Deck 13: The Costs of Production
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/191
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: The Costs of Production
1
Economists and accountants agree on the inclusion of implicit costs into the cost analysis of a firm.
False
2
Variable costs usually change as the firm alters the quantity of output produced.
True
3
Variable costs equal fixed costs when nothing is produced.
False
4
If the total cost curve becomes steeper as output increases, then this reveals diminishing marginal product.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The shape of the total cost curve is unrelated to the shape of the production function.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
When trying to understand the decision making process of different firms, economists assume that people think at the margin.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The cost of capital includes both any interest payments in loans as well as any forgone interest on savings used to finance the business.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Examination of the costs of production is unnecessary to the field of industrial organisation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Accountants keep track of the money that flows into and out of firms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Implicit costs that do not require a money outlay are typically ignored by economists.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Diminishing marginal product exists when the production function becomes flatter as inputs increase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The cost of producing an additional unit of a good is not the same as the average cost of the good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Even if a firm was to produce nothing, it still incurs some variable costs in the short-run.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The fact that many decisions are fixed in the short run but variable in the long run has an impact on the firm's cost curves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Economists normally assume that the goal of a firm is to maximise revenue.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Several related measures of cost can be derived from a firm's total cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Economists and accountants both include forgone income as a cost to a small business owner.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
When economists speak of a firm's costs, they are usually excluding the opportunity costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
In the long run there are no fixed inputs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Average variable cost is equal to the quantity of output divided by the total variable cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Because of the greater flexibility that firms have in the long run, all short-run cost curves lie on or above the long-run curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
As a firm moves along its long-run average cost curve, it is adjusting the size of its factory to the quantity of production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Adam Smith's example of the pin factory demonstrates that economies of scale result from specialisation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
In some cases, specialisation allows larger factories to produce goods at a lower average cost than smaller factories.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
The marginal cost curve can rise even if the average total cost is falling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The firm's total cost can be used to determine both the firm's average total cost and its marginal cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The use of specialisation to achieve economies of scale is one reason modern societies are as prosperous as they are.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The marginal product of a firm's workers is revealed by the shape of the marginal cost curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The average total cost curve is unaffected by diminishing marginal product.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
A second or third worker may have a higher marginal product than the first worker in certain circumstances.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The marginal cost curve bisects the average total cost curve at the minimum point of the average total cost curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The adage 'Jack of all trades, master of none' helps explain why some firms experience economies of scale.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Jack received all As in his classes last semester. If Jack gets all Cs in his classes this semester, his grade point average may or may not fall.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The average total cost curve reflects the shape of both the average fixed cost and average variable cost curves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Suppose that as a firm expands and notices that its long-run average total costs are declining. The most likely explanation for this is economies of scale.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Average total cost reveals how much total cost will change as the firm alters its level of production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Implicit costs are costs that do not require an outlay of cash by the firm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The time it takes for a firm to reach the long run depends on the firm and the products it makes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
When average total cost rises if a producer either increases or decreases production, then the firm is said to be operating at efficient scale.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Fixed costs are those costs that remain fixed no matter how long the time horizon is.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
An example of an implicit cost of production for a forestry company would be:
A) the costs of planting an area with trees
B) the interest income that could have been earned in a bank if the company hadn't used its profit to finance a new replanting
C) the cost of transporting the logs to a sawmill
D) all of the above
A) the costs of planting an area with trees
B) the interest income that could have been earned in a bank if the company hadn't used its profit to finance a new replanting
C) the cost of transporting the logs to a sawmill
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The amount of money that a firm receives from the sale of its output is called:
A) total revenue
B) total gross profit
C) total net profit
D) net revenue
A) total revenue
B) total gross profit
C) total net profit
D) net revenue

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Economists normally assume that a firm would? (i) sell a higher output if this would increase revenue
(ii) sell a lower output and collect less revenue, if this would increase profit
(iii) sell a higher output and incur more costs, if this would increase profit
A) (i) and (ii)
B) (i) and (iii)
C) (ii) and (iii)
D) none of the above
(ii) sell a lower output and collect less revenue, if this would increase profit
(iii) sell a higher output and incur more costs, if this would increase profit
A) (i) and (ii)
B) (i) and (iii)
C) (ii) and (iii)
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
A firm's profit is equivalent to:
A) its total sales
B) average revenue minus average total cost
C) marginal revenue minus marginal cost
D) total revenue minus total cost
A) its total sales
B) average revenue minus average total cost
C) marginal revenue minus marginal cost
D) total revenue minus total cost

