Deck 4: Choice
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/63
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 4: Choice
1
Millie's utility function is U(x, y) = min{x, y}. She maximizes her utility subject to a budget constraint. The price of x is the same as the price of y. If the price of x rises and the price of y and her income remain constant, then her consumption of y will certainly decrease.
True
2
If a consumer does not have convex preferences, then a point of tangency between her indifference curve and her budget line must be an optimal consumption point.
False
3
George has $49 which he decides to spend on x and y. Commodity x costs $5 per unit and commodity y costs $11 per unit. He has the utility function U(x, y) = 3x2 + 6y2 and he can purchase fractional units of x and y. George will choose
A) only y.
B) some of each commodity but more x than y.
C) only x.
D) some of each commodity but more y than x.
E) equal amounts of the two commodities.
A) only y.
B) some of each commodity but more x than y.
C) only x.
D) some of each commodity but more y than x.
E) equal amounts of the two commodities.
C
4
Henri's utility function is min{x, 5y + 2z}. The price of x is $1, the price of y is $15, and the price of z is $7. Henri's income is $44. How many units of x does Henri demand?
A) 9.78
B) 11
C) 5
D) 3
E) None of the above.
A) 9.78
B) 11
C) 5
D) 3
E) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
If a consumer doesn't consume any snails but does consume Big Macs, then his marginal rate of substitution between snails and Big Macs when his snail consumption is zero must be equal to the ratio of the price of snails to the price of Big Macs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Ambrose's utility function is 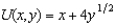 . The price of x is $1 and the price of y is $2. If his income rises from $100 to $150, his consumption of y increases by more than 10% but less than 50%.
. The price of x is $1 and the price of y is $2. If his income rises from $100 to $150, his consumption of y increases by more than 10% but less than 50%.
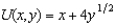 . The price of x is $1 and the price of y is $2. If his income rises from $100 to $150, his consumption of y increases by more than 10% but less than 50%.
. The price of x is $1 and the price of y is $2. If his income rises from $100 to $150, his consumption of y increases by more than 10% but less than 50%.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Mary Granola's utility function is U(x, y) = min{x + 2y, y + 2x}. Mary maximizes her utility subject to a budget constraint. If she chooses the bundle (5, 6), then the price of x must be exactly twice the price of y.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Clara's utility function is U(x, y) = (x + 2)(y + 1). If her consumption of both x and y are doubled, then her marginal rate of substitution between x and y remains constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Linus has utility function U(x, y) = x + 2y. If the price of x is $1 and the price of y is .50 cents then Linus must consume equal amounts of both goods in order to maximize his utility.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
At a boundary optimum, a consumer's indifference curve must be tangent to her budget line.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Hans has $27 which he decides to spend on x and y. Commodity x costs $16 per unit and commodity y costs $10 per unit. He has the utility function U(x, y) = 5x2 + 2y2 and he can purchase fractional units of x and y. Hans will choose
A) only x.
B) only y.
C) some of each commodity but more y than x.
D) some of each commodity but more x than y.
E) equal amounts of the two commodities.
A) only x.
B) only y.
C) some of each commodity but more y than x.
D) some of each commodity but more x than y.
E) equal amounts of the two commodities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Peter consumes no commodities other than Miller Lite and Bud Light. His annual budget for these two commodities is described by the equation 5x + 30y = 300, where x is sixpacks of Miller Lite and y is cases of Bud Light. Peter considers 2 cases of Bud Light to be perfect substitutes for 6 sixpacks of Miller Lite.
A) He will consume 60 sixpacks of Miller Lite per year.
B) He will consume 10 cases of Bud Light per year.
C) He will consume 14 cases of Bud Light per year.
D) He will consume 12 sixpacks of Miller Lite per year.
E) He is indifferent between any two bundles that use up his entire income.
A) He will consume 60 sixpacks of Miller Lite per year.
B) He will consume 10 cases of Bud Light per year.
C) He will consume 14 cases of Bud Light per year.
D) He will consume 12 sixpacks of Miller Lite per year.
E) He is indifferent between any two bundles that use up his entire income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Wanda Littlemore's utility function is U(x, y) = x + 47y - 3y2. Her income is $107. If the price of x is $1 and the price of y is $23, how many units of good x will Wanda demand?
