Deck 11: Audit Sampling Part Four: Completion and Communication
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 11: Audit Sampling Part Four: Completion and Communication
1
Sam Shoe, an auditor, is planning substantive tests of additions to property. There are 75 additions and he plans to vouch all those over $10 000, of which there are 15 and apply analytical tests to the remaining balance. The audit approach may be described most precisely as:
A) Non-statistical sampling.
B) Audit sampling.
C) Statistical sampling.
D) None of the given answers.
A) Non-statistical sampling.
B) Audit sampling.
C) Statistical sampling.
D) None of the given answers.
D
2
Which of the following best illustrates the concept of sampling risk?
A) An auditor may select audit procedures that are not appropriate to achieve the specific objective.
B) A randomly chosen sample may not be representative of the population as a whole on the characteristic of interest.
C) The documents related to the chosen sample may not be available for inspection.
D) An auditor may fail to recognise errors in the documents examined for the chosen sample.
A) An auditor may select audit procedures that are not appropriate to achieve the specific objective.
B) A randomly chosen sample may not be representative of the population as a whole on the characteristic of interest.
C) The documents related to the chosen sample may not be available for inspection.
D) An auditor may fail to recognise errors in the documents examined for the chosen sample.
B
3
Which of the following factors does an auditor generally most need to consider in planning a particular audit sample for a test of controls?
A) Total dollar amount of the items to be sampled.
B) Number of items in the population.
C) Risk of assessing control risk too high.
D) Risk of assessing control risk too low.
A) Total dollar amount of the items to be sampled.
B) Number of items in the population.
C) Risk of assessing control risk too high.
D) Risk of assessing control risk too low.
D
4
Joe Costa, an auditor, is planning tests of controls over cash receipts. There are 7000 receipts and he plans to vouch 30 picked haphazardly from the cash receipts journal for the period 1 January to 30 September 20X0. This audit approach may be described most precisely as:
A) statistical sampling.
B) non-statistical sampling.
C) a non-sampling technique called selective examination.
D) None of the given answers.
A) statistical sampling.
B) non-statistical sampling.
C) a non-sampling technique called selective examination.
D) None of the given answers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
When selecting items for testing, the auditor concentrates their selection on high dollar value items. This approach is:
A) never appropriate in performing audit procedures under Australian auditing standards.
B) not an audit sampling technique but is often an appropriate evidence collection technique.
C) appropriate only if the auditor is undertaking statistical sampling.
D) generally a useful and efficient method for all audit tests.
A) never appropriate in performing audit procedures under Australian auditing standards.
B) not an audit sampling technique but is often an appropriate evidence collection technique.
C) appropriate only if the auditor is undertaking statistical sampling.
D) generally a useful and efficient method for all audit tests.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Audit sampling is the application of an audit procedure:
A) using statistical methods to evaluate the propriety of the account balance or class of transactions.
B) to less than 100 per cent of the items within an account balance or class of transactions for the purpose of evaluating some characteristics of the balance or class.
C) applied to items selected randomly.
D) on a test basis.
A) using statistical methods to evaluate the propriety of the account balance or class of transactions.
B) to less than 100 per cent of the items within an account balance or class of transactions for the purpose of evaluating some characteristics of the balance or class.
C) applied to items selected randomly.
D) on a test basis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
In dollar-unit sampling, population size is:
A) the number of items in an account.
B) the dollar balance of an account.
C) included in the denominator of the formula to determine sample size.
D) unrelated to sample size.
A) the number of items in an account.
B) the dollar balance of an account.
C) included in the denominator of the formula to determine sample size.
D) unrelated to sample size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
An advantage of using statistical sampling techniques is that such techniques:
A) have been held in the courts to be superior to judgmental sampling.
B) define the values of precision and reliability required to provide audit satisfaction.
C) eliminate the need for judgmental decisions.
D) mathematically measure risk.
A) have been held in the courts to be superior to judgmental sampling.
B) define the values of precision and reliability required to provide audit satisfaction.
C) eliminate the need for judgmental decisions.
D) mathematically measure risk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
If the size of the sample to be used in a particular test of controls has not been determined by utilising statistical concepts, but the sample has been chosen in accordance with random selection procedures:
A) the auditor has committed a non-sampling error.
B) no inferences can be drawn from the sample.
C) the auditor will have to evaluate the results by reference to the principles of discovery sampling.
D) the auditor may or may not achieve desired precision at the planned level of assessing control risk too low.
