Deck 8: Reproduction and Development
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/41
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Reproduction and Development
1
Pregnancy begins with
A)implantation.
B)blastocyst formation.
C)gastrulation.
D)conception.
E)formation of the amnion.
A)implantation.
B)blastocyst formation.
C)gastrulation.
D)conception.
E)formation of the amnion.
A
2
All of the following are parts of the sperm except
A)mitochondria.
B)a nucleus.
C)a flagellum.
D)a diploid set of chromosomes.
E)an acrosome.
A)mitochondria.
B)a nucleus.
C)a flagellum.
D)a diploid set of chromosomes.
E)an acrosome.
D
3
Luteinizing hormone (LH)and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)are
A)constantly secreted into the bloodstream of males.
B)produced in both male and female humans.
C)produced in the ovaries.
D)produced in the testes.
E)only produced in female humans.
A)constantly secreted into the bloodstream of males.
B)produced in both male and female humans.
C)produced in the ovaries.
D)produced in the testes.
E)only produced in female humans.
B
4
This structure serves to block more than one sperm from entering the fertilized egg.
A)acrosome
B)yolk
C)amnion
D)fertilization membrane
E)mitochondria
A)acrosome
B)yolk
C)amnion
D)fertilization membrane
E)mitochondria

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Animals that possess both male and female sexual organs
A)are parthenogenetic and typically self-fertilize.
B)are hermaphroditic and typically self-fertilize.
C)are dioecious and typically cross-fertilize.
D)are dioecious and typically self-fertilize.
E)are hermaphroditic and typically cross-fertilize.
A)are parthenogenetic and typically self-fertilize.
B)are hermaphroditic and typically self-fertilize.
C)are dioecious and typically cross-fertilize.
D)are dioecious and typically self-fertilize.
E)are hermaphroditic and typically cross-fertilize.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The average human ejaculation contains
A)120,000 to 400,000 sperm.
B)1,200,000 to 4,000,000 sperm.
C)12 million to 40 million sperm.
D)120 million to 400 million sperm.
E)1.2 billion to 4 billion sperm.
A)120,000 to 400,000 sperm.
B)1,200,000 to 4,000,000 sperm.
C)12 million to 40 million sperm.
D)120 million to 400 million sperm.
E)1.2 billion to 4 billion sperm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
After being produced in the seminiferous tubules, sperm mature in the
A)epididymis.
B)vas deferens.
C)ejaculatory duct.
D)seminal vesicle.
E)urethra.
A)epididymis.
B)vas deferens.
C)ejaculatory duct.
D)seminal vesicle.
E)urethra.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Fertilization usually occurs in the
A)uterus.
B)corpus luteum.
C)ovary.
D)vagina.
E)fallopian tubes.
A)uterus.
B)corpus luteum.
C)ovary.
D)vagina.
E)fallopian tubes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Embryonic development includes all of the following except
A)cleavage.
B)fertilization.
C)gastrulation.
D)organogenesis.
E)growth.
A)cleavage.
B)fertilization.
C)gastrulation.
D)organogenesis.
E)growth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Negative feedback loops act to
A)control sperm production.
B)cause uterine contractions during childbirth.
C)cause milk production after childbirth.
D)cause expulsion of milk during breastfeeding.
E)cause an erection of the penis when stimulated.
A)control sperm production.
B)cause uterine contractions during childbirth.
C)cause milk production after childbirth.
D)cause expulsion of milk during breastfeeding.
E)cause an erection of the penis when stimulated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Immature eggs are called
A)oocytes.
B)blastocysts.
C)follicles.
D)basal cells.
E)ovaries.
A)oocytes.
B)blastocysts.
C)follicles.
D)basal cells.
E)ovaries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Sperm-producing cells are referred to as
A)spermatocytes.
B)Sertoli cells.
C)interstitial cells.
D)seminiferous cells.
E)spermatogenic cells.
A)spermatocytes.
B)Sertoli cells.
C)interstitial cells.
D)seminiferous cells.
E)spermatogenic cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
External fertilization is most commonly seen
A)in land animals.
B)in plants.
C)in aquatic animals.
D)during dry seasons.
E)among all animals.
A)in land animals.
B)in plants.
C)in aquatic animals.
D)during dry seasons.
E)among all animals.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The interstitial cells of the seminiferous tubules
A)will divide to become sperm cells.
B)are present to nourish the sperm.
C)produce testosterone.
D)produce cholesterol.
E)produce estrogen.
A)will divide to become sperm cells.
B)are present to nourish the sperm.
C)produce testosterone.
D)produce cholesterol.
E)produce estrogen.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Which of the following chemicals plays a part in a man's erection?
A)carbon dioxide
B)carbon monoxide
C)nitric oxide
D)phosphoric acid
E)carbonic acid
A)carbon dioxide
B)carbon monoxide
C)nitric oxide
D)phosphoric acid
E)carbonic acid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
A)is produced by the amnion.
B)can be used to reveal pregnancy.
C)is stored in the ovaries.
D)acts as a hormone signaling menstruation.
E)is needed to form the placenta.
A)is produced by the amnion.
B)can be used to reveal pregnancy.
C)is stored in the ovaries.
D)acts as a hormone signaling menstruation.
E)is needed to form the placenta.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Chemical compounds secreted by mammals and insects to communicate sexual readiness are called
A)pheromones.
B)developers.
C)hormones.
D)testosterones.
E)estrogens.
A)pheromones.
B)developers.
C)hormones.
D)testosterones.
E)estrogens.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
As opposed to external fertilization, internal fertilization ensures that
A)sperm and egg will be released simultaneously.
B)only the fittest of sperm and egg combinations will survive.
C)sperm will be protected until they can unite with the eggs.
D)all of the sperm will fertilize eggs.
E)the number of sperm and eggs produced will be equal.
A)sperm and egg will be released simultaneously.
B)only the fittest of sperm and egg combinations will survive.
C)sperm will be protected until they can unite with the eggs.
D)all of the sperm will fertilize eggs.
E)the number of sperm and eggs produced will be equal.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
In most male mammals, the testes are present
A)within the abdomen.
B)close to the body to maintain body temperature.
C)from puberty on.
D)in the scrotum.
E)for part of their lives.
A)within the abdomen.
B)close to the body to maintain body temperature.
C)from puberty on.
D)in the scrotum.
E)for part of their lives.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The primary male hormone is
A)produced throughout a male's entire lifetime.
B)testosterone.
C)estrogen.
D)only involved in sperm production.
E)produced in the brain.
A)produced throughout a male's entire lifetime.
B)testosterone.
C)estrogen.
D)only involved in sperm production.
E)produced in the brain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Describe the events occurring during gastrulation. What is the destination of the cells in the three layers?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Describe the process of ovulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Describe the primary membranes surrounding the human fetus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
This is a structure at the head of a sperm cell that allows it to penetrate an egg cell.
A)acrosome
B)labia
C)centriole
D)cortical granule
E)somite
A)acrosome
B)labia
C)centriole
D)cortical granule
E)somite