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
To an economist, the field of industrial organisation answers which of the following questions?
A) How does the difference in the number of firms affect prices and efficiency of market outcomes?
B) Why are consumers subject to the law of demand?
C) Why do firms experience falling marginal product of labour?
D) Why do firms consider production costs when determining product supply?
A) How does the difference in the number of firms affect prices and efficiency of market outcomes?
B) Why are consumers subject to the law of demand?
C) Why do firms experience falling marginal product of labour?
D) Why do firms consider production costs when determining product supply?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The amount of money that a firm pays to buy inputs is called:
A) variable cost
B) marginal cost
C) fixed cost
D) total cost
A) variable cost
B) marginal cost
C) fixed cost
D) total cost

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Which of the following would be categorised as an opportunity cost? (i) wages of workers
(ii) raw material costs
(iii) forgone investment opportunities
A) (i) and (iii)
B) (iii) only
C) (ii) and (iii)
D) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(ii) raw material costs
(iii) forgone investment opportunities
A) (i) and (iii)
B) (iii) only
C) (ii) and (iii)
D) (i), (ii) and (iii)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Which of the following is an implicit cost? (i) a business owner forgoing an opportunity to earn a large salary working for a Wall Street brokerage firm
(ii) interest on debt
(iii) uncollected revenue
A) (i) only
B) (i) and (ii)
C) (ii) and (iii)
D) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(ii) interest on debt
(iii) uncollected revenue
A) (i) only
B) (i) and (ii)
C) (ii) and (iii)
D) (i), (ii) and (iii)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Opportunity costs are comprised of:
A) explicit costs
B) implicit costs
C) forgone income
D) all of the above
A) explicit costs
B) implicit costs
C) forgone income
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The relationship between the quantity of inputs and quantity of output is called the production function.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
An example of an explicit cost of production would be:
A) having to give up wages to become an entrepreneur
B) the cost of glass for a lens manufacturer
C) an entrepreneur using their own savings for finance and giving up on the interest payments they were previously getting
D) none of the above
A) having to give up wages to become an entrepreneur
B) the cost of glass for a lens manufacturer
C) an entrepreneur using their own savings for finance and giving up on the interest payments they were previously getting
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Total revenue equals:
A) total output multiplied by the unit cost of output
B) total output multiplied by profit
C) total output multiplied by the unit price of output
D) total output divided by profit
A) total output multiplied by the unit cost of output
B) total output multiplied by profit
C) total output multiplied by the unit price of output
D) total output divided by profit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Suppose a firm produced 500 units of output but sold only 400 of the units it produced. The average cost of production for each unit of output produced was $100. Each of the 400 units sold were sold for a price of $80. The total revenue of this firm would be:
A) $50 000
B) $40 000
C) $32 000
D) -$8 000
A) $50 000
B) $40 000
C) $32 000
D) -$8 000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
As a starting point, economists assume that firms are organised to: (i) maximise their sales
(ii) maximise their profit
(iii) minimise their tax
A) (i) only
B) (i) and (ii)
C) (ii) only
D) (i) and (iii)
(ii) maximise their profit
(iii) minimise their tax
A) (i) only
B) (i) and (ii)
C) (ii) only
D) (i) and (iii)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Those things that must be forgone to acquire a good are called:
A) competitors
B) substitutes
C) opportunity costs
D) explicit costs
A) competitors
B) substitutes
C) opportunity costs
D) explicit costs

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Economists are primarily interested in:
A) the marginal cost of production in a firm
B) the accounting profits generated by a firm
C) how firms make production and pricing decisions
D) the value of a firm as manifest in stock price
A) the marginal cost of production in a firm
B) the accounting profits generated by a firm
C) how firms make production and pricing decisions
D) the value of a firm as manifest in stock price

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Cost of capital can also be seen as implicit costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Industrial organisation is the study of how:
A) industries organise for political advantage
B) firms' decisions regarding prices and quantities depend on the market conditions they face
C) labour unions organise workers in industries
D) profitable firms are in organised industries
A) industries organise for political advantage
B) firms' decisions regarding prices and quantities depend on the market conditions they face
C) labour unions organise workers in industries
D) profitable firms are in organised industries

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Profit plus total costs equals:
A) total revenue
B) net profit
C) capital profit
D) operational profit
A) total revenue
B) net profit
C) capital profit
D) operational profit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The law of supply states that:
A) the supply curve slopes downward
B) the demand curve slopes upwards
C) firms are willing to produce a greater quantity of a good when the price of the good is higher
D) supply creates its own demand
A) the supply curve slopes downward
B) the demand curve slopes upwards
C) firms are willing to produce a greater quantity of a good when the price of the good is higher
D) supply creates its own demand

