Deck 17: Stabilization in an Integrated World Economy
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/306
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 17: Stabilization in an Integrated World Economy
1
Which of the following scenarios can be classified as passive policy making?
A) The Federal Reserve cuts the federal funds rate in order to increase economic activity.
B) The federal government increases spending in order to create jobs.
C) The Federal Reserve adjusts the money supply as appropriate to attain a target rate of inflation.
D) Congress increases expenditures in an effort to stimulate economic activity.
A) The Federal Reserve cuts the federal funds rate in order to increase economic activity.
B) The federal government increases spending in order to create jobs.
C) The Federal Reserve adjusts the money supply as appropriate to attain a target rate of inflation.
D) Congress increases expenditures in an effort to stimulate economic activity.
C
2
Suppose a constitutional amendment is passed that mandates a balanced federal budget every year and the President and Congress consistently carry this mandate out. This would be an example of
A) active policy making.
B) decisive policy making.
C) nondiscretionary policy making.
D) cooperative policy making.
A) active policy making.
B) decisive policy making.
C) nondiscretionary policy making.
D) cooperative policy making.
C
3
Policy making that is carried out in response to a rule is
A) active policy making.
B) passive policy making.
C) restrictive policy making.
D) determined policy making.
A) active policy making.
B) passive policy making.
C) restrictive policy making.
D) determined policy making.
B
4
If a policy is carried out by a rule, then we have an example of
A) active policy making.
B) discretionary policy making.
C) nondiscretionary policy making.
D) natural policy making.
A) active policy making.
B) discretionary policy making.
C) nondiscretionary policy making.
D) natural policy making.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements has been proposed as a benefit of passive policy making?
A) Passive policy making allows for making immediate changes in response to an anticipated change in economic performance.
B) Passive policy making utilizes the rational expectations hypothesis.
C) When using passive policy making there is no tradeoff between price stability and unemployment.
D) Passive policy making does not wait for the time lag between recognition of a problem and policy action before engaging in economic policies to stabilize the economy.
A) Passive policy making allows for making immediate changes in response to an anticipated change in economic performance.
B) Passive policy making utilizes the rational expectations hypothesis.
C) When using passive policy making there is no tradeoff between price stability and unemployment.
D) Passive policy making does not wait for the time lag between recognition of a problem and policy action before engaging in economic policies to stabilize the economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Which of the following would be an example of passive policy making?
A) Establishing a system of automatic tax stabilizers
B) Marginal rate tax cuts intended to increase real Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
C) Government spending decreases intended to decrease real Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
D) None of the above
A) Establishing a system of automatic tax stabilizers
B) Marginal rate tax cuts intended to increase real Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
C) Government spending decreases intended to decrease real Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
D) None of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The Federal Reserve is anticipating a contractionary period in the economy. The Fed decides to engage in open market operations to stimulate the economy. This action is
A) active policy making.
B) passive policy making.
C) the monetary rule.
D) Phillips policy making.
A) active policy making.
B) passive policy making.
C) the monetary rule.
D) Phillips policy making.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
If a policy maker is convinced that time lags frequently negate the impact of short-run stabilization efforts, it is likely she would favor ________ policy making.
A) nondiscretionary
B) discretionary
C) active
D) aggressive
A) nondiscretionary
B) discretionary
C) active
D) aggressive

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
When policy makers base their actions on a rule there is
A) active policy making.
B) passive policy making.
C) rationalization policy making.
D) rational expectations policy making.
A) active policy making.
B) passive policy making.
C) rationalization policy making.
D) rational expectations policy making.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
With discretionary policy making, fiscal and monetary policies are usually
A) undertaken in response to or anticipation of some change in the overall economy.
B) set according to pre-established standards that do not take into account any changes in the economy.
C) immune to any political overtones.
D) immune to any lag times that might counter their effectiveness.
A) undertaken in response to or anticipation of some change in the overall economy.
B) set according to pre-established standards that do not take into account any changes in the economy.
C) immune to any political overtones.
