Deck 21: Organic Chemistry II: Reactions
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/96
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 21: Organic Chemistry II: Reactions
1
Give the organic product for the following reaction. CH3CH2CH2NH2 + HCl
A)ClCH2CH2CH2NH2
B)CH3CHClCH2NH2
C)CH3CH2CHClNH2
D)CH3CH2CH2NHCl
E)CH3CH2CH2NH3+Cl-
A)ClCH2CH2CH2NH2
B)CH3CHClCH2NH2
C)CH3CH2CHClNH2
D)CH3CH2CH2NHCl
E)CH3CH2CH2NH3+Cl-
CH3CH2CH2NH3+Cl-
2
In which of the following families would the strongest organic acids be found?
A)ethers
B)alcohols
C)amines
D)esters
E)alkanes
A)ethers
B)alcohols
C)amines
D)esters
E)alkanes
alcohols
3
In which of the following families would the strongest organic bases be found?
A)amines
B)ethers
C)esters
D)alcohols
E)ketones
A)amines
B)ethers
C)esters
D)alcohols
E)ketones
amines
4
Arrange the following in order from most oxidized to least oxidized. 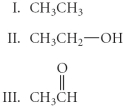
A)II > I > III
B)III > II > I
C)III > I > II
D)I > II > III
E)II > III > I
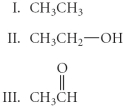
A)II > I > III
B)III > II > I
C)III > I > II
D)I > II > III
E)II > III > I

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Determine the product(s)of the reduction of the following compound: 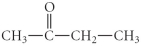
A)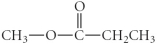
B)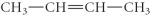
C)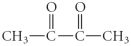
D)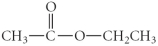
E)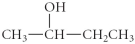
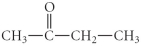
A)
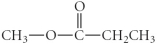
B)
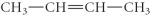
C)
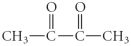
D)
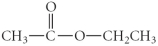
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Find the suitable base for the following reaction: CH3C(=O)CH3 + :B → CH3C(=O)CH2:- + H:B+
The pKa for CH3C(=O)CH3 (acetone)is 20. The formula for the base is followed by the pKa of its conjugate acid.
A)H2O, pKa = 15.74
B)NH3, pKa = 9.25
C)CH3CH2O-, pKa = 16
D)C6H5O-, pKa = 9.88
E)NH2-, pKa = 38
The pKa for CH3C(=O)CH3 (acetone)is 20. The formula for the base is followed by the pKa of its conjugate acid.
A)H2O, pKa = 15.74
B)NH3, pKa = 9.25
C)CH3CH2O-, pKa = 16
D)C6H5O-, pKa = 9.88
E)NH2-, pKa = 38

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Choose the weak acid from the compounds below.
A)CH3CH2NH2
B)CH3CH2CO2H
C)CH3CH2OCH3
D)CH3CH2F
E)CH3COOC2H5
A)CH3CH2NH2
B)CH3CH2CO2H
C)CH3CH2OCH3
D)CH3CH2F
E)CH3COOC2H5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Arrange the following in order from least oxidized to most oxidized. 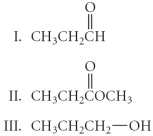
A)II < I < III
B)III < I = II
C)III < I < II
D)I < II < III
E)I < III < II

A)II < I < III
B)III < I = II
C)III < I < II
D)I < II < III
E)I < III < II

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Find the suitable reagent for the transformation: 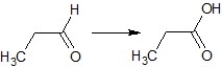
A)CrO3, H3O+
B)pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)
C)K2Cr2O7, H2SO4
D)KMnO4, H2SO4
E)K2Cr2O7, HNO3

A)CrO3, H3O+
B)pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)
C)K2Cr2O7, H2SO4
D)KMnO4, H2SO4
E)K2Cr2O7, HNO3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Find the suitable reagent for the transformation: 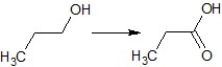
A)CrO3, H3O+
B)pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)
C)K2Cr2O7, H2SO4
D)KMnO4, H2SO4
E)K2Cr2O7, HNO3

A)CrO3, H3O+
B)pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)
C)K2Cr2O7, H2SO4
D)KMnO4, H2SO4
E)K2Cr2O7, HNO3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Choose the weak base from the compounds below.
A)(CH3)2NH
B)CH3CO2H
C)CH3COCH3
D)CH3CH3
E)CH3CH2F
A)(CH3)2NH
B)CH3CO2H
C)CH3COCH3
D)CH3CH3
E)CH3CH2F

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Find the suitable base for the following reaction: C6H5OH + :B → C6H5O:- + H:B+
The pKa for C6H5OH (phenol)is 9.88. The formula for the base is followed by the pKa of its conjugate acid.
A)CN-, pKa = 9.31
B)CF3COO-, pKa = 0.23
C)CH3C(=O)CH3, pKa = -7.2
D)CH3COO-, pKa = 4.74
E)OH-, pKa = 15.73
The pKa for C6H5OH (phenol)is 9.88. The formula for the base is followed by the pKa of its conjugate acid.
A)CN-, pKa = 9.31
B)CF3COO-, pKa = 0.23
C)CH3C(=O)CH3, pKa = -7.2
D)CH3COO-, pKa = 4.74
E)OH-, pKa = 15.73

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Find the suitable reagent for the transformation: 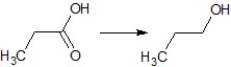
A)NaBH4
B)LiAlH4
C)Pd/H2
D)NaH
E)Pd/C

A)NaBH4
B)LiAlH4
C)Pd/H2
D)NaH
E)Pd/C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
What are secondary alcohols oxidized to?
A)tertiary alcohols
B)ethers
C)esters
D)aldehydes
E)ketones
A)tertiary alcohols
B)ethers
C)esters
D)aldehydes
E)ketones

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Identify the most oxidized compound.
A)CH3CH2COOH
B)CH3CH2CHO
C)CH3CH2CH3
D)CH3CH2OCH3
E)CH3CH2CH2OH
A)CH3CH2COOH
B)CH3CH2CHO
C)CH3CH2CH3
D)CH3CH2OCH3
E)CH3CH2CH2OH

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Which is the strongest organic acid?
A)F3CCOOH
B)F2HCCOOH
C)H3COOH
D)ClH2CCOOH
E)FH2CCOOH
A)F3CCOOH
B)F2HCCOOH
C)H3COOH
D)ClH2CCOOH
E)FH2CCOOH

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Find the suitable reagent for the transformation: 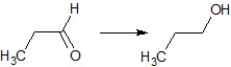
A)NaBH4
B)LiAlH4
C)Pd/H2
D)NaH
E)Pd/C

