Deck 12: Riches in Rock: Energy and Mineral Resources
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 12: Riches in Rock: Energy and Mineral Resources
1
Which of the following petroleum product would be the least viscous?
A) heating oil
B) gasoline
C) motor oil
D) tar
A) heating oil
B) gasoline
C) motor oil
D) tar
B
2
Chemically,oil and gas are both examples of ________.
A) carbon-bearing minerals
B) carbohydrates
C) hydrocarbons
D) carbonate minerals
A) carbon-bearing minerals
B) carbohydrates
C) hydrocarbons
D) carbonate minerals
C
3
Oil taken directly from the ground,without treatment at a refinery,is termed ________.
A) crude oil
B) raw oil
C) crass oil
D) kerogen
A) crude oil
B) raw oil
C) crass oil
D) kerogen
A
4
A rock that has the potential to generate oil or gas if subjected to elevated temperature and pressure is known as a
A) kerogen.
B) coal.
C) source rock.
D) reservoir rock.
A) kerogen.
B) coal.
C) source rock.
D) reservoir rock.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
To produce a commercially viable oil deposit,there must be a source rock,a reservoir rock,a seal rock,and a(n)________.
A) large fracture connecting the reservoir rock to the surface of the Earth
B) porous filter rock that removes impurities
C) igneous heater rock that heats the oil and gives it buoyancy
D) trap that denies the oil passage to the surface
A) large fracture connecting the reservoir rock to the surface of the Earth
B) porous filter rock that removes impurities
C) igneous heater rock that heats the oil and gives it buoyancy
D) trap that denies the oil passage to the surface

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Given a typical geothermal gradient of 25°C/km,oil is generated from kerogen at ______,corresponding to temperatures of _____.
A) 100-400 m; 25-45°C
B) 3.5-6.5 km; 90-150°C
C) 1.0-2.5 km; 50-80°C
D) 7.0-10.0 km; 180-360°C
A) 100-400 m; 25-45°C
B) 3.5-6.5 km; 90-150°C
C) 1.0-2.5 km; 50-80°C
D) 7.0-10.0 km; 180-360°C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Global use of fossil fuels today is approximately __________ as/than it was in the year 1920. 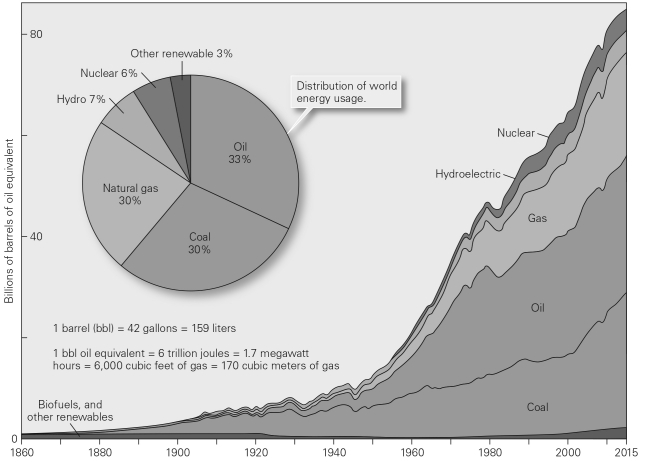
A) ten times greater
B) 50 percent greater
C) twice as large
D) half as large

A) ten times greater
B) 50 percent greater
C) twice as large
D) half as large

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
_______ describes how much of a rock consists of open pore spaces,while _______ describes how well-connected pore spaces allow gases and liquid to flow through the rock.
A) Permeability; porosity
B) Viscosity; migration
C) Porosity; permeability
D) Density; migration
A) Permeability; porosity
B) Viscosity; migration
C) Porosity; permeability
D) Density; migration

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Most of the world's energy supply comes from ________.
A) fossil fuels
B) wind
C) nuclear power
D) water
A) fossil fuels
B) wind
C) nuclear power
D) water