A) the auditor has committed a non-sampling error.
B) no inferences can be drawn from the sample.
C) the auditor will have to evaluate the results by reference to the principles of discovery sampling.
D) the auditor may or may not achieve desired precision at the planned level of assessing control risk too low.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Auditors who prefer statistical to non-statistical sampling believe that the principal advantage of statistical sampling flows from its ability to:
A) provide a mathematical measurement of uncertainty.
B) define the precision required to provide audit satisfaction.
C) promote a more legally defensible procedural approach.
D) establish conclusive audit evidence with decreased audit effort.
A) provide a mathematical measurement of uncertainty.
B) define the precision required to provide audit satisfaction.
C) promote a more legally defensible procedural approach.
D) establish conclusive audit evidence with decreased audit effort.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Which of the following best describes the distinguishing feature of statistical sampling compared with non-statistical sampling?
A) It provides a means for measuring mathematically the degree of uncertainty that results from examining only part of a population.
B) It requires the examination of a smaller number of supporting documents.
C) It is evaluated in terms of two parameters: statistical mean and random selection.
D) It reduces the problems associated with the auditor's judgment concerning materiality.
A) It provides a means for measuring mathematically the degree of uncertainty that results from examining only part of a population.
B) It requires the examination of a smaller number of supporting documents.
C) It is evaluated in terms of two parameters: statistical mean and random selection.
D) It reduces the problems associated with the auditor's judgment concerning materiality.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Stratified sampling is a statistical technique that may be more efficient than unstratified sampling because it usually:
A) yields a weighted sum of the strata standard deviations that is greater than the standard deviation of the population.
B) increases the variability among items in a stratum by grouping sampling units with similar characteristics.
C) produces an estimate having a desired level of precision with a smaller sample size.
D) is applied to populations where many monetary errors are expected to occur.
A) yields a weighted sum of the strata standard deviations that is greater than the standard deviation of the population.
B) increases the variability among items in a stratum by grouping sampling units with similar characteristics.
C) produces an estimate having a desired level of precision with a smaller sample size.
D) is applied to populations where many monetary errors are expected to occur.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Which of the following best illustrates the concept of sampling risk?
A) The documents related to the chosen sample may not be available for inspection.
B) An auditor may fail to recognise deviations in the documents examined for the chosen sample.
C) An auditor may select audit procedures that are not appropriate to achieve the specific objective.
D) A randomly chosen sample may not be representative of the population as a whole for the characteristic of interest.
A) The documents related to the chosen sample may not be available for inspection.
B) An auditor may fail to recognise deviations in the documents examined for the chosen sample.
C) An auditor may select audit procedures that are not appropriate to achieve the specific objective.
D) A randomly chosen sample may not be representative of the population as a whole for the characteristic of interest.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
An advantage of using statistical over non-statistical sampling methods in tests of controls is that the statistical methods:
A) provide an objective basis for quantitatively evaluating sampling risk.
B) afford greater assurance than a non-statistical sample of equal size.
C) eliminate the need to use judgment in determining appropriate sample sizes.
D) can more easily convert the sample into a dual-purpose test useful for substantive testing.
A) provide an objective basis for quantitatively evaluating sampling risk.
B) afford greater assurance than a non-statistical sample of equal size.
C) eliminate the need to use judgment in determining appropriate sample sizes.
D) can more easily convert the sample into a dual-purpose test useful for substantive testing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
In assessing sampling risk, the risk of incorrect rejection and the risk of assessing control risk too high relate to the:
A) effectiveness of the audit.
B) efficiency of the audit.
C) audit quality controls.
D) selection of the sample.
A) effectiveness of the audit.
B) efficiency of the audit.
C) audit quality controls.
D) selection of the sample.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Which of the following is an audit sampling approach?
A) The auditor identifies all items greater than $10 000 from the cash receipts journals and tests 50 per cent of these items.
B) The auditor randomly selects 10 per cent of the items from a cash receipts journal, for vouching back to supporting documents.
C) The auditor identifies all cash receipts from a particular customer and tests 50 per cent of these items.
D) All of the above.
A) The auditor identifies all items greater than $10 000 from the cash receipts journals and tests 50 per cent of these items.
B) The auditor randomly selects 10 per cent of the items from a cash receipts journal, for vouching back to supporting documents.
C) The auditor identifies all cash receipts from a particular customer and tests 50 per cent of these items.