D) immune to any lag times that might counter their effectiveness.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Active policy making refers to
A) actions taken by policy makers in response to or in anticipation of some change in the overall economy.
B) policy making that is carried out in response to a rule.
C) relying on policies that act as automatic stabilizers.
D) nondiscretionary policy making.
A) actions taken by policy makers in response to or in anticipation of some change in the overall economy.
B) policy making that is carried out in response to a rule.
C) relying on policies that act as automatic stabilizers.
D) nondiscretionary policy making.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
When policy makers take actions in response to or in anticipation of some change in the overall economy, there is
A) active policy making.
B) passive policy making.
C) rationalization policy making.
D) rational expectations policy making.
A) active policy making.
B) passive policy making.
C) rationalization policy making.
D) rational expectations policy making.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Monetary and fiscal policy making that is carried out in response to a pre-set rule and does not respond to changes in economic activity is known as
A) active policy making.
B) discretionary policy making.
C) nondiscretionary policy making.
D) Keynesian policy making.
A) active policy making.
B) discretionary policy making.
C) nondiscretionary policy making.
D) Keynesian policy making.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
What best defines active policy making?
A) taking action to offset a change in economic performance
B) taking action to increase long-term economic growth
C) taking action to make markets more competitive so as to improve efficiency
D) taking action to make markets less competitive so as to improve equity
A) taking action to offset a change in economic performance
B) taking action to increase long-term economic growth
C) taking action to make markets more competitive so as to improve efficiency
D) taking action to make markets less competitive so as to improve equity

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Active policy making would include all of the following EXCEPT
A) interest rate changes by the Fed.
B) tax increases.
C) unemployment insurance benefits.
D) increased government spending by the Congress.
A) interest rate changes by the Fed.
B) tax increases.
C) unemployment insurance benefits.
D) increased government spending by the Congress.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
An example of nondiscretionary policy making is
A) a rule under which the Fed targets the inflation rate.
B) expansionary fiscal policy.
C) changes in the interest rate initiated by the Fed.
D) a Congressional tax-rate cut aimed at boosting real GDP.
A) a rule under which the Fed targets the inflation rate.
B) expansionary fiscal policy.
C) changes in the interest rate initiated by the Fed.
D) a Congressional tax-rate cut aimed at boosting real GDP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Proponents of passive policy making believe that
A) the existence of time lags makes active policy ineffective or even procyclical.
B) time lags do not exist so the economy will adjust too rapidly with active policy.
C) government should not follow any particular policy.
D) fiscal policy is always better than monetary policy in stabilizing the economy.
A) the existence of time lags makes active policy ineffective or even procyclical.
B) time lags do not exist so the economy will adjust too rapidly with active policy.
C) government should not follow any particular policy.
D) fiscal policy is always better than monetary policy in stabilizing the economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which one of the following is an example of passive policy making?
A) introducing expansionary monetary policy to combat a recession
B) introducing expansionary monetary policy to combat inflation
C) introducing expansionary fiscal policy to combat a recession
D) following a predetermined monetary policy rule
A) introducing expansionary monetary policy to combat a recession
B) introducing expansionary monetary policy to combat inflation
C) introducing expansionary fiscal policy to combat a recession
D) following a predetermined monetary policy rule

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Actions on the part of monetary and fiscal policy makers that are undertaken in response to some change in the overall economy are known as
A) nondiscretionary policy making.
B) passive policy making.
C) creative policy making.
D) active policy making.
A) nondiscretionary policy making.
B) passive policy making.
C) creative policy making.
D) active policy making.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The idea of policy making taking place in response to a predetermined set of rules is referred to as
A) active policy making.
B) discretionary policy making.
C) passive policy making.
D) Keynesianism.
A) active policy making.
B) discretionary policy making.
C) passive policy making.
D) Keynesianism.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The natural rate of unemployment includes
A) frictional and cyclical unemployment.
B) only cyclical unemployment.
C) only unemployment due to layoffs and corporate downsizing.
D) frictional unemployment and structural unemployment.
A) frictional and cyclical unemployment.
