Deck 9: The Mechanisms of Evolution
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/57
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 9: The Mechanisms of Evolution
1
Which of the following phrases is used to describe J. B. Lamarck's hypothesis of evolutionary change?
A)inheritance of ancestral identity
B)inheritance of acquired characteristics
C)natural selection
D)survival of the fittest
E)intelligent design
A)inheritance of ancestral identity
B)inheritance of acquired characteristics
C)natural selection
D)survival of the fittest
E)intelligent design
B
2
A population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
A)consists of allele frequencies that are constantly changing.
B)is under no selective pressures.
C)consists of genotype frequencies that are constantly changing.
D)is very common in nature.
E)requires a small population size.
A)consists of allele frequencies that are constantly changing.
B)is under no selective pressures.
C)consists of genotype frequencies that are constantly changing.
D)is very common in nature.
E)requires a small population size.
B
3
Support for evolution has come from fossil evidence. All of the following statements about the fossil records are true except one. Choose the exception.
A)Fossils found in adjacent rock layers are more similar to each other than those found in distant layers.
B)Many organisms that lived previously were different from today's living organisms.
C)All types of organisms have left a fossil record.
D)Different organisms were present at different times in Earth's history.
E)In general, simpler forms of organisms are found in older rocks; more complex forms in younger rocks.
A)Fossils found in adjacent rock layers are more similar to each other than those found in distant layers.
B)Many organisms that lived previously were different from today's living organisms.
C)All types of organisms have left a fossil record.
D)Different organisms were present at different times in Earth's history.
E)In general, simpler forms of organisms are found in older rocks; more complex forms in younger rocks.
C
4
This type of selection favors both extremes of the phenotype spectrum within a population.
A)directional
B)stabilizing
C)disruptive
D)natural
E)neutral
A)directional
B)stabilizing
C)disruptive
D)natural
E)neutral

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Based on genetic comparisons,
A)people of different races often have more genetic similarities than many individuals within a race.
B)humans have a more ancient origin than chimpanzees.
C)there is much genetic diversity among cheetahs.
D)among humans, many genetic variations are restricted to certain racial groups.
E)there is no difference between different races of humans.
A)people of different races often have more genetic similarities than many individuals within a race.
B)humans have a more ancient origin than chimpanzees.
C)there is much genetic diversity among cheetahs.
D)among humans, many genetic variations are restricted to certain racial groups.
E)there is no difference between different races of humans.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Vestigial organs
A)did not have a function when they first developed, but do so today.
B)are similar in many organisms.
C)must have evolved individually in different organisms.
D)are not found in present-day organisms.
E)include the human appendix and wisdom teeth and a snake's hipbones.
A)did not have a function when they first developed, but do so today.
B)are similar in many organisms.
C)must have evolved individually in different organisms.
D)are not found in present-day organisms.
E)include the human appendix and wisdom teeth and a snake's hipbones.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Charles Darwin and Alfred Russell Wallace are both credited with developing key ideas about evolution. Each of the following statements expresses their ideas except one. Choose the exception.
A)The survival of the population is the key to evolution.
B)All living organisms are the descendants of common ancestors.
C)Increased survival and reproduction are the keys to evolution.
D)The better adapted individuals are to an environment, the more likely they are to survive and reproduce.
E)Modification of body plans and behaviors of organisms has led to descent with modification.
A)The survival of the population is the key to evolution.
B)All living organisms are the descendants of common ancestors.
C)Increased survival and reproduction are the keys to evolution.
D)The better adapted individuals are to an environment, the more likely they are to survive and reproduce.
E)Modification of body plans and behaviors of organisms has led to descent with modification.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Up until the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, many naturalists believed that all species of living organism(s)had been created separately and had remained unchanged since the creation. Around that time, scientific research provided findings that were contradictory to that idea. All of the following are findings that contradict the idea of a single creation. Choose the exception.
A)As scientists explored more of the earth, they found that different groups of organisms were found in the different regions.
B)Even though the limbs of various mammals carry out different functions (swimming, gliding, running, holding, etc.), the bone patterns are very similar.
C)Some fossils of extinct organisms are quite different from living organisms.
D)The limbs of some mammals serve the same purpose but their bone patterns are very different.
E)The platypus is only found in Australia and the dodo was only found on Madagascar.
A)As scientists explored more of the earth, they found that different groups of organisms were found in the different regions.
B)Even though the limbs of various mammals carry out different functions (swimming, gliding, running, holding, etc.), the bone patterns are very similar.
C)Some fossils of extinct organisms are quite different from living organisms.
D)The limbs of some mammals serve the same purpose but their bone patterns are very different.
E)The platypus is only found in Australia and the dodo was only found on Madagascar.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Which of the following is the best description of an adaptation?
A)a trait that was beneficial to survival in the past
B)a trait that is currently beneficial to survival
C)a trait that will be beneficial in the future
D)a trait that is of no advantage to survival
E)an environmental change that selects for certain traits
A)a trait that was beneficial to survival in the past
B)a trait that is currently beneficial to survival
C)a trait that will be beneficial in the future
D)a trait that is of no advantage to survival
E)an environmental change that selects for certain traits

