Deck 2: Confronting Scarcity: Choices in Production
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/198
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 2: Confronting Scarcity: Choices in Production
1
The model that shows the goods and services the economy is capable of producing is the model of:
A) utility.
B) the fallacy of composition.
C) production possibilities.
D) scarcity.
A) utility.
B) the fallacy of composition.
C) production possibilities.
D) scarcity.
production possibilities.
2
The three broad types of resources used to produce goods and services are also known as:
A) economic systems.
B) factors of production.
C) production possibilities.
D) financial capital.
A) economic systems.
B) factors of production.
C) production possibilities.
D) financial capital.
factors of production.
3
The three broad types of factors of production are:
A) capital, labor, and natural resources.
B) money, profit, and interest.
C) stocks, bonds, and financial assets.
D) technology, human capital, and comparative advantage.
A) capital, labor, and natural resources.
B) money, profit, and interest.
C) stocks, bonds, and financial assets.
D) technology, human capital, and comparative advantage.
capital, labor, and natural resources.
4
One of the two criteria for a resource to be considered capital is that it must:
A) occur naturally.
B) be part of a factory or building.
C) be a skill or talent possessed by a person.
D) be possible to use it to produce other goods and services.
A) occur naturally.
B) be part of a factory or building.
C) be a skill or talent possessed by a person.
D) be possible to use it to produce other goods and services.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
For a factor of production to be called capital it must:
A) be produced.
B) occur in the natural environment.
C) be a part of human skill.
D) be a result of a stock issue.
A) be produced.
B) occur in the natural environment.
C) be a part of human skill.
D) be a result of a stock issue.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A factor of production that has been produced for use in the production of other goods and services is:
A) labor.
B) money.
C) capital.
D) natural resources.
A) labor.
B) money.
C) capital.
D) natural resources.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
An example of capital is:
A) cash.
B) a factory building.
C) money in a checking account.
D) the existing state of technology.
A) cash.
B) a factory building.
C) money in a checking account.
D) the existing state of technology.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Human effort that can be applied in the production process is called:
A) natural resources.
B) technology.
C) labor.
D) specialization.
A) natural resources.
B) technology.
C) labor.
D) specialization.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
To be considered capital, a factor of production must:
A) have been produced.
B) occur naturally.
C) be part of a factory or building.
D) be a skill or talent possessed by a person.
A) have been produced.
B) occur naturally.
C) be part of a factory or building.
D) be a skill or talent possessed by a person.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Labor is the _____ that can be applied to production.
A) the natural environment.
B) produced resources.
C) financial assets.
D) human effort.
A) the natural environment.
B) produced resources.
C) financial assets.
D) human effort.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Any factor of production is capital if it:
A) was produced and can be used to produce other goods and services.
B) generates utility.
C) uses human effort to produce goods and services.
D) is included in financial capital.
A) was produced and can be used to produce other goods and services.
B) generates utility.
C) uses human effort to produce goods and services.
D) is included in financial capital.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Resources from nature that can be used to produce other goods and services are called:
A) money.
B) natural resources.
C) labor.
D) capital.
A) money.
B) natural resources.
C) labor.
D) capital.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A factor of production that is produced in order to produce something else is called:
A) money.
B) labor.
C) technology.
D) capital.
A) money.
B) labor.
C) technology.
D) capital.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which of the following is an example of capital?
A) a gravel truck
B) a savings account
C) a share of General Motors stock
D) a lake
A) a gravel truck
B) a savings account
C) a share of General Motors stock
D) a lake

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
An economic system is the set of rules that define _______ and _______.
A) resources; prices
B) who gets to vote; when elections will be held
C) market prices; factors of production
D) how an economy's resources are to be owned; how decisions about the resources are to be made
A) resources; prices
B) who gets to vote; when elections will be held
C) market prices; factors of production
D) how an economy's resources are to be owned; how decisions about the resources are to be made