A)NaBH4
B)LiAlH4
C)Pd/H2
D)NaH
E)Pd/C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Determine the products of the following reaction: 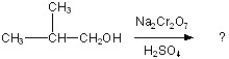
A)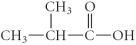
B)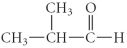
C)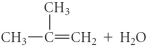
D)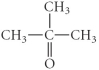
E)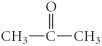
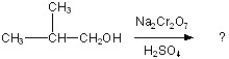
A)
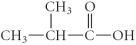
B)
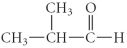
C)
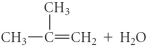
D)

E)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Write a balanced chemical reaction to represent the combustion of 2,2-dimethylpropane.
A)C5H12 + 8O2 → 5CO2 + 6H2O
B)C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
C)C5H12 + H2 → CH4 + 2C2H6
D)C3H8 + H2 → CH4 + C2H6
E)2 C3H8 + O2 → 3CH4 + 2H2O
A)C5H12 + 8O2 → 5CO2 + 6H2O
B)C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
C)C5H12 + H2 → CH4 + 2C2H6
D)C3H8 + H2 → CH4 + C2H6
E)2 C3H8 + O2 → 3CH4 + 2H2O

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
What are primary alcohols oxidized to?
A)secondary alcohols
B)ethers
C)esters
D)aldehydes
E)ketones
A)secondary alcohols
B)ethers
C)esters
D)aldehydes
E)ketones

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Give the product of the oxidation of the following compound: 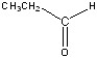
A)CH3CH2CHO
B)CH3CH2CH2OH
C)CH3CH2CH3
D)CH3CH2COOH
E)CH3CH2OCH3

A)CH3CH2CHO
B)CH3CH2CH2OH
C)CH3CH2CH3
D)CH3CH2COOH
E)CH3CH2OCH3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)The nucleophile strongly influences both SN1 and SN2 reactions, while the nature of the nucleophile and the substrate structure are only important in SN2 reactions.
B)The structure of the substrate is the only important factor for SN1 reactions, while the nucleophile, leaving group, and the structure of the substrate are all important for SN2 reactions.
C)For SN2 reactions the only important factor to consider is the leaving group; for SN1 reactions the structure of the substrate and the nature of the nucleophile are the most important factors.
D)The nucleophile and leaving group are both important in SN2 reactions, while for the SN1 reactions the leaving group and the structure of the substrate are very significant.
E)The nucleophile is not important for SN2 reactions, but the structure of the substrate is very important; for SN1 reactions the opposite is true.
A)The nucleophile strongly influences both SN1 and SN2 reactions, while the nature of the nucleophile and the substrate structure are only important in SN2 reactions.
B)The structure of the substrate is the only important factor for SN1 reactions, while the nucleophile, leaving group, and the structure of the substrate are all important for SN2 reactions.
C)For SN2 reactions the only important factor to consider is the leaving group; for SN1 reactions the structure of the substrate and the nature of the nucleophile are the most important factors.
D)The nucleophile and leaving group are both important in SN2 reactions, while for the SN1 reactions the leaving group and the structure of the substrate are very significant.
E)The nucleophile is not important for SN2 reactions, but the structure of the substrate is very important; for SN1 reactions the opposite is true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)The SN2 mechanism does not have any intermediates and has only one transition state.
B)Tertiary alkylchlorides are the best substrates for SN2 reactions.
C)Only the strength of the nucleophile is important for SN2 reactions, not the nature of the leaving group.
D)SN1 reactions have a carbanion as an intermediate.
E)SN2 reactions result in the racemic product if we start from one enantiomer of a chiral substrate
A)The SN2 mechanism does not have any intermediates and has only one transition state.
B)Tertiary alkylchlorides are the best substrates for SN2 reactions.
C)Only the strength of the nucleophile is important for SN2 reactions, not the nature of the leaving group.
D)SN1 reactions have a carbanion as an intermediate.
E)SN2 reactions result in the racemic product if we start from one enantiomer of a chiral substrate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which of the following five substrates is the most likely to be the substrate in an SN1 reaction? 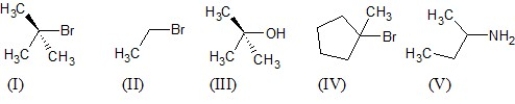
A)(I)
B)(II)
C)(III)
D)(IV)
E)(V)

A)(I)
B)(II)
C)(III)
D)(IV)
E)(V)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Determine the products of the following reaction: 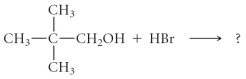
A)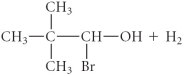
B)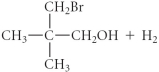
C)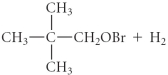
D)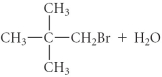
E)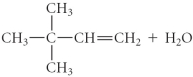
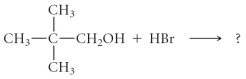
A)
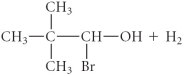
B)
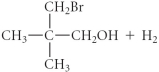
C)
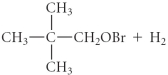
D)
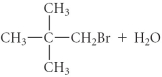
E)
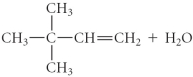

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)Elimination reactions proceed via either an E1 mechanism, which is a one-step mechanism, or an E2 mechanism, which is a two-step mechanism.
B)The E1 mechanism is somewhat similar to the SN1 mechanism: they both start with a dissociation step in which a carbocation is formed.
C)Primary alcohols and alkylhalides are very likely to react via an E1 mechanism because they produce stable carbocations.
D)The strength of base used in elimination reactions is not important for the E2 mechanism because the base contributes only to the second step of the E2 mechanism.
E)E2 elimination reactions can occur at primary carbon centres but not at secondary and tertiary carbon atoms.
A)Elimination reactions proceed via either an E1 mechanism, which is a one-step mechanism, or an E2 mechanism, which is a two-step mechanism.
B)The E1 mechanism is somewhat similar to the SN1 mechanism: they both start with a dissociation step in which a carbocation is formed.
C)Primary alcohols and alkylhalides are very likely to react via an E1 mechanism because they produce stable carbocations.
D)The strength of base used in elimination reactions is not important for the E2 mechanism because the base contributes only to the second step of the E2 mechanism.
E)E2 elimination reactions can occur at primary carbon centres but not at secondary and tertiary carbon atoms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
What are the major and minor products of the following reaction: 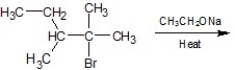
A)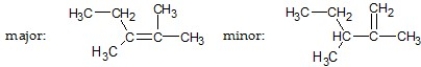
B)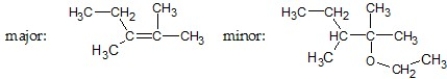
C)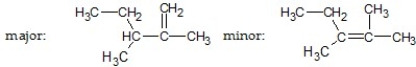
D)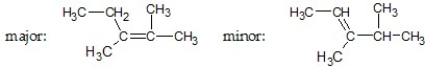
E)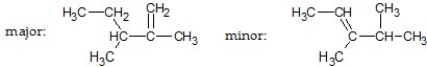

