Deck 32: Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Radiation
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/137
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 32: Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Radiation
1
The two strongest forces that act between protons in a nucleus are
A)the weak nuclear and electromagnetic forces.
B)the weak nuclear and the gravitational forces.
C)the electrostatic and the gravitational forces.
D)the strong nuclear and the electrostatic forces.
A)the weak nuclear and electromagnetic forces.
B)the weak nuclear and the gravitational forces.
C)the electrostatic and the gravitational forces.
D)the strong nuclear and the electrostatic forces.
the strong nuclear and the electrostatic forces.
2
The symbol for a certain isotope of polonium is 
Po.How many neutrons are there in the nucleus of this isotope?
A)84
B)130
C)214
D)298
E)314

Po.How many neutrons are there in the nucleus of this isotope?
A)84
B)130
C)214
D)298
E)314
130
3
All nuclei of a given element have the same number of
A)neutrons.
B)protons.
C)nucleons.
D)protons + neutrons.
A)neutrons.
B)protons.
C)nucleons.
D)protons + neutrons.
protons.
4
The main reason that there is a limit to the size of a stable nucleus is
A)the limited range of the gravitational force.
B)the short range nature of the strong nuclear force.
C)the weakness of the gravitational force.
D)the weakness of the electrostatic force.
A)the limited range of the gravitational force.
B)the short range nature of the strong nuclear force.
C)the weakness of the gravitational force.
D)the weakness of the electrostatic force.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The symbol for a certain isotope of radium is 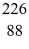
Ra.How many nucleons are there in the nucleus of this isotope?
A)88
B)138
C)214
D)226
E)314
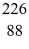
Ra.How many nucleons are there in the nucleus of this isotope?
A)88
B)138
C)214
D)226
E)314

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The mass number of an atom is equal to the number of what particles in the nucleus?
A)protons
B)neutrons
C)nucleons
D)electrons
E)positrons
A)protons
B)neutrons
C)nucleons
D)electrons
E)positrons

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The atomic number and mass number for calcium-39 are 20 and 39,respectively.How many neutrons are in one atom?
A)1
B)19
C)20
D)39
E)59
A)1
B)19
C)20
D)39
E)59

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The symbol for a certain isotope of strontium is 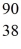
Sr.What is the mass number of this isotope?
A)38
B)52
C)88
D)90
E)128
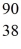
Sr.What is the mass number of this isotope?
A)38
B)52
C)88
D)90
E)128

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
In massive stars,three helium nuclei fuse together,forming a carbon nucleus,and this reaction heats the core of the star.The net mass of the three helium nuclei must therefore be
A)higher than that of the carbon nucleus.
B)less than that of the carbon nucleus.
C)the same as that of the carbon nucleus because mass is always conserved.
D)the same as that of the carbon nucleus because energy is always conserved.
A)higher than that of the carbon nucleus.
B)less than that of the carbon nucleus.
C)the same as that of the carbon nucleus because mass is always conserved.
D)the same as that of the carbon nucleus because energy is always conserved.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
A stable nucleus contains many protons very close to each other,all positively charged.Why do the protons not fly apart due to mutual Coulomb repulsion?
A)An attractive nuclear force in the nucleus counteracts the effect of the Coulomb forces.
B)There are an equal number of electrons in the nucleus which neutralize the protons.
C)The neutrons in the nucleus shield the protons from each other.
D)The Coulomb force does not operate within nuclei.
E)The gravity of the protons and neutrons overcomes their repulsion at such close distances.
A)An attractive nuclear force in the nucleus counteracts the effect of the Coulomb forces.
B)There are an equal number of electrons in the nucleus which neutralize the protons.
C)The neutrons in the nucleus shield the protons from each other.
D)The Coulomb force does not operate within nuclei.
E)The gravity of the protons and neutrons overcomes their repulsion at such close distances.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Atomic nuclei that are all isotopes of an element all have the same
A)number of nucleons.
B)mass.
C)number of protons.
D)number of neutrons.
A)number of nucleons.
B)mass.
C)number of protons.
D)number of neutrons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The atomic mass unit is defined as
A)the mass of a proton.
B)the mass of an electron.
C)the mass of a hydrogen-1 atom.
D)one twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
E)the mass of a carbon-12 nucleus.
A)the mass of a proton.
B)the mass of an electron.
C)the mass of a hydrogen-1 atom.
D)one twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
E)the mass of a carbon-12 nucleus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
What is true of an element of atomic number 15 that has an isotope of mass number 32? (There could be more than one correct choice. )
A)The number of protons in the nucleus is 15.
B)The number of neutrons in the nucleus is 15.
C)The number of protons in the nucleus is 32.
D)The number of nucleons in the nucleus is 47.
E)The number of neutrons in the nucleus is 17.
A)The number of protons in the nucleus is 15.
B)The number of neutrons in the nucleus is 15.
C)The number of protons in the nucleus is 32.
D)The number of nucleons in the nucleus is 47.
E)The number of neutrons in the nucleus is 17.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
In a 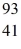
Nb nucleus,how many protons,neutrons,and electrons are found there?
A)41,52,93
B)41,52,41
C)52,41,41
D)41,52,0
E)93,41,93
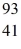
Nb nucleus,how many protons,neutrons,and electrons are found there?
A)41,52,93
B)41,52,41
C)52,41,41
D)41,52,0
E)93,41,93