A) 11
B) 19
C) 0
D) 18
E) 15
A) 11
B) 19
C) 0
D) 18
E) 15

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Max Gross has the utility function U(x, y) = max{x, y}. If the price of x is the same as the price of y, Max will buy equal amounts of x and y.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Sharon spends all of her income on peaches and strawberries. Peaches are a normal good for her. Her income increased by 20 percent and prices did not change. Her consumption of strawberries could not have increased by more than 20 percent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Leo's utility function is min{x, 3y + 2z}. The price of x is $1, the price of y is $9, and the price of z is $8. Leo's income is $8. How many units of x does Leo demand?
A) 2
B) 1.60
C) 5
D) 7
E) None of the above.
A) 2
B) 1.60
C) 5
D) 7
E) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Other things being equal, a lump sum tax is at least as good for a consumer as a sales tax that collects the same revenue from him.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Roger consumes no commodities other than Miller Lite and Bud Light. His annual budget for these two commodities is described by the equation 5x + 25y = 300, where x is sixpacks of Miller Lite and y is cases of Bud Light. Roger considers 2 cases of Bud Light to be perfect substitutes for 6 sixpacks of Miller Lite.
A) He will consume 12 cases of Bud Light per year.
B) He will consume 12 sixpacks of Miller Lite per year.
C) He will consume 16 cases of Bud Light per year.
D) He will consume 60 sixpacks of Miller Lite per year.
E) He is indifferent between any two bundles that use up his entire income.
A) He will consume 12 cases of Bud Light per year.
B) He will consume 12 sixpacks of Miller Lite per year.
C) He will consume 16 cases of Bud Light per year.
D) He will consume 60 sixpacks of Miller Lite per year.
E) He is indifferent between any two bundles that use up his entire income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Wanda Littlemore's utility function is U(x, y) = x + 46y - 2y2. Her income is $135. If the price of x is $1 and the price of y is $18, how many units of good x will Wanda demand?
A) 5
B) 12
C) 16
D) 0
E) 9
A) 5
B) 12
C) 16
D) 0
E) 9

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Charlie's utility function is U(x, y) = xy2. His marginal rate of substitution between x and y does not change if the amount of both goods doubles.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Martha's utility function is U(x, y) = min{x + 2y, 2x + y}. George's utility function is U(x, y) = min{ 2x + 4y, 4x + 2y}. If George and Martha have the same income and face the same prices for the goods x and y,
A) George and Martha will both demand the same amount of y.
B) Martha will always prefer George's consumption bundle to her own.
C) George will always prefer Martha's consumption bundle to his own.
D) George will demand more x than Martha demands.
E) None of the above.
A) George and Martha will both demand the same amount of y.
B) Martha will always prefer George's consumption bundle to her own.
C) George will always prefer Martha's consumption bundle to his own.
D) George will demand more x than Martha demands.
E) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Badger Madison consumes only beer and sausages. His income is $100. Beer costs him $.50 per can and sausages cost $1 each. Where x is the number of cans of beer and y the number of sausages he consumes per week, Badger's utility function is U(x, y) = -[(x - 50)2 + (y - 40)2].
A) Badger must always be unhappy since whatever he consumes, his utility is negative.
B) He has monotonic preferences.
C) If his income increases, he won't change the commodity bundle that he buys.
D) If the price of beer goes down, he will buy more beer.
E) More than one of the above statements is true.
A) Badger must always be unhappy since whatever he consumes, his utility is negative.
B) He has monotonic preferences.
C) If his income increases, he won't change the commodity bundle that he buys.
D) If the price of beer goes down, he will buy more beer.
E) More than one of the above statements is true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Coke and Pepsi are perfect substitutes for Mr. Drinker and the slope of his indifference curves is - 1. One day he bought 2 cans of Coke and 20 cans of Pepsi. (The cans of both drinks are the same size.)
A) Coke is less expensive than Pepsi.
B) Coke is more expensive than Pepsi.
C) Coke and Pepsi cost the same.
D) Mr. Drinker prefers Pepsi to Coke.
E) None of the above.
A) Coke is less expensive than Pepsi.
B) Coke is more expensive than Pepsi.
