Deck 11: Trade Policy in Developing Countries
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/43
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 11: Trade Policy in Developing Countries
1
Which trade strategy have developing countries used to restrict imports of manufactured goods so that the domestic market is preserved for home producers?
A) international commodity agreement
B) export promotion
C) multilateral contract
D) import substitution
E) export subsidies
A) international commodity agreement
B) export promotion
C) multilateral contract
D) import substitution
E) export subsidies
D
2
The infant industry argument calls for active government involvement
A) only if the government forecasts are accurate.
B) only if some market failure can be identified.
C) only if the industry is not one already dominated by industrial countries.
D) only if the industry has a high value added.
E) only if the industry is independently able to earn high returns.
A) only if the government forecasts are accurate.
B) only if some market failure can be identified.
C) only if the industry is not one already dominated by industrial countries.
D) only if the industry has a high value added.
E) only if the industry is independently able to earn high returns.
B
3
Which of the following could explain why the terms of trade of developing countries might deteriorate over time?
A) Developing country exports consist mainly of manufactured goods.
B) Developing country exports consist mainly of primary products.
C) Commodity export prices are determined in highly competitive markets.
D) Commodity export prices are solely determined by developing countries.
E) Developing country exports are too diverse.
A) Developing country exports consist mainly of manufactured goods.
B) Developing country exports consist mainly of primary products.
C) Commodity export prices are determined in highly competitive markets.
D) Commodity export prices are solely determined by developing countries.
E) Developing country exports are too diverse.
C
4
Brazil's export record in 1999 illustrated the principle that
A) a large country will tend to have few exports.
B) a small country will tend to have a high export ratio.
C) protectionist policies tend to discourage exports.
D) export-promoting policies do not tend to work.
E) import substitution policies helped the Brazilian economy.
A) a large country will tend to have few exports.
B) a small country will tend to have a high export ratio.
C) protectionist policies tend to discourage exports.
D) export-promoting policies do not tend to work.
E) import substitution policies helped the Brazilian economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
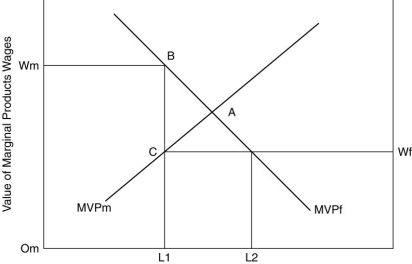
Refer to above figure. If OmL1 workers are employed in manufacturing then what is the marginal productivity of labor in manufacturing?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The imperfect capital market justification for infant industry promotion
A) assumes that new industries will tend to have low profits.
B) assumes that infant industries will soon mature.
C) assumes that infant industries will be in products of comparative advantage.
D) assumes that banks can allocate resources efficiently.
E) assumes that developing country will reward the donor country.
A) assumes that new industries will tend to have low profits.
B) assumes that infant industries will soon mature.
C) assumes that infant industries will be in products of comparative advantage.
D) assumes that banks can allocate resources efficiently.
E) assumes that developing country will reward the donor country.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A reason why it is difficult for developing countries to maintain a cartel is that
A) the elasticity of demand for a cartel's output decreases over time.
B) producers in the cartel have an economic incentive to cheat.
C) economic profits discourage other producers from entering the industry.
D) producers in the cartel have the motivation to lower prices but not to raise prices.
E) tariffs allow producers in the cartel to produce items that make no profit.
A) the elasticity of demand for a cartel's output decreases over time.
B) producers in the cartel have an economic incentive to cheat.
C) economic profits discourage other producers from entering the industry.
D) producers in the cartel have the motivation to lower prices but not to raise prices.
E) tariffs allow producers in the cartel to produce items that make no profit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Import substitution policies make use of
A) tariffs that discourage goods from entering a country.
B) quotas applied to goods that are shipped abroad.
C) production subsidies granted to industries with comparative advantage.
D) tax breaks granted to industries with comparative advantage.
E) production facilities provided by industrialized countries.
A) tariffs that discourage goods from entering a country.
B) quotas applied to goods that are shipped abroad.
C) production subsidies granted to industries with comparative advantage.
D) tax breaks granted to industries with comparative advantage.
E) production facilities provided by industrialized countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Sophisticated theoretical arguments supporting import-substitution policies include
A) terms of trade effects.
B) scale economy arguments.
C) learning curve considerations.
D) the problem of appropriability.
E) domestic market failure arguments.
A) terms of trade effects.
B) scale economy arguments.
C) learning curve considerations.
D) the problem of appropriability.
E) domestic market failure arguments.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10

Refer to above figure. If manufacturing labor were to increase to OmL2, how much value would the economy as a whole gain?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11