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Why is a trap necessary to create a conventional reserve? 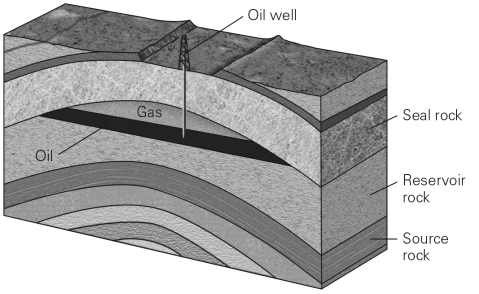
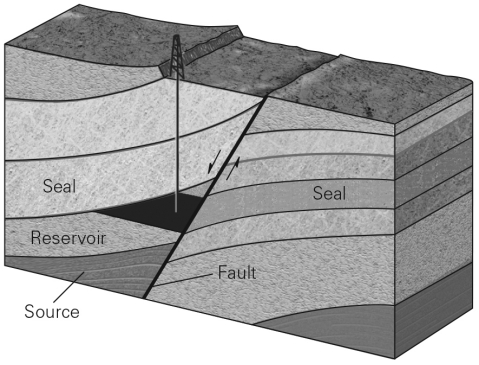
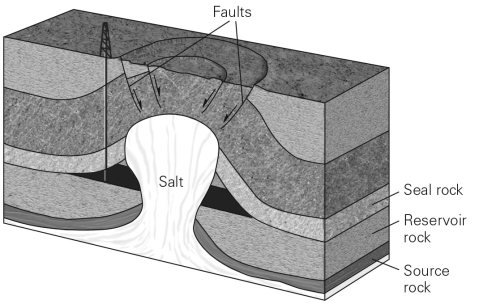
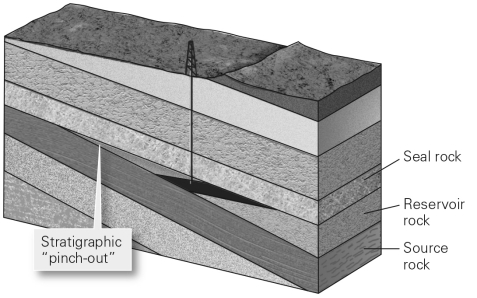
A) Without a trap,temperatures within the Earth would be too high for hydrocarbon formation.
B) A trap is the porous and permeable reservoir in which conventional hydrocarbon reserves reside.
C) A trap is the source rock for the accumulation and creation of hydrocarbon resources.
D) Without a trap,hydrocarbons would rise buoyantly and seep onto the Earth's surface.




A) Without a trap,temperatures within the Earth would be too high for hydrocarbon formation.
B) A trap is the porous and permeable reservoir in which conventional hydrocarbon reserves reside.
C) A trap is the source rock for the accumulation and creation of hydrocarbon resources.
D) Without a trap,hydrocarbons would rise buoyantly and seep onto the Earth's surface.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
As an energy supply,the use of fossil fuels relies on ________.
A) fusion,where light radioactive atoms are bombarded with protons and neutrons to yield energy
B) combustion,where materials are burned in reactions with oxygen to yield energy
C) fission,where heavy radioactive atoms split apart to release protons,neutrons,and energy
D) gravitation,where potential energy is released when material descends in elevation
A) fusion,where light radioactive atoms are bombarded with protons and neutrons to yield energy
B) combustion,where materials are burned in reactions with oxygen to yield energy
C) fission,where heavy radioactive atoms split apart to release protons,neutrons,and energy
D) gravitation,where potential energy is released when material descends in elevation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
In which geologic setting are oil and gas reserves most likely to be found?
A) in volcanic arcs adjacent to a subduction zone
B) in continent-continent collision zones with low-grade regional metamorphism
C) in the accretionary wedge sediments along a subduction zone
D) in sedimentary basins along passive continental margins
A) in volcanic arcs adjacent to a subduction zone
B) in continent-continent collision zones with low-grade regional metamorphism
C) in the accretionary wedge sediments along a subduction zone
D) in sedimentary basins along passive continental margins

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Which of the following would make the best reservoir rock in a conventional hydrocarbon system?
A) high-porosity,high-permeability rock
B) low-porosity,low-permeability rock
C) high-porosity,low-permeability rock
D) low-porosity,high-permeability rock
A) high-porosity,high-permeability rock
B) low-porosity,low-permeability rock
C) high-porosity,low-permeability rock
D) low-porosity,high-permeability rock