A)
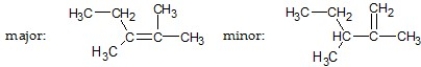
B)
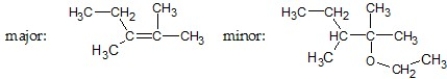
C)
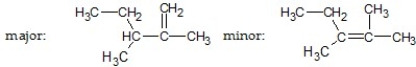
D)
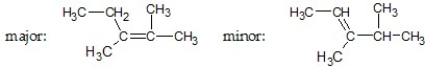
E)
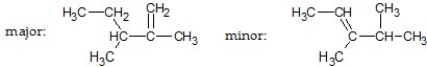

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)H-X molecules add across C=C bonds with retention of absolute configuration.
B)The addition of H-X molecules to alkenes and alkynes is a one-step mechanism.
C)The rate of H-X addition depends strongly on the nature of the leaving group.
D)According to Markovnikov's rule, the hydrogen cation adds to the C=C bond in such a way as to generate the most stable carbocation.
E)The hydrogen cation adds to the more substituted carbon atom of the C=C bond, a fact known as the Markovnikov's rule.
A)H-X molecules add across C=C bonds with retention of absolute configuration.
B)The addition of H-X molecules to alkenes and alkynes is a one-step mechanism.
C)The rate of H-X addition depends strongly on the nature of the leaving group.
D)According to Markovnikov's rule, the hydrogen cation adds to the C=C bond in such a way as to generate the most stable carbocation.
E)The hydrogen cation adds to the more substituted carbon atom of the C=C bond, a fact known as the Markovnikov's rule.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Which of the following five substrates is the most likely to be the substrate in an SN2 reaction? 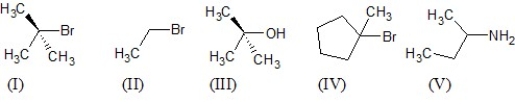
A)(I)
B)(II)
C)(III)
D)(IV)
E)(V)

A)(I)
B)(II)
C)(III)
D)(IV)
E)(V)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)The slow step in an SN1 mechanism is the dissociation step, which produces a carbanion and a leaving group.
B)In an SN1 mechanism, during the second step the nucleophile attacks the carbocation formed in the first step.
C)Primary alkylhalides are the best substrates for SN1 reactions.
D)The hydroxyl (OH-)group is an excellent leaving group in SN1 reactions.
E)During SN1 reactions the absolute configuration of the substrate is retained in the product.
A)The slow step in an SN1 mechanism is the dissociation step, which produces a carbanion and a leaving group.
B)In an SN1 mechanism, during the second step the nucleophile attacks the carbocation formed in the first step.
C)Primary alkylhalides are the best substrates for SN1 reactions.
D)The hydroxyl (OH-)group is an excellent leaving group in SN1 reactions.
E)During SN1 reactions the absolute configuration of the substrate is retained in the product.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)Elimination reactions take place with the retention of the absolute configuration.
B)The most common substrates in elimination reactions are ketones and amines.
C)A dehydration reaction produces an alkane and one equivalent of water.
D)The major product in an elimination reaction is the less substituted alkene.
E)A dehydrohalogenation reaction requires the presence of a strong base and heat.
A)Elimination reactions take place with the retention of the absolute configuration.
B)The most common substrates in elimination reactions are ketones and amines.
C)A dehydration reaction produces an alkane and one equivalent of water.
D)The major product in an elimination reaction is the less substituted alkene.
E)A dehydrohalogenation reaction requires the presence of a strong base and heat.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
What is the product for the dehydration of CH3CH2CH2OH?
A)CH3CH2CH2OCH2CH2CH3
B)CH3CH=CH2
C)CH3CH=CHCH3
D)CH3CH2CH=CH2
E)CH2=C=CH2
A)CH3CH2CH2OCH2CH2CH3
B)CH3CH=CH2
C)CH3CH=CHCH3
D)CH3CH2CH=CH2
E)CH2=C=CH2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Predict the correct mechanism and product for the following reaction: 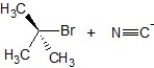
A)SN1 mechanism, the product is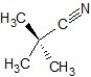
B)SN2 mechanism, the product is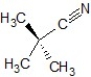
C)SN2 mechanism, the product is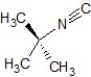
D)SN1 mechanism, the product is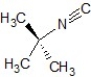
E)E1 mechanism, the product is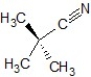
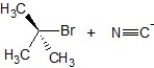
A)SN1 mechanism, the product is

B)SN2 mechanism, the product is

C)SN2 mechanism, the product is

D)SN1 mechanism, the product is

E)E1 mechanism, the product is


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Which of the following is a balanced chemical equation that represents the reaction of 3-ethyl-2-methylhexane with Br2?
A)C7H14 + Br2 → C7H12Br + HBr
B)C9H20 + Br2 → C9H19Br + HBr
C)C6H12 + Br2 → C6H10Br2 + H2
D)C9H18 + Br2 → C9H16Br2 + H2
E)C6H12 + Br2 → C6H11Br + HBr
A)C7H14 + Br2 → C7H12Br + HBr
B)C9H20 + Br2 → C9H19Br + HBr
C)C6H12 + Br2 → C6H10Br2 + H2
D)C9H18 + Br2 → C9H16Br2 + H2
E)C6H12 + Br2 → C6H11Br + HBr