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Economic resources used in the production process are called:
A) free gifts of the natural environment.
B) factors of production.
C) consumer items.
D) money capital.
A) free gifts of the natural environment.
B) factors of production.
C) consumer items.
D) money capital.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The factors of production are:
A) money, labor, natural resources, and capital.
B) technology, human capital, and natural resources.
C) money, capital, and natural resources.
D) labor, capital, and natural resources.
A) money, labor, natural resources, and capital.
B) technology, human capital, and natural resources.
C) money, capital, and natural resources.
D) labor, capital, and natural resources.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Capital is best considered as:
A) the natural environment.
B) a factor of production that has been produced.
C) financial assets.
D) money.
A) the natural environment.
B) a factor of production that has been produced.
C) financial assets.
D) money.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Factors of production are:
A) the resources the economy has available to produce goods and services.
B) generally unlimited in modern economies.
C) always employed in modern economies.
D) the knowledge that can be applied to the production of goods and services.
A) the resources the economy has available to produce goods and services.
B) generally unlimited in modern economies.
C) always employed in modern economies.
D) the knowledge that can be applied to the production of goods and services.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Increasing the level of education in the United States will:
A) shift the production possibilities curve to the left.
B) improve the level of technology.
C) lead to increased natural resource use.
D) lead to workers possessing greater human capital.
A) shift the production possibilities curve to the left.
B) improve the level of technology.
C) lead to increased natural resource use.
D) lead to workers possessing greater human capital.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Guns and Butter
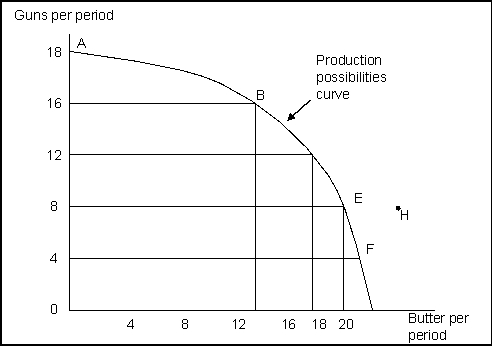
(Exhibit: Guns and Butter) Points A, B, E, and F:
A) indicate combinations of guns and butter that society can produce using all of its factors efficiently.
B) show that the opportunity cost of more guns increases, but that of more butter decreases as more of each good is produced..
C) indicate that society wants butter more than guns.
D) indicate constant costs for guns and increasing costs for butter.
Exhibit: Guns and Butter

(Exhibit: Guns and Butter) Points A, B, E, and F:
A) indicate combinations of guns and butter that society can produce using all of its factors efficiently.
B) show that the opportunity cost of more guns increases, but that of more butter decreases as more of each good is produced..
C) indicate that society wants butter more than guns.
D) indicate constant costs for guns and increasing costs for butter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
In drawing a production possibilities curve, it is assumed that:
A) technology does not change.
B) the economy is fully employed and may not be efficient.
C) there are increasing qualities of the factors of production.
D) all of the above are true.
A) technology does not change.
B) the economy is fully employed and may not be efficient.
C) there are increasing qualities of the factors of production.
D) all of the above are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Which of the following is not capital?
A) a computer in the office of an accountant
B) a migrant worker in the fields of California
C) a wrench in an auto-repair shop
D) a new machine used for producing microchips
A) a computer in the office of an accountant
B) a migrant worker in the fields of California
C) a wrench in an auto-repair shop
D) a new machine used for producing microchips

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Production Possibilities Schedule 1
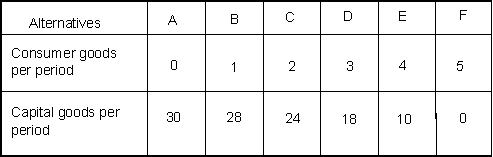
(Exhibit: Production Possibilities Schedule 1) If the economy produces 2 units of consumer goods per period, it also can produce at most _______ units of capital goods per period.
A) 30
B) 28
C) 24
D) 18
Exhibit: Production Possibilities Schedule 1

(Exhibit: Production Possibilities Schedule 1) If the economy produces 2 units of consumer goods per period, it also can produce at most _______ units of capital goods per period.
A) 30
B) 28
C) 24
D) 18

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Production Possibilities Schedule 1

(Exhibit: Production Possibilities Schedule 1) If the economy produces 10 units of capital goods per period, it also can produce at most _______ unit(s) of consumer goods per period.
A) 5
B) 4
C) 3
D) 2
Exhibit: Production Possibilities Schedule 1

(Exhibit: Production Possibilities Schedule 1) If the economy produces 10 units of capital goods per period, it also can produce at most _______ unit(s) of consumer goods per period.
A) 5
B) 4
C) 3
D) 2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Production Possibilities Schedule 1

(Exhibit: Production Possibilities Schedule 1) The opportunity cost of producing the fourth unit of consumer goods is ___ __ units of capital goods.
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
Exhibit: Production Possibilities Schedule 1