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The primary reason that very large nuclei are unstable is due to
A)the cumulative repulsive force of the protons.
B)the cumulative attractive force between the protons and the orbiting electrons.
C)the repulsive force between the neutrons and the protons.
D)the extreme weakness of the gravitational attraction of the protons.
A)the cumulative repulsive force of the protons.
B)the cumulative attractive force between the protons and the orbiting electrons.
C)the repulsive force between the neutrons and the protons.
D)the extreme weakness of the gravitational attraction of the protons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
A fusion reaction releases energy because the binding energy of the resulting nucleus
A)is greater than the binding energy of the original nuclei.
B)is equal to the binding energy of the original nuclei.
C)is less than the binding energy of the original nuclei.
D)is released in the process.
E)is absorbed in the process.
A)is greater than the binding energy of the original nuclei.
B)is equal to the binding energy of the original nuclei.
C)is less than the binding energy of the original nuclei.
D)is released in the process.
E)is absorbed in the process.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of what particles in the nucleus?
A)protons
B)neutrons
C)nucleons
D)electrons
E)positrons
A)protons
B)neutrons
C)nucleons
D)electrons
E)positrons

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The binding energy per nucleon of a nucleus
A)increases steadily as we go to heavier elements.
B)decreases steadily as we go to heavier elements.
C)is approximately constant throughout the periodic table,except for very light nuclei.
D)has a maximum near iron in the periodic table and decreases after that for heavier elements.
E)has a minimum near iron in the periodic table and increases after that for heavier elements.
A)increases steadily as we go to heavier elements.
B)decreases steadily as we go to heavier elements.
C)is approximately constant throughout the periodic table,except for very light nuclei.
D)has a maximum near iron in the periodic table and decreases after that for heavier elements.
E)has a minimum near iron in the periodic table and increases after that for heavier elements.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
An yttrium isotope has 39 protons and 50 neutrons in its nucleus.Which one of the following symbols accurately represents this isotope?
A)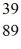 Y
Y
B)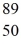 Y
Y
C)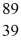 Y
Y
D)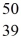 Y
Y
E)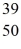 Y
Y
A)
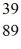 Y
YB)
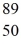 Y
YC)
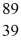 Y
YD)
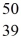 Y
YE)
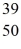 Y
Y
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements is not true of the strong nuclear force?
A)The nuclear force has a short range,of the order of nuclear dimensions.
B)For two protons that are very close together,the nuclear force and the electric force have about the same magnitudes.
C)The nuclear force does not depend on charge.
D)A nucleon in a large nucleus interacts via the nuclear force only with nearby nucleons,not with ones far away in the nucleus.
E)The nuclear force affects both neutrons and protons.
A)The nuclear force has a short range,of the order of nuclear dimensions.
B)For two protons that are very close together,the nuclear force and the electric force have about the same magnitudes.
C)The nuclear force does not depend on charge.
D)A nucleon in a large nucleus interacts via the nuclear force only with nearby nucleons,not with ones far away in the nucleus.
E)The nuclear force affects both neutrons and protons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
During β- decay
A)a neutron is transformed to a proton.
B)a proton is transformed to a neutron.
C)a neutron is ejected from the nucleus.
D)a proton is ejected from the nucleus.
E)the number of nucleons increases.
A)a neutron is transformed to a proton.
B)a proton is transformed to a neutron.
C)a neutron is ejected from the nucleus.
D)a proton is ejected from the nucleus.
E)the number of nucleons increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
In β- decay,the number of protons in the nucleus is
A)decreased by 1.
B)decreased by 2.
C)increased by 1.
D)increased by 2.
E)remains unchanged.
A)decreased by 1.
B)decreased by 2.
C)increased by 1.
D)increased by 2.
E)remains unchanged.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
A radioactive isotope of atomic number Z emits a beta-minus particle,and then the daughter nucleus emits a gamma ray.What is the atomic number of the resulting nucleus after both processes?
A)Z - 1
B)Z + 1
C)Z - 2
D)Z - 3
A)Z - 1
B)Z + 1
C)Z - 2
D)Z - 3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The nuclei of 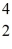
He are also known as
A)α particles.
B)β particles.
C)γ rays.
D)x-rays.
E)positrons.
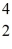
He are also known as
A)α particles.
B)β particles.
C)γ rays.
D)x-rays.