D) All of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Alicia Wong, an auditor, is planning confirmation of accounts receivable. There are 500 customer balances and based on the condition of the accounting records and her past experience with the client, she plans to send 50 confirmation requests to customers she selected from the aged trial balance of accounts receivable. Alicia plans to evaluate confirmation responses qualitatively and by multiplying the average error in the 50 responses by 500. This audit approach may be described most precisely as:
A) statistical sampling.
B) exception reporting.
C) non-statistical sampling.
D) None of the given answers.
A) statistical sampling.
B) exception reporting.
C) non-statistical sampling.
D) None of the given answers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Maria Lee, an auditor, uses statistical sampling to test control procedures. Why does Lee use this statistical sampling technique?
A) It reduces the use of judgment required by Lee because there are established numerical criteria for this type of testing.
B) It provides a means of measuring the sampling risk that results from examining only a part of the data.
C) It is specified by auditing standards.
D) It increases Lees' knowledge of the client's prescribed procedures and their limitations.
A) It reduces the use of judgment required by Lee because there are established numerical criteria for this type of testing.
B) It provides a means of measuring the sampling risk that results from examining only a part of the data.
C) It is specified by auditing standards.
D) It increases Lees' knowledge of the client's prescribed procedures and their limitations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which of the following is a distinguishing feature between statistical sampling and non-statistical sampling?
A) Stratification.
B) The use of probability theory to evaluate sample results.
C) Allowing every item in the population a chance of selection.
D) Definition of the population.
A) Stratification.
B) The use of probability theory to evaluate sample results.
C) Allowing every item in the population a chance of selection.
D) Definition of the population.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
How would increases in tolerable misstatement and assessed level of control risk affect the sample size in a substantive test of details?
A) An increase in tolerable misstatement would increase sample size, but an increase in assessed level of control risk would decrease sample size.
B) Both an increase in tolerable misstatement and an increase in assessed level of control risk would increase sample size.
C) Both an increase in tolerable misstatement and an increase in assessed level of control risk would decrease sample size.
D) An increase in tolerable misstatement would decrease sample size, but an increase in assessed level of control risk would increase sample size
A) An increase in tolerable misstatement would increase sample size, but an increase in assessed level of control risk would decrease sample size.
B) Both an increase in tolerable misstatement and an increase in assessed level of control risk would increase sample size.
C) Both an increase in tolerable misstatement and an increase in assessed level of control risk would decrease sample size.
D) An increase in tolerable misstatement would decrease sample size, but an increase in assessed level of control risk would increase sample size

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Which of the following is appropriate in the selection of a statistical sample?
A) Random selection.
B) Block selection.
C) Stratified selection.
D) All of the given answers.
A) Random selection.
B) Block selection.
C) Stratified selection.
D) All of the given answers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
An underlying feature of random selection of items is that each:
A) item in the accounting population be randomly ordered.
B) stratum of the accounting population be given equal representation in the sample.
C) item must be systematically selected using replacement.
D) item in the accounting population should have an opportunity to be selected.
A) item in the accounting population be randomly ordered.
B) stratum of the accounting population be given equal representation in the sample.
C) item must be systematically selected using replacement.
D) item in the accounting population should have an opportunity to be selected.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
In determining the sample size for a test of controls, an auditor should consider the likely rate of deviations, desired confidence level and the:
A) tolerable deviation rate.
B) risk of incorrect acceptance.
C) nature and cause of deviations.
D) population size.
A) tolerable deviation rate.
B) risk of incorrect acceptance.
C) nature and cause of deviations.
D) population size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
When planning a sample for a substantive test of balances, an auditor should consider tolerable misstatement for the sample.This consideration should:
A) not be changed during the audit.
B) be related to preliminary judgments about materiality levels.
C) not be adjusted for qualitative factors.
D) be related to the auditor's business risk assessment.
A) not be changed during the audit.
B) be related to preliminary judgments about materiality levels.
C) not be adjusted for qualitative factors.
D) be related to the auditor's business risk assessment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
An auditor selecting a sample may use any of the following methods except:
A) haphazard selection.
B) stratified selection.
C) simple random selection.
D) block selection.
A) haphazard selection.
B) stratified selection.
C) simple random selection.
D) block selection.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
An auditor uses sampling tables to determine planned sample size for a test of controls. If they specify a risk of assessing control risk too low of five per cent and a tolerable deviation rate of six per cent and expects no deviations, the planned sample size should be: (Use the following table to determine your answer.)