(Exhibit: Production Possibilities Schedule 1) The opportunity cost of producing the fourth unit of consumer goods is ___ __ units of capital goods.
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
One of the two criteria for a resource to be considered as a natural resource is that it must:
A) have been produced.
B) not be part of the environment.
C) be part of a factory or building.
D) be available for the production of goods and services.
A) have been produced.
B) not be part of the environment.
C) be part of a factory or building.
D) be available for the production of goods and services.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A person who seeks to earn profits by finding ways to organize factors of production is called a(n):
A) foreman
B) finance capitalist.
C) entrepreneur.
D) manager.
A) foreman
B) finance capitalist.
C) entrepreneur.
D) manager.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Who may benefit from technological progress?
A) consumers
B) workers
C) firms.
D) all of the above.
A) consumers
B) workers
C) firms.
D) all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The textbook classifies technology as _______ and entrepreneurs as _______ .
A) knowledge; persons who seek profit by finding new ways to organize factors of production
B) capital; labor
C) labor skills; capital
D) a factor of production; a factor of production
A) knowledge; persons who seek profit by finding new ways to organize factors of production
B) capital; labor
C) labor skills; capital
D) a factor of production; a factor of production

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The set of acquired skills and abilities that workers bring to the production of goods and services is:
A) money.
B) wealth.
C) human capital.
D) natural ability.
A) money.
B) wealth.
C) human capital.
D) natural ability.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The difference between iron ore deposits and the steel produced from these deposits that is later used to make factory equipment illustrates the difference between:
A) labor and a natural resource.
B) labor and capital.
C) a natural resource and capital.
D) a natural resource and entrepreneurship.
A) labor and a natural resource.
B) labor and capital.
C) a natural resource and capital.
D) a natural resource and entrepreneurship.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Knowledge that can be applied to the production of goods and services is:
A) natural resources.
B) specialization.
C) technology.
D) comparative advantage.
A) natural resources.
B) specialization.
C) technology.
D) comparative advantage.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Improvements in technology provide benefits to:
A) consumers, through lower prices.
B) workers, although some jobs may be eliminated.
C) firms, through lower production costs.
D) all of the above.
A) consumers, through lower prices.
B) workers, although some jobs may be eliminated.
C) firms, through lower production costs.
D) all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Two components of labor are:
A) residential location and education.
B) natural ability and human capital.
C) money and financial wealth.
D) ingenuity and job-specific machinery.
A) residential location and education.
B) natural ability and human capital.
C) money and financial wealth.
D) ingenuity and job-specific machinery.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The production possibilities curve represents the fact that:
A) the economy will automatically end up at full employment.
B) an economy's productive capacity increases proportionally with its population.
C) if all resources of an economy are being used efficiently, more of one good can be produced only if less of another good is produced.
D) economic production possibilities have no limit.
A) the economy will automatically end up at full employment.
B) an economy's productive capacity increases proportionally with its population.
C) if all resources of an economy are being used efficiently, more of one good can be produced only if less of another good is produced.
D) economic production possibilities have no limit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Technology is:
A) knowledge that can be applied to the production of goods and services.
B) generally unlimited in modern economies.
C) a graphical illustration of the alternative combinations of goods and services an economy can produce.
D) the resources the economy has available to produce goods and services.
A) knowledge that can be applied to the production of goods and services.
B) generally unlimited in modern economies.
C) a graphical illustration of the alternative combinations of goods and services an economy can produce.
D) the resources the economy has available to produce goods and services.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
An example of a natural resource is:
A) oil in the ground.
B) oil in storage tanks.
C) a factory.
D) a computer program.
A) oil in the ground.
B) oil in storage tanks.
C) a factory.
D) a computer program.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
One of the two criteria for a resource to be considered as a natural resource is that it must:
A) have been produced.
B) be found in nature.
C) be part of a factory or building.
D) not be used to produce goods and services.
A) have been produced.
B) be found in nature.
C) be part of a factory or building.
D) not be used to produce goods and services.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Human capital is:
A) the set of acquired skills and abilities that workers bring to the production of goods and services.
B) the financial wealth the economy has available to produce goods and services.
C) the ability to produce one of two goods at relatively lower cost.
D) a factor of production only if it occurs naturally.
A) the set of acquired skills and abilities that workers bring to the production of goods and services.
B) the financial wealth the economy has available to produce goods and services.
C) the ability to produce one of two goods at relatively lower cost.
D) a factor of production only if it occurs naturally.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Guns and Butter

(Exhibit: Guns and Butter) If the economy were producing 8 units of guns and 12 units of butter per period:
A) this is a possible choice, but would involve unemployment and/or inefficiency.
B) the notion of increasing opportunity cost is invalidated.
C) the economy is still efficient but has made a decision not to buy as much as it could.
D) something must be done to reduce the amount of employment.
Exhibit: Guns and Butter