E)positrons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A β+ particle is also known as
A)an electron.
B)a positron.
C)a helium nucleus.
D)a high-energy photon.
A)an electron.
B)a positron.
C)a helium nucleus.
D)a high-energy photon.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
A radioactive isotope of atomic number Z emits an alpha particle,and the daughter nucleus then emits a beta-minus particle.What is the atomic number of the resulting nucleus?
A)Z -1
B)Z + 1
C)Z - 2
D)Z - 3
A)Z -1
B)Z + 1
C)Z - 2
D)Z - 3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Polonium-216 decays to lead-212 by emitting what kind of nuclear radiation?
A)alpha
B)beta-minus
C)beta-plus
D)gamma
E)x-rays.
A)alpha
B)beta-minus
C)beta-plus
D)gamma
E)x-rays.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
In positron decay,the number of protons in the nucleus is
A)decreased by 1.
B)decreased by 2.
C)increased by 1.
D)increased by 2.
E)remains unchanged.
A)decreased by 1.
B)decreased by 2.
C)increased by 1.
D)increased by 2.
E)remains unchanged.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
When a β+ particle is emitted from an unstable nucleus,the atomic number of the nucleus
A)increases by 1.
B)decreases by 1.
C)increases by 2.
D)decreases by 2.
E)does not change.
A)increases by 1.
B)decreases by 1.
C)increases by 2.
D)decreases by 2.
E)does not change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
What is the mass number of alpha particles?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)6
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
In beta-minus decay
A)a proton is emitted.
B)a neutron is emitted.
C)an electron is emitted.
D)an electron decays into another particle.
E)a proton is transformed into a neutron.
A)a proton is emitted.
B)a neutron is emitted.
C)an electron is emitted.
D)an electron decays into another particle.
E)a proton is transformed into a neutron.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
During β+ decay
A)a neutron is transformed to a proton.
B)a proton is transformed to a neutron.
C)a neutron is ejected from the nucleus.
D)a proton is ejected from the nucleus.
E)the number of nucleons decreases.
A)a neutron is transformed to a proton.
B)a proton is transformed to a neutron.
C)a neutron is ejected from the nucleus.
D)a proton is ejected from the nucleus.
E)the number of nucleons decreases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
When a β- particle is emitted from an unstable nucleus,the atomic mass number of the nucleus
A)increases by 1.
B)decreases by 1.
C)increases by 2.
D)does not change.
A)increases by 1.
B)decreases by 1.
C)increases by 2.
D)does not change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The atom 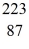
Fr decays to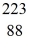
Ra by emitting what kind of nuclear radiation?
A)alpha
B)beta-minus
C)beta-plus
D)gamma
E)x-rays.
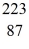
Fr decays to
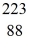
Ra by emitting what kind of nuclear radiation?
A)alpha
B)beta-minus
C)beta-plus
D)gamma
E)x-rays.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
When a β- particle is emitted from an unstable nucleus,the atomic number of the nucleus
A)increases by 1.
B)decreases by 1.
C)increases by 2.
D)decreases by 2.
E)does not change.
A)increases by 1.
B)decreases by 1.
C)increases by 2.
D)decreases by 2.
E)does not change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
An α particle is also known as
A)an electron.
B)a positron.
C)a helium nucleus.
D)a high-energy photon.
A)an electron.
B)a positron.
C)a helium nucleus.
D)a high-energy photon.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
A β- decay occurs in an unstable nucleus when
A)a proton is converted to an electron by the strong force.
B)a proton is converted to a neutron by the strong force.
C)a neutron is converted to a proton by the weak force.
D)a neutron is converted to an alpha particle by the weak force.
E)a neutron is converted to a positron by the weak force.
A)a proton is converted to an electron by the strong force.
B)a proton is converted to a neutron by the strong force.
C)a neutron is converted to a proton by the weak force.
D)a neutron is converted to an alpha particle by the weak force.
E)a neutron is converted to a positron by the weak force.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
In β- decay,the number of neutrons in the nucleus is
A)decreased by 1.
B)decreased by 2.
C)increased by 1.
D)increased by 2.
E)remains unchanged.
A)decreased by 1.
B)decreased by 2.
C)increased by 1.
D)increased by 2.
E)remains unchanged.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
A gamma ray is also known as
A)an electron.
B)a positron.
C)a helium nucleus.
D)a high-energy photon.
A)an electron.
B)a positron.
C)a helium nucleus.
D)a high-energy photon.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
A β- particle is also known as
A)an electron.
B)a positron.
C)a helium nucleus.
D)a high-energy photon.
A)an electron.
B)a positron.
C)a helium nucleus.
D)a high-energy photon.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Carbon-14 decays by β- emission.What nucleus is left after this decay?
A)carbon-13
B)carbon-14
C)carbon-15
D)nitrogen-14
E)nitrogen-15
A)carbon-13
B)carbon-14
C)carbon-15
D)nitrogen-14
E)nitrogen-15