Number of factors for sampling risks of:
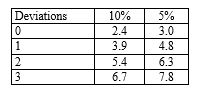
A) 60.
B) 50.
C) 18.
D) Some other amount.
Number of factors for sampling risks of:

A) 60.
B) 50.
C) 18.
D) Some other amount.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
An auditor planning tests of controls specifies a risk of assessing control risk too low of 10 per cent and a tolerable deviation rate of eight per cent and expects one deviation. For these specifications, the planned sample size should be in which range: (Use the following table to determine your answer.)
Number of factors for sampling risks of:

A) 30-40.
B) 40-50.
C) 50-60.
D) More than 60.
Number of factors for sampling risks of:

A) 30-40.
B) 40-50.
C) 50-60.
D) More than 60.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The tolerable deviation rate for a test of controls is generally:
A) unrelated to the expected deviation rate in the related accounting records.
B) identical to the expected deviation rate in the related accounting records.
C) higher than the expected deviation rate in the related accounting records.
D) lower than the expected deviation rate in the related accounting records.
A) unrelated to the expected deviation rate in the related accounting records.
B) identical to the expected deviation rate in the related accounting records.
C) higher than the expected deviation rate in the related accounting records.
D) lower than the expected deviation rate in the related accounting records.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
In audit sampling for substantive testing, a 10 per cent change in which of the following factors normally will have the least effect on the size of a statistical sample?
A) Population size.
B) Tolerable deviation rate.
C) Expected population deviation rate.
D) Standard deviation.
A) Population size.
B) Tolerable deviation rate.
C) Expected population deviation rate.
D) Standard deviation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
When performing a test of controls with respect to control over cash disbursements, an auditor may use a systematic sampling technique with a start at any randomly selected item. The biggest disadvantage of this type of sampling is that the items in the population:
A) must be systematically replaced in the population after sampling.
B) may systematically occur more than once in the sample.
C) may be ordered in a systematic pattern, thus destroying the sample randomness.
D) must be recorded in a systematic pattern before the sample can be drawn.
A) must be systematically replaced in the population after sampling.
B) may systematically occur more than once in the sample.
C) may be ordered in a systematic pattern, thus destroying the sample randomness.
D) must be recorded in a systematic pattern before the sample can be drawn.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
An auditor planning tests of controls specifies a risk of assessing control risk too low of five per cent and a tolerable deviation rate of six per cent and expects one deviation. For these specifications, the planned sample size should be: (Use the following table to determine your answer.)
Number of factors for sampling risks of:
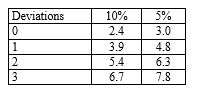
A) 60.
B) 50.
C) 80.
D) Some other amount.
Number of factors for sampling risks of:

A) 60.
B) 50.
C) 80.
D) Some other amount.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The auditor has decided to use systematic selection of cash payments when testing the control that cheque payments are supported by a supplier's invoice, a purchase requisition and a goods received note. Each cheque comprises a sampling unit. There are 5000 cheques drawn (numbered 1-5000) and the total amount of cash payments is $10 million. The sample size is 20 and the random start is 127. Given this information, the sample interval is:
A) 500 000.
B) 250.
C) 127.
D) Some other amount.
A) 500 000.
B) 250.
C) 127.
D) Some other amount.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
When performing a test of controls with respect to control over cash receipts, an auditor may use a systematic sampling technique with a start at any randomly selected item. The biggest disadvantage of this type of sampling is that the items in the population:
A) may systematically occur more than once in the sample.
B) must be systematically replaced in the population after sampling.
C) may occur in a systematic pattern, thus destroying the sample randomness.
D) must be recorded in a systematic pattern before the sample can be drawn.
A) may systematically occur more than once in the sample.
B) must be systematically replaced in the population after sampling.
C) may occur in a systematic pattern, thus destroying the sample randomness.
D) must be recorded in a systematic pattern before the sample can be drawn.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
An auditor plans to examine the supporting documentation for a sample of 20 payments as prescribed by the client's internal control procedures. For one of the payments in the chosen sample of 20, the supporting documentation cannot be found. The auditor should:
A) treat the missing supporting documentation as a deviation for the purpose of evaluating the sample.
B) evaluate the results as if the sample size had been 19.
C) choose another payment to replace the payment with the missing supporting documentation in the sample.
D) treat the missing supporting documentation in the same manner as the majority of the other supporting documentation (i.e. whether it supported the payments or not).