(Exhibit: Guns and Butter) If the economy were producing 8 units of guns and 12 units of butter per period:
A) this is a possible choice, but would involve unemployment and/or inefficiency.
B) the notion of increasing opportunity cost is invalidated.
C) the economy is still efficient but has made a decision not to buy as much as it could.
D) something must be done to reduce the amount of employment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Guns and Butter

(Exhibit: Guns and Butter) This production possibilities curve is:
A) linear and because of the constant cost and
B) bowed in toward the origin because of increasing opportunity costs.
C) bowed in toward the origin because of constant cost of guns and butter.
D) bowed out from the origin because of increasing opportunity costs.
Exhibit: Guns and Butter

(Exhibit: Guns and Butter) This production possibilities curve is:
A) linear and because of the constant cost and
B) bowed in toward the origin because of increasing opportunity costs.
C) bowed in toward the origin because of constant cost of guns and butter.
D) bowed out from the origin because of increasing opportunity costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
If the production possibilities curve were a straight line sloping down from left to right, this would suggest that:
A) more of both goods could be produced moving along the curve.
B) the two products must have the same price.
C) no factor of production has any particular comparative advantage over other resources.
D) the utility of the two goods must be equal to consumers.
A) more of both goods could be produced moving along the curve.
B) the two products must have the same price.
C) no factor of production has any particular comparative advantage over other resources.
D) the utility of the two goods must be equal to consumers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The concept of comparative advantage is based upon:
A) absolute labor productivity.
B) relative labor costs.
C) dollar prices of labor.
D) relative opportunity costs.
A) absolute labor productivity.
B) relative labor costs.
C) dollar prices of labor.
D) relative opportunity costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Guns and Butter

(Exhibit: Guns and Butter) If the economy were operating at point B, producing 16 units of guns and 12 units of butter per period, a decision to move to point E and produce 18 units of butter:
A) indicates you can have more butter and guns simultaneously.
B) makes it clear that this economy experiences decreasing opportunity costs.
C) involves a loss of 8 units of guns per period.
D) involves a loss of 4 units of guns per period.
Exhibit: Guns and Butter

(Exhibit: Guns and Butter) If the economy were operating at point B, producing 16 units of guns and 12 units of butter per period, a decision to move to point E and produce 18 units of butter:
A) indicates you can have more butter and guns simultaneously.
B) makes it clear that this economy experiences decreasing opportunity costs.
C) involves a loss of 8 units of guns per period.
D) involves a loss of 4 units of guns per period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The law of increasing opportunity cost means that:
A) higher wages, rents, and interest will increase opportunity costs.
B) opportunity cost will decrease the more you decide to produce more of one good along a production possibilities curve.
C) opportunity cost increases when you produce more of one good while moving along a production possibilities curve.
D) costs of production decrease at first, but then eventually rise.
A) higher wages, rents, and interest will increase opportunity costs.
B) opportunity cost will decrease the more you decide to produce more of one good along a production possibilities curve.
C) opportunity cost increases when you produce more of one good while moving along a production possibilities curve.
D) costs of production decrease at first, but then eventually rise.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
When moving along a production possibilities curve, the opportunity cost to society of getting more of the good on the horizontal axis:
A) is constant.
B) is measured in dollar terms.
C) is measured by the amount of the other good that must be given up.
D) usually decreases.
A) is constant.
B) is measured in dollar terms.
C) is measured by the amount of the other good that must be given up.
D) usually decreases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
If Farmer Sam MacDonald can produce 200 pounds of cabbages and 0 pounds of potatoes or 0 pounds of cabbages and 100 pounds of potatoes and faces a linear production possibilities curve for his farm, the opportunity cost of producing an additional pound of potatoes is _____ _ pound(s) of cabbage.
A) 1/2
B) 2
C) 100
D) 200
A) 1/2
B) 2
C) 100
D) 200

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Comparative advantage leads to producing at a:
A) higher opportunity cost.
B) lower opportunity cost.
C) higher dollar cost.
D) point where costs just begin to fall.
A) higher opportunity cost.
B) lower opportunity cost.
C) higher dollar cost.
D) point where costs just begin to fall.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Guns and Butter