B) only cyclical unemployment.
C) only unemployment due to layoffs and corporate downsizing.
D) frictional unemployment and structural unemployment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
What types of unemployment will still exist when the economy is at the natural rate of unemployment?
A) frictional and cyclical unemployment only
B) frictional and structural unemployment only
C) structural and cyclical unemployment only
D) frictional, structural, and cyclical unemployment
A) frictional and cyclical unemployment only
B) frictional and structural unemployment only
C) structural and cyclical unemployment only
D) frictional, structural, and cyclical unemployment

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
According to the text, minimum-wage laws cause increases in
A) employment possibilities.
B) structural unemployment.
C) poverty.
D) productivity.
A) employment possibilities.
B) structural unemployment.
C) poverty.
D) productivity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Explain the difference between active and passive policy making.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
The Phillips curve shows the relationship between
A) the price level and real Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
B) the tax rate and tax revenues.
C) the unemployment rate and inflation rate.
D) the interest rate and exchange rate.
A) the price level and real Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
B) the tax rate and tax revenues.
C) the unemployment rate and inflation rate.
D) the interest rate and exchange rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The idea of policy making being undertaken as a response to a change in the economy is referred to as
A) active policy making.
B) non-discretionary policy making.
C) passive policy making.
D) Keynesianism.
A) active policy making.
B) non-discretionary policy making.
C) passive policy making.
D) Keynesianism.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Structural unemployment is likely to be affected by
A) recessions and expansions.
B) the reservation wage curves of people.
C) minimum wage laws and other "rigidities" in the economy.
D) the amount of the money supply.
A) recessions and expansions.
B) the reservation wage curves of people.
C) minimum wage laws and other "rigidities" in the economy.
D) the amount of the money supply.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
According to the text, the probability of an unemployed person finding a job doubles when
A) his unemployment benefits expire.
B) his unemployment benefits are extended.
C) the economy enters a recessionary phase.
D) he is threatened with arrest.
A) his unemployment benefits expire.
B) his unemployment benefits are extended.
C) the economy enters a recessionary phase.
D) he is threatened with arrest.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
An increase in unemployment insurance and other transfer payments may
A) increase the natural rate of unemployment.
B) increase the number of discouraged workers.
C) reduce the rate of inflation at every level of unemployment.
D) lead to less unanticipated inflation.
A) increase the natural rate of unemployment.
B) increase the number of discouraged workers.
C) reduce the rate of inflation at every level of unemployment.
D) lead to less unanticipated inflation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The natural rate of unemployment is
A) zero.
B) the unemployment rate when there is no structural unemployment.
C) the unemployment rate when there is no structural or cyclical unemployment.
D) the unemployment rate that exists in long-run equilibrium, after adjustments to all changes have occurred.
A) zero.
B) the unemployment rate when there is no structural unemployment.
C) the unemployment rate when there is no structural or cyclical unemployment.
D) the unemployment rate that exists in long-run equilibrium, after adjustments to all changes have occurred.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
During a recession, the overall unemployment rate
A) falls rapidly.
B) exceeds the natural rate of unemployment.
C) falls below the natural rate of unemployment.
D) equals the inflation rate.
A) falls rapidly.
B) exceeds the natural rate of unemployment.
C) falls below the natural rate of unemployment.
D) equals the inflation rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
From the late 1980s to 2000, the natural rate of unemployment
A) climbed sharply.
B) held constant.
C) fluctuated up and down, following the path of the actual rate of unemployment.
D) gradually declined.
A) climbed sharply.
B) held constant.
C) fluctuated up and down, following the path of the actual rate of unemployment.
D) gradually declined.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
If the rate of growth in the money supply is predetermined on the basis of a monetary rule, this is known as
A) direct policy making.
B) active policy making.
C) passive policy making.
D) fiscal policy making.
A) direct policy making.
B) active policy making.
C) passive policy making.
D) fiscal policy making.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The natural rate of unemployment is defined as the rate of unemployment that
A) prevails in long-run macroeconomic equilibrium, when all workers and employers have fully adjusted to any changes in the economy.