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements about the egg cell is false?
A)It is relatively small compared to other body cells.
B)It contains a haploid nucleus.
C)It contains lipids.
D)It contains mitochondria.
E)It is located in a follicle.
A)It is relatively small compared to other body cells.
B)It contains a haploid nucleus.
C)It contains lipids.
D)It contains mitochondria.
E)It is located in a follicle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Match the following structures with their functions.
10. __ seminiferous tubules
11. __ prostate gland
12. __ epididymis
13. __ seminal vesicles
14. ___vasdeferens
A. a single structure, contributes to the semen
B. paired organs that contribute to the semen
C. site of sperm formation
D. tube leading from the epididymis
E. site of sperm maturation
10. __ seminiferous tubules
11. __ prostate gland
12. __ epididymis
13. __ seminal vesicles
14. ___vasdeferens
A. a single structure, contributes to the semen
B. paired organs that contribute to the semen
C. site of sperm formation
D. tube leading from the epididymis
E. site of sperm maturation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
What is a negative feedback loop? How does this apply to sperm production?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Match the following structures with their functions.
10. ___ovaries
11. ___oviducts
12. ___ corpus luteum
13. ___ uterus
14. ____ vagina
A. Where sperm typically fertilize eggs
B. to receive sperm
C. where embryo implants
D. to produce eggs
E. to produce progesterone
10. ___ovaries
11. ___oviducts
12. ___ corpus luteum
13. ___ uterus
14. ____ vagina
A. Where sperm typically fertilize eggs
B. to receive sperm
C. where embryo implants
D. to produce eggs
E. to produce progesterone

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
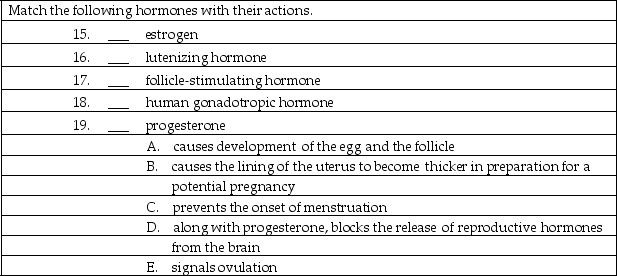

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Describe the pathway of sperm during ejaculation, from production to exiting the body. Include the contributions of various accessory ducts and glands.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The male reproductive system contains all of the following structures except the
A)seminal vesicles.
B)prostate gland.
C)clitoris.
D)seminal vesicles.
E)epididymis.
A)seminal vesicles.
B)prostate gland.
C)clitoris.
D)seminal vesicles.
E)epididymis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements is true of the blastula?
A)It is the earliest stage of embryonic development.
B)Three cell layers are evident.
C)The neural tube forms.
D)Limb buds may be seen.
E)It is haploid.
A)It is the earliest stage of embryonic development.
B)Three cell layers are evident.
C)The neural tube forms.
D)Limb buds may be seen.
E)It is haploid.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Put the major stages of development in order.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Name the male accessory sexual glands and characterize the organs and their secretions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The female reproductive system contains all of the following structures except the
A)cervix.
B)Bartholin's gland.
C)clitoris.
D)acrosome.
E)labia.
A)cervix.
B)Bartholin's gland.
C)clitoris.
D)acrosome.
E)labia.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