Refer to above figure. If OmL1 workers are employed in manufacturing then what is the marginal productivity of labor in agriculture?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The disappointment with import-substitution policies is in part because
A) of the rapid and continuous growth record of South American countries.
B) many countries pursuing this strategy experienced stagnation in their growth.
C) this policy is inconsistent with sophisticated economic growth models.
D) this policy tended to create world-class industrial competitors.
E) of the financial investment lost by the U.S.
A) of the rapid and continuous growth record of South American countries.
B) many countries pursuing this strategy experienced stagnation in their growth.
C) this policy is inconsistent with sophisticated economic growth models.
D) this policy tended to create world-class industrial competitors.
E) of the financial investment lost by the U.S.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
General equilibrium considerations lead to the realization that import-substituting policies have an effect of
A) discouraging exports.
B) encouraging exports.
C) encouraging an efficient use of a country's resources.
D) generating large tariff revenues for the government.
E) creating competitive manufacturing sectors.
A) discouraging exports.
B) encouraging exports.
C) encouraging an efficient use of a country's resources.
D) generating large tariff revenues for the government.
E) creating competitive manufacturing sectors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The United States, as it began its long and successful growth in the early 19th century, consciously promoted domestic production through such activities as tariffs, Clay's American System, and many direct subsidies to railroads, canal companies, farmers (free land) etc. Today we view this blatant example of large scale and extensive import-substitution industrialization as having been very successful. Comment on this.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The high correlation between rapid growth in exports and rapid economic growth observed in several East Asia countries in recent decades
A) proves that export promoting trade policy leads to relatively rapid economic growth.
B) proves that a free-trade orientation of trade policy results in rapid economic growth.
C) proves that exports help growth, whereas imports impede growth.
D) proves that trade policy is the most important policy area for promotion of economic development.
E) does not prove that trade liberalization always leads to rapid economic growth.
A) proves that export promoting trade policy leads to relatively rapid economic growth.
B) proves that a free-trade orientation of trade policy results in rapid economic growth.
C) proves that exports help growth, whereas imports impede growth.
D) proves that trade policy is the most important policy area for promotion of economic development.
E) does not prove that trade liberalization always leads to rapid economic growth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
It is argued that import substitution is a misguided trade policy if the intent is to promote long-term economic growth. Explain the reasons underlying this argument.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17

Refer to above figure. Why would workers not shift from agriculture to manufacturing in the initial situation where wages are higher in the latter?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The infant industry argument was an important theoretical basis for
A) neo-colonialist theory of international exploitation.
B) import-substituting industrialization.
C) historiography of the industrial revolution in Western Europe.
D) the East-Asian miracle.
E) the reduction of tariffs on Western Europe.
A) neo-colonialist theory of international exploitation.
B) import-substituting industrialization.
C) historiography of the industrial revolution in Western Europe.
D) the East-Asian miracle.
E) the reduction of tariffs on Western Europe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The infant industry argument is that
A) comparative advantage is irrelevant to economic growth.
B) developing countries have a comparative advantage in agricultural goods.
C) developing countries have a comparative advantage in manufacturing.
D) developing countries have a potential comparative advantage in manufacturing.
E) developing countries have no chance to compete with industrialized countries.
A) comparative advantage is irrelevant to economic growth.
B) developing countries have a comparative advantage in agricultural goods.
C) developing countries have a comparative advantage in manufacturing.
D) developing countries have a potential comparative advantage in manufacturing.
E) developing countries have no chance to compete with industrialized countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20

Refer to above figure. If the economy were in the initial position (where OmL1 workers were in manufacturing, what trade policy might gain ABC of economic welfare?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The relatively rapid economic growth experienced by Chile in the late 1980s
A) supported the conventional Latin American reliance on import substitution.
B) relied on the Harris-Todaro model to explain this growth.
C) rejected the conventional Latin American reliance on import substitution.
D) demonstrated the importance of market failure as a reason for import substitution.
E) relied on high tariffs and import substitution.
A) supported the conventional Latin American reliance on import substitution.
B) relied on the Harris-Todaro model to explain this growth.
C) rejected the conventional Latin American reliance on import substitution.
D) demonstrated the importance of market failure as a reason for import substitution.
E) relied on high tariffs and import substitution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
In 2003, the per-capita income in China was roughly ________ of that in the U.S.
A) one hundredth
B) one eighth
C) one half
D) the same as
E) one twentieth
A) one hundredth
B) one eighth
C) one half
D) the same as
E) one twentieth