(Exhibit: Guns and Butter) The maximum amounts of guns and butter this economy can produce is:
A) 18 units of guns and 0 units of butter per period.
B) 0 units of guns and 20 units of butter per period.
C) 16 units of guns and 12 units of butter per period.
D) all of the above combinations are maximum possible combinations.
Exhibit: Guns and Butter

(Exhibit: Guns and Butter) The maximum amounts of guns and butter this economy can produce is:
A) 18 units of guns and 0 units of butter per period.
B) 0 units of guns and 20 units of butter per period.
C) 16 units of guns and 12 units of butter per period.
D) all of the above combinations are maximum possible combinations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
If an economy has to sacrifice only one unit of good X for each unit of good Y produced throughout the relevant range, then its production possibilities curve has a(n):
A) zero slope.
B) constant, negative slope.
C) increasing, negative slope.
D) decreasing, negative slope.
A) zero slope.
B) constant, negative slope.
C) increasing, negative slope.
D) decreasing, negative slope.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Guns and Butter

(Exhibit: Guns and Butter) The combination of guns and butter at point H:
A) can be obtained, but would cost too much.
B) cannot be attained given the level of technology and the factors of production available.
C) has no meaning since it does not relate to the
Exhibit: Guns and Butter

(Exhibit: Guns and Butter) The combination of guns and butter at point H:
A) can be obtained, but would cost too much.
B) cannot be attained given the level of technology and the factors of production available.
C) has no meaning since it does not relate to the

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The law of increasing opportunity costs is a result of the fact that:
A) the value of the dollar has declined over time.
B) wage rates rise as the economy reaches full employment.
C) consumers tend to value a good more when they don't have much of it.
D) resources are not equally productive in all output categories.
A) the value of the dollar has declined over time.
B) wage rates rise as the economy reaches full employment.
C) consumers tend to value a good more when they don't have much of it.
D) resources are not equally productive in all output categories.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
An economy is said to have a comparative advantage in the production of a good if it can:
A) produce that good with more resources than another economy.
B) produce that good with a higher opportunity cost than another economy.
C) produce that good outside its production possibilities curve.
D) produce the good at a lower opportunity cost than another economy.
A) produce that good with more resources than another economy.
B) produce that good with a higher opportunity cost than another economy.
C) produce that good outside its production possibilities curve.
D) produce the good at a lower opportunity cost than another economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
An economy is said to have a comparative advantage in producing a particular good if it:
A) can produce more of all goods than another economy.
B) can produce less of all goods than another economy.
C) has the highest cost for producing that good.
D) has the lowest cost for producing that good.
A) can produce more of all goods than another economy.
B) can produce less of all goods than another economy.
C) has the highest cost for producing that good.
D) has the lowest cost for producing that good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Guns and Butter

(Exhibit: Guns and Butter) A movement from producing 12 units of guns and 16 units of butter per period to point B means a:
A) gain of 4 units of guns and a loss of 6 units of butter per period.
B) gain of 2 units of guns and a loss of 4 units of butter per period.
C) loss of 4 units of butter and a gain of 4 units of guns per period.
D) loss of 2 units of guns and a gain of 4 units of butter per period.
Exhibit: Guns and Butter

(Exhibit: Guns and Butter) A movement from producing 12 units of guns and 16 units of butter per period to point B means a:
A) gain of 4 units of guns and a loss of 6 units of butter per period.
B) gain of 2 units of guns and a loss of 4 units of butter per period.
C) loss of 4 units of butter and a gain of 4 units of guns per period.
D) loss of 2 units of guns and a gain of 4 units of butter per period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
If an economy has to sacrifice increasing amounts of good X for each additional unit of good Y produced, then its production possibilities curve is:
A) bowed out from the origin.
B) bowed in toward the origin.
C) a straight line.
D) a vertical line.
A) bowed out from the origin.
B) bowed in toward the origin.
C) a straight line.
D) a vertical line.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
The slope of a typical production possibilities curve is:
A) 0.
B) vertical.
C) positive.
D) negative.
A) 0.
B) vertical.
C) positive.
D) negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
An economy that has the lowest cost for producing a particular good is said to have a(n):
A) technological advantage.
B) comparative advantage.
C) convex news production possibilities curve.
D) all of the above are correct and
A) technological advantage.
B) comparative advantage.
C) convex news production possibilities curve.
D) all of the above are correct and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
If Farmer Sam MacDonald can produce 200 pounds of cabbages and 0 pounds of potatoes or 0 pounds of cabbages and 100 pounds of potatoes and faces a linear possibilities curve for his farm, the opportunity cost of producing an additional pound of cabbage is ____ __ pound(s) of potatoes.
A) 1/2
B) 2
C) 100
D) 200
A) 1/2
B) 2
C) 100
D) 200