C) Coke and Pepsi cost the same.
D) Mr. Drinker prefers Pepsi to Coke.
E) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Ed and Al both consume only bread and cheese. Both of them always choose to have some bread and some cheese, and both have strictly convex preferences. However, Ed likes to have a great deal of bread with a little cheese, and Al likes lots of cheese with a little bread. Both face the same prices for both goods and have chosen bundles to maximize their utilities subject to their budgets.
A) Al's marginal rate of substitution is larger in absolute value than Ed's.
B) Ed's marginal rate of substitution is larger in absolute value than Al's.
C) Their marginal rates of substitution are the same.
D) Who has the larger marginal rate of substitution depends on income levels.
E) There is not enough information for us to be able to tell who has the larger marginal rate of substitution.
A) Al's marginal rate of substitution is larger in absolute value than Ed's.
B) Ed's marginal rate of substitution is larger in absolute value than Al's.
C) Their marginal rates of substitution are the same.
D) Who has the larger marginal rate of substitution depends on income levels.
E) There is not enough information for us to be able to tell who has the larger marginal rate of substitution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Harold's utility function is U(x, y) = (x + 3)(y + 2). The price of x is $1. The price of y is $2. At all incomes for which Harold consumes positive amounts of both goods, he will consume
A) more than twice as many units of x as of y.
B) more than twice as many units of y as of x.
C) 1 more unit of x than of y.
D) 1 more unit of y than of x.
E) as many units of y as of x.
A) more than twice as many units of x as of y.
B) more than twice as many units of y as of x.
C) 1 more unit of x than of y.
D) 1 more unit of y than of x.
E) as many units of y as of x.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Howard has the utility function 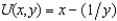 . His income is $30.
. His income is $30.
A) Howard does not like good y.
B) Howard has a bliss point.
C) If the price of good x is $4 and the price of good y is $1, Howard will buy 2 units of y.
D) Howard will buy good y only if it is cheaper than good x.
E) None of the above.
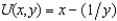 . His income is $30.
. His income is $30.A) Howard does not like good y.
B) Howard has a bliss point.
C) If the price of good x is $4 and the price of good y is $1, Howard will buy 2 units of y.
D) Howard will buy good y only if it is cheaper than good x.
E) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Isobel consumes positive quantities of both jam and juice. The price of jam is 5 cents per unit and the price of juice is 10 cents per unit. Her marginal utility of jam is 10 and her marginal utility of juice is 5.
A) Without changing her total expenditures, she could increase her utility by consuming more jam and less juice.
B) Without changing her total expenditures, she could increase her utility by consuming more juice and less jam.
C) Without changing her total expenditures on jam and juice, she could not increase her utility.
D) She should spend more money on both jam and juice.
E) We can't tell whether any of the other statements are true or false without knowing the quantities she consumes.
A) Without changing her total expenditures, she could increase her utility by consuming more jam and less juice.
B) Without changing her total expenditures, she could increase her utility by consuming more juice and less jam.
C) Without changing her total expenditures on jam and juice, she could not increase her utility.
D) She should spend more money on both jam and juice.
E) We can't tell whether any of the other statements are true or false without knowing the quantities she consumes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Danny Featherweight is taking a tough course in law school. His professor agreed to give him a course grade of max{ 2x, 3y} where x and y are the number of answers he gets right on the first and second midterms, respectively. Danny needs a course grade of 150 to pass. He finds that for the first midterm, for every A minutes of study, he will get one more answer right. For the second midterm, for every B minutes that he studies, he will get one more answer right. If he doesn't study at all, Danny will get nothing right on either exam. All Danny cares about is passing. He doesn't want to waste any time getting a higher grade than he needs.
A) If, then Danny will not study for the second exam.
B) The ratio of the time Danny spends on exam 1 to the time he spends on exam 2 will be.
C) The ratio of the time Danny spends on exam 2 to the time he spends on exam 1 will be.
D) If A < B, then Danny will not study for the first exam.
E) Danny will spendminutes studying for each exam.
A) If, then Danny will not study for the second exam.
B) The ratio of the time Danny spends on exam 1 to the time he spends on exam 2 will be.