B) prevails in the short-run macroeconomic equilibrium, before workers and employers have had a chance to adjust to an economic shock.
C) exists due to welfare and unemployment benefits that reduce potential workers' incentives to find work.
D) exists only during periods of recession or depression in the economy.
A) prevails in long-run macroeconomic equilibrium, when all workers and employers have fully adjusted to any changes in the economy.
B) prevails in the short-run macroeconomic equilibrium, before workers and employers have had a chance to adjust to an economic shock.
C) exists due to welfare and unemployment benefits that reduce potential workers' incentives to find work.
D) exists only during periods of recession or depression in the economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
If the Fed engages in open market sales in direct response to an increase in the rate of inflation, this is known as
A) direct policy making.
B) active policy making.
C) passive policy making.
D) fiscal policy making.
A) direct policy making.
B) active policy making.
C) passive policy making.
D) fiscal policy making.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Frictional and structural unemployment both exist when
A) the economy is in an expansionary phase.
B) the economy is in long-run equilibrium.
C) the economy is at the peak of the business cycle.
D) the economy is in short-run equilibrium.
A) the economy is in an expansionary phase.
B) the economy is in long-run equilibrium.
C) the economy is at the peak of the business cycle.
D) the economy is in short-run equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Which of the following is the rate of unemployment that occurs after all adjustments in the labor market have occurred?
A) the frictional rate of unemployment.
B) the natural rate of unemployment.
C) the cyclical rate of unemployment.
D) the structural rate of unemployment.
A) the frictional rate of unemployment.
B) the natural rate of unemployment.
C) the cyclical rate of unemployment.
D) the structural rate of unemployment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Your friend recently graduated from college and is actively looking for employment. The economy has completely recovered from the last recession and your friend is taking her time, looking for the "perfect" job. In the meantime, the unemployment she is experiencing is categorized as
A) cyclical.
B) structural.
C) seasonal.
D) frictional.
A) cyclical.
B) structural.
C) seasonal.
D) frictional.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Structural unemployment may result from all of the following factors EXCEPT
A) union wage contracts.
B) government-imposed licensing arrangements that restrict entry into certain professions.
C) improved elementary and secondary education.
D) welfare and unemployment benefits.
A) union wage contracts.
B) government-imposed licensing arrangements that restrict entry into certain professions.
C) improved elementary and secondary education.
D) welfare and unemployment benefits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
From 1950 until the late 1980s, the natural rate of unemployment in the United States
A) fell sharply as government retraining programs helped put the unemployed back to work.
B) cycled up and down in tandem with the actual rate of unemployment.
C) rose sharply, always exceeding the actual rate of unemployment.
D) trended upward.
A) fell sharply as government retraining programs helped put the unemployed back to work.
B) cycled up and down in tandem with the actual rate of unemployment.
C) rose sharply, always exceeding the actual rate of unemployment.
D) trended upward.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Critics of the Phillips curve argue that in the long run,
A) there is a trade-off between unemployment and inflation.
B) for any given unemployment level there is a corresponding inflation rate to which the economy will automatically revert.
C) employees are not able to anticipate future rates of inflation, and therefore unemployment can always be reduced by inflating the economy.
D) there is no trade-off between inflation and unemployment because workers' expectations adjust to any systematic attempts to reduce unemployment below the natural rate.
A) there is a trade-off between unemployment and inflation.
B) for any given unemployment level there is a corresponding inflation rate to which the economy will automatically revert.
C) employees are not able to anticipate future rates of inflation, and therefore unemployment can always be reduced by inflating the economy.
D) there is no trade-off between inflation and unemployment because workers' expectations adjust to any systematic attempts to reduce unemployment below the natural rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Which type of unemployment is associated with the slump in aggregate demand that accompanies a recession?
A) Expansionary unemployment
B) Cyclical unemployment
C) Frictional unemployment
D) Structural unemployment
A) Expansionary unemployment
B) Cyclical unemployment
C) Frictional unemployment
D) Structural unemployment

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
If cyclical unemployment is negative, then
A) the actual unemployment rate is below the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the natural rate of unemployment is getting smaller.