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains
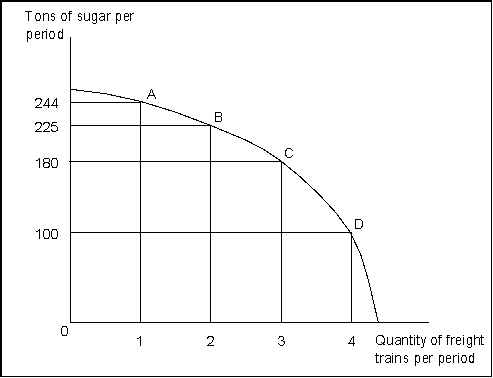
(Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains) Suppose the economy is operating at point B. The opportunity cost of producing the third freight train would be:
A) 6 tons of sugar.
B) 19 tons of sugar.
C) 45 tons of sugar.
D) 80 tons of sugar.
Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains

(Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains) Suppose the economy is operating at point B. The opportunity cost of producing the third freight train would be:
A) 6 tons of sugar.
B) 19 tons of sugar.
C) 45 tons of sugar.
D) 80 tons of sugar.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 2
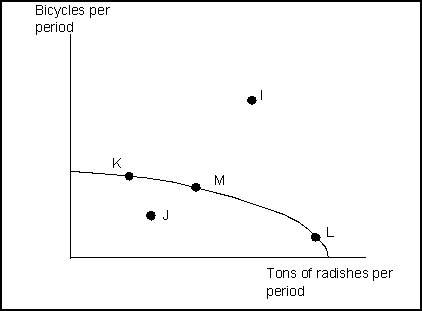
(Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 2) The country depicted in this exhibit is currently operating at point M. It could achieve production at point I only if it:
A) used its resources more efficiently.
B) devoted more resources to radish production.
C) devoted more resources to bicycle production.
D) increased the quantities of capital, natural resources, or labor available or improved its technology.
Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 2

(Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 2) The country depicted in this exhibit is currently operating at point M. It could achieve production at point I only if it:
A) used its resources more efficiently.
B) devoted more resources to radish production.
C) devoted more resources to bicycle production.
D) increased the quantities of capital, natural resources, or labor available or improved its technology.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 1
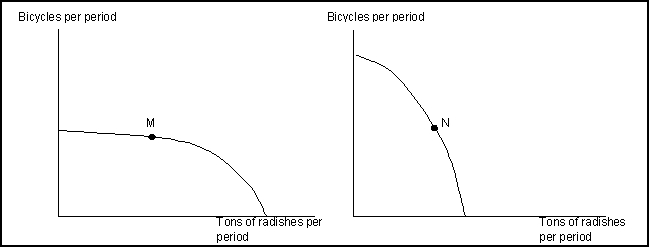
(Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 1) The exhibit shows production possibilities curves for two countries that produce only radishes and bicycles. The axes of both graphs are measured in equivalent units. Country A is now operating at point M, and Country B is now operating at point N. Suppose Country B wants to be able to produce more radishes and more bicycles. To do this, it must:
A) Use its resources more efficiently.
B) achieve full employment in its use of resources.
C) acquire more capital, more labor, more natural resources, and/or better technology.
D) do all of the above.
Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 1

(Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 1) The exhibit shows production possibilities curves for two countries that produce only radishes and bicycles. The axes of both graphs are measured in equivalent units. Country A is now operating at point M, and Country B is now operating at point N. Suppose Country B wants to be able to produce more radishes and more bicycles. To do this, it must:
A) Use its resources more efficiently.
B) achieve full employment in its use of resources.
C) acquire more capital, more labor, more natural resources, and/or better technology.
D) do all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains

(Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains) Suppose the economy is producing 180 tons of sugar and 2 freight trains. This implies that:
A) the economy is operating at full employment.
B) the economy is operating efficiently.
C) the economy is not producing as much as it could.
D) economic growth would help the economy move to its production possibilities curve.
Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains

(Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains) Suppose the economy is producing 180 tons of sugar and 2 freight trains. This implies that:
A) the economy is operating at full employment.
B) the economy is operating efficiently.
C) the economy is not producing as much as it could.
D) economic growth would help the economy move to its production possibilities curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 1

(Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 1) The exhibit shows production possibilities curves for two countries that produce only radishes and bicycles. The axes of both graphs are measured in equivalent units. Country A is now operating at point M, and Country B is now operating at point N. The opportunity cost of producing an additional ton of radishes would be greater in:
A) Country A.
B) Country B.
C) neither; the opportunity cost would be the same in both countries.
D) there is not enough information given to answer the question.
Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 1

(Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 1) The exhibit shows production possibilities curves for two countries that produce only radishes and bicycles. The axes of both graphs are measured in equivalent units. Country A is now operating at point M, and Country B is now operating at point N. The opportunity cost of producing an additional ton of radishes would be greater in:
A) Country A.
B) Country B.
C) neither; the opportunity cost would be the same in both countries.
D) there is not enough information given to answer the question.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
The law of increasing opportunity cost is associated with the slope of the:
A) demand curve.
B) supply curve.
C) output curve.
D) production possibilities curve.
A) demand curve.
B) supply curve.
C) output curve.
D) production possibilities curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
The fact that a society's production possibilities curve is bowed out from the origin of a graph demonstrates the law of:
A) increasing opportunity cost.
B) decreasing opportunity cost.
C) constant opportunity cost.
D) convex opportunity cost.
A) increasing opportunity cost.
B) decreasing opportunity cost.
C) constant opportunity cost.
D) convex opportunity cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
The proposition that states that as output increases for one good in an economy that is on its production possibilities curve, the cost of additional units of the good on the horizontal axis will be greater and greater is the:
A) law of absolute advantage.
B) law of increasing opportunity cost.
C) law of policy ineffectiveness.
D) law of demand.
A) law of absolute advantage.
B) law of increasing opportunity cost.
C) law of policy ineffectiveness.
D) law of demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains

(Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains) Suppose the economy is operating at point A, producing 244 tons of sugar and 1 freight train. The opportunity cost of producing the second freight train is:
A) 225 tons of sugar.
B) 25 tons of sugar.
C) 19 tons of sugar.
D) 6 tons of sugar.
Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains

(Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains) Suppose the economy is operating at point A, producing 244 tons of sugar and 1 freight train. The opportunity cost of producing the second freight train is:
A) 225 tons of sugar.
B) 25 tons of sugar.
C) 19 tons of sugar.
D) 6 tons of sugar.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
The economy's factors of production are not equally suitable for producing different types of goods. This principle generates:
A) economic growth.
B) technical efficiency.
C) resource underutilization.
D) the law of increasing opportunity cost.
A) economic growth.
B) technical efficiency.
C) resource underutilization.
D) the law of increasing opportunity cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 2

(Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 2) In the country depicted in this exhibit, the opportunity cost of an additional ton of radishes would be greater at:
A) point K.
B) point M.
C) point L.
D) none of the above points; the opportunity cost is the same at every point on a production possibilities curve.
Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 2

(Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 2) In the country depicted in this exhibit, the opportunity cost of an additional ton of radishes would be greater at:
A) point K.
B) point M.
C) point L.
D) none of the above points; the opportunity cost is the same at every point on a production possibilities curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
If a production possibilities curve were bowed in or convex to the origin of a graph, it would demonstrate:
A) increasing opportunity cost.
B) decreasing opportunity cost.
C) constant opportunity cost.
D) fluctuating opportunity cost.
A) increasing opportunity cost.
B) decreasing opportunity cost.
C) constant opportunity cost.
D) fluctuating opportunity cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains

(Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains) The downward slope of the production possibilities curve implies:
A) resources in the economy are scarce.
B) the economy must be controlled by the government.
C) sugar is more important than freight trains.
D) the economy produces more sugar than freight trains.
Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains

(Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains) The downward slope of the production possibilities curve implies:
A) resources in the economy are scarce.
B) the economy must be controlled by the government.
C) sugar is more important than freight trains.
D) the economy produces more sugar than freight trains.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
In the 1980s, the federal government undertook a major build-up of the military sector, leading to reports that prices charged by military contractors were spiraling upward. According to production possibilities analysis, this result is not surprising due to:
A) the law of increasing opportunity cost.
B) economic efficiency.
C) technical efficiency.
D) resource underutilization.
A) the law of increasing opportunity cost.
B) economic efficiency.
C) technical efficiency.
D) resource underutilization.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 1

(Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 1) The exhibit shows production possibilities curves for two countries that produce only radishes and bicycles. The axes of both graphs are measured in equivalent units. Country A is now operating at point M, and Country B is now operating at point N. Suppose Country A discovered a new technology that greatly increased its ability to produce bicycles. This would:
A) lower the opportunity cost of producing radishes in Country A.
B) increase the opportunity cost of producing radishes in Country A.
C) have no effect on the opportunity cost of producing radishes in country A.
D) increase the opportunity cost of producing radishes in Country B.
Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 1