C) The ratio of the time Danny spends on exam 2 to the time he spends on exam 1 will be.
D) If A < B, then Danny will not study for the first exam.
E) Danny will spendminutes studying for each exam.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Ollie has a utility function U(x, y) = (x + 2)(y + 3). The price of x is $1 and the price of y is $1. When he maximizes his utility subject to his budget constraint, he consumes positive amounts of both goods. Ollie consumes
A) exactly as many units of x as of y.
B) 1 more unit of x than he consumes of y.
C) 1 more unit of y than he consumes of x.
D) 2 more units of x than he consumes of y.
E) None of the above.
A) exactly as many units of x as of y.
B) 1 more unit of x than he consumes of y.
C) 1 more unit of y than he consumes of x.
D) 2 more units of x than he consumes of y.
E) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which of the following could possibly change a rational consumer's demand?
A) Changing his utility function by cubing it
B) Changing his utility function by multiplying it by 3 and subtracting 100 from it
C) Increasing all prices and his income by $3
D) Multiplying all prices and income by 2.2
E) More than one of the above
A) Changing his utility function by cubing it
B) Changing his utility function by multiplying it by 3 and subtracting 100 from it
C) Increasing all prices and his income by $3
D) Multiplying all prices and income by 2.2
E) More than one of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Minnie Applesauce is shopping for a summer lake cottage. Minnie hates mosquito bites, but the cheapest lake cottages have the most mosquitos. The price of a lake cabin is related to b, the number of mosquito bites you can expect per hour, according to the formula p = $20,000 - 100b. Minnie's utility function is u = x - 5b2, where x is her expenditure on all goods other than her lake cabin. If Minnie makes her best choice of lake cabin, how many mosquito bites per hour will she get?
A) 10
B) 5
C) 20
D) 25
E) None of the above.
A) 10
B) 5
C) 20
D) 25
E) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Mary Granola consumes tomatoes and nectarines. Mary's indifference curves are kinky. When she is consuming more tomatoes than nectarines, she is just willing to trade 3 tomatoes for 1 nectarine. When she is consuming more nectarines than tomatoes, she is just willing to trade 4 nectarines for 1 tomato. Let P1 be the price of nectarines, and P2 the price of tomatoes. Mary maximizes her utility subject to her budget constraint. (Hint: Sketch one of her indifference curves.)
A) When P1 > P2, she must consume only tomatoes.
B) When P1 > P2, she must consume 3 times as many tomatoes as nectarines.
C) When P1 > 3P2, she must consume only tomatoes.
D) When 4P1 > P2, she must consume only nectarines.
E) She must consume equal numbers of both.
A) When P1 > P2, she must consume only tomatoes.
B) When P1 > P2, she must consume 3 times as many tomatoes as nectarines.
C) When P1 > 3P2, she must consume only tomatoes.
D) When 4P1 > P2, she must consume only nectarines.
E) She must consume equal numbers of both.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Paul's utility function is min{x + 3y, 3x + y}. Simon's utility function is min{ 3x + 9y, 9x + 3y}. Paul and Simon have the same income and face the same prices.
A) Paul and Simon will demand the same amount of good x.
B) Paul will demand more of good y than Simon.
C) Simon will demand more of good y than Paul.
D) Each will prefer the other's consumption bundle to his own.
E) None of the above.
A) Paul and Simon will demand the same amount of good x.
B) Paul will demand more of good y than Simon.
C) Simon will demand more of good y than Paul.
D) Each will prefer the other's consumption bundle to his own.
E) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Jane's utility function is U(x, y) = x + 2y, where x is her consumption of good X and y is her consumption of good Y. Her income is $2. The price of Y is $2. The cost per unit of X depends on how many units she buys. The total cost of x units of X is the square root of x.
A) The bundle () is Jane's utility maximizing choice, given her budget.
B) The bundle () is Jane's utility maximizing choice, given her budget.
C) Given her budget, Jane would maximize her utility by spending all of her income on good X.
D) Given her budget, Jane would maximize her utility by spending all of her income on good Y.
E) None of the above.
A) The bundle () is Jane's utility maximizing choice, given her budget.
B) The bundle () is Jane's utility maximizing choice, given her budget.
C) Given her budget, Jane would maximize her utility by spending all of her income on good X.