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)Dehydration is an example of a 1,2-elimination reaction in which an alcohol loses one water molecule, forming an alkene.
B)Dehydrohalogenation is an example of a 1,2 elimination reaction in which an organic molecule loses one water molecule and a halogen atom to produce an alkyne.
C)There is only one possible mechanistic pathway for an elimination reaction, called the E1 mechanism.
D)1,2-elimination reactions are frequently in competition with addition reactions.
E)Dehydration and dehydrohalogenation are two distinct steps in every 1,2-elimination reaction.
A)Dehydration is an example of a 1,2-elimination reaction in which an alcohol loses one water molecule, forming an alkene.
B)Dehydrohalogenation is an example of a 1,2 elimination reaction in which an organic molecule loses one water molecule and a halogen atom to produce an alkyne.
C)There is only one possible mechanistic pathway for an elimination reaction, called the E1 mechanism.
D)1,2-elimination reactions are frequently in competition with addition reactions.
E)Dehydration and dehydrohalogenation are two distinct steps in every 1,2-elimination reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)Alkenes are as unreactive as alkanes.
B)Electrophilic addition reactions proceed via either an E1 or E2 mechanism.
C)The first step of an H-X electrophilic addition is the formation of a carbanion.
D)Carbon-carbon double bonds are electron rich and are nucleophilic.
E)During the addition of an H-X molecule, the H atom behaves as a nucleophile while the X atom behaves as an electrophile.
A)Alkenes are as unreactive as alkanes.
B)Electrophilic addition reactions proceed via either an E1 or E2 mechanism.
C)The first step of an H-X electrophilic addition is the formation of a carbanion.
D)Carbon-carbon double bonds are electron rich and are nucleophilic.
E)During the addition of an H-X molecule, the H atom behaves as a nucleophile while the X atom behaves as an electrophile.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Which of the following is the balanced chemical equation that represents the addition of Cl2 to CH3CH=CH2?
A)CH3CH=CH2 + Cl2 → CH3CHClCH3 + HCl
B)CH3CH=CH2 + Cl2 → CH3CCl=CHCl + H2
C)CH3CH=CH2 + Cl2 → CH3CHClCH2Cl
D)CH3CH=CH2 + 2Cl2 → CH3CHCl2 + CH2Cl2
E)CH3CH=CH2 + 2Cl2 → CH3CCl2CHCl2 + H2
A)CH3CH=CH2 + Cl2 → CH3CHClCH3 + HCl
B)CH3CH=CH2 + Cl2 → CH3CCl=CHCl + H2
C)CH3CH=CH2 + Cl2 → CH3CHClCH2Cl
D)CH3CH=CH2 + 2Cl2 → CH3CHCl2 + CH2Cl2
E)CH3CH=CH2 + 2Cl2 → CH3CCl2CHCl2 + H2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Determine the products of the following reaction: 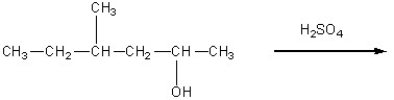
A)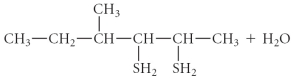
B)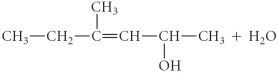
C)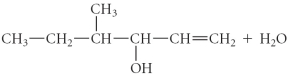
D)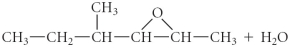
E)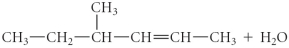

A)
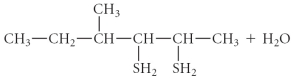
B)
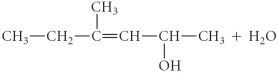
C)
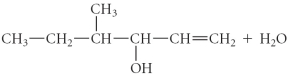
D)

E)
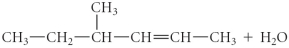

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Identify the major product in the following reaction: 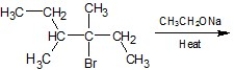
A)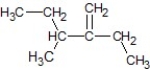
B)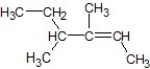
C)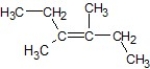
D)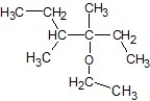
E)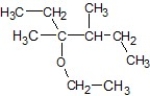

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)In nucleophilic substitution reactions at a saturated carbon atom, a carbon with a positive charge behaves as a nucleophile.
B)Nucleophilic substitution reactions at a saturated carbon atom can follow one of three mechanisms: SN1, SN2, and SN3.
C)A carbon atom with a partial positive charge can react with a nucleophile, a molecule, or ion that has a lone pair of electrons.
D)Alkanes are an example of saturated organic compounds that easily participate in nucleophilic substitution reactions at a saturated carbon atom.
E)In nucleophilic substitution reactions at a saturated carbon atom, the replaced group is called an electrophile.
A)In nucleophilic substitution reactions at a saturated carbon atom, a carbon with a positive charge behaves as a nucleophile.
B)Nucleophilic substitution reactions at a saturated carbon atom can follow one of three mechanisms: SN1, SN2, and SN3.
C)A carbon atom with a partial positive charge can react with a nucleophile, a molecule, or ion that has a lone pair of electrons.
D)Alkanes are an example of saturated organic compounds that easily participate in nucleophilic substitution reactions at a saturated carbon atom.
E)In nucleophilic substitution reactions at a saturated carbon atom, the replaced group is called an electrophile.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Complete and balance the following complete hydrogenation reaction: CH3CH2C  CCH3 + 2H2 → ?
CCH3 + 2H2 → ?
A)CH3CH2C CCH3 + 3H2 → CH3CH2CH3 + CH3CH3
CCH3 + 3H2 → CH3CH2CH3 + CH3CH3
B)CH3CH2C CCH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
CCH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
C)CH3CH2C CCH3 + 6H2 → 5CH4
CCH3 + 6H2 → 5CH4
D)2CH3CH2C CCH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
CCH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
E)CH3CH2C CCH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH2
CCH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH2
 CH2CH3
CH2CH3
 CCH3 + 2H2 → ?
CCH3 + 2H2 → ?A)CH3CH2C
 CCH3 + 3H2 → CH3CH2CH3 + CH3CH3
CCH3 + 3H2 → CH3CH2CH3 + CH3CH3B)CH3CH2C
 CCH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
CCH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3C)CH3CH2C
 CCH3 + 6H2 → 5CH4
CCH3 + 6H2 → 5CH4D)2CH3CH2C
 CCH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
CCH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3E)CH3CH2C
 CCH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH2
CCH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH2  CH2CH3
CH2CH3
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Which of the following is the balanced chemical equation for the catalytic hydrogenation (addition of H2)to CH3C≡CH?
A)CH3C≡CH + H2 → CH3CH=CH2
B)CH3C≡CH + 2H2 → CH3CH=CH2
C)CH3C≡CH + H2 → CH3CH2CH3
D)CH3C≡CH + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH3
E)CH3C≡CH + H2 → CH2=C=CH2
A)CH3C≡CH + H2 → CH3CH=CH2
B)CH3C≡CH + 2H2 → CH3CH=CH2
C)CH3C≡CH + H2 → CH3CH2CH3
D)CH3C≡CH + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH3
E)CH3C≡CH + H2 → CH2=C=CH2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Which of the following is the balanced chemical equation for the addition of two equivalents of Br2 to CH3C≡CH?
A)CH3C≡CH + 2Br2 → CH3CBr2CHBr2
B)CH3C≡CH + 2Br2 → CH3CBr=CHBr
C)CH3C≡CH + 2Br2 → CH3CH2CHBr2
D)CH3C≡CH + 2Br2 → CH3CBr2CH3
E)CH3C≡CH + 2Br2 → CH3CHBrCH2Br
A)CH3C≡CH + 2Br2 → CH3CBr2CHBr2
B)CH3C≡CH + 2Br2 → CH3CBr=CHBr
C)CH3C≡CH + 2Br2 → CH3CH2CHBr2
D)CH3C≡CH + 2Br2 → CH3CBr2CH3
E)CH3C≡CH + 2Br2 → CH3CHBrCH2Br