A) treat the missing supporting documentation as a deviation for the purpose of evaluating the sample.
B) evaluate the results as if the sample size had been 19.
C) choose another payment to replace the payment with the missing supporting documentation in the sample.
D) treat the missing supporting documentation in the same manner as the majority of the other supporting documentation (i.e. whether it supported the payments or not).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
How would decreases in tolerable misstatement and assessed level of control risk affect the sample size in a substantive test of details?
A) A decrease in tolerable misstatement would decrease sample size, while a decrease in assessed level of control risk would increase sample size.
B) Decreases in both tolerable misstatement and assessed level of control risk would decrease sample size.
C) Decreases in both tolerable misstatement and assessed level of control risk would increase sample size.
D) A decrease in tolerable misstatement would increase sample size, while a decrease in assessed level of control risk would decrease sample size.
A) A decrease in tolerable misstatement would decrease sample size, while a decrease in assessed level of control risk would increase sample size.
B) Decreases in both tolerable misstatement and assessed level of control risk would decrease sample size.
C) Decreases in both tolerable misstatement and assessed level of control risk would increase sample size.
D) A decrease in tolerable misstatement would increase sample size, while a decrease in assessed level of control risk would decrease sample size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The tolerable deviation rate for tests of controls necessary to justify assessing control risk at less than maximum depends primarily on which of the following?
A) The assessed level of control risk.
B) The cause of deviations.
C) The tolerable deviation rate used in audits of similar clients.
D) The amount of any identified substantive misstatements.
A) The assessed level of control risk.
B) The cause of deviations.
C) The tolerable deviation rate used in audits of similar clients.
D) The amount of any identified substantive misstatements.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
An auditor planning tests of controls specifies a risk of assessing control risk too low of 10 per cent and a tolerable deviation rate of six per cent and expects no deviations. For these specifications, the planned sample size should be: (Use the following table to determine your answer.)
Number of factors for sampling risks of:
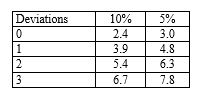
A) 60.
B) 50.
C) 40.
D) Some other amount.
Number of factors for sampling risks of:

A) 60.
B) 50.
C) 40.
D) Some other amount.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
An auditor is selecting a random sample of cash disbursements. One of the corresponding source documents for a selected random number is a voided cheque. The auditor should:
A) treat the cheque as a deviation.
B) reduce the sample size by one.
C) select the cheque immediately before or after the one that corresponds to the random number.
D) None of the given answers.
A) treat the cheque as a deviation.
B) reduce the sample size by one.
C) select the cheque immediately before or after the one that corresponds to the random number.
D) None of the given answers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
When using a statistical sampling plan for a test of controls, the auditor would probably require a smaller sample if the:
A) tolerable deviation rate decreases.
B) population increases.
C) expected deviation rate increases.
D) allowable risk of over-reliance increases.
A) tolerable deviation rate decreases.
B) population increases.
C) expected deviation rate increases.
D) allowable risk of over-reliance increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The auditor has decided to use systematic selection of cash payments when testing the control that cheque payments are supported by a supplier's invoice, a purchase requisition and a goods received note. Each cheque comprises a sampling unit. There are 5000 cheques drawn (numbered 1-5000) and the total amount of cash payments is $10 million. The sample size is 20 and the random start is 127. Given this information, the second item selected will be item no:
A) Cheque number 5127.
B) Cheque number 627.
C) Cheque number 377.
D) Some other item number.
A) Cheque number 5127.
B) Cheque number 627.
C) Cheque number 377.
D) Some other item number.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
As a result of tests of controls, an auditor found that they had assessed control risk as too low (their planned reliance on internal control was too high). This assessment occurred because the deviation rate in the sample was:
A) more than the risk of assessing control risk too low based on the auditor's sample.
B) more than the auditor's planned deviation rate.
C) less than the risk of assessing control risk too low based on the auditor's sample.
D) less than the auditor's planned deviation rate.
A) more than the risk of assessing control risk too low based on the auditor's sample.
B) more than the auditor's planned deviation rate.
C) less than the risk of assessing control risk too low based on the auditor's sample.
D) less than the auditor's planned deviation rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
An auditor is using the probability proportional to size selection method. Using this method, the chance of selecting a $100 account balance compared to selecting a $500 account balance is:
A) 50 per cent.
B) 20 per cent.
C) less but not determinable without knowing the dollar amount of the population.
D) greater but not determinable without knowing the dollar amount of the population.