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
China's recent experience supports the proposition that
A) "economic miracles" are solely to be expected in small countries.
B) central planning and socialism can promote sustained economic growth.
C) a lessening of income disparities is a prerequisite for economic growth.
D) growth in a large country cannot be affected by its foreign sector.
E) policy changed can dramatically prompt export oriented growth
A) "economic miracles" are solely to be expected in small countries.
B) central planning and socialism can promote sustained economic growth.
C) a lessening of income disparities is a prerequisite for economic growth.
D) growth in a large country cannot be affected by its foreign sector.
E) policy changed can dramatically prompt export oriented growth

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The growth successes of the high performance Asian economies
A) supports the belief that economic development requires import substitution policies.
B) rejects the belief that export-oriented industrialization is likely to promote economic development.
C) rejects the belief that economic development requires import substitution policies.
D) suggests that free trade policies are required for successful economic development.
E) enforces United States' hesitation to trade with developing countries.
A) supports the belief that economic development requires import substitution policies.
B) rejects the belief that export-oriented industrialization is likely to promote economic development.
C) rejects the belief that economic development requires import substitution policies.
D) suggests that free trade policies are required for successful economic development.
E) enforces United States' hesitation to trade with developing countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
To help developing nations strengthen their international competitiveness, many industrial nations have granted tariff reductions to developing nations under the
A) international commodity agreements program.
B) multilateral contract program.
C) generalized system of preferences program.
D) export led growth program.
E) import substitution policy.
A) international commodity agreements program.
B) multilateral contract program.
C) generalized system of preferences program.
D) export led growth program.
E) import substitution policy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Historically those few developing countries which have succeeded in significantly raising their per-capita income levels
A) did not accomplish this with import-substituting industrialization.
B) did accomplish this with import-substituting industrialization.
C) tended to provide heavy protection to domestic industrial sectors.
D) favored industrial to agricultural or service sectors.
E) did so to the detriment of their nearest neighbors.
A) did not accomplish this with import-substituting industrialization.
B) did accomplish this with import-substituting industrialization.
C) tended to provide heavy protection to domestic industrial sectors.
D) favored industrial to agricultural or service sectors.
E) did so to the detriment of their nearest neighbors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Which industrialization policy used by developing countries places emphasis on the comparative advantage principle as a guide to resource allocation?
A) xport promotion
B) import substitution
C) international commodity agreements
D) Infant Industry promotion
E) intra-industry trade practice
A) xport promotion
B) import substitution
C) international commodity agreements
D) Infant Industry promotion
E) intra-industry trade practice

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Taiwan and South Korea are examples of developing nations that have recently pursued these industrialization policies
A) import substitution.
B) export promotion.
C) commercial dumping.
D) multilateral contract.
E) trade embargoes.
A) import substitution.
B) export promotion.
C) commercial dumping.
D) multilateral contract.
E) trade embargoes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
An efficient economy would set the marginal product in the traditional sector
A) lower than that in the modern non-traditional sector.
B) higher than that in the modern sophisticated sector.
C) equal to that in the modern sophisticated sector.
D) lower in the relatively capital intensive sector.
E) higher in the relatively capital intensive sector.
A) lower than that in the modern non-traditional sector.
B) higher than that in the modern sophisticated sector.
C) equal to that in the modern sophisticated sector.
D) lower in the relatively capital intensive sector.
E) higher in the relatively capital intensive sector.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The experience of Chile's foreign sector in the last two decades of the 20th century supports the proposition that economic growth is supported by
A) import substitution.
B) industrialization policies.
C) trade liberalization policies.
D) intra-industry trading.
E) trade embargoes.
A) import substitution.
B) industrialization policies.
C) trade liberalization policies.
D) intra-industry trading.
E) trade embargoes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Statistical evidence suggests that
A) free trade policies promote economic growth more effectively than do import substitution policies.
B) import substituting policies tend to promote effective exploitation of scale economies.
C) import substitution tends to lead to relatively low effective rates of protection.
D) import substitution is to this day the preferred growth strategy promoted by the World Bank.
E) import substitution proved to be the most effective aid for developing countries before 1970.
A) free trade policies promote economic growth more effectively than do import substitution policies.
B) import substituting policies tend to promote effective exploitation of scale economies.
C) import substitution tends to lead to relatively low effective rates of protection.
D) import substitution is to this day the preferred growth strategy promoted by the World Bank.
E) import substitution proved to be the most effective aid for developing countries before 1970.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The HPAE (High Performance Asian Economies) countries
A) have all consistently supported free trade policies.
B) have all consistently maintained import-substitution policies.
C) have all consistently maintained non-biased efficient free capital markets.
D) have all maintained openness to international trade.
E) have all outperformed the U.S.
A) have all consistently supported free trade policies.
B) have all consistently maintained import-substitution policies.
C) have all consistently maintained non-biased efficient free capital markets.
D) have all maintained openness to international trade.
E) have all outperformed the U.S.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Export-led growth tends to
A) discourage competition in the global economy.
B) exploit domestic comparative advantages.
C) lead to unemployment among domestic workers.
D) help firms benefit from diseconomies of large-scale production.
E) lower the overall volume of imports.
A) discourage competition in the global economy.
B) exploit domestic comparative advantages.
C) lead to unemployment among domestic workers.
D) help firms benefit from diseconomies of large-scale production.
E) lower the overall volume of imports.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The "East Asian Miracle" is
A) the ability of so many people to live in such small areas.
B) the fact that so many Influenza varieties originate from this region.
C) the fact that poor dualistic economies managed to escape the vicious circle of poverty.
D) the ability to maintain large positive trade balances with the U.S.
E) the advent of completely free labor mobility between east Asian countries.
A) the ability of so many people to live in such small areas.
B) the fact that so many Influenza varieties originate from this region.
C) the fact that poor dualistic economies managed to escape the vicious circle of poverty.
D) the ability to maintain large positive trade balances with the U.S.
E) the advent of completely free labor mobility between east Asian countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
All the following nations except ________ have recently utilized export-led growth policies.
A) Hong Kong
B) South Korea
C) Argentina
D) Singapore
E) Taiwan
A) Hong Kong
B) South Korea
C) Argentina
D) Singapore
E) Taiwan