(Exhibit: Bicycles and Radishes 1) The exhibit shows production possibilities curves for two countries that produce only radishes and bicycles. The axes of both graphs are measured in equivalent units. Country A is now operating at point M, and Country B is now operating at point N. Suppose Country A discovered a new technology that greatly increased its ability to produce bicycles. This would:
A) lower the opportunity cost of producing radishes in Country A.
B) increase the opportunity cost of producing radishes in Country A.
C) have no effect on the opportunity cost of producing radishes in country A.
D) increase the opportunity cost of producing radishes in Country B.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
The law of increasing opportunity cost says that:
A) opportunity costs of production always tend to increase.
B) increases in wages cause increases in the opportunity costs of production.
C) as output increases for one good on its production possibilities curve, the opportunity cost of additional units of the other good will be greater and greater.
D) along a production possibilities curve, as output increases in the production of one good, the opportunity costs of additional units of the other good will be less and less.
A) opportunity costs of production always tend to increase.
B) increases in wages cause increases in the opportunity costs of production.
C) as output increases for one good on its production possibilities curve, the opportunity cost of additional units of the other good will be greater and greater.
D) along a production possibilities curve, as output increases in the production of one good, the opportunity costs of additional units of the other good will be less and less.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains

(Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains) The "bowed-out" shape of the production possibilities curve shown here demonstrates:
A) that freight trains cost more than sugar.
B) that sugar costs more than freight trains.
C) that the opportunity cost of additional freight trains increases as the economy produces more and more of them.
D) that the opportunity cost of additional freight trains decreases as the economy produces more and more of them.
Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains

(Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains) The "bowed-out" shape of the production possibilities curve shown here demonstrates:
A) that freight trains cost more than sugar.
B) that sugar costs more than freight trains.
C) that the opportunity cost of additional freight trains increases as the economy produces more and more of them.
D) that the opportunity cost of additional freight trains decreases as the economy produces more and more of them.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Strawberries and Submarines
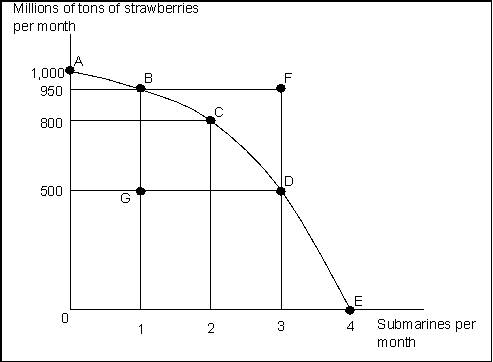
(Exhibit: Strawberries and Submarines) Suppose the economy is now operating at point G. This implies that:
A) the economy can move to a point such as C only if it improves its technology.
B) the economy is experiencing unemployment and/or inefficient allocation of resources.
C) the economy lacks the resources to achieve a combination such as C.
D) people in this economy don't really like strawberries and submarines.
Exhibit: Strawberries and Submarines

(Exhibit: Strawberries and Submarines) Suppose the economy is now operating at point G. This implies that:
A) the economy can move to a point such as C only if it improves its technology.
B) the economy is experiencing unemployment and/or inefficient allocation of resources.
C) the economy lacks the resources to achieve a combination such as C.
D) people in this economy don't really like strawberries and submarines.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Strawberries and Submarines

(Exhibit: Strawberries and Submarines) Suppose the economy is now operating at point A. The first submarine, which is achieved at point B, would have an opportunity cost of _______ million tons of strawberries.
A) 50
B) 150
C) 400
D) 950
Exhibit: Strawberries and Submarines

(Exhibit: Strawberries and Submarines) Suppose the economy is now operating at point A. The first submarine, which is achieved at point B, would have an opportunity cost of _______ million tons of strawberries.
A) 50
B) 150
C) 400
D) 950

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Use the following to answer question(s):
Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains

(Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains) Suppose the economy is operating at point C. The opportunity cost of producing the fourth freight train would be:
A) 19 tons of sugar.
B) 45 tons of sugar.
C) 80 tons of sugar.
D) 3 freight trains.
Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains

(Exhibit: Sugar and Freight Trains) Suppose the economy is operating at point C. The opportunity cost of producing the fourth freight train would be:
A) 19 tons of sugar.
B) 45 tons of sugar.
C) 80 tons of sugar.
D) 3 freight trains.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 198 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








