Deck 8: A Violent Pulse: Earthquakes
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: A Violent Pulse: Earthquakes
1
Faulting and earthquakes are examples of what type of deformation?
A) brittle
B) elastic
C) ductile
D) fluid
A) brittle
B) elastic
C) ductile
D) fluid
A
2
At any point along the surface of any nonvertical fault,as is shown in the figure below,the 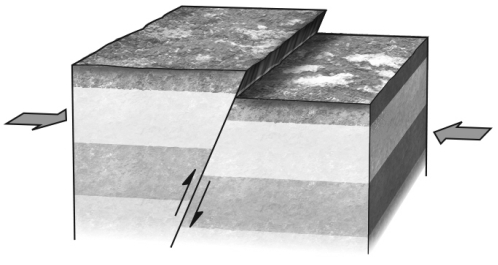
A) hanging wall lies vertically above the footwall.
B) footwall lies vertically above the hanging wall.
C) hanging wall lies to the left of the footwall.
D) footwall lies to the left of the hanging wall.

A) hanging wall lies vertically above the footwall.
B) footwall lies vertically above the hanging wall.
C) hanging wall lies to the left of the footwall.
D) footwall lies to the left of the hanging wall.
A
3
The displacement that occurs during the largest earthquakes can be as long as
A) several millimeters.
B) several centimeters.
C) several meters.
D) several kilometers.
A) several millimeters.
B) several centimeters.
C) several meters.
D) several kilometers.
C
4
If a fault is nearly vertical in orientation and the two walls of rock on opposite sides slide past one another horizontally,the fault is termed a ________ fault.Refer to the figure below for an example of such a feature. 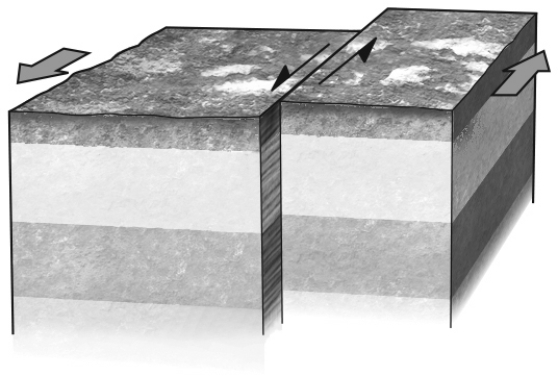
A) normal
B) reverse
C) strike-slip
D) thrust

A) normal
B) reverse
C) strike-slip
D) thrust

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Geologists who specifically study earthquakes are called
A) seismologists.
B) paleontologists.
C) volcanologists.
D) speleologists.
A) seismologists.
B) paleontologists.
C) volcanologists.
D) speleologists.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
During an earthquake,if a hanging wall slides downward relative to a footwall,the fault is termed a ________ fault.Refer to the figure below for an example of such a feature. 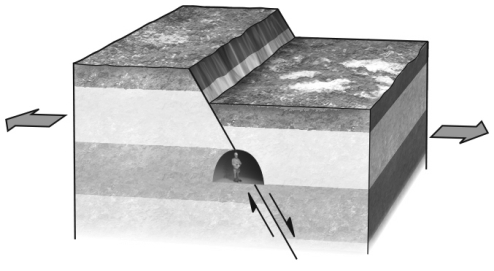
A) normal
B) reverse
C) strike-slip
D) thrust

A) normal
B) reverse
C) strike-slip
D) thrust

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The intersection between a fault plane and the ground surface is called the
A) dip line.
B) plunge.
C) fault trace.
D) seismic interface.
A) dip line.
B) plunge.
C) fault trace.
D) seismic interface.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Faults that have moved recently or are likely to move in the future are referred to as ________ faults.
A) passive
B) active
C) normal
D) reverse
A) passive
B) active
C) normal
D) reverse

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
A ____________ is a scientific instrument used to record the ground motions produced by an earthquake.
A) seismic wave
B) seismometer
C) tidal gauge
D) strain gauge
A) seismic wave
B) seismometer
C) tidal gauge
D) strain gauge

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
During an earthquake,if the hanging wall slides upward relative to the footwall,the fault is termed a ________ fault if the fault is steep (closer to vertical than horizontal).Refer to the figure below for an example of such a feature. 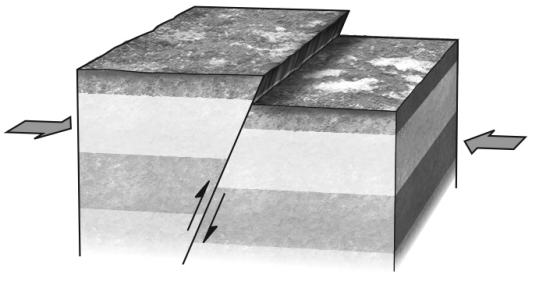
A) normal
B) reverse
C) strike-slip
D) thrust