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The chief hazard of radiation damage to living cells is
A)due to heating.
B)due to ionization.
C)due to the creation of chemical impurities.
D)the creation of new isotopes within the body.
E)the creation of radioactive material within the body.
A)due to heating.
B)due to ionization.
C)due to the creation of chemical impurities.
D)the creation of new isotopes within the body.
E)the creation of radioactive material within the body.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Modern in-air nuclear bomb tests have created an extra high level of 14C in our atmosphere.If future archaeologists date samples from this era,without knowing of this testing,will their carbon-14 dates be too young,too old,or correct? If correct,why?
A)Too young.
B)Too old.
C)Correct,since 14C from bomb tests is different from that produced naturally.
D)Correct,because modern biological materials do not gather 14C from bomb tests.
A)Too young.
B)Too old.
C)Correct,since 14C from bomb tests is different from that produced naturally.
D)Correct,because modern biological materials do not gather 14C from bomb tests.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Leptons can interact by which of the following forces?
A)strong nuclear force,weak nuclear force,electromagnetic force,gravitation
B)strong nuclear force,weak nuclear force,electromagnetic force
C)weak nuclear force,electromagnetic force,gravitation
D)strong nuclear force,weak nuclear force
E)strong nuclear force,electromagnetic force,gravitation
A)strong nuclear force,weak nuclear force,electromagnetic force,gravitation
B)strong nuclear force,weak nuclear force,electromagnetic force
C)weak nuclear force,electromagnetic force,gravitation
D)strong nuclear force,weak nuclear force
E)strong nuclear force,electromagnetic force,gravitation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
When an unstable nucleus decays by emitting an alpha particle,the atomic mass number A of the nucleus
A)increases by 4.
B)increases by 2.
C)decreases by 2.
D)decreases by 4.
E)remains unchanged.
A)increases by 4.
B)increases by 2.
C)decreases by 2.
D)decreases by 4.
E)remains unchanged.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The proton is made up of which one of the following quark combinations (up,down,strange,charm,top,bottom)?
A)uud
B)ddu
C)udd
D)ttb
E)bst
A)uud
B)ddu
C)udd
D)ttb
E)bst