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The numerous, different species of Hawaiian honeycreepers that can be identified are a classic example of what concept?
A)adaptive radiation
B)convergent evolution
C)reticulate evolution
D)homology
E)punctuated equilibrium
A)adaptive radiation
B)convergent evolution
C)reticulate evolution
D)homology
E)punctuated equilibrium

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
We refer to favorable traits within a population as
A)selections.
B)adaptations.
C)selective.
D)divergent.
E)directional.
A)selections.
B)adaptations.
C)selective.
D)divergent.
E)directional.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which term refers to anatomical features that serve no current function?
A)homologous structures
B)adaptations
C)original elements
D)genetic weaknesses
E)vestigial organs
A)homologous structures
B)adaptations
C)original elements
D)genetic weaknesses
E)vestigial organs

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Most mutations lead to a decreased chance of survival for the mutant organism. Rarely, a mutation can provide an increased chance of survival. These rare mutations provide a(n)_____________________ for the mutant.
A)adaptive
B)directional shift
C)selective disadvantage
D)environmental susceptibility
E)selective advantage
A)adaptive
B)directional shift
C)selective disadvantage
D)environmental susceptibility
E)selective advantage

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Jean Baptiste Lamarck developed a hypothesis that has been referred to as "inheritance of acquired characteristics." In it he proposed that
A)giraffes were created with long necks.
B)giraffes with slightly longer necks would be better able to reproduce.
C)changes in structure size in an individual can be inherited.
D)all members of a species must change identically.
E)giraffes developed longer necks to compensate for shorter legs.
A)giraffes were created with long necks.
B)giraffes with slightly longer necks would be better able to reproduce.
C)changes in structure size in an individual can be inherited.
D)all members of a species must change identically.
E)giraffes developed longer necks to compensate for shorter legs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Homologous organs
A)are the results of very different genetic blueprints.
B)can have different functions.
C)show structural differences in the embryos but are similar in the adult organisms.
D)are only found within a species.
E)have the same function.
A)are the results of very different genetic blueprints.
B)can have different functions.
C)show structural differences in the embryos but are similar in the adult organisms.
D)are only found within a species.
E)have the same function.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements about natural selection is true?
A)Natural selection causes variations to arise within a population.
B)Natural selection leads to increased likelihood of survival for certain individuals based on variation.The variation must come from outside the population.
C)All individuals within a population have an equal likelihood of survival.Survival is based on chance.
D)Natural selection results in those individuals within a population who are best-adapted surviving and producing more offspring.
E)Natural selection leads to extinction.
A)Natural selection causes variations to arise within a population.
B)Natural selection leads to increased likelihood of survival for certain individuals based on variation.The variation must come from outside the population.
C)All individuals within a population have an equal likelihood of survival.Survival is based on chance.
D)Natural selection results in those individuals within a population who are best-adapted surviving and producing more offspring.
E)Natural selection leads to extinction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Reproductive isolating mechanisms
A)occur within a species.
B)can prevent members of the same species from reproducing.
C)only act after fertilization.
D)can prevent members of different species from interbreeding.
E)only act before fertilization.
A)occur within a species.
B)can prevent members of the same species from reproducing.
C)only act after fertilization.
D)can prevent members of different species from interbreeding.
E)only act before fertilization.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
On a molecular level, all organisms
A)show no similarities.
B)have the same bases in DNA and RNA, the same amino acids in proteins, but use different genetic codes.
C)use different means of storing genetic information.