A) normal
B) reverse
C) strike-slip
D) thrust

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The point within the Earth where an earthquake originates is termed the
A) hypocenter (focus).
B) epicenter.
C) eye of the fault.
D) vertex.
A) hypocenter (focus).
B) epicenter.
C) eye of the fault.
D) vertex.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Aftershocks after a major earthquake
A) may continue for days,weeks,or years after the initial earthquake.
B) are equivalent in magnitude to the original earthquake.
C) always occur on the same fault as the original earthquake.
D) typically occur only on reverse faults in subduction zones as a result of high pressures.
A) may continue for days,weeks,or years after the initial earthquake.
B) are equivalent in magnitude to the original earthquake.
C) always occur on the same fault as the original earthquake.
D) typically occur only on reverse faults in subduction zones as a result of high pressures.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Periods of intermittent sliding on a fault because of stress release during episodes of slip,followed by stress buildup to the point that the fault is reactivated,are termed
A) chaotic faulting.
B) thrust faulting.
C) stick-slip behavior.
D) reverse faulting.
A) chaotic faulting.
B) thrust faulting.
C) stick-slip behavior.
D) reverse faulting.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Before an earthquake,rocks can respond to applied stress to a small degree by bending and warping without breaking.This is termed _________.
A) elastic behavior
B) faulting
C) seismic velocity
D) brittle deformation
A) elastic behavior
B) faulting
C) seismic velocity
D) brittle deformation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Faults occur in many locations,but most faults had displacement in the distant past and are unlikely to move again in the future.This means that most faults are
A) active faults.
B) thrust faults.
C) inactive faults.
D) submarine faults.
A) active faults.
B) thrust faults.
C) inactive faults.
D) submarine faults.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The energy that is released during an earthquake travels through the Earth as vibrations termed _______.
A) gravity waves
B) tsunamis
C) seismic waves
D) sound waves
A) gravity waves
B) tsunamis
C) seismic waves
D) sound waves

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
An earthquake occurs with an epicenter in the town of New Madrid,Missouri,in the interior of the North American Plate.What is the most likely location of the hypocenter?
A) in New Madrid (hypocenter and epicenter mean precisely the same thing)
B) 20 km south of New Madrid
C) 20 km beneath New Madrid
D) 200 km beneath New Madrid
A) in New Madrid (hypocenter and epicenter mean precisely the same thing)
B) 20 km south of New Madrid
C) 20 km beneath New Madrid
D) 200 km beneath New Madrid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The quantity of motion that occurs along a fault is termed
A) fault gouge.
B) the fault gauge.
C) displacement.
D) accumulation.
A) fault gouge.
B) the fault gauge.
C) displacement.
D) accumulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Most earthquakes are a result of
A) a sudden change in atmospheric pressure.
B) mantle upwelling.
C) erosion of bedrock.
D) movement of rocks along faults.
A) a sudden change in atmospheric pressure.
B) mantle upwelling.
C) erosion of bedrock.
D) movement of rocks along faults.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The point on the Earth's surface directly above the point where an earthquake occurs is termed the
A) hypocenter (focus).
B) epicenter.
C) eye of the fault.
D) vertex.
A) hypocenter (focus).
B) epicenter.
C) eye of the fault.
D) vertex.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Which of the following hazards is most likely to occur several days to weeks after an earthquake?
A) fire
B) liquefaction
C) disease
D) foreshocks
A) fire
B) liquefaction
C) disease
D) foreshocks

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
At a minimum,how many seismic stations are necessary to locate the epicenter of an earthquake?
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Which geological setting is likely to experience the least amount of seismic activity?
A) a rift valley
B) a transform boundary
C) a collisional mountain belt
D) the interior of a tectonic plate
A) a rift valley
B) a transform boundary
C) a collisional mountain belt
D) the interior of a tectonic plate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which earthquake severity scale varies from locality to locality for a single earthquake?
A) the Richter scale
B) the Mercalli scale
C) the moment magnitude scale
D) the surface-wave magnitude scale
A) the Richter scale
B) the Mercalli scale
C) the moment magnitude scale
D) the surface-wave magnitude scale