C) there have been some errors in classifying the type of unemployment experienced by some people.
D) structural unemployment must be increasing.
A) the actual unemployment rate is below the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the natural rate of unemployment is getting smaller.
C) there have been some errors in classifying the type of unemployment experienced by some people.
D) structural unemployment must be increasing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Cyclical unemployment is
A) the difference between the unemployment rate when the economy is in a recession and the unemployment rate when the economy is at the peak of an expansion.
B) the difference between the actual unemployment rate and the natural rate of unemployment.
C) the unemployment due to union activities and government-imposed restrictions to entry into specific occupations.
D) the unemployment due to the unemployment benefits and welfare programs of the government.
A) the difference between the unemployment rate when the economy is in a recession and the unemployment rate when the economy is at the peak of an expansion.
B) the difference between the actual unemployment rate and the natural rate of unemployment.
C) the unemployment due to union activities and government-imposed restrictions to entry into specific occupations.
D) the unemployment due to the unemployment benefits and welfare programs of the government.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
The Phillips curve shows
A) a positive relationship in the long run between the rate of inflation and the rate of unemployment.
B) a negative relationship between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate, at least in the short run.
C) a positive relationship between contractionary monetary policy and higher price levels.
D) a positive relationship between price stability and constant, small-increment changes in the fiscal policy on the part of the Fed.
A) a positive relationship in the long run between the rate of inflation and the rate of unemployment.
B) a negative relationship between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate, at least in the short run.
C) a positive relationship between contractionary monetary policy and higher price levels.
D) a positive relationship between price stability and constant, small-increment changes in the fiscal policy on the part of the Fed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The short-run Phillips curve suggests what policy making implications?
A) Active policy making does not yield any predictable results.
B) Passive policy making is more effective than active policy making.
C) Using discretionary policies, it may be possible to achieve just the right unemployment and inflation mix.
D) Maintaining both the inflation and unemployment rates at low levels is possible if policy makers will rely solely on nondiscretionary policy making.
A) Active policy making does not yield any predictable results.
B) Passive policy making is more effective than active policy making.
C) Using discretionary policies, it may be possible to achieve just the right unemployment and inflation mix.
D) Maintaining both the inflation and unemployment rates at low levels is possible if policy makers will rely solely on nondiscretionary policy making.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
What happens to the Phillips curve when the expected rate of inflation rises?
A) The curve shifts to the right
B) The curve shifts to the left
C) The curve becomes horizontal
D) The Phillips curve is unaffected
A) The curve shifts to the right
B) The curve shifts to the left
C) The curve becomes horizontal
D) The Phillips curve is unaffected

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The Phillips Curve will shift when
A) the expected inflation rate changes.
B) the price level falls.
C) the overall employment rate remains unchanged.
D) none of the above.
A) the expected inflation rate changes.
B) the price level falls.
C) the overall employment rate remains unchanged.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
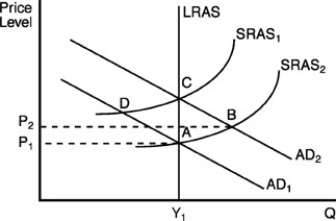
In the above figure, if A is the initial equilibrium point and there is an unanticipated rise in aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2, then
A) the new short-run equilibrium will be at point B.
B) the new long-run equilibrium will be at point B.
C) the new short-run equilibrium will be at point D.
D) real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per year will fall below Y1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50

In the above figure, if initial equilibrium is at point A and if there is an unanticipated increase in aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2, then
A) in the short run real output will remain at Y1.
B) in the short run real output will increase above Y1, but in the long run it will return to Y1.
C) in the long run real output will increase above Y1.
D) real output will increase above Y1 in both the short run and in the long run.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
An unexpected increase in aggregate demand typically causes
A) frictional unemployment to increase but structural unemployment to decrease.
B) the price level to increase but has no effect on the unemployment rate.