D)have the same bases in DNA and RNA, the same amino acids in proteins, and use the same genetic code.
E)have the same bases in DNA and RNA, but different amino acids in proteins.
A)show no similarities.
B)have the same bases in DNA and RNA, the same amino acids in proteins, but use different genetic codes.
C)use different means of storing genetic information.
D)have the same bases in DNA and RNA, the same amino acids in proteins, and use the same genetic code.
E)have the same bases in DNA and RNA, but different amino acids in proteins.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Darwin's ideas on evolution were based on a number of observations. Among the most important observation was that
A)all the types of organisms that have lived on Earth are present today.
B)individuals within a population are all virtually identical to each other.
C)there is usually ample food and water for all populations.
D)when natural resources become scarce, competition occurs between members of the same species.
E)populations will only produce as many offspring as can be accommodated by the environment.
A)all the types of organisms that have lived on Earth are present today.
B)individuals within a population are all virtually identical to each other.
C)there is usually ample food and water for all populations.
D)when natural resources become scarce, competition occurs between members of the same species.
E)populations will only produce as many offspring as can be accommodated by the environment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The majority of fossils are found in
A)sedimentary rock.
B)Antarctica.
C)peat bogs.
D)tar pits.
E)volcanic deposits.
A)sedimentary rock.
B)Antarctica.
C)peat bogs.
D)tar pits.
E)volcanic deposits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Random changes in gene frequency that occur in small populations describes the concept of
A)genetic drift.
B)convergent evolution.
C)adaptive radiation.
D)sympatric speciation.
E)parapatric speciation.
A)genetic drift.
B)convergent evolution.
C)adaptive radiation.
D)sympatric speciation.
E)parapatric speciation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Many biologists believe that macroevolution is just an accumulation of microevolutionary events. Does this mean they assume a gradualist perspective over a punctuated one? Why or why not?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
How did the concept of biogeography shape Darwin's thinking?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which of the three modes of selection would be most likely to result in speciation? Why?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
How would reducing the load of antibiotics in our everyday environment reduce the number of antibiotic-resistant bacteria?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The evolution of a number of ecologically diverse species from a common ancestral species is
A)parapatric speciation.
B)sympatric speciation.
C)adaptive radiation.
D)phyletic gradualism.
E)convergent evolution.
A)parapatric speciation.
B)sympatric speciation.
C)adaptive radiation.
D)phyletic gradualism.
E)convergent evolution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
When a population is greatly reduced in size and then increases again, there is likely a reduction in genetic diversity within the population. What is this phenomenon called?
A)gene flow
B)bottleneck effect
C)founder effect
D)genetic drift
E)effective population size
A)gene flow
B)bottleneck effect
C)founder effect
D)genetic drift
E)effective population size

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The formation of new species from populations that are not isolated from each other is called
A)convergent evolution.
B)gene flow.
C)allopatric speciation.
D)sympatric speciation.
E)parapatric speciation.
A)convergent evolution.
B)gene flow.
C)allopatric speciation.
D)sympatric speciation.
E)parapatric speciation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
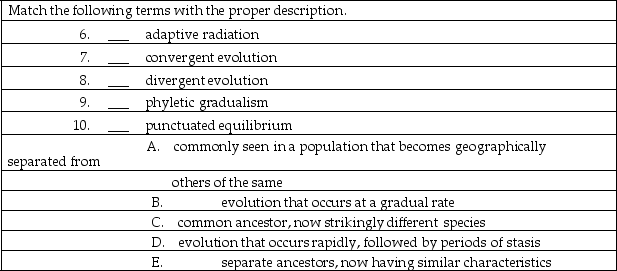 Match the following terms with the proper description.
Match the following terms with the proper description. 6. ____ adaptive radiation
7. ____ convergent evolution
8. ___ divergent evolution
9. ___ phyletic gradualism
10. ____ punctuated equilibrium
A. commonly seen in a population that becomes geographically separated from others of the same
B. evolution that occurs at a gradual rate
C. common ancestor, now strikingly different species
D. evolution that occurs rapidly, followed by periods of stasis
E. separate ancestors, now having similar characteristics