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
What is the product obtained after a reaction between an aldehyde and Grignard reagent is worked-up with dilute acid?
A)a ketone
B)a primary alcohol
C)a secondary alcohol
D)a tertiary alcohol
E)a carboxylic acid
A)a ketone
B)a primary alcohol
C)a secondary alcohol
D)a tertiary alcohol
E)a carboxylic acid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)Addition is the predominant reaction observed in acyl compounds.
B)Acyl chlorides are the least reactive of all acyl compounds, while amides are the most.
C)Fischer esterification is the reaction between carboxylic acids with alcohols to produce esters.
D)Fischer esterification is catalyzed by a strong base.
E)Transesterification is a reaction in which an ester group is transferred from one organic group to another.
A)Addition is the predominant reaction observed in acyl compounds.
B)Acyl chlorides are the least reactive of all acyl compounds, while amides are the most.
C)Fischer esterification is the reaction between carboxylic acids with alcohols to produce esters.
D)Fischer esterification is catalyzed by a strong base.
E)Transesterification is a reaction in which an ester group is transferred from one organic group to another.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
What is transesterification?
A)Transesterification is a reaction that increases the oxidation number of carbon in esters.
B)An acid-catalyzed conversion of one ester to another is called transesterification.
C)Transesterification is a reaction in which the starting ester is transformed into any other organic family.
D)An interconversion reaction sequence (carboxylic acid)→ (ester)→ (carbocylic acid)is called transesterification.
E)A reaction that produces more reactive acyl compounds (such as acyl chlorides)from esters is called transesterification.
A)Transesterification is a reaction that increases the oxidation number of carbon in esters.
B)An acid-catalyzed conversion of one ester to another is called transesterification.
C)Transesterification is a reaction in which the starting ester is transformed into any other organic family.
D)An interconversion reaction sequence (carboxylic acid)→ (ester)→ (carbocylic acid)is called transesterification.
E)A reaction that produces more reactive acyl compounds (such as acyl chlorides)from esters is called transesterification.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Determine the product of the following reaction: 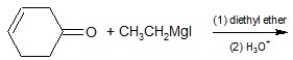
A)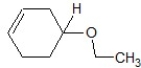
B)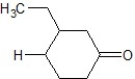
C)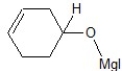
D)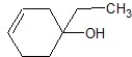
E)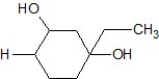
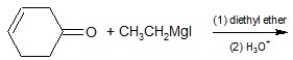
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
What are the correct products of the following reaction performed in the presence of an acid? C3H7COOH + C2H5OH →
A)C3H7COOC2H5 + H2O
B)C3H7COC2H5 + H2O + 1/2O2
C)C3H7C(OH)OC2H5 + H3O+
D)C3H7OH + HOOCC2H5 + H3O+
E)C3H7C(=O)-O-O-C2H5 + H2O
A)C3H7COOC2H5 + H2O
B)C3H7COC2H5 + H2O + 1/2O2
C)C3H7C(OH)OC2H5 + H3O+
D)C3H7OH + HOOCC2H5 + H3O+
E)C3H7C(=O)-O-O-C2H5 + H2O