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Most of the hydrocarbons within oil and natural gas are derived from the breakdown of organic matter from once-living ________.
A) dinosaurs
B) plankton
C) terrestrial plants
D) mammals
A) dinosaurs
B) plankton
C) terrestrial plants
D) mammals

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Most of the world's energy and mineral resources derive from
A) solar materials and processes.
B) geologic materials and processes.
C) hydrosphere materials and process.
D) biological materials and processes.
A) solar materials and processes.
B) geologic materials and processes.
C) hydrosphere materials and process.
D) biological materials and processes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
An impermeable rock,regardless of lithology,is a good candidate to serve as a(n)________ in an oil-producing scenario.
A) reservoir rock
B) seal rock
C) source rock
D) unconventional rock
A) reservoir rock
B) seal rock
C) source rock
D) unconventional rock

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
A permeable and porous rock,regardless of lithology,is a good candidate to serve as a ________ in an oil-producing scenario.
A) reservoir rock
B) seal rock
C) source rock
D) filter rock
A) reservoir rock
B) seal rock
C) source rock
D) filter rock

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Oil and gas source rocks are always __________.
A) igneous
B) sedimentary
C) metamorphic
D) porous
A) igneous
B) sedimentary
C) metamorphic
D) porous

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which of the following lists contains only fossil fuels?
A) coal,oil,natural gas
B) coal,geothermal,wind
C) coal,wood,natural gas
D) hydroelectric,geothermal,wind
A) coal,oil,natural gas
B) coal,geothermal,wind
C) coal,wood,natural gas
D) hydroelectric,geothermal,wind

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Conventional oil and gas reserves are those
A) that occur in belts or zones in the subsurface.
B) that can be drilled into on land.
C) from which oil and gas can be pumped relatively easily.
D) in which the source rock is also the reservoir rock.
A) that occur in belts or zones in the subsurface.
B) that can be drilled into on land.
C) from which oil and gas can be pumped relatively easily.
D) in which the source rock is also the reservoir rock.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Drilling for an oil or gas well that allows the well bore to bend in curves and extend for long distances within an underground target is called 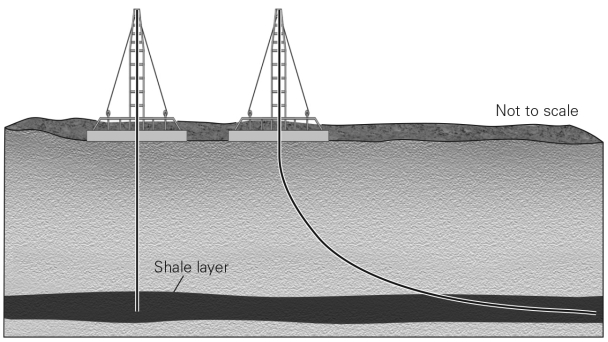
A) hydraulic fracturing.
B) seismic reflection profiling.
C) directional drilling.
D) conventional drilling.

A) hydraulic fracturing.
B) seismic reflection profiling.
C) directional drilling.
D) conventional drilling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Uranium,the fuel that drives nuclear energy,is found in which geologic setting?
A) in the zone of contact metamorphism along ultramafic intrusions
B) in the mineral deposits adjacent to hydrothermal vents at mid-ocean ridges
C) in Precambrian sandstones deposited before the Earth's atmosphere contained oxygen
D) in fracture-filling veins where hydrothermal fluids circulated through granitic plutons
A) in the zone of contact metamorphism along ultramafic intrusions
B) in the mineral deposits adjacent to hydrothermal vents at mid-ocean ridges
C) in Precambrian sandstones deposited before the Earth's atmosphere contained oxygen
D) in fracture-filling veins where hydrothermal fluids circulated through granitic plutons

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Gypsum,sand,and copper ore are examples of _______.
A) energy resources
B) renewable resources
C) mineral resources
D) unconventional resources
A) energy resources
B) renewable resources
C) mineral resources
D) unconventional resources

