
C) reacts to the follower's decision.
D) differentiates its output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
If an incumbent faces an identical potential entrant with no costs of entry,the incumbent will
A) produce the Cournot duopolist level of output.
B) produce the Stackelberg leader level of output.
C) set price equal to marginal cost.
D) shut down.
A) produce the Cournot duopolist level of output.
B) produce the Stackelberg leader level of output.
C) set price equal to marginal cost.
D) shut down.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
An incumbent's threat to retaliate after a potential competitor enters the market will be taken seriously by potential competitors if
A) the incumbent can still earn a profit after carrying out the threat.
B) the incumbent earns greater profit carrying out the threat than by accommodating entry.
C) the potential entrant cannot earn a profit if the threat is carried out.
D) the potential entrant's profit exceeds the incumbent's if the threat is carried out.
A) the incumbent can still earn a profit after carrying out the threat.
B) the incumbent earns greater profit carrying out the threat than by accommodating entry.
C) the potential entrant cannot earn a profit if the threat is carried out.
D) the potential entrant's profit exceeds the incumbent's if the threat is carried out.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Assume a firm lowers price below marginal cost to deter entry.
A) This strategy is not credible.
B) This strategy is credible.
C) This strategy is illegal.
D) This strategy is immoral.
A) This strategy is not credible.
B) This strategy is credible.
C) This strategy is illegal.
D) This strategy is immoral.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
If a Cournot duopolist announced that it will double its output,
A) it becomes the leader.
B) the other firm does not view the announcement as credible.
C) the other firm will shut down.
D) the other firm will double output also.
A) it becomes the leader.
B) the other firm does not view the announcement as credible.
C) the other firm will shut down.
D) the other firm will double output also.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79

The above figure shows the payoff matrix facing an incumbent firm and a potential entrant.Assuming a fixed cost of entry,the outcome will be that the incumbent
A) deters entry.
B) chooses the Stackelberg leader level of output but the potential entrant does not enter anyway.
C) chooses the Stackelberg leader level of output and the potential entrant enters.
D) deters entry and earns zero profit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80

The above figure shows the payoff matrix facing an incumbent firm and a potential entrant.What policy could government adopt to prevent entry deterrence by the incumbent?
A) production quotas
B) price ceiling
C) safety standards
D) None of the above is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 109 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