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Elementary particles that experience the weak nuclear force but not the strong nuclear force are called
A)leptons.
B)hadrons.
C)mesons.
D)bosons.
E)baryons.
A)leptons.
B)hadrons.
C)mesons.
D)bosons.
E)baryons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
What happens to the half-life of a radioactive substance as we increase its temperature?
A)It does not change.
B)It increases.
C)It decreases at a constant rate.
D)It decreases at an exponential rate.
A)It does not change.
B)It increases.
C)It decreases at a constant rate.
D)It decreases at an exponential rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Two radioactive isotopes,X and Y,both decay to stable products.The half-life of X is about a day,while that of Y is about a week.Suppose a radioactive sample consists of a mixture of these two nuclides.If the mixture is such that the activities arising from X and Y are initially equal,then a few days later the activity of the sample will be due
A)predominantly to Y.
B)predominantly to X.
C)entirely to Y.
D)to X and Y equally.
A)predominantly to Y.
B)predominantly to X.
C)entirely to Y.
D)to X and Y equally.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The neutron is made up of which one of the following quark combinations (up,down,strange,charm,top,bottom)?
A)uud
B)ddu
C)udd
D)ttb
E)bst
A)uud
B)ddu
C)udd
D)ttb
E)bst

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Suppose the half-life of an isotope is 2 days.You purchase 10 grams of the isotope,but it was produced in a laboratory 4 days before it was delivered to you.How much of this isotope will you have 3 days after it was delivered to you?
A)more than 2.5 grams but less than 5 grams
B)2.5 grams
C)more than 1.25 grams but less than 2.5 grams
D)1.25 grams
E)less than 1.25 grams
A)more than 2.5 grams but less than 5 grams
B)2.5 grams
C)more than 1.25 grams but less than 2.5 grams
D)1.25 grams
E)less than 1.25 grams

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
If the half-life of a material is 45 years,how much of it will be left after 100 years?
A)more than 1/2
B)less than 1/2 but more than 1/4
C)more than 1/4 but less than 1/2
D)less than 1/4 but more than 1/8
E)less than 1/8
A)more than 1/2
B)less than 1/2 but more than 1/4
C)more than 1/4 but less than 1/2
D)less than 1/4 but more than 1/8
E)less than 1/8

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Inside the nucleus,the weakest of the four fundamental forces is
A)the weak nuclear force.
B)the electromagnetic force.
C)the gravitational force.
D)the strong nuclear force.
A)the weak nuclear force.
B)the electromagnetic force.
C)the gravitational force.
D)the strong nuclear force.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
When an unstable nucleus decays by emitting an alpha particle,the atomic number Z of the nucleus
A)increases by 4.
B)increases by 2.
C)decreases by 2.
D)decreases by 4.
E)remains unchanged.
A)increases by 4.
B)increases by 2.
C)decreases by 2.
D)decreases by 4.
E)remains unchanged.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Which of the following particles are leptons? (There may be more than one correct choice. )
A)protons
B)neutrons
C)electrons
D)photons
E)quarks
A)protons
B)neutrons
C)electrons
D)photons
E)quarks

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Inside the nucleus,the strongest of the four fundamental forces is
A)the weak nuclear force.
B)the electromagnetic force.
C)the gravitational force.
D)the strong nuclear force.
A)the weak nuclear force.
B)the electromagnetic force.
C)the gravitational force.
D)the strong nuclear force.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
The half-life of cobalt-60 is 5.3 years,while that of strontium-90 is about 29 years.Suppose you have samples of both isotopes,and that they initially have the same activity (number of decays per second).What must be true of the numbers of cobalt-60 and strontium-90 nuclei in these samples?
A)There are more strontium-90 than cobalt-60 nuclei.
B)There are equal numbers of cobalt-60 and strontium-90 nuclei.
C)There are more cobalt-60 than strontium-90 nuclei.
D)It is not possible to compare numbers of nuclei without knowing the masses of the samples.
A)There are more strontium-90 than cobalt-60 nuclei.
B)There are equal numbers of cobalt-60 and strontium-90 nuclei.
C)There are more cobalt-60 than strontium-90 nuclei.
D)It is not possible to compare numbers of nuclei without knowing the masses of the samples.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
What happens to the half-life of a radioactive substance as it decays?
A)It remains constant.
B)It increases.
C)It decreases at a constant rate.
D)It decreases at an exponential rate.
A)It remains constant.
B)It increases.
C)It decreases at a constant rate.
D)It decreases at an exponential rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
A person receives an absorbed dose of protons of 20 millirads.The RBE of protons is 5.What is this person's equivalent dose in rem?
A)4 millirem
B)15 millirem
C)20 millirem
D)25 millirem
E)100 millirem
A)4 millirem
B)15 millirem
C)20 millirem
D)25 millirem
E)100 millirem