A) 50 per cent.
B) 20 per cent.
C) less but not determinable without knowing the dollar amount of the population.
D) greater but not determinable without knowing the dollar amount of the population.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
If auditors conducting attribute sampling found that the client deviated from a prescribed control in six of the first 10 items examined, the auditor is most likely to:
A) increase the computed upper deviation rate.
B) increase sample size.
C) stop the test and increase control risk.
D) decrease the tolerable deviation rate.
A) increase the computed upper deviation rate.
B) increase sample size.
C) stop the test and increase control risk.
D) decrease the tolerable deviation rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Which of the following would be an improper technique when using statistical sampling in an audit of accounts receivable?
A) Using a sampling technique in which the same account balance could be selected more than once.
B) Combining negative and positive dollar misstatements in the evaluation of a sample.
C) Defining the sampling unit in the population as an individual dollar and not as an individual account balance.
D) Selecting a random starting point and then sampling every Nth dollar.
A) Using a sampling technique in which the same account balance could be selected more than once.
B) Combining negative and positive dollar misstatements in the evaluation of a sample.
C) Defining the sampling unit in the population as an individual dollar and not as an individual account balance.
D) Selecting a random starting point and then sampling every Nth dollar.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
An auditor is preparing to sample a client's customer receivables for overstatement. A statistical sampling method that automatically provides stratification when using systematic selection (in that all items greater than the sample interval will be selected) is:
A) ratio-estimation sampling.
B) attribute sampling.
C) mean-per-unit sampling.
D) dollar-unit sampling.
A) ratio-estimation sampling.
B) attribute sampling.
C) mean-per-unit sampling.
D) dollar-unit sampling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
An auditor is planning the confirmation of accounts receivable. The total of debit balances in the aged trial balance of receivables is $2 million. The auditor has decided that the tolerable misstatement (basic precision) for this sampling application is $50 000, the risk of incorrect acceptance is five per cent and zero error is expected. There are 2500 customer balances. The auditor has the following statistical tables available. The auditor decides to use dollar-unit sampling.Number of risk of incorrect acceptance: 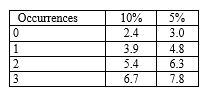 Assume a sample size of 100. The sampling interval for dollar-unit sampling using the systematic selection method
Assume a sample size of 100. The sampling interval for dollar-unit sampling using the systematic selection method
Is approximately:
A) 25.
B) 500.
C) 100.
D) 20 000.
 Assume a sample size of 100. The sampling interval for dollar-unit sampling using the systematic selection method
Assume a sample size of 100. The sampling interval for dollar-unit sampling using the systematic selection methodIs approximately:
A) 25.
B) 500.
C) 100.
D) 20 000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
A sample selection procedure that is beneficial for helping ensure that items are continuously sampled over the period of interest is:
A) haphazard sampling.
B) random sampling.
C) block sampling.
D) systematic sampling.
A) haphazard sampling.
B) random sampling.
C) block sampling.
D) systematic sampling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
If an auditor is evaluating a sample for a test of controls of 50 items and specifies a risk of assessing control risk too low of 10 per cent and finds two deviations, the approximate maximum deviation rate (rounded to the nearest one per cent) is: (Use the following table to determine your answer.)
Number of factors for sampling risks of:
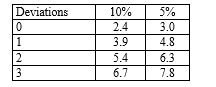
A) 10 per cent.
B) six per cent.
C) 11 per cent.
D) four per cent.
Number of factors for sampling risks of:

A) 10 per cent.
B) six per cent.
C) 11 per cent.
D) four per cent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
All of the following are true for dollar-unit sampling except:
A) it is not necessary to estimate the standard deviation of the population.
B) large items have a higher probability of selection.
C) several account balances can be combined and treated as one sampling unit.
D) understated items have a lower probability of selection than they would otherwise.
A) it is not necessary to estimate the standard deviation of the population.
B) large items have a higher probability of selection.
C) several account balances can be combined and treated as one sampling unit.
D) understated items have a lower probability of selection than they would otherwise.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Projection of sample results is required in evaluation of:
A) all audit samples, both statistical and non-statistical.
B) all statistical samples.
C) all audit tests, whether sampling is being performed or not.
D) non-statistical audit samples only.
A) all audit samples, both statistical and non-statistical.
B) all statistical samples.
C) all audit tests, whether sampling is being performed or not.