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
An important implicit cost of almost every business is the:
A) cost of accounting services
B) cost of compliance with government regulation
C) opportunity cost of financial capital that has been invested in the business
D) cost of debt
A) cost of accounting services
B) cost of compliance with government regulation
C) opportunity cost of financial capital that has been invested in the business
D) cost of debt

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Accountants are primarily interested in the:
A) stock of assets of firms
B) marginal costs of production of firms
C) taxes due on capital assets of firms
D) flow of cash into and out of firms
A) stock of assets of firms
B) marginal costs of production of firms
C) taxes due on capital assets of firms
D) flow of cash into and out of firms

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
A production function is a relationship between inputs and:
A) revenue
B) costs
C) profit
D) quantity of output
A) revenue
B) costs
C) profit
D) quantity of output

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Graph 13-1
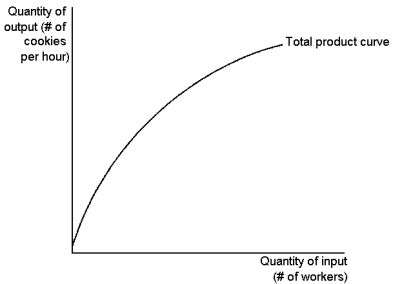 This graph depicts a production function for a firm that produces cookies. Use the
This graph depicts a production function for a firm that produces cookies. Use the
graph to answer the following question(s).
Refer to Graph 13-1. With regard to cookie production, the figure implies:
A) decreasing cost of cookie production
B) diminishing marginal product of workers
C) increasing marginal product of workers
D) diminishing marginal cost of cookie production
 This graph depicts a production function for a firm that produces cookies. Use the
This graph depicts a production function for a firm that produces cookies. Use thegraph to answer the following question(s).
Refer to Graph 13-1. With regard to cookie production, the figure implies:
A) decreasing cost of cookie production
B) diminishing marginal product of workers
C) increasing marginal product of workers
D) diminishing marginal cost of cookie production

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Accounting profit:
A) will never exceed economic profit
B) is a better measure of profitability than economic profit
C) is generally as large as economic profit
D) is most often equal to economic profit
A) will never exceed economic profit
B) is a better measure of profitability than economic profit
C) is generally as large as economic profit
D) is most often equal to economic profit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
The marginal product of labour can be defined as (where denotes 'change'):
A) output/ labour
B) labour/ output
C) profit/ labour
D) labour/ total cost
A) output/ labour
B) labour/ output
C) profit/ labour
D) labour/ total cost

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Amy owns a photography business. Her friend who is an economist most likely includes which of the following costs on her financial statements?
A) the bank interest payments on her savings before she used them to buy her cameras and lenses
B) the cost of developing her film
C) the salary Amy is paying herself
D) all of the above
A) the bank interest payments on her savings before she used them to buy her cameras and lenses
B) the cost of developing her film
C) the salary Amy is paying herself
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
The amount of money that an orchardist could have earned if he had planted orange trees rather than apple trees is termed:
A) explicit cost
B) accounting cost
C) implicit cost
D) total sales
A) explicit cost
B) accounting cost
C) implicit cost
D) total sales

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Identify the statement about the production function that is true?
A) the slope of the production function measures the average product of labour
B) the slope of the production function measures marginal cost
C) the slope of the production function measures the marginal product of a worker
D) the square-root of the production function measures the marginal product of labour
A) the slope of the production function measures the average product of labour
B) the slope of the production function measures marginal cost
C) the slope of the production function measures the marginal product of a worker
D) the square-root of the production function measures the marginal product of labour

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Economic profit is equal to:
A) total revenue minus the opportunity cost of producing goods and services
B) total revenue minus the accounting cost of producing goods and services
C) total revenue minus the explicit cost of producing goods and services
D) average revenue minus the average cost of producing the last unit of a good or service
A) total revenue minus the opportunity cost of producing goods and services
B) total revenue minus the accounting cost of producing goods and services
C) total revenue minus the explicit cost of producing goods and services
D) average revenue minus the average cost of producing the last unit of a good or service