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The half-life of cobalt-60 is 5.3 years,while that of strontium-90 is about 29 years.Suppose you have samples of both isotopes,and that they initially contain equal numbers of atoms of these isotopes.How will the activities (number of decays per second)of the samples compare?
A)The activity of the cobalt-60 sample will be greater.
B)The activities cannot be compared without more information.
C)The activities will be equal.
D)The activity of the strontium-90 sample will be greater.
A)The activity of the cobalt-60 sample will be greater.
B)The activities cannot be compared without more information.
C)The activities will be equal.
D)The activity of the strontium-90 sample will be greater.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
What are the possible charges of a quark (not an antiquark)?
A)-e,0,e
B)-2/3 e,-1/3 e,+1/3 e,+2/3 e
C)-2/3 e,+1/3 e
D)-1/3 e,+2/3 e
E)-1/3 e,+1/3 e
A)-e,0,e
B)-2/3 e,-1/3 e,+1/3 e,+2/3 e
C)-2/3 e,+1/3 e
D)-1/3 e,+2/3 e
E)-1/3 e,+1/3 e

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Which of the following particles are not made up of quarks? (There could be more than one correct choice. )
A)alpha particle
B)electron
C)proton
D)positron
E)neutron
A)alpha particle
B)electron
C)proton
D)positron
E)neutron

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
A beryllium-8 nucleus at rest undergoes double alpha decay as follows: 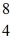
Be →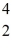
He +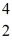
He
The known atomic masses are: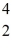
He: 4.002603 u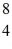
Be: 8.005305 u
What is the kinetic energy of each departing alpha particle? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)46 keV
B)65 keV
C)92 keV
D)130 keV
E)180 keV
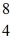
Be →
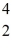
He +
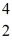
He
The known atomic masses are:
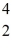
He: 4.002603 u
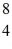
Be: 8.005305 u
What is the kinetic energy of each departing alpha particle? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)46 keV
B)65 keV
C)92 keV
D)130 keV
E)180 keV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
One of the fusion reactions that occurs in the sun is: 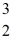
He +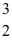
He →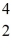
He +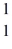
H +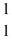
H
The following atomic masses are known: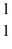
H: 1.007825 u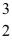
He: 3.016029 u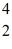
He: 4.002603 u
What is the reaction energy released in this fusion reaction? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)11 MeV
B)13 MeV
C)15 MeV
D)17 MeV
E)19 MeV
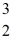
He +
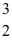
He →
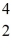
He +
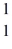
H +
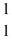
H
The following atomic masses are known:
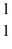
H: 1.007825 u
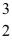
He: 3.016029 u
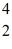
He: 4.002603 u
What is the reaction energy released in this fusion reaction? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)11 MeV
B)13 MeV
C)15 MeV
D)17 MeV
E)19 MeV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
How many quarks are in a deuteron, 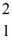
H?
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)6
E)9
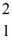
H?
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)6
E)9

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
The diameter of an atom is 1.4 × 10-10 m and the diameter of its nucleus is 1.0 × 10-14 m.What fraction of the atom's volume is occupied by its nucleus?
A)3.6 × 10-13
B)7.1 × 10-5
C)5.1 × 10-9
D)2.6 × 10-17
A)3.6 × 10-13
B)7.1 × 10-5
C)5.1 × 10-9
D)2.6 × 10-17

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
The stability of 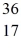
Cl with respect to alpha,beta-plus and beta-minus decay is to be determined.The following atomic masses are known: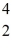
He: 4.002603 u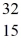
P: 31.973907 u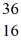
S: 35.967081 u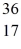
Cl: 35.968307 u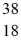
Ar: 35.967546 u
The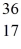
Cl nucleus is
A)not subject to alpha,beta-plus or beta-minus decay.
B)subject to alpha decay only.
C)subject to beta-plus decay only.
D)subject to beta-minus decay only.
E)subject to beta-plus or beta-minus decay,but not to alpha decay.
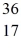
Cl with respect to alpha,beta-plus and beta-minus decay is to be determined.The following atomic masses are known:
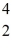
He: 4.002603 u
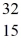
P: 31.973907 u
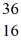
S: 35.967081 u
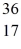
Cl: 35.968307 u
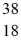
Ar: 35.967546 u
The
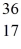
Cl nucleus is
A)not subject to alpha,beta-plus or beta-minus decay.
B)subject to alpha decay only.
C)subject to beta-plus decay only.
D)subject to beta-minus decay only.
E)subject to beta-plus or beta-minus decay,but not to alpha decay.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
When a stationary plutonium-239, 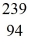
Pu,decays into uranium-235 plus an alpha particle,the energy released in the process is 5.24 MeV.The following masses are known: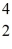
He: 4.002603 u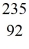
U: 235.043924 u
What is the mass of the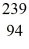
Pu nucleus,in amu? (1 u = 931.494 MeV/c2)
A)239.05215 u
B)239.02775 u
C)239.00189 u
D)238.99919 u
E)238.98884 u
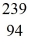
Pu,decays into uranium-235 plus an alpha particle,the energy released in the process is 5.24 MeV.The following masses are known:
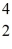
He: 4.002603 u
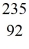
U: 235.043924 u
What is the mass of the
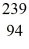
Pu nucleus,in amu? (1 u = 931.494 MeV/c2)
A)239.05215 u
B)239.02775 u
C)239.00189 u
D)238.99919 u
E)238.98884 u