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which sequence correctly shows an increase in coal rank from lowest to highest?
A) anthracite,bituminous,lignite
B) lignite,bituminous,anthracite
C) bituminous,lignite,anthracite
D) bituminous,anthracite,lignite
A) anthracite,bituminous,lignite
B) lignite,bituminous,anthracite
C) bituminous,lignite,anthracite
D) bituminous,anthracite,lignite

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A resource is considered renewable if ________.
A) it is used at rates greater than it is naturally replaced
B) nature can replace it within a short time span relative to human consumption
C) nature can replace it within hundreds or thousands of years
D) nature can replace it within a million years
A) it is used at rates greater than it is naturally replaced
B) nature can replace it within a short time span relative to human consumption
C) nature can replace it within hundreds or thousands of years
D) nature can replace it within a million years

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Most ores belong to which mineral class(es)?
A) sulfates and halides
B) silicates
C) sulfides and oxides
D) phosphates
A) sulfates and halides
B) silicates
C) sulfides and oxides
D) phosphates

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
In which geologic setting were most of the world's coal reserves deposited?
A) Precambrian fluvial and shallow marine systems
B) shallow epicontinental seas with abundant carbonate-producing organisms
C) tropical and subtropical fluvial and shallow marine systems where swamps could occur
D) in sedimentary basins along passive continental margins
A) Precambrian fluvial and shallow marine systems
B) shallow epicontinental seas with abundant carbonate-producing organisms
C) tropical and subtropical fluvial and shallow marine systems where swamps could occur
D) in sedimentary basins along passive continental margins

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which is the most abundant gas produced from the burning of coal,oil,and natural gas?
A) sulfur dioxide
B) carbon monoxide
C) carbon dioxide
D) oxygen
A) sulfur dioxide
B) carbon monoxide
C) carbon dioxide
D) oxygen

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Nonmetals extracted from metals during smelting are termed ________.
A) slag
B) cull
C) sludge
D) spar
A) slag
B) cull
C) sludge
D) spar

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
________ create(s)an easy route for oil to follow from the rock to a well.
A) Hydrofracking
B) Seismic reflection
C) Drilling mud
D) Pumps
A) Hydrofracking
B) Seismic reflection
C) Drilling mud
D) Pumps

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
_______ is an environmental issue in which groundwater and surface water can become polluted with sulfuric acid that is produced when sulfur-bearing minerals are exposed to conditions at the Earth's surface.
A) Ocean acidification
B) Acid mine runoff
C) Mountain-top removal
D) Strip mining
A) Ocean acidification
B) Acid mine runoff
C) Mountain-top removal
D) Strip mining

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Which of the following is a renewable energy resource?
A) coal
B) oil
C) wind
D) natural gas
A) coal
B) oil
C) wind
D) natural gas

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Which of the following is a metallic mineral resource?
A) gypsum
B) bauxite
C) phosphate
D) gravel
A) gypsum
B) bauxite
C) phosphate
D) gravel

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Metals are very useful to modern society because they _______ and ___________.
A) are expensive; are rare
B) conduct electricity; are malleable
C) are widely available; replace fossil fuels
D) generate electricity; are renewable
A) are expensive; are rare
B) conduct electricity; are malleable
C) are widely available; replace fossil fuels
D) generate electricity; are renewable