D) Given her budget, Jane would maximize her utility by spending all of her income on good Y.
E) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The prices of goods x and y are each $1. Jane has $20 to spend and is considering choosing 10 units of x and 10 units of y. Jane has nice convex preferences and more of each good is better for her. Where x is drawn on the horizontal axis and y is drawn on the vertical axis, the slope of her indifference curve at the bundle (10, 10) is -2.
A) The bundle (10, 10) is the best she can afford.
B) She would be better off consuming more of good x and less of good y.
C) She would be better off consuming more of good y and less of good x.
D) She must dislike one of the goods.
E) More than one of the above is true.
A) The bundle (10, 10) is the best she can afford.
B) She would be better off consuming more of good x and less of good y.
C) She would be better off consuming more of good y and less of good x.
D) She must dislike one of the goods.
E) More than one of the above is true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Mary Granola consumes apples and uglifruits. Mary's indifference curves are kinky. When she is consuming more apples than uglifruits, she is just willing to trade 3 apples for 1 uglifruit. When she is consuming more uglifruits than apples, she is just willing to trade 4 uglifruits for 1 apple. Let P1 be the price of uglifruits and P2 the price of apples. Mary maximizes her utility subject to her budget constraint. (Hint: Sketch one of her indifference curves.)
A) When P1 > 3P2, she must consume only apples.
B) When P1 > P2, she must consume 3 times as many apples as uglifruits.
C) When 4P1 > P2, she must consume only uglifruits.
D) When P1 > P2, she must consume only apples.
E) She must consume equal numbers of both.
A) When P1 > 3P2, she must consume only apples.
B) When P1 > P2, she must consume 3 times as many apples as uglifruits.
C) When 4P1 > P2, she must consume only uglifruits.
D) When P1 > P2, she must consume only apples.
E) She must consume equal numbers of both.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Janet consumes two commodities x and y. Her utility function is min{x + 2y, y + 2x}. She chooses to buy 10 units of good x and 20 units of good y. The price of good x is $1. Janet's income is
A) $40.
B) $50.
C) $30.
D) $20.
E) There is not enough information in the problem to determine her income because we are not told the price of good y.
A) $40.
B) $50.
C) $30.
D) $20.
E) There is not enough information in the problem to determine her income because we are not told the price of good y.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
If his wage rate increases, then a utility maximizing consumer will necessarily
A) increase (or leave constant) his labor supply.
B) increase (or leave constant) his labor supply if leisure is a normal good but otherwise might reduce his labor supply.
C) increase (or leave constant) his labor supply if leisure is an inferior good but otherwise might reduce his labor supply.
D) decrease (or leave constant) his labor supply.
E) none of the above.
A) increase (or leave constant) his labor supply.
B) increase (or leave constant) his labor supply if leisure is a normal good but otherwise might reduce his labor supply.
C) increase (or leave constant) his labor supply if leisure is an inferior good but otherwise might reduce his labor supply.
D) decrease (or leave constant) his labor supply.
E) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
As you may know, Mungoites each have two left feet and one right foot. Their preferences for left and right shoes display perfect complementarity. Mungoites find shoes useful only in trios of two lefts and a right. The price of each type of shoe is $10 a shoe, and Mungoites consume nothing other than shoes. A Mungoite's Engel curve for right shoes has the equation
A) R =.
B) R = m - 10.
C) R = 2m.
D) R = 10m.
E) R =.
A) R =.
B) R = m - 10.
C) R = 2m.
D) R = 10m.
E) R =.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Charlie has a utility function U(x, y) = (x + 3)(y + 4). The price of x is $1 and the price of y is $1. When he maximizes his utility subject to his budget constraint, he consumes positive amounts of both goods. Charlie consumes
A) 2 more units of x than he consumes of y.
B) 1 more unit of x than he consumes of y.
C) exactly as many units of x as of y.
D) 1 more unit of y than he consumes of x.
E) None of the above.
A) 2 more units of x than he consumes of y.
B) 1 more unit of x than he consumes of y.
C) exactly as many units of x as of y.
D) 1 more unit of y than he consumes of x.
E) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Charlie's utility function is U(xA, xB) = xAxB. If Charlie's income is $40, the price of apples is $4, and the price of bananas is $2, how many apples are there in the best bundle that Charlie can afford?
A) 10
B) 8
C) 12
D) 9
E) 5
A) 10
B) 8
C) 12
D) 9
E) 5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Elmer's utility function is U(x, y) = min{x, y2}. If the price of x is $10 and the price of y is $15 and if Elmer chooses to consume 4 units of y, what must his income be?
A) $220
B) $100
C) $320
D) $440
E) There is not enough information to determine his income.
A) $220
B) $100
C) $320
D) $440
E) There is not enough information to determine his income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Our old friend, Edmund Stench, of Chapter 2 loves punk rock video tapes. He has no income and therefore has to accept garbage in his backyard in return for money. Each video tape cost $2 and each sack of garbage that he accepts brings him $1. His utility function is given by U(c, g) = min{ 2c, 20 - g}, where c is the number of video tapes and g is the number of sacks of garbage that he gets per month. Each month he will choose to accept
A) 20 sacks of garbage.
B) no garbage.
C) 5 sacks of garbage.
D) 10 sacks of garbage.
E) 15 sacks of garbage.
A) 20 sacks of garbage.
B) no garbage.
C) 5 sacks of garbage.
D) 10 sacks of garbage.
E) 15 sacks of garbage.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Charlie has a utility function U(xA, xB) = xAxB, the price of apples is $1, and the price of bananas is $2. If Charlie's income were $200, how many units of bananas would he consume if he chose the bundle that maximized his utility subject to his budget constraint?
A) 25
B) 50
C) 10
D) 100
E) 150
A) 25
B) 50
C) 10
D) 100
E) 150

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Ambrose's utility function is U(x1, x2) = 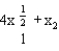 . If the price of nuts (good 1) is $1, the price of berries (good 2) is $6, and his income is $264, how many units of nuts will Ambrose choose?
. If the price of nuts (good 1) is $1, the price of berries (good 2) is $6, and his income is $264, how many units of nuts will Ambrose choose?
A) 20
B) 144
C) 288
D) 147
E) 72
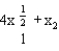 . If the price of nuts (good 1) is $1, the price of berries (good 2) is $6, and his income is $264, how many units of nuts will Ambrose choose?
. If the price of nuts (good 1) is $1, the price of berries (good 2) is $6, and his income is $264, how many units of nuts will Ambrose choose?A) 20
B) 144
C) 288
D) 147
E) 72

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Lorenzo lives on x and y alone. His utility function is U(x, y) = min{ 3x + 4y, 7y}. The prices of both goods are positive. He will
A) never buy more x than y.
B) buy equal amounts of the two goods.
C) always buy more y than x.
D) always buy more x than y.
E) More than one of the above is true.
A) never buy more x than y.
B) buy equal amounts of the two goods.
C) always buy more y than x.
D) always buy more x than y.
E) More than one of the above is true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Joseph's utility function is given by UJ = xA + 2xB, where xA denotes his consumption of apples and xB his consumption of bananas. Clara's utility function is given by UC = 3xA + 2xB. Joseph and Clara shop at the same grocery store.
A) When we observe that Joseph leaves the store with some bananas, then we can deduce that Clara also buys some bananas.
B) There exist prices of apples and bananas such that both consumers buy strictly positive amounts of both goods.
C) When we observe that Joseph leaves the store with some apples and some bananas, then we can deduce that Clara also buys some apples and some bananas.
D) When we observe that Joseph leaves the store with some apples, then we can deduce that Clara also buys some apples.
E) Apples and bananas are perfect complements for Joseph.
A) When we observe that Joseph leaves the store with some bananas, then we can deduce that Clara also buys some bananas.
B) There exist prices of apples and bananas such that both consumers buy strictly positive amounts of both goods.
C) When we observe that Joseph leaves the store with some apples and some bananas, then we can deduce that Clara also buys some apples and some bananas.
D) When we observe that Joseph leaves the store with some apples, then we can deduce that Clara also buys some apples.
E) Apples and bananas are perfect complements for Joseph.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Arthur's preferences are defined over two basic food groups, beer, x1, and ice cream, x2. His utility function is u(x1, x2) = x21 + x2. He has $100 to spend, and each of these goods costs $10 per quart.