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Which of the following compounds is a Grignard reagent?
A)(C2H5)2Mg
B)LiC4H9
C)CH3Mg(OH)
D)CH3CH2MgBr
E)CH3MgOCH3
A)(C2H5)2Mg
B)LiC4H9
C)CH3Mg(OH)
D)CH3CH2MgBr
E)CH3MgOCH3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Which of the following is the product of the following reaction? 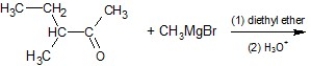
A)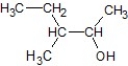
B)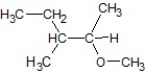
C)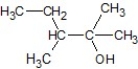
D)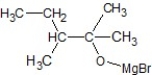
E)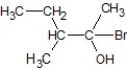
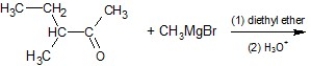
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Determine the product(s)of the following reaction: 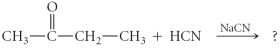
A)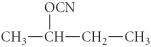
B)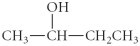
C)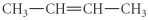
D)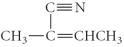
E)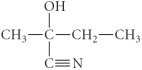
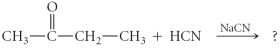
A)
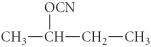
B)
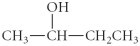
C)
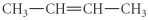
D)
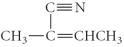
E)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Complete and balance the following addition reaction: CH3C  CCH3 + 2Cl2 → ?
CCH3 + 2Cl2 → ?
A)CH3C CCH3 + 2Cl2 → CH3CCl2CCl2CH3
CCH3 + 2Cl2 → CH3CCl2CCl2CH3
B)CH3C CCH3 + 3Cl2 → 2CH3CCl3
CCH3 + 3Cl2 → 2CH3CCl3
C)CH3C CCH3 + 2Cl2 → 4CH3Cl
CCH3 + 2Cl2 → 4CH3Cl
D)CH3C CCH3 + 4Cl2 → 4CH2Cl2
CCH3 + 4Cl2 → 4CH2Cl2
E)CH3C CCH3 + Cl2 → CH3CHClCHClCH3
CCH3 + Cl2 → CH3CHClCHClCH3
 CCH3 + 2Cl2 → ?
CCH3 + 2Cl2 → ?A)CH3C
 CCH3 + 2Cl2 → CH3CCl2CCl2CH3
CCH3 + 2Cl2 → CH3CCl2CCl2CH3B)CH3C
 CCH3 + 3Cl2 → 2CH3CCl3
CCH3 + 3Cl2 → 2CH3CCl3C)CH3C
 CCH3 + 2Cl2 → 4CH3Cl
CCH3 + 2Cl2 → 4CH3ClD)CH3C
 CCH3 + 4Cl2 → 4CH2Cl2
CCH3 + 4Cl2 → 4CH2Cl2E)CH3C
 CCH3 + Cl2 → CH3CHClCHClCH3
CCH3 + Cl2 → CH3CHClCHClCH3
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
What is a hemiacetal?
A)A hemiacetal, prepared from an alcohol and an aldehyde, is a compound that contains both OH and OR groups on the same carbon.
B)Compounds prepared from ketones and alcohols and with OH and OR groups on the same carbon are known as hemiacetals.
C)A hemiacetal is a product of acetyl group hydrolysis; it contains a COOH group.
D)A hemiacetal is formed from alcohols and acetic acid; a hemiacetal has both acetyl and OH groups on the same carbon atom.
E)A hemiacetal, formed from an aldehyde and an alcohol, has OH and aldehyde groups on adjacent carbon atoms in its structure.
A)A hemiacetal, prepared from an alcohol and an aldehyde, is a compound that contains both OH and OR groups on the same carbon.
B)Compounds prepared from ketones and alcohols and with OH and OR groups on the same carbon are known as hemiacetals.
C)A hemiacetal is a product of acetyl group hydrolysis; it contains a COOH group.
D)A hemiacetal is formed from alcohols and acetic acid; a hemiacetal has both acetyl and OH groups on the same carbon atom.
E)A hemiacetal, formed from an aldehyde and an alcohol, has OH and aldehyde groups on adjacent carbon atoms in its structure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Which of the following is the balanced chemical equation for the addition of HBr to CH2=CHCH2CH3?
A)CH2=CHCH2CH3 + HBr → CH2BrCH2CH2CH3
B)CH2=CHCH2CH3 + 2HBr → 2CH2BrCH3
C)CH2=CHCH2CH3 + 2HBr → CH3Br + CH2BrCH2CH3
D)CH2=CHCH2CH3 + 4HBr → 4CH3Br
E)CH2=CHCH2CH3 + HBr → CH3CHBrCH2CH3
A)CH2=CHCH2CH3 + HBr → CH2BrCH2CH2CH3
B)CH2=CHCH2CH3 + 2HBr → 2CH2BrCH3
C)CH2=CHCH2CH3 + 2HBr → CH3Br + CH2BrCH2CH3
D)CH2=CHCH2CH3 + 4HBr → 4CH3Br
E)CH2=CHCH2CH3 + HBr → CH3CHBrCH2CH3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
What is the product obtained after a reaction between a ketone and Grignard reagent is worked-up with dilute acid?
A)an aldehyde
B)a primary alcohol
C)a secondary alcohol
D)a tertiary alcohol
E)a carboxylic acid
A)an aldehyde
B)a primary alcohol
C)a secondary alcohol
D)a tertiary alcohol
E)a carboxylic acid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
What is the correct order of increasing reactivity among acyl groups?
A)acyl chloride < acid anhydride < carboxylic acid < amide
B)acyl chloride < carboxylic acid < acid anhydride < amide
C)acyl chloride < amide < carboxylic acid < acid anhydride
D)amide < carboxylic acid < acid anhydride < acyl chloride
E)amide < acyl chloride < acid anhydride < carboxylic acid
A)acyl chloride < acid anhydride < carboxylic acid < amide
B)acyl chloride < carboxylic acid < acid anhydride < amide
C)acyl chloride < amide < carboxylic acid < acid anhydride
D)amide < carboxylic acid < acid anhydride < acyl chloride
E)amide < acyl chloride < acid anhydride < carboxylic acid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
What is a hemiketal?
A)A hemiketal, prepared from an alcohol and an aldehyde, is a compound that contains both OH and OR groups on the same carbon.
B)Compounds prepared from ketones and alcohols and with OH and OR groups on the same carbon are known as hemiketals.
C)A hemiketal is a product of acetyl group hydrolysis; it contains a COOH functional group.
D)A hemiketal is formed from alcohols and acetic acid; a hemiacetal has both acetyl and OH groups on the same carbon atom.
E)A hemiketal, formed from a ketone and an alcohol, has OH and keto groups on adjacent carbon atoms in its structure.
A)A hemiketal, prepared from an alcohol and an aldehyde, is a compound that contains both OH and OR groups on the same carbon.
B)Compounds prepared from ketones and alcohols and with OH and OR groups on the same carbon are known as hemiketals.
C)A hemiketal is a product of acetyl group hydrolysis; it contains a COOH functional group.
D)A hemiketal is formed from alcohols and acetic acid; a hemiacetal has both acetyl and OH groups on the same carbon atom.
E)A hemiketal, formed from a ketone and an alcohol, has OH and keto groups on adjacent carbon atoms in its structure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
What is the product obtained from the reaction between an aldehyde and a primary alcohol?
A)a secondary alcohol
B)a tertiary alcohol
C)a hemiacetal
D)a hemiketal
E)a carboxylic acid
A)a secondary alcohol
B)a tertiary alcohol
C)a hemiacetal
D)a hemiketal
E)a carboxylic acid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
What is the product obtained from the reaction between a ketone and a primary alcohol?
A)a secondary alcohol
B)a tertiary alcohol
C)a hemiacetal
D)a hemiketal
E)a carboxylic acid
A)a secondary alcohol
B)a tertiary alcohol
C)a hemiacetal
D)a hemiketal
E)a carboxylic acid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Which of the following is the balanced chemical equation for the catalytic hydrogenation (addition of H2)to CH3CH=CHCH3?
A)CH3CH=CHCH3 + 2H2 → 2CH3CH3
B)CH3CH=CHCH3 + 3H2 → CH3CH3 + 2 CH4
C)CH3CH=CHCH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH3 + CH4
D)CH3CH=CHCH3 + H2 → CH3CH2CH2CH3
E)CH3CH=CHCH3 + 4H2 → 4CH4
A)CH3CH=CHCH3 + 2H2 → 2CH3CH3
B)CH3CH=CHCH3 + 3H2 → CH3CH3 + 2 CH4
C)CH3CH=CHCH3 + 2H2 → CH3CH2CH3 + CH4
D)CH3CH=CHCH3 + H2 → CH3CH2CH2CH3
E)CH3CH=CHCH3 + 4H2 → 4CH4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Predict the products of the following reaction: 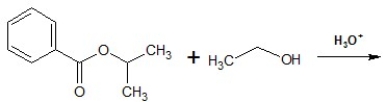
A)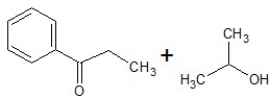
B)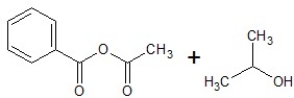
C)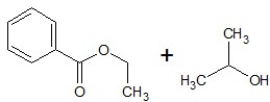
D)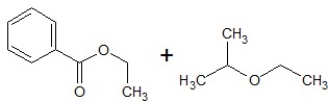
E)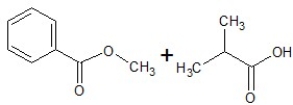
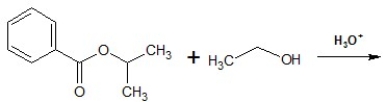
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)
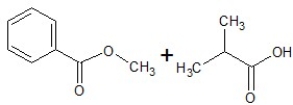