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Nuclear energy relies on ________.
A) fusion,where light radioactive atoms are bombarded with protons and neutrons to yield energy
B) combustion,where chemically reduced elements react with oxygen to yield energy
C) fission,where heavy radioactive atoms split apart to release protons,neutrons,and energy
D) gravitation,where potential energy is released when material descends in elevation
A) fusion,where light radioactive atoms are bombarded with protons and neutrons to yield energy
B) combustion,where chemically reduced elements react with oxygen to yield energy
C) fission,where heavy radioactive atoms split apart to release protons,neutrons,and energy
D) gravitation,where potential energy is released when material descends in elevation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
________ is harnessed from the potential energy of water.
A) Hydroelectric power
B) Solar energy
C) Biofuel
D) Hydrologic energy
A) Hydroelectric power
B) Solar energy
C) Biofuel
D) Hydrologic energy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Iceland and New Zealand are two places in the world where geothermal energy provides a cost-effective energy resource because ________. 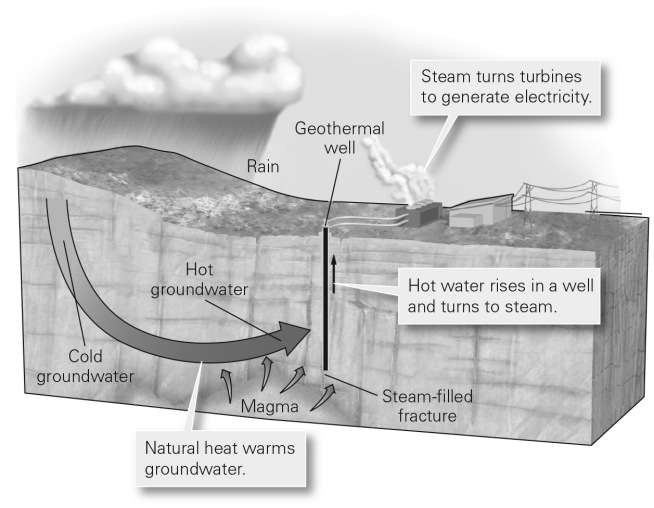
A) these are places where there is ample groundwater
B) these are places where high temperatures exist at relatively shallow depths
C) these are places without other sources of energy
D) these are places where laws prohibit use of fossil fuels

A) these are places where there is ample groundwater
B) these are places where high temperatures exist at relatively shallow depths
C) these are places without other sources of energy
D) these are places where laws prohibit use of fossil fuels

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
________ is/are an example of unconventional hydrocarbon sources.
A) Gas hydrate
B) Tar sands
C) Coal
D) Natural gas
A) Gas hydrate
B) Tar sands
C) Coal
D) Natural gas

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Coal is formed when heat and pressure alter deposits of ancient ________.
A) kerogen
B) plankton
C) terrestrial plants
D) tar
A) kerogen
B) plankton
C) terrestrial plants
D) tar

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The industrial process that separates metals from ore material is known as ____________.
A) quarrying
B) mountaintop removal mining
C) smelting
D) ore processing
A) quarrying
B) mountaintop removal mining
C) smelting
D) ore processing

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
In the geologic setting shown in the picture,the dense minerals of the ore are concentrated in stream sediments after eroding,while less dense minerals are washed away.This is known as a 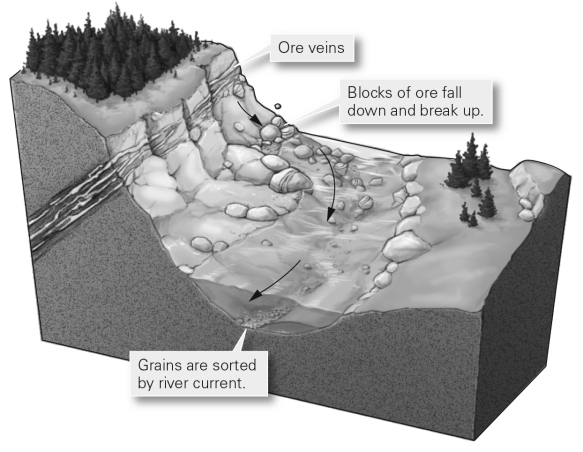
A) massive sulfide deposit.
B) residual mineral deposit.
C) sedimentary deposit.
D) placer.

A) massive sulfide deposit.
B) residual mineral deposit.
C) sedimentary deposit.
D) placer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Categorize the differences between a renewable and nonrenewable resource.What are some examples of each?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
How does a nuclear power plant generate electricity?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Smelting is a technique applied to ________.
A) native metals
B) ore minerals
C) quarried stone
D) alloys
A) native metals
B) ore minerals
C) quarried stone
D) alloys