A) Arthur will consume 5 quarts of ice cream and 5 quarts of beer.
B) Arthur will find that 10 quarts of beer and no ice cream is the best bundle.
C) Arthur will find that 10 quarts of ice cream and no beer is the best bundle.
D) Arthur is indifferent between any two points on the line that connects (5, 5) and (10, 10).
E) Arthur will spendof his income on beer andof his income on ice cream.
A) Arthur will consume 5 quarts of ice cream and 5 quarts of beer.
B) Arthur will find that 10 quarts of beer and no ice cream is the best bundle.
C) Arthur will find that 10 quarts of ice cream and no beer is the best bundle.
D) Arthur is indifferent between any two points on the line that connects (5, 5) and (10, 10).
E) Arthur will spendof his income on beer andof his income on ice cream.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Elmer's utility function is U(x, y) = min{x, y2}. If the price of x is $25 and the price of y is $15 and if Elmer chooses to consume 7 units of y, what must his income be?
A) $2,660
B) $280
C) $1,430
D) $1,330
E) There is not enough information to determine his income.
A) $2,660
B) $280
C) $1,430
D) $1,330
E) There is not enough information to determine his income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Charlie's utility function is U(xA, xB) = xAxB. If Charlie's income is $40, the price of apples is $4, and the price of bananas is $2, how many apples are there in the best bundle that Charlie can afford?
A) 10
B) 12
C) 8
D) 9
E) 5
A) 10
B) 12
C) 8
D) 9
E) 5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Max has the utility function U(x, y) = x(y + 1). The price of x is $2 and the price of y is $1. Income is $10. How much x does Max demand? How much y? If his income doubles and prices stay unchanged, will Max's demand for both goods double?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
If a consumer maximizes her preferences subject to her budget by choosing a consumption bundle where the ratio of her marginal utilities of shelter and food, 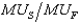 , is greater than the ratio of the prices of shelter and food,
, is greater than the ratio of the prices of shelter and food, 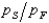 , then she must
, then she must
A) be consuming food but no shelter.
B) be consuming shelter but no food.
C) believe that shelter is a "bad."
D) be consuming both food and shelter.
E) not be spending all of her income.
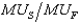 , is greater than the ratio of the prices of shelter and food,
, is greater than the ratio of the prices of shelter and food, 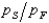 , then she must
, then she mustA) be consuming food but no shelter.
B) be consuming shelter but no food.
C) believe that shelter is a "bad."
D) be consuming both food and shelter.
E) not be spending all of her income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Clara's utility function is U(x, Y) = (x + 2)(Y + 1). If her marginal rate of substitution is -3 and she is consuming 12 units of good x, how many units of good Y must she be consuming?
A) 15
B) 46
C) 24
D) 41
E) 7
A) 15
B) 46
C) 24
D) 41
E) 7

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Mort's utility function is U(x1, x2) = x1x2. His income is $100. The price of good 2 is $10. Good 1 is priced as follows. The first 6 units cost $10 per unit and any additional units cost $5 per unit. What consumption bundle does Mort choose?
A) (5, 5)
B) (7, 3.5)
C) (9, 3)
D) (6, 4)
E) None of the above.
A) (5, 5)
B) (7, 3.5)
C) (9, 3)
D) (6, 4)
E) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Charlie has a utility function U(xA, xB) = xAxB, the price of apples is $1, and the price of bananas is $2. If Charlie's income were $120, how many units of bananas would he consume if he chose the bundle that maximized his utility subject to his budget constraint?
A) 30
B) 15
C) 60
D) 6
E) 90
A) 30
B) 15
C) 60
D) 6
E) 90

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Andrew's utility function is U(x1, x2) = 4x21 + x2. Andrew's income is $32, the price of good 1 is $16 per unit, and the price of good 2 is $1 per unit. What happens if Andrew's income increases to $80 and prices do not change? (Hint: Does he have convex preferences?)
A) He will consume 48 more units of good 2 and the same number of units of good 1 as before.
B) He will increase his consumption of both goods.
C) He will reduce his consumption of good 2.
D) He will consume the same number of units of good 2 and 3 more units of good 1 as before.