D) non-statistical audit samples only.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Sarah Jones, an auditor, believes the industry-wide occurrence rate of client billing errors is three per cent and has established a tolerable deviation rate of five per cent. In the review of client invoices to test that the invoice is properly checked and authorised, Jones should use:
A) attribute sampling.
B) discovery sampling.
C) variable sampling.
D) stratified sampling.
A) attribute sampling.
B) discovery sampling.
C) variable sampling.
D) stratified sampling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
An auditor is planning the confirmation of accounts receivable. The total of debit balances in the aged trial balance of receivables is $2 million. The auditor has decided that the tolerable misstatement (basic precision) for this sampling application is $50 000, the risk of incorrect acceptance is five per cent and zero error is expected. There are 2500 customer balances. The auditor has the following statistical tables available. The auditor decides to use dollar-unit sampling.(Use the following table to determine your answer.) Number of risk of incorrect acceptance:
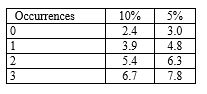 The auditor's estimated sample size is approximately:
The auditor's estimated sample size is approximately:
A) 120.
B) 80.
C) 200.
D) 160.
 The auditor's estimated sample size is approximately:
The auditor's estimated sample size is approximately:A) 120.
B) 80.
C) 200.
D) 160.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
If an auditor is evaluating a sample for a test of controls of 50 items and specifies a risk of assessing control risk too low of five per cent and finds one deviation, the approximate achieved maximum deviation rate, (rounded to the nearest one per cent) is: (Use the following table to determine your answer.)
Number of factors for sampling risks of:
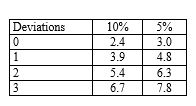
A) 10 per cent.
B) six per cent.
C) 11 per cent.
D) four per cent.
Number of factors for sampling risks of:

A) 10 per cent.
B) six per cent.
C) 11 per cent.
D) four per cent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The auditor selects all items above $10 000, which comprise 10 per cent of the items in the population and tests 100 per cent of these items. The auditor does not test items below $10 000. The misstatements found in audit testing total $20 000. Which of the following statements is false?
A) The auditor cannot extrapolate the results of the audit testing to the population.
B) The auditor has not used an audit sampling approach.
C) The audit testing approach undertaken is not in breach of auditing standards.
D) The auditor's best estimate of error in the population is $200 000.
A) The auditor cannot extrapolate the results of the audit testing to the population.
B) The auditor has not used an audit sampling approach.
C) The audit testing approach undertaken is not in breach of auditing standards.
D) The auditor's best estimate of error in the population is $200 000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Dollar-unit sampling is said to eliminate the need to stratify the sample because:
A) the risk of incorrect acceptance is inversely related to sample size.
B) sample items are selected in proportion to their dollar amount.
C) the upper limit on misstatements can be computed based on statistical principles.
D) tolerable misstatement is considered when determining sample size.
A) the risk of incorrect acceptance is inversely related to sample size.
B) sample items are selected in proportion to their dollar amount.
C) the upper limit on misstatements can be computed based on statistical principles.
D) tolerable misstatement is considered when determining sample size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Based on a five per cent risk of assessing control risk too low, how would an auditor interpret a computed upper deviation rate of seven per cent?
A) There is a five per cent chance that the deviation rate in the population is less than seven per cent.
B) The auditor is willing to tolerate a deviation rate of seven per cent before deciding not to rely on the control.
C) There is a 95 per cent chance that the deviation rate in the population equals seven per cent.
D) There is a five per cent chance that the deviation rate in the population exceeds seven per cent.
A) There is a five per cent chance that the deviation rate in the population is less than seven per cent.
B) The auditor is willing to tolerate a deviation rate of seven per cent before deciding not to rely on the control.
C) There is a 95 per cent chance that the deviation rate in the population equals seven per cent.
D) There is a five per cent chance that the deviation rate in the population exceeds seven per cent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
An auditor is planning the confirmation of accounts receivable. The total of debit balances in the aged trial balance of receivables is $4 million. The auditor has decided that the tolerable misstatement (basic precision) for this sampling application is $50 000, the risk of incorrect acceptance is five per cent and zero error is expected. There are 2500 customer balances. The auditor decides to use dollar-unit sampling and determines a sample size of 100. The sampling interval for dollar-unit sampling using the systematic selection method is approximately:
A) 50.
B) 200.
C) 1 000.
D) 40 000.
A) 50.
B) 200.
C) 1 000.