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Explain how sources of energy for society have changed over time.Be sure to include both the timescale of this figure as well as likely energy sources prior to 1860. 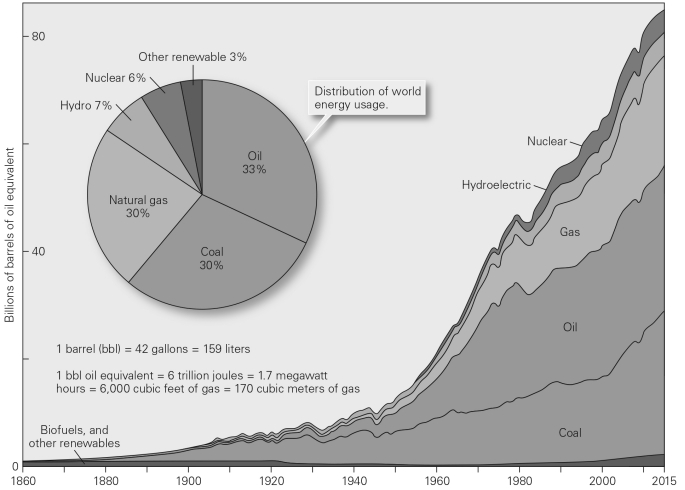


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Which of these best describes the sustainability of most mineral resources?
A) They are renewable because they are naturally formed.
B) They are renewable because we use them at slower rates than they are formed.
C) They are nonrenewable because they are formed at slower rates than we use them.
D) They are nonrenewable because they are no longer formed.
A) They are renewable because they are naturally formed.
B) They are renewable because we use them at slower rates than they are formed.
C) They are nonrenewable because they are formed at slower rates than we use them.
D) They are nonrenewable because they are no longer formed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Describe the different types of rock structures that can create hydrocarbon traps and the tools that geologists could use to discover these traps.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
How is oil formed? Make sure to address what organisms must accumulate,in what environment they must be deposited,and how the oil window affects the formation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
_________ is a construction product formed by heating limestone,sandstone,and shale in a kiln,driving off CO2,and forming a material that hardens when mixed with water.
A) Dimension stone
B) Aggregate
C) Cement
D) Drywall
A) Dimension stone
B) Aggregate
C) Cement
D) Drywall

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Aluminum atoms are found in feldspars,which are a common mineral component of granite.Why then is granite NOT mined as an ore for aluminum? If not from granite,how do we obtain metals like aluminum?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
The blocks of rock used in construction are termed ________.
A) dimension stone
B) gemstone
C) ore
D) lodestone
A) dimension stone
B) gemstone
C) ore
D) lodestone

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
________ is a nonmetal evaporite mineral used in the construction of interior walls in homes and other buildings.
A) Sulfur
B) Gypsum
C) Zinc
D) Marble
A) Sulfur
B) Gypsum
C) Zinc
D) Marble

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
How are ore deposits distributed among the countries around the globe? What are strategic minerals? Why is international trade necessary to ensure the supply of different minerals?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Waste rock left over after a mine has removed the ore is known as ________.
A) tailings
B) adits
C) ingots
D) slag
A) tailings
B) adits
C) ingots
D) slag

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
How does coal form? How does this process differ from the ones that yield oil and gas?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Stone used for buildings,chemicals in fertilizers,and sand used to make glass are all examples of mineral resources known as ________.
A) tailings
B) industrial minerals
C) clinker
D) slag
A) tailings
B) industrial minerals
C) clinker
D) slag

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
What is meant by the term fossil fuel? Where did the energy in a fossil fuel originate? What three energy resources are fossil fuels?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
A ________ is a type of ore deposit that forms when sulfide minerals crystallize in lenses or bands directly from magma.
A) hydrothermal ore
B) placer
C) Mississippi-Valley-Type deposit
D) massive sulfide deposit
A) hydrothermal ore
B) placer
C) Mississippi-Valley-Type deposit
D) massive sulfide deposit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Despite the fact that nonrenewable energy resources will eventually run out and that many tend to be large sources of pollution,why are they still used so prevalently in our society?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
A drawback to mining of sulfide minerals is the risk of ________.
A) underground fires
B) tunnel collapse
C) rock bursts
D) acid mine runoff
A) underground fires
B) tunnel collapse
C) rock bursts
D) acid mine runoff

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