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
According to the moment magnitude scale (Mw),the amplitude of ground shaking during a magnitude 8 earthquake would be 1,000 times greater than a magnitude ________ earthquake.
A) 9
B) 5
C) 7
D) 4
A) 9
B) 5
C) 7
D) 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Generally,which of the following types of earthquake waves travel with the slowest velocity?
A) S-waves
B) P-waves
C) surface waves
D) All earthquake waves travel at the same speed.
A) S-waves
B) P-waves
C) surface waves
D) All earthquake waves travel at the same speed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Which type of seismic wave has the fastest velocity?
A) L-wave
B) P-wave
C) R-wave
D) S-wave
A) L-wave
B) P-wave
C) R-wave
D) S-wave

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Earthquake waves that travel along the Earth's surface are termed
A) interior waves.
B) S-waves.
C) surface waves.
D) body waves.
A) interior waves.
B) S-waves.
C) surface waves.
D) body waves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Most medium- and deep-focus earthquakes occur at
A) convergent-plate boundaries.
B) divergent-plate boundaries.
C) transform-plate boundaries.
D) hot spots.
A) convergent-plate boundaries.
B) divergent-plate boundaries.
C) transform-plate boundaries.
D) hot spots.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which earthquake scale measures the amplitude of deflection of a seismograph pen,standardized to an idealized distance of 100 km between the epicenter and the seismograph?
A) the Richter scale
B) the Mercalli scale
C) the moment magnitude scale
D) the surface-wave magnitude scale
A) the Richter scale
B) the Mercalli scale
C) the moment magnitude scale
D) the surface-wave magnitude scale

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Which earthquake scale is used to assess the effects of an earthquake on humans and human-made structures?
A) Richter scale
B) Mercalli scale
C) moment magnitude scale
D) surface-wave magnitude scale
A) Richter scale
B) Mercalli scale
C) moment magnitude scale
D) surface-wave magnitude scale

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Body waves include
A) both S- and P-waves.
B) both L- and R-waves.
C) both surface and interior waves.
D) P-waves only.
A) both S- and P-waves.
B) both L- and R-waves.
C) both surface and interior waves.
D) P-waves only.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Earthquake waves that pass through the Earth's interior are termed
A) interior waves.
B) R-waves.
C) surface waves.
D) body waves.
A) interior waves.
B) R-waves.
C) surface waves.
D) body waves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The vast majority of earthquakes occur
A) along transform-plate boundaries only.
B) near hot spots.
C) along passive margins.
D) along any plate boundary.
A) along transform-plate boundaries only.
B) near hot spots.
C) along passive margins.
D) along any plate boundary.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Wet and unconsolidated substrates are uniquely susceptible to ________ during an earthquake.
A) displacement
B) collapse
C) liquefaction
D) faulting
A) displacement
B) collapse
C) liquefaction
D) faulting

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Surface waves
A) travel more rapidly than body waves.
B) produce most of the damage to buildings during earthquakes.
C) are the first waves produced in an earthquake.
D) are the first waves to arrive at a seismograph station after an earthquake.
A) travel more rapidly than body waves.
B) produce most of the damage to buildings during earthquakes.
C) are the first waves produced in an earthquake.
D) are the first waves to arrive at a seismograph station after an earthquake.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
As shown in the figure below,a coiled spring would be useful in illustrating any ________ wave. 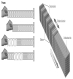
A) surface
B) body
C) shear
D) compressional

A) surface
B) body
C) shear
D) compressional

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A long delay between the arrival of P-waves and S-waves at a seismometer means that
A) the earthquake only produced P-waves.
B) the focus of the earthquake was very deep in the Earth's crust.
C) the seismometer is located far from the earthquake.
D) the earthquake had a very small displacement.
A) the earthquake only produced P-waves.
B) the focus of the earthquake was very deep in the Earth's crust.
C) the seismometer is located far from the earthquake.
D) the earthquake had a very small displacement.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
On average,there are _______occurrences of light and minor earthquakes compared to the number of major and great earthquakes each year.
A) many thousands more
B) approximately ten times as many
C) about the same number of
D) many fewer
A) many thousands more
B) approximately ten times as many
C) about the same number of
D) many fewer

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Earthquakes that occur in a band called the ________ can be used to track the motion of subducted oceanic lithosphere.
A) Wegener belt
B) seismic gap
C) Wadati-Benioff zone
D) Richter zone
A) Wegener belt
B) seismic gap
C) Wadati-Benioff zone
D) Richter zone