C) the price level to increase and the unemployment rate to fall.
D) the price level to increase and the unemployment rate to increase.
A) frictional unemployment to increase but structural unemployment to decrease.
B) the price level to increase but has no effect on the unemployment rate.
C) the price level to increase and the unemployment rate to fall.
D) the price level to increase and the unemployment rate to increase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
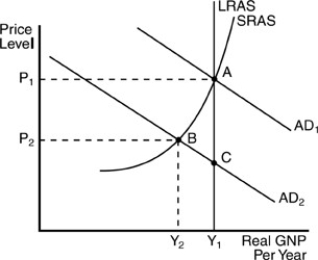
In the above figure, start with the economy in equilibrium at point A. Then an unanticipated reduction in aggregate demand triggers a shift from AD1 to AD2. In the short run, this would cause
A) the price level to fall from P1 to P2, real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) to fall from Y1 to Y2, and the rate of unemployment to increase.
B) the price level to move from P1 to P2, but real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) would stay at Y1.
C) the price level to fall by some amount less than P1 but greater than P2, and the rate of unemployment would decrease.
D) no change in either the price level or real Gross Domestic Product (GDP), but a decrease in unemployment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Which of the following unemployment rates can be negative?
A) the cyclical unemployment rate
B) the natural unemployment rate
C) the seasonal unemployment rate
D) the official unemployment rate reported by the Bureau of Labor Statistics
A) the cyclical unemployment rate
B) the natural unemployment rate
C) the seasonal unemployment rate
D) the official unemployment rate reported by the Bureau of Labor Statistics

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The Phillips curve shows
A) the relationship between the rate of interest and planned investment.
B) the relationship between the money supply and the price level.
C) that an increase in government spending will decrease real national income.
D) that an increase in inflation may be associated with a decrease in the rate of unemployment.
A) the relationship between the rate of interest and planned investment.
B) the relationship between the money supply and the price level.
C) that an increase in government spending will decrease real national income.
D) that an increase in inflation may be associated with a decrease in the rate of unemployment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The Phillips curve trade-off relationship implies that
A) the government can fine-tune the economy and generate both the natural rate of unemployment and zero inflation.
B) the government can fine-tune the economy and pick the most preferred combination of unemployment and inflation.
C) low unemployment can be obtained only by generating rapidly increasing inflation.
D) there is no relationship between inflation and unemployment, at least in the long run.
A) the government can fine-tune the economy and generate both the natural rate of unemployment and zero inflation.
B) the government can fine-tune the economy and pick the most preferred combination of unemployment and inflation.
C) low unemployment can be obtained only by generating rapidly increasing inflation.
D) there is no relationship between inflation and unemployment, at least in the long run.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56

Suppose the economy is initially operating at point A in the above figure. Which of the following statements is true?
A) An unexpected reduction in aggregate demand will cause the economy to move from point A to point B in the long run.
B) An unexpected reduction in aggregate demand will cause the economy to move from point A to point B in the short run.
C) An unexpected reduction in aggregate demand will cause the economy to move from point A to point C in the short run.
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
On average, the greater the unexpected decline in aggregate demand,
A) the weaker is the resulting deflation.
B) the greater is the resulting deflation.
C) the greater is the resulting inflation.
D) the greater is the rise in the price level.
A) the weaker is the resulting deflation.
B) the greater is the resulting deflation.
C) the greater is the resulting inflation.
D) the greater is the rise in the price level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Based on the work of economist A.W. Phillips, economists concluded that
A) there is no trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B) high inflation rates are associated with low unemployment rates.
C) unemployment can be effectively combated by raising wages.
D) higher rates of inflation are associated with higher rates of unemployment.
A) there is no trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B) high inflation rates are associated with low unemployment rates.
C) unemployment can be effectively combated by raising wages.
D) higher rates of inflation are associated with higher rates of unemployment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59

In the above figure, if initial equilibrium is at point A and there is a fully anticipated increase in aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2 due to an anticipated increase in the money supply, then
A) the economy will move directly from point A to point C without passing through point B.