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
The neutral deuterium atom, 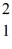
H,has a mass of 2.014102 u;a neutral ordinary hydrogen atom has a mass of 1.007825 u;a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 u;and a proton has a mass of 1.007277 u.What is the binding energy of the deuterium nucleus? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)1.1 MeV
B)1.7 MeV
C)2.2 MeV
D)2.9 MeV
E)3.4 MeV
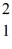
H,has a mass of 2.014102 u;a neutral ordinary hydrogen atom has a mass of 1.007825 u;a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 u;and a proton has a mass of 1.007277 u.What is the binding energy of the deuterium nucleus? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)1.1 MeV
B)1.7 MeV
C)2.2 MeV
D)2.9 MeV
E)3.4 MeV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Uranium-238 decays into thorium-234 plus an alpha particle.The known masses are 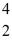
He: 4.002603 u
Th: 234.043583 u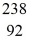
U: 238.050786 u
How much energy is released in this process? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)4.28 MeV
B)3.76 MeV
C)3.18 MeV
D)2.89 MeV
E)5.05 MeV
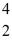
He: 4.002603 u
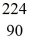
Th: 234.043583 u
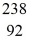
U: 238.050786 u
How much energy is released in this process? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)4.28 MeV
B)3.76 MeV
C)3.18 MeV
D)2.89 MeV
E)5.05 MeV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
How many quarks are in a tritium isotope, 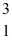
H?
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)6
E)9
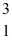
H?
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)6
E)9