E) None of the above.
A) He will consume 48 more units of good 2 and the same number of units of good 1 as before.
B) He will increase his consumption of both goods.
C) He will reduce his consumption of good 2.
D) He will consume the same number of units of good 2 and 3 more units of good 1 as before.
E) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Ambrose's utility function is U(x1, x2) = 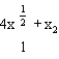 . If the price of nuts (good 1) is $1, the price of berries (good 2) is $5, and his income is $145, how many units of nuts will Ambrose choose?
. If the price of nuts (good 1) is $1, the price of berries (good 2) is $5, and his income is $145, how many units of nuts will Ambrose choose?
A) 100
B) 200
C) 9
D) 103
E) 50
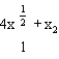 . If the price of nuts (good 1) is $1, the price of berries (good 2) is $5, and his income is $145, how many units of nuts will Ambrose choose?
. If the price of nuts (good 1) is $1, the price of berries (good 2) is $5, and his income is $145, how many units of nuts will Ambrose choose?A) 100
B) 200
C) 9
D) 103
E) 50

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Justin consumes goods x and y and has a utility function U(x, y) = x2 + y. The price per unit of x is px and the price per unit of y is py. He has enough money so that he can afford at least 1 unit of either good. When he chooses his best affordable bundle,
A) his budget line must be tangent to the indifference curve passing through this bundle.
B) he must consume only x.
C) he must consume only y ifexceeds his income.
D) he must consume some of each good if px = py.
E) he must consume some of each good if.
A) his budget line must be tangent to the indifference curve passing through this bundle.
B) he must consume only x.
C) he must consume only y ifexceeds his income.
D) he must consume some of each good if px = py.
E) he must consume some of each good if.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Angela consumes only two goods, x and y. Her income doubles and the prices of the two goods remain unchanged. Assuming that she is a utility maximizer and likes both goods,
A) she will consume more of both goods.
B) the ratio of her consumption of x to y remains constant.
C) her utility doubles.
D) if her preferences are convex, she must consume more x.
E) None of the above.
A) she will consume more of both goods.
B) the ratio of her consumption of x to y remains constant.
C) her utility doubles.
D) if her preferences are convex, she must consume more x.
E) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Clara's utility function is U(x, y) = (x + 2)(y + 1). If her marginal rate of substitution is -4 and she is consuming 14 units of good x, how many units of good y must she be consuming?
A) 30
B) 68
C) 18
D) 63
E) 9
A) 30
B) 68
C) 18
D) 63
E) 9

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Is the following statement true or false? Briefly explain your answer. "A utility maximizer will always choose a bundle at which his indifference curve is tangent to his budget line."

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Casper consumes cocoa and cheese. Cocoa is sold in an unusual way. There is only one supplier, and the more cocoa you buy from him, the higher the price you have to pay per unit. In fact y units of cocoa will cost Casper y2 dollars. Cheese is sold in the usual way at a price of 2 dollars per unit. Casper's income is 20 dollars and his utility function is U(x, y) = x + 2y, where x is his consumption of cheese and y is his consumption of cocoa.
a. Sketch Casper's budget set and shade it in.
b. Sketch some of his indifference curves and label the point that he chooses.
c. Calculate the amount of cheese and the amount of cocoa that Casper demands at these prices and this income.
a. Sketch Casper's budget set and shade it in.
b. Sketch some of his indifference curves and label the point that he chooses.
c. Calculate the amount of cheese and the amount of cocoa that Casper demands at these prices and this income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Max has a utility function U(x, y) = 2xy + 1. The prices of x and y are both $1 and Max has an income of $20.
a. How much of each good will he demand?
b. A tax is placed on x so that x now costs Max $2 while his income and the price of y stay the same. How much of good x does he now demand?
c. Would Max be as well off as he was before the tax if when the tax was imposed, his income rose by an amount equal to $1 times the answer to part (b)?
a. How much of each good will he demand?
b. A tax is placed on x so that x now costs Max $2 while his income and the price of y stay the same. How much of good x does he now demand?
c. Would Max be as well off as he was before the tax if when the tax was imposed, his income rose by an amount equal to $1 times the answer to part (b)?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