B) the economy will move directly from point A to point B, and will remain at point B in the long run.
C) the price level will shift to P2 in the short run.
D) the price level will shift to P2 in the long run.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
One result of an unanticipated reduction in aggregate demand would be that
A) fewer firms would be hiring.
B) more firms would be hiring.
C) there would be no change in hiring.
D) the price level would rise.
A) fewer firms would be hiring.
B) more firms would be hiring.
C) there would be no change in hiring.
D) the price level would rise.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
An important source of structural unemployment is
A) seasonal variations in aggregate demand.
B) unemployment insurance benefits.
C) people looking for the right job decide to change jobs.
D) recessions.
A) seasonal variations in aggregate demand.
B) unemployment insurance benefits.
C) people looking for the right job decide to change jobs.
D) recessions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
We observe the duration of unemployment falling and wage rates rising. It is likely that
A) the government has initiated expansionary fiscal policy but the policies haven't taken effect yet.
B) summer has arrived.
C) aggregate demand has increased.
D) aggregate supply has increased.
A) the government has initiated expansionary fiscal policy but the policies haven't taken effect yet.
B) summer has arrived.
C) aggregate demand has increased.
D) aggregate supply has increased.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Suppose there was an unexpected increase in aggregate demand. We would expect to observe
A) frictional unemployment to increase.
B) the duration of unemployment and the amount of unemployment to decrease.
C) higher wages, with the duration of unemployment and the amount of unemployment unchanged.
D) a decrease in aggregate demand.
A) frictional unemployment to increase.
B) the duration of unemployment and the amount of unemployment to decrease.
C) higher wages, with the duration of unemployment and the amount of unemployment unchanged.
D) a decrease in aggregate demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Deviations of the actual unemployment rate away from the natural rate are
A) cyclical unemployment.
B) frictional unemployment.
C) structural unemployment.
D) the monetary rule.
A) cyclical unemployment.
B) frictional unemployment.
C) structural unemployment.
D) the monetary rule.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
The natural rate of unemployment is
A) the unemployment rate when cyclical unemployment is the only type of unemployment.
B) the unemployment rate when there is no frictional unemployment.
C) the rate of unemployment associated with long-run equilibrium.
D) zero.
A) the unemployment rate when cyclical unemployment is the only type of unemployment.
B) the unemployment rate when there is no frictional unemployment.
C) the rate of unemployment associated with long-run equilibrium.
D) zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
When the economy is operating at a level of real GDP that is greater than its potential level, we know that
A) the actual unemployment rate is greater than the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the structural rate of unemployment is negative.
C) the frictional unemployment is zero.
D) the cyclical rate of unemployment is negative.
A) the actual unemployment rate is greater than the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the structural rate of unemployment is negative.
C) the frictional unemployment is zero.
D) the cyclical rate of unemployment is negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Deviations of the actual unemployment rate from the natural rate of unemployment are called
A) frictional unemployment.
B) cyclical unemployment.
C) seasonal unemployment.
D) underemployment.
A) frictional unemployment.
B) cyclical unemployment.
C) seasonal unemployment.
D) underemployment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
When the actual unemployment rate is greater than the NAIRU, the inflation rate
A) tends to increase.
B) tends to decrease.
C) remains unchanged.
D) falls to zero.
A) tends to increase.
B) tends to decrease.
C) remains unchanged.
D) falls to zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Assume that the government decides to use fiscal or monetary policy to stimulate the economy and that this action comes as a surprise to most individuals and businesses. In the short run, the result will be
A) a decrease in the average duration of unemployment and a decrease in the unemployment rate.
B) an increase in the average duration of unemployment and an increase in the unemployment rate.
C) a decrease in aggregated demand and a rise in the price level.
D) an increase in aggregate demand and a fall in the price level.
A) a decrease in the average duration of unemployment and a decrease in the unemployment rate.
B) an increase in the average duration of unemployment and an increase in the unemployment rate.
C) a decrease in aggregated demand and a rise in the price level.