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
The following masses are known: 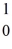
N 1.008665 u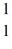
H 1.007825 u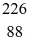
Ra 226.025403 u
What is the binding energy of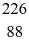
Ra? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)1,700 MeV
B)1,900 MeV
C)2,100 MeV
D)2,300 MeV
E)2,500 MeV
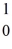
N 1.008665 u
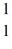
H 1.007825 u
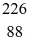
Ra 226.025403 u
What is the binding energy of
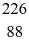
Ra? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)1,700 MeV
B)1,900 MeV
C)2,100 MeV
D)2,300 MeV
E)2,500 MeV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Radium-226 decays into radon-222 plus an alpha particle.The relevant masses are 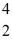
He: 4.002603 u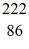
Rn: 222.017570 u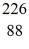
Ra: 226.025402 u
How much energy is released in this process? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)4.24 MeV
B)3.76 MeV
C)4.87 MeV
D)5.05 MeV
E)5.39 MeV
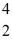
He: 4.002603 u
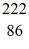
Rn: 222.017570 u
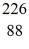
Ra: 226.025402 u
How much energy is released in this process? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)4.24 MeV
B)3.76 MeV
C)4.87 MeV
D)5.05 MeV
E)5.39 MeV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Bismuth 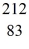
Bi is known to be radioactive.The stability of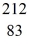
Bi with respect to alpha,beta-plus and beta-minus decay is to be determined.The following atomic masses are known:
He: 4.002603 u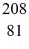
Tl: 207.981998 u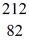
Pb: 211.991871 u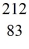
Bi: 211.991255 u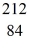
Po: 211.988842 u
The
Bi nucleus is
A)subject to alpha decay only.
B)subject to beta-plus decay only.
C)subject to beta-minus decay only.
D)subject to alpha or beta-plus decay,but not beta-minus decay.
E)subject to alpha or beta-minus decay,but not beta-plus decay.
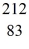
Bi is known to be radioactive.The stability of
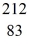
Bi with respect to alpha,beta-plus and beta-minus decay is to be determined.The following atomic masses are known:
He: 4.002603 u
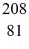
Tl: 207.981998 u
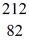
Pb: 211.991871 u
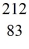
Bi: 211.991255 u
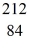
Po: 211.988842 u
The
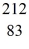
Bi nucleus is
A)subject to alpha decay only.
B)subject to beta-plus decay only.
C)subject to beta-minus decay only.
D)subject to alpha or beta-plus decay,but not beta-minus decay.
E)subject to alpha or beta-minus decay,but not beta-plus decay.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
A carbon-14 nucleus decays to a nitrogen-14 nucleus by beta-minus decay.How much energy (in MeV)is released if carbon-14 has a mass of 14.003242 u and nitrogen-14 has a mass of 14.003074 u? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)0.0156 MeV
B)0.156 MeV
C)1.56 MeV
D)15.6 MeV
A)0.0156 MeV
B)0.156 MeV
C)1.56 MeV
D)15.6 MeV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
The neutral helium atom, 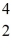
He,has a mass of 4.002603 u,a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 u,a proton has a mass of 1.007277 u,and a neutral hydrogen atom has a mass of 1.007825 u.What is the binding energy of the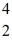
He nucleus? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)20.5 MeV
B)22.4 MeV
C)27.3 MeV
D)28.3 MeV
E)23.4 MeV
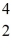
He,has a mass of 4.002603 u,a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 u,a proton has a mass of 1.007277 u,and a neutral hydrogen atom has a mass of 1.007825 u.What is the binding energy of the
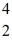
He nucleus? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)20.5 MeV
B)22.4 MeV
C)27.3 MeV
D)28.3 MeV
E)23.4 MeV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
A summary of the nuclear reactions that power our sun is 4p → 4He + 2e-,with masses of 938.272 MeV/c2 for a proton,3727.38 MeV/c2 for the helium nucleus,and 0.511 MeV/c2 for each electron.How much energy is released by each of these reactions?
A)24.69 MeV
B)28.3 MeV
C)2790.13 MeV
D)279.01 MeV
A)24.69 MeV
B)28.3 MeV
C)2790.13 MeV
D)279.01 MeV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Which of the following particles (or groups of particles)are made up of quarks?
A)protons,neutrons,and electrons
B)electrons and neutrinos
C)photons
D)protons and neutrons
E)All particles except for photons are made up of quarks.
A)protons,neutrons,and electrons
B)electrons and neutrinos
C)photons
D)protons and neutrons
E)All particles except for photons are made up of quarks.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
When a stationary plutonium-239 nucleus decays into a uranium-235 nucleus plus an alpha particle,the energy released in the process is 5.24 MeV.The following masses are known: 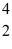
He: 4.002603 u
U: 235.043924 u
What is the kinetic energy of the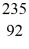
U nucleus? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)0.0829 MeV
B)0.0837 MeV
C)0.0852 MeV
D)0.0863 MeV
E)0.0877 MeV
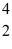
He: 4.002603 u

U: 235.043924 u
What is the kinetic energy of the
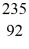
U nucleus? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A)0.0829 MeV
B)0.0837 MeV
C)0.0852 MeV
D)0.0863 MeV
E)0.0877 MeV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
The stability of 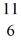
C with respect to alpha,beta-plus and beta-minus decay is to be determined.The following atomic masses are known: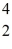
He: 4.002603 u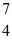
Be: 7.016928 u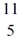
B: 11.009305 u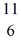
C: 11.011433 u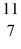
N: 11.026742 u
The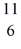
C nucleus is
A)not subject to alpha,beta-plus or beta-minus decay.
B)subject to alpha decay only.
C)subject to beta-plus decay only.
D)subject to beta-minus decay only.
E)subject to beta-plus or beta-minus decay,but not to alpha decay.
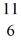
C with respect to alpha,beta-plus and beta-minus decay is to be determined.The following atomic masses are known:
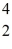
He: 4.002603 u
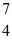
Be: 7.016928 u
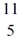
B: 11.009305 u
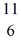
C: 11.011433 u
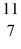
N: 11.026742 u
The
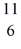
C nucleus is
A)not subject to alpha,beta-plus or beta-minus decay.
B)subject to alpha decay only.
C)subject to beta-plus decay only.
D)subject to beta-minus decay only.
E)subject to beta-plus or beta-minus decay,but not to alpha decay.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