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Amy owns a photography business. Her accountant most likely includes which of the following costs on her financial statements?
A) the bank interest payments on her savings before she used them to buy her cameras and lenses
B) the cost of developing her film
C) the salary Amy was previously earning as a teacher
D) all of the above
A) the bank interest payments on her savings before she used them to buy her cameras and lenses
B) the cost of developing her film
C) the salary Amy was previously earning as a teacher
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Which of the following describes the marginal product of labour?
A) the increase in labour necessary to generate a one-unit increase in output
B) the increase in output obtained from a one-unit increase in labour
C) the additional profit created with a one-unit increase in labour
D) the additional cost created with a one-unit increase in labour
A) the increase in labour necessary to generate a one-unit increase in output
B) the increase in output obtained from a one-unit increase in labour
C) the additional profit created with a one-unit increase in labour
D) the additional cost created with a one-unit increase in labour

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Which of the following is equivalent to economic profit? (i) total revenue less explicit costs and less implicit costs
(ii) total revenue less opportunity costs
(iii) accounting profit
A) (i) only
B) (i) and (ii)
C) (ii) and (iii)
D) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(ii) total revenue less opportunity costs
(iii) accounting profit
A) (i) only
B) (i) and (ii)
C) (ii) and (iii)
D) (i), (ii) and (iii)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Diminishing marginal product of labour is NOT likely to be observed when:
A) experienced workers in labour teams will not share their skills with others
B) there are enough personal computers to allocate them to new staff in an office
C) there are shortages of skilled workers in the forestry sector
D) new workers have to use the oldest technology in a plant
A) experienced workers in labour teams will not share their skills with others
B) there are enough personal computers to allocate them to new staff in an office
C) there are shortages of skilled workers in the forestry sector
D) new workers have to use the oldest technology in a plant

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Accounting profit is equal to which of the following? (i) economic profit + implicit costs
(ii) total revenue - implicit costs
(iii) total revenue - opportunity costs
A) (iii) only
B) (i) and (ii)
C) (i) only
D) none of the above
(ii) total revenue - implicit costs
(iii) total revenue - opportunity costs
A) (iii) only
B) (i) and (ii)
C) (i) only
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Graph 13-1
 This graph depicts a production function for a firm that produces cookies. Use the
This graph depicts a production function for a firm that produces cookies. Use the
graph to answer the following question(s).
Refer to Graph 13-1. As the number of workers increases:
A) total output increases, but at a decreasing rate
B) marginal product increases but at a decreasing rate
C) marginal product increases
D) total output decreases
 This graph depicts a production function for a firm that produces cookies. Use the
This graph depicts a production function for a firm that produces cookies. Use thegraph to answer the following question(s).
Refer to Graph 13-1. As the number of workers increases:
A) total output increases, but at a decreasing rate
B) marginal product increases but at a decreasing rate
C) marginal product increases
D) total output decreases

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Graph 13-1
 This graph depicts a production function for a firm that produces cookies. Use the
This graph depicts a production function for a firm that produces cookies. Use the
graph to answer the following question(s).
Refer to Graph 13-1. The slope of the total product curve reveals information about the:
A) average product of workers
B) fixed product of workers
C) total product of workers
D) marginal product of workers
 This graph depicts a production function for a firm that produces cookies. Use the
This graph depicts a production function for a firm that produces cookies. Use thegraph to answer the following question(s).
Refer to Graph 13-1. The slope of the total product curve reveals information about the:
A) average product of workers
B) fixed product of workers
C) total product of workers
D) marginal product of workers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Which of the following is an implicit cost of owning a business? (i) forgone savings account interest when personal money is invested in the business
(ii) interest expense on existing business loans
(iii) damaged or lost inventory
A) (i) only
B) (ii) only
C) (i) and (ii)
D) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(ii) interest expense on existing business loans
(iii) damaged or lost inventory
A) (i) only
B) (ii) only
C) (i) and (ii)
D) (i), (ii) and (iii)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Diminishing marginal product of labour occurs when adding another unit of labour:
A) increases output but not by as large a margin as previous units of labour
B) decreases output
C) increases output by more than the margin of previously employed labour
D) none of the above are true
A) increases output but not by as large a margin as previous units of labour
B) decreases output
C) increases output by more than the margin of previously employed labour
D) none of the above are true

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Accounting profit is equal to:
A) total revenue minus the explicit cost of producing goods and services
B) total revenue minus the opportunity cost of producing goods and services
C) average revenue minus the average cost of producing the last unit of a good or service
D) marginal revenue minus marginal cost
A) total revenue minus the explicit cost of producing goods and services
B) total revenue minus the opportunity cost of producing goods and services
C) average revenue minus the average cost of producing the last unit of a good or service
D) marginal revenue minus marginal cost

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 191 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