D) an increase in aggregate demand and a fall in the price level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Empirical evidence suggests that, when unemployment benefits run out, the probability that an unemployed person will find a job
A) remains constant.
B) goes down by 20 percent.
C) about doubles.
D) about triples.
A) remains constant.
B) goes down by 20 percent.
C) about doubles.
D) about triples.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
A trade-off between unemployment and inflation is reflected in the
A) natural rate of unemployment.
B) Phillips Curve.
C) economic stability.
D) nonaccelerating inflation rate of unemployment (NAIRU).
A) natural rate of unemployment.
B) Phillips Curve.
C) economic stability.
D) nonaccelerating inflation rate of unemployment (NAIRU).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Suppose the government abolished the minimum wage law and the law that requires union wage rates to be paid on all government contract jobs. We would expect to see
A) a decline in the natural rate of unemployment.
B) an increase in claims for unemployment benefits.
C) the duration of unemployment to increase.
D) a recession.
A) a decline in the natural rate of unemployment.
B) an increase in claims for unemployment benefits.
C) the duration of unemployment to increase.
D) a recession.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
During a recession, the
A) natural rate of unemployment has fallen.
B) cyclical rate of unemployment is positive.
C) cyclical rate of unemployment is zero.
D) cyclical rate of unemployment is negative.
A) natural rate of unemployment has fallen.
B) cyclical rate of unemployment is positive.
C) cyclical rate of unemployment is zero.
D) cyclical rate of unemployment is negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Which of the following is NOT a possible cause of structural unemployment?
A) individuals take the time to search for the best job opportunities
B) a mismatch of worker training and skills with requirements of employers
C) government-imposed minimum wage laws
D) union activity that sets wages above the equilibrium level
A) individuals take the time to search for the best job opportunities
B) a mismatch of worker training and skills with requirements of employers
C) government-imposed minimum wage laws
D) union activity that sets wages above the equilibrium level

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Suppose the natural rate of unemployment is 5 percent. If the actual unemployment rate is 7 percent, then the cyclical unemployment rate
A) is 2 percent.
B) is -2 percent.
C) is 12 percent.
D) cannot be determined given the information.
A) is 2 percent.
B) is -2 percent.
C) is 12 percent.
D) cannot be determined given the information.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
When the economy is in long-run equilibrium, there will be
A) no unemployment.
B) frictional and structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment only.
D) cyclical and seasonal unemployment.
A) no unemployment.
B) frictional and structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment only.
D) cyclical and seasonal unemployment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Suppose that the inflation rate has been 3 percent per year for several years, and the unemployment rate has been stable at 5 percent. Unanticipated changes in government policy cause the inflation rate to increase to 6 percent. In the short run, we would expect the unemployment rate to
A) remain constant.
B) increase to 10 percent.
C) increase, but the exact amount cannot be known for sure.
D) decrease.
A) remain constant.
B) increase to 10 percent.
C) increase, but the exact amount cannot be known for sure.
D) decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
The natural rate of unemployment consists of
A) no workers looking for employment.
B) only seasonal unemployment.
C) only structural unemployment.
D) structural and frictional unemployment.
A) no workers looking for employment.
B) only seasonal unemployment.
C) only structural unemployment.
D) structural and frictional unemployment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
In the short run, unanticipated inflation typically leads to
A) higher rates of unemployment.
B) decreases in aggregate demand.
C) lower rates of unemployment.
D) workers' thinking the real wage has been reduced.
A) higher rates of unemployment.
B) decreases in aggregate demand.
C) lower rates of unemployment.
D) workers' thinking the real wage has been reduced.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Suppose the natural rate of unemployment is 5 percent. If the actual unemployment rate is 4 percent, then the cyclical unemployment rate is
A) 9 percent.
B) 1 percent.
C) -1 percent.
D) 0 percent as cyclical unemployment cannot be less than zero.
A) 9 percent.
B) 1 percent.
C) -1 percent.
D) 0 percent as cyclical unemployment cannot be less than zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 306 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