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The remarkable success of the HPAEs proves that
A) trade policy is the key to successful economic growth.
B) trade policy is irrelevant to successful economic growth.
C) high educational standards is the key to successful economic growth.
D) dual economies must suffer economic stagnation.
E) trade policy can lead to a higher standard of living for developing countries.
A) trade policy is the key to successful economic growth.
B) trade policy is irrelevant to successful economic growth.
C) high educational standards is the key to successful economic growth.
D) dual economies must suffer economic stagnation.
E) trade policy can lead to a higher standard of living for developing countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The consensus today is that import-substitution protectionist industrial policy has not served the developing countries' growth ambitions well. This fact proves that policies relying on export-driven growth are the "winning ticket" for these countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The experience of sub-Saharan Africa, as compared to that of "Other Asia" (not including the HPAEs) supports the argument that
A) high rates of protection tend to harm economic growth.
B) the poorer is the country the easier it is for it to "catch up" economically.
C) low rates of protection tend to promote economic growth.
D) free trade always best stimulates a developing country's economy.
E) neither trade liberalization nor import substitution is a foolproof strategy for economic development.
A) high rates of protection tend to harm economic growth.
B) the poorer is the country the easier it is for it to "catch up" economically.
C) low rates of protection tend to promote economic growth.
D) free trade always best stimulates a developing country's economy.
E) neither trade liberalization nor import substitution is a foolproof strategy for economic development.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
The development of countries like South Korea has been supported by all of the following except
A) high domestic interest rates.
B) high domestic saving rates.
C) large endowments of human capital.
D) high levels of labor productivity.
E) reduced government regulation.
A) high domestic interest rates.
B) high domestic saving rates.
C) large endowments of human capital.
D) high levels of labor productivity.
E) reduced government regulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
To help developing countries expand their industrial base, some industrial countries have reduced tariffs on designated manufactured imports from developing countries below the levels applied to imports from industrial countries. This policy is called
A) export-led growth.
B) generalized system of preferences.
C) Most Favored Nation.
D) reciprocal trade agreement.
E) outsourcing.
A) export-led growth.
B) generalized system of preferences.
C) Most Favored Nation.
D) reciprocal trade agreement.
E) outsourcing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The HPAE "economic miracle" illustrates a clear case in which
A) exports and growth were positively related.
B) exports were promoted by successful economic growth.
C) economic growth was determined by successful export promotion.
D) trade policy dominated other considerations in promoting economic growth.
E) import substitution enhanced economic development.
A) exports and growth were positively related.
B) exports were promoted by successful economic growth.
C) economic growth was determined by successful export promotion.
D) trade policy dominated other considerations in promoting economic growth.
E) import substitution enhanced economic development.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Classical and Neoclassical trade theory makes the case that free trade can bring a country to an optimum and economically efficient use of its resources; and hence is an optimal trade-policy, if the objective is maximizing long term economic growth. There are those who argue that the experience of the Asian Miracle countries, such as Taiwan, South Korea and Singapore verify this argument in the real world. Explain. There are others who argue that the experience of these countries cannot be used to verify or support the argument above. Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The "East Asian Miracle" of the "Four Tigers" in the 1960s was replicated by
A) developing countries around the world.
B) other East Asian countries.
C) Sub Sahara African countries.
D) Industrialized countries.
E) Eastern European countries.
A) developing countries around the world.
B) other East Asian countries.
C) Sub Sahara African countries.
D) Industrialized countries.
E) Eastern European countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 43 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