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
What are polymers?
A)Polymers are long, chain-like molecules composed of small, repeating units called monomers.
B)Polymers are long, chain-like molecules composed of small, repeating units called copolymers.
C)Polymers are long, chain-like molecules without fixed composition or structure, commonly of low molecular weight.
D)Polymers are long, chain-like molecules formed when smaller units, monomers, crystalize together from solution.
E)Polymers are long, chain-like molecules composed of small, repeating units called oligomers.
A)Polymers are long, chain-like molecules composed of small, repeating units called monomers.
B)Polymers are long, chain-like molecules composed of small, repeating units called copolymers.
C)Polymers are long, chain-like molecules without fixed composition or structure, commonly of low molecular weight.
D)Polymers are long, chain-like molecules formed when smaller units, monomers, crystalize together from solution.
E)Polymers are long, chain-like molecules composed of small, repeating units called oligomers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Which combination of reagents is used in the Friedel-Crafts acylation?
A)acyl chloride, RC(=O)Cl, and aluminum hydroxide, Al(OH)3
B)acyl fluoride, RC(=O)F, and aluminum fluoride, AlF3
C)alkyl chloride, RCH2Cl, and aluminum chloride, AlCl3
D)acyl chloride, RC(=O)Cl, and aluminum oxide, Al2O3
E)acyl chloride, RC(=O)Cl, and aluminum chloride, AlCl3
A)acyl chloride, RC(=O)Cl, and aluminum hydroxide, Al(OH)3
B)acyl fluoride, RC(=O)F, and aluminum fluoride, AlF3
C)alkyl chloride, RCH2Cl, and aluminum chloride, AlCl3
D)acyl chloride, RC(=O)Cl, and aluminum oxide, Al2O3
E)acyl chloride, RC(=O)Cl, and aluminum chloride, AlCl3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Which combination of reagents is used in the Friedel-Crafts alkylation?
A)alkyl chloride, R-Cl, and aluminum hydroxide, Al(OH)3
B)alkyl chloride, R-Cl, and aluminum fluoride, AlF3
C)alkyl chloride, R-Cl, and aluminum chloride, AlCl3
D)alkyl chloride, R-Cl, and aluminum oxide, Al2O3
E)acyl chloride, RC(=O)Cl, and aluminum chloride, AlCl3
A)alkyl chloride, R-Cl, and aluminum hydroxide, Al(OH)3
B)alkyl chloride, R-Cl, and aluminum fluoride, AlF3
C)alkyl chloride, R-Cl, and aluminum chloride, AlCl3
D)alkyl chloride, R-Cl, and aluminum oxide, Al2O3
E)acyl chloride, RC(=O)Cl, and aluminum chloride, AlCl3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Determine the products of the following reaction: Benzene + CH3CH2Cl 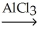 ?
?
A)ethylbenzene and HCl
B)1,2-dimethylbenzene and H2
C)chlorobenzene and CH3CH2Al
D)chlorobenzene and CH3CH3
E)1,4-diethylbenzene and Cl2
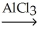 ?
?A)ethylbenzene and HCl
B)1,2-dimethylbenzene and H2
C)chlorobenzene and CH3CH2Al
D)chlorobenzene and CH3CH3
E)1,4-diethylbenzene and Cl2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)During the electrophilic aromatic substitutions, the resonance stabilized carbocation reacts with a base to give the addition product.
B)Aromatic compounds are very reactive because they contain more than one C=C double bond in their structure.
C)The rate-determining (slow)step of electrophilic aromatic substitutions is the deprotonation of the carbocation intermediate.
D)Unlike alkenes, aromatic compounds almost always prefer electrophilic substitution over electrophilic addition.
E)During the electrophilic aromatic substitution a Bronsted or Lewis acid is required to generate the nucleophile from an aromatic substrate.
A)During the electrophilic aromatic substitutions, the resonance stabilized carbocation reacts with a base to give the addition product.
B)Aromatic compounds are very reactive because they contain more than one C=C double bond in their structure.
C)The rate-determining (slow)step of electrophilic aromatic substitutions is the deprotonation of the carbocation intermediate.
D)Unlike alkenes, aromatic compounds almost always prefer electrophilic substitution over electrophilic addition.
E)During the electrophilic aromatic substitution a Bronsted or Lewis acid is required to generate the nucleophile from an aromatic substrate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
What are addition polymers?
A)Addition polymers are formed from monomers that bond together and eliminate a small molecule, usually water.
B)Addition polymers are polymers formed when monomers add together without formation of covalent bonds.
C)Addition polymers are formed when small molecules (such as water and HX)add across unsaturated C-C bonds in the polymeric chain.
D)Addition polymers are formed from monomers that link together without the elimination of a small molecule.
E)Addition polymers are polymers that grow by adding small monomers to the existing polymer chain with elimination of a water molecule for each new bond formed.
A)Addition polymers are formed from monomers that bond together and eliminate a small molecule, usually water.
B)Addition polymers are polymers formed when monomers add together without formation of covalent bonds.
C)Addition polymers are formed when small molecules (such as water and HX)add across unsaturated C-C bonds in the polymeric chain.
D)Addition polymers are formed from monomers that link together without the elimination of a small molecule.
E)Addition polymers are polymers that grow by adding small monomers to the existing polymer chain with elimination of a water molecule for each new bond formed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
What type of polymers are polyamides?
A)Polyamides, formed via step-growth polymerization of diacids and diamines, have the monomers connected through hydrogen bonds.
B)Polyamides, formed via step-growth polymerization of diacids and diamines, have the monomers connected through amine bonds.
C)Polyamides, formed via addition polymerization of diacids and diamines, have the monomers connected through amide bonds.
D)Polyamides, formed via step-growth polymerization of acids and amines, have the monomers connected through amide groups.
E)Polyamides, formed via step-growth polymerization of diacids and diamines, have the monomers connected through amide groups.
A)Polyamides, formed via step-growth polymerization of diacids and diamines, have the monomers connected through hydrogen bonds.
B)Polyamides, formed via step-growth polymerization of diacids and diamines, have the monomers connected through amine bonds.
C)Polyamides, formed via addition polymerization of diacids and diamines, have the monomers connected through amide bonds.
D)Polyamides, formed via step-growth polymerization of acids and amines, have the monomers connected through amide groups.
E)Polyamides, formed via step-growth polymerization of diacids and diamines, have the monomers connected through amide groups.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
What are the correct products of the following reaction performed in the presence of an acid? C3H7COOCH3 + C2H5OH →
A)C3H7COOC2H5 + CH3OH
B)CH3COOC2H5 + C3H7OH
C)C3H7COC2H5 + CH3COOH
D)C3H7OH + C2H5COOCH3 + H3O+
E)C3H7CH(OCH3)(OC2H5)+ H2O
A)C3H7COOC2H5 + CH3OH
B)CH3COOC2H5 + C3H7OH
C)C3H7COC2H5 + CH3COOH
D)C3H7OH + C2H5COOCH3 + H3O+
E)C3H7CH(OCH3)(OC2H5)+ H2O