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Why do deep-focus earthquakes occur along convergent plate boundaries? Why are they absent along divergent or transform boundaries?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Describe two earthquake-related hazards.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
How is the Mercalli intensity scale used to determine the magnitude of an earthquake? What errors might be associated with this technique?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Designing and retrofitting building to withstand the effects of earthquakes is a type of
A) earthquake zoning.
B) earthquake engineering.
C) seismic hazard mapping.
D) seismic retrofitting.
A) earthquake zoning.
B) earthquake engineering.
C) seismic hazard mapping.
D) seismic retrofitting.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Determining where roads and building should be built based on where land is stable and less prone to landslide or liquefaction during an earthquake is an example of ________.
A) earthquake zoning
B) earthquake engineering
C) seismic hazard mapping
D) seismic retrofitting
A) earthquake zoning
B) earthquake engineering
C) seismic hazard mapping
D) seismic retrofitting

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
What is an early earthquake warning system,and why does this differ from a short-term earthquake prediction tool?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The average length of time between earthquakes along a fault is termed the ______.
A) elastic strain
B) S-P time
C) seismic gap
D) recurrence interval
A) elastic strain
B) S-P time
C) seismic gap
D) recurrence interval

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Short-term predictions of earthquake behavior have
A) saved millions of lives in the past decade alone.
B) been largely unreliable.
C) been primarily based on the behavior patterns of farm animals.
D) been correct approximately 50 percent of the time.
A) saved millions of lives in the past decade alone.
B) been largely unreliable.
C) been primarily based on the behavior patterns of farm animals.
D) been correct approximately 50 percent of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Seismic retrofitting is the process of
A) predicting future earthquakes.
B) strengthening existing buildings and structures.
C) mapping areas prone to earthquakes.
D) fitting earthquake data after an event to see if it should have been predicted.
A) predicting future earthquakes.
B) strengthening existing buildings and structures.
C) mapping areas prone to earthquakes.
D) fitting earthquake data after an event to see if it should have been predicted.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Explain why "tidal wave" is actually a poor term for tsunamis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Where do earthquakes occur? Please explain your answer in the context of plate tectonics.Are there exceptions?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Tsunamis are more destructive than wind-driven storm waves primarily because
A) tsunamis always have larger heights (amplitude).
B) tsunamis have longer wavelengths and thus larger volumes of water are involved.
C) the tides that cause tsunamis can be very erratic and unpredictable.
D) tsunamis also generate seismic waves that can destroy buildings.
A) tsunamis always have larger heights (amplitude).
B) tsunamis have longer wavelengths and thus larger volumes of water are involved.
C) the tides that cause tsunamis can be very erratic and unpredictable.
D) tsunamis also generate seismic waves that can destroy buildings.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Sketch a seismogram that has recorded an earthquake.Be sure to label the arrival of each of the three main types of seismic waves (P-waves,S-waves,and surface waves).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
What kind of information is shown on a seismic hazard map?
A) the probability that different regions will experience a large earthquake
B) the likely magnitude of future earthquakes in different regions
C) the distribution of small and large earthquakes in different regions
D) the locations of large earthquakes in the past
A) the probability that different regions will experience a large earthquake
B) the likely magnitude of future earthquakes in different regions
C) the distribution of small and large earthquakes in different regions
D) the locations of large earthquakes in the past

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
How is the epicenter of an earthquake different from the focus? Why are both terms useful?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Earthquake early warning systems
A) are based on long-term predictions of earthquakes,allowing planners to schedule evacuations.
B) alert people just before an earthquake takes place,allowing them to evacuate buildings.
C) alert people when an earthquake has taken place,possibly giving them seconds to get to a safer place.
D) do not yet exist,but the technology is something seismologists are working on.
A) are based on long-term predictions of earthquakes,allowing planners to schedule evacuations.
B) alert people just before an earthquake takes place,allowing them to evacuate buildings.
C) alert people when an earthquake has taken place,possibly giving them seconds to get to a safer place.
D) do not yet exist,but the technology is something seismologists are working on.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
A tsunami is
A) a seawave generated by an earthquake,landslide,or submarine volcanic eruption that may destroy coastal cities thousands of kilometers from its source.
B) a sloshing of water back and forth within a lake or a bay.
C) a wave caused by unusually large tidal forces.
D) the tendency of wet,clay-rich soils to behave like a liquid during an earthquake.
A) a seawave generated by an earthquake,landslide,or submarine volcanic eruption that may destroy coastal cities thousands of kilometers from its source.
B) a sloshing of water back and forth within a lake or a bay.
C) a wave caused by unusually large tidal forces.
D) the tendency of wet,clay-rich soils to behave like a liquid during an earthquake.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Why is an empty field a very safe place to be in an earthquake?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Compare and contrast P- and S-waves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Tsunamis are most commonly generated by sudden _________ movement of the seafloor during an earthquake.
A) strike-slip
B) horizontal
C) vertical
D) circular
A) strike-slip
B) horizontal
C) vertical
D) circular

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