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Which of the following is not an assumption of the Hardy-Weinberg principle?
A)no mutation
B)no migration
C)small population size
D)random mating
E)no selection
A)no mutation
B)no migration
C)small population size
D)random mating
E)no selection

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Match the following terms with the proper description.
11. ___ directional selection
12. __ disruptive selection
13. __ stabilizing selection
14. ___ nonrandom mating
15. ___ artificial selection
A. favors phenotypes at both extremes
B. favors phenotypes with intermediate characteristics
C. may result in inbreeding depression
D. favors phenotypes at one extreme
E. natural selection directed by humans
11. ___ directional selection
12. __ disruptive selection
13. __ stabilizing selection
14. ___ nonrandom mating
15. ___ artificial selection
A. favors phenotypes at both extremes
B. favors phenotypes with intermediate characteristics
C. may result in inbreeding depression
D. favors phenotypes at one extreme
E. natural selection directed by humans

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Explain how species that are not closely related can look or behave so similarly. Give an example.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Match the following reproductive isolating mechanisms with the proper description.
16. __ temporal mechanisms
17. __ behavioral mechanisms
18. __ mechanical mechanisms
19. __ chemical mechanisms
20. __ postfertilization mechanisms
A. Members of different species produce different phermones.
B. Hybrids are nonviable or sterile.
C. Members of different species have different courtship rituals.
D. Members of different species are ready to breed in different seasons.
E. Members of different species don’t “fit together,” preventing mating.
16. __ temporal mechanisms
17. __ behavioral mechanisms
18. __ mechanical mechanisms
19. __ chemical mechanisms
20. __ postfertilization mechanisms
A. Members of different species produce different phermones.
B. Hybrids are nonviable or sterile.
C. Members of different species have different courtship rituals.
D. Members of different species are ready to breed in different seasons.
E. Members of different species don’t “fit together,” preventing mating.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Why would the evolution of a better eye be a disadvantage for a mole?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
An environment that favors individuals with intermediate phenotypes results in what type of selection?
A)gradual
B)punctuated
C)disruptive
D)directional
E)stabilizing
A)gradual
B)punctuated
C)disruptive
D)directional
E)stabilizing

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Although Lamarck's hypothesis was wrong, it is significant. Why?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Describe how mutations can lead to whole populations of bacteria becoming resistant to certain antibiotics.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Define and give examples of several homologous structures.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
List several types of fossils. Why are they more commonly found in sedimentary rock?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Mutation is a source of new genetic variation. New genes can only be introduced into the population when individuals reproduce. Considering this, would you expect more variation in a population of mice or elephants, over the same time period, assuming that the populations were the same size? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Provide evidence for the following statement. "At the time of Darwin's journey, geology was more influential in the development of evolutionary thought than was biology."

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Which of the following is not true of the punctuated equilibrium theory?
A)It was inspired in part by patterns observed in the fossil record.
B)It proposes that most evolutionary change is concentrated in relatively brief episodes of change.
C)It suggests that subgroups diverge and evolve at about equal and constant rates.
D)It suggests that most species undergo little phenotypic change during most of their evolutionary duration.
E)It appears to be well supported by the fossil record.
A)It was inspired in part by patterns observed in the fossil record.
B)It proposes that most evolutionary change is concentrated in relatively brief episodes of change.
C)It suggests that subgroups diverge and evolve at about equal and constant rates.
D)It suggests that most species undergo little phenotypic change during most of their evolutionary duration.
E)It appears to be well supported by the fossil record.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
What can we learn about evolution from molecular evidence?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
There are two types of genetic drift. Describe and give an example of the founder effect.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Define and give examples of several vestigial structures.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Define and give an example of divergent evolution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Define and give an example of convergent evolution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Define and give an example of adaptive radiation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Explain the basic principle of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
What can we learn about evolution of the vertebrates by examination of embryos?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
There are two types of genetic drift. Describe and give an example of the bottleneck effect.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
What is genetic diversity? Why is it important to maintain genetic diversity?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 57 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