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Which of the following properties is typical for most polymers?
A)high reactivity
B)durability
C)softness
D)soluble in water
E)high toxicity
A)high reactivity
B)durability
C)softness
D)soluble in water
E)high toxicity

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Identify reagents A and B required for the following transformation of acyl groups: C2H5COOH 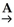 C2H5COCl
C2H5COCl 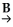 C2H5CONHCH3 + HCl
C2H5CONHCH3 + HCl
A)A = HCl; B = H2NCH3
B)A = NaCl; B = HCONHCH3
C)A = SOCl2; B = HCONHCH3
D)A = NaCl; B = H2NCH3
E)A = SOCl2; B = H2NCH3
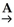 C2H5COCl
C2H5COCl 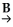 C2H5CONHCH3 + HCl
C2H5CONHCH3 + HClA)A = HCl; B = H2NCH3
B)A = NaCl; B = HCONHCH3
C)A = SOCl2; B = HCONHCH3
D)A = NaCl; B = H2NCH3
E)A = SOCl2; B = H2NCH3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Which combination of reagents would you use to brominate an aromatic compound?
A)Br2 and FeCl3
B)HBr and H2SO4
C)Br2 and FeBr3
D)HBrO and FeBr3
E)HBr and HNO3
A)Br2 and FeCl3
B)HBr and H2SO4
C)Br2 and FeBr3
D)HBrO and FeBr3
E)HBr and HNO3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Determine the products of the following reaction: Benzene + Br2 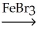 ?
?
A)1,2-dibromobenzene and H2
B)1,4-dibromobenzene and HBr
C)ferrobenzene and H2
D)perbromobenzene and HBr
E)bromobenzene and HBr
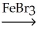 ?
?A)1,2-dibromobenzene and H2
B)1,4-dibromobenzene and HBr
C)ferrobenzene and H2
D)perbromobenzene and HBr
E)bromobenzene and HBr

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Identify reagents A and B required for the following transformation of acyl groups: 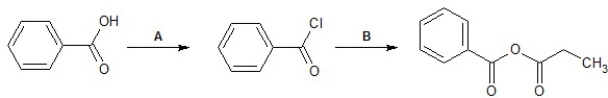
A)A = (COCl)2; B = C2H5CHO
B)A = (COCl)2; B = C2H5COOH
C)A = HCl; B = C2H5COOH
D)A = (COCl)2; B = C2H5-CH2OH
E)A = HCl; B = C2H5CHO

A)A = (COCl)2; B = C2H5CHO
B)A = (COCl)2; B = C2H5COOH
C)A = HCl; B = C2H5COOH
D)A = (COCl)2; B = C2H5-CH2OH
E)A = HCl; B = C2H5CHO

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Which of the following is a compound that is acid anhydride?
A)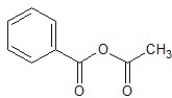
B)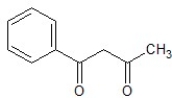
C)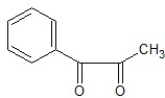
D)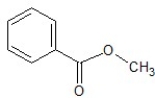
E)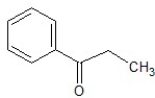
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Which pair of compounds would react to produce a polymer?
A)an acid and a diol
B)a diacid and an alcohol
C)a diacid and a diol
D)an alcohol and an acid
E)a diacid and a diketone
A)an acid and a diol
B)a diacid and an alcohol
C)a diacid and a diol
D)an alcohol and an acid
E)a diacid and a diketone

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Which combination of reagents would you use to prepare chlorobenzene (C6H5Cl)from benzene (C6H6)?
A)Cl2 and FeBr3
B)HCl and H2SO4
C)Cl2 and FeCl3
D)HClO and FeCl3
E)HCl and HNO3
A)Cl2 and FeBr3
B)HCl and H2SO4
C)Cl2 and FeCl3
D)HClO and FeCl3
E)HCl and HNO3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Identify the organic product for the following reaction. CH3CH2COOH + CH3CH2CH2NH2 
A)CH3CH2NHCH2CH2CH3
B)CH3CH2CON(CH2CH2CH3)2
C)CH3CH2CH2CONHCH2CH3
D)CH3CH2CONHCH2CH2CH3
E)CH3CH2N(CH2CH2CH3)2

A)CH3CH2NHCH2CH2CH3
B)CH3CH2CON(CH2CH2CH3)2
C)CH3CH2CH2CONHCH2CH3
D)CH3CH2CONHCH2CH2CH3
E)CH3CH2N(CH2CH2CH3)2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Predict the products of the following reaction: C5H11COOH + (COCl)2 →
A)C5H11Cl + HCl + CO + 2CO2
B)C5H11COCl + H2O+ COCl + CO2
C)C5H11COCl2 + 2H2CO3
D)C5H11COCl + HCl + CO + CO2
E)C5H11COCl + HCl + (CO)2
A)C5H11Cl + HCl + CO + 2CO2
B)C5H11COCl + H2O+ COCl + CO2
C)C5H11COCl2 + 2H2CO3
D)C5H11COCl + HCl + CO + CO2
E)C5H11COCl + HCl + (CO)2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
To prepare nitrobenzene (C6H5NO2)from benzene (C6H6), two strong mineral acids are required. Which ones?
A)HNO3 and H2SO4
B)HNO3 and H2SO3
C)HNO3 and H2S
D)HNO2 and H2SO4
E)HNO3 and H2S2O7
A)HNO3 and H2SO4
B)HNO3 and H2SO3
C)HNO3 and H2S
D)HNO2 and H2SO4
E)HNO3 and H2S2O7

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