D) 40 000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
An account balance is $300 000 and there are 80 items in the account, six of which have balances that equal or exceed $15 000. The auditor plans to use a dollar-unit sampling plan with systematic sample selection. To ensure that all accounts with balances of at least $15 000 are selected, the sampling interval should be:
A) 80.
B) 6.
C) 15 000.
D) 12 000.
A) 80.
B) 6.
C) 15 000.
D) 12 000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
An auditor selects a sample of 50 for a test of controls and finds two transactions are not processed in accordance with the controls. The tolerable deviation rate was specified as six per cent. Using the extrapolation approach specified in the auditing standards, the sample results:
A) do not support the planned assessed level of control risk.
B) support the planned assessed level of control risk.
C) are indeterminate without more data.
D) None of the given answers.
A) do not support the planned assessed level of control risk.
B) support the planned assessed level of control risk.
C) are indeterminate without more data.
D) None of the given answers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
For dollar-unit sampling, the number of individual accounts tested is:
A) always greater than the sample size.
B) always equal to the sample size.
C) always less than or equal to the sample size.
D) always greater than or equal to the sample size.
A) always greater than the sample size.
B) always equal to the sample size.
C) always less than or equal to the sample size.
D) always greater than or equal to the sample size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
In applying variables sampling, an auditor attempts to:
A) determine various rates of occurrence for specified attributes.
B) estimate a qualitative characteristic of interest.
C) predict a monetary population value within a range of precision.
D) discover at least one instance of a critical deviation.
A) determine various rates of occurrence for specified attributes.
B) estimate a qualitative characteristic of interest.
C) predict a monetary population value within a range of precision.
D) discover at least one instance of a critical deviation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Which of the following sampling methods would be used to estimate a numerical measurement of a population, such as a dollar value?
A) Stop-or-go sampling.
B) Attribute sampling.
C) Random-number sampling.
D) Variables sampling.
A) Stop-or-go sampling.
B) Attribute sampling.
C) Random-number sampling.
D) Variables sampling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Using statistical sampling to assist in verifying the year-end accounts payable balance, an auditor has accumulated the following data:
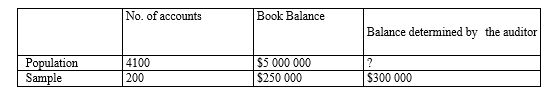 Using the ratio estimation technique, the auditor's estimate of the year-end accounts payable balance would be:
Using the ratio estimation technique, the auditor's estimate of the year-end accounts payable balance would be:
A) $6 000 000.
B) $6 150 000.
C) $5 050 000.
D) $5 125 000.
 Using the ratio estimation technique, the auditor's estimate of the year-end accounts payable balance would be:
Using the ratio estimation technique, the auditor's estimate of the year-end accounts payable balance would be:A) $6 000 000.
B) $6 150 000.
C) $5 050 000.
D) $5 125 000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Using statistical sampling to assist in verifying the year-end accounts payable balance, an auditor has accumulated the following data:
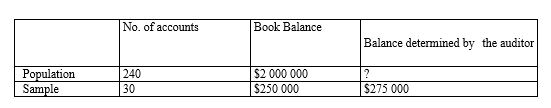 Using the ratio estimation technique, the auditor's estimate of the year-end accounts payable balance would be:
Using the ratio estimation technique, the auditor's estimate of the year-end accounts payable balance would be:
A) $2 000 000.
B) $2 025 000.
C) $2 200 000.
D) $2 250 000.
 Using the ratio estimation technique, the auditor's estimate of the year-end accounts payable balance would be:
Using the ratio estimation technique, the auditor's estimate of the year-end accounts payable balance would be:A) $2 000 000.
B) $2 025 000.
C) $2 200 000.
D) $2 250 000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
The accounting department reports that the balance of accounts receivable is $210 000. You are willing to accept that balance if it is within $15 000 of the actual balance. Using a variables sampling plan, you compute a 95 per cent confidence interval of $208 000 to $225 000. You would therefore:
A) not be able to determine the acceptability of the receivable balance.
B) accept the balance but with a lower level of confidence.
C) take a larger sample before totally rejecting the balance and requiring adjustments.
D) accept the $210 000 balance because the confidence interval is within the materiality limits.
A) not be able to determine the acceptability of the receivable balance.
B) accept the balance but with a lower level of confidence.
C) take a larger sample before totally rejecting the balance and requiring adjustments.
D) accept the $210 000 balance because the confidence interval is within the materiality limits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








