Deck 14: Accounting for Financial Instruments
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/90
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 14: Accounting for Financial Instruments
1
Under AASB 9,an entity is required to recognise a financial asset or liability on its statement of financial position when,and only when,it becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instrument.
True
2
AASB 132 does not apply to obligations arising under insurance contracts.
True
3
When initially recognising the liability and equity components of a compound financial instrument,gains and losses arise and must be recognised.
False
4
An entity that has taken a buy position in a futures contract on a particular item will make a gain when the price of the item decreases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Compound instruments contain both a financial liability and equity component but exclude convertible notes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The most commonly issued equity instrument would be a redeemable preference share.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
In a convertible note,AASB 132 Financial Instruments:
Recognition and Measurement requires the holder of such a financial instrument to present the liability component and the equity component separately on the statement of financial position.
Recognition and Measurement requires the holder of such a financial instrument to present the liability component and the equity component separately on the statement of financial position.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
It has been common practice to keep derivative financial instruments 'off balance sheet':

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The central issue in classifying a financial liability is the existence of a present obligation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
For a designated cash flow hedge,AASB 139 Financial Instruments:
Recognition and Measurement requires the gain or loss on the hedging instrument to be transferred initially to equity and subsequently to profit or loss to offset the gains or losses on the hedged item.
Recognition and Measurement requires the gain or loss on the hedging instrument to be transferred initially to equity and subsequently to profit or loss to offset the gains or losses on the hedged item.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
A key characteristic of a financial instrument is that it involves the ultimate transfer of an equity instrument.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
An entity that holds a well diversified portfolio of shares and wishes to use futures to protect its investments for possible downturns should enter into a sell position in a futures contract.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
An equity instrument of another entity is classified as a 'financial instrument'.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
In a convertible note,the embedded option to convert the liability into the equity of the issuer has a fair value of zero on initial recognition when the option is out of the money.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Derivatives are sometimes called 'secondary' financial instruments.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Companies may be motivated to enter into a foreign currency swap in order to hedge receivables held in the currency of the loan,the obligations of which they will undertake in the swap.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
A change in classification of a financial instrument may occur as a result of 'revised probabilities' of,for example,conversion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Once a financial instrument has been classified as a liability in the statement of financial position,under AASB 132 the reporting entity is not permitted to reclassify it unless a specific transaction or other specific action by the holder or issuer of the instrument alters the substance of the financial instrument.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Derivative instruments generally result in a transfer of the underlying primary financial instrument on maturity of the contract.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
A put option on a company's shares entitles the holder to buy that company's shares at a future time for a specified price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Partridge Ltd holds a well-diversified portfolio of shares with a current market value on 1 April 2014 of $1 million.On this date Partridge Ltd decides to hedge the portfolio by taking a sell position in 15 SPI futures units.The All Ordinaries SPI is 3130 on 1 April 2014.A unit contract in SPI futures is priced based on All Ordinaries SPI and a price of $25.The futures broker requires a deposit of $80 000.On 30 June the All Ordinaries SPI has fallen to 2980 and the value of the company's share portfolio has fallen to $950 000.On 1 July 2014 Partridge Ltd decides to sell its shares and close out its futures contract.At this date the portfolio has a market value of $925 000 and the All Ordinaries SPI is 2900.Assume all entries have been made mark to market on the futures contract and record changes in the deposit up to 1 July.What are the entries to record the transactions of 1 July 2014 (only)?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Financial instruments have recently been developed and used for what purposes?
A) increasing the volatility of primary financial instruments
B) making speculative gains
C) reducing risks
D) making speculative gains and reducing risks
A) increasing the volatility of primary financial instruments
B) making speculative gains
C) reducing risks
D) making speculative gains and reducing risks

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Golden Doors enters into a forward exchange rate contract to purchase US$300 000 on 1 September at a rate of A$1 = US$0.69.On 2 September Golden Doors takes delivery of inventory from its US supplier at a price of US$300 000.On 2 September A$1 = US$ 0.65.Calculate the amount Golden Doors would have paid on 2 September in A$ if it had not entered into the forward exchange rate contract,and any gain or loss it has made (rounded to the nearest dollar).
A) cost in A$434 782; loss of $134 782
B) cost in A$434 782; loss of $26 756
C) cost in A$461 538; gain of $161 538
D) cost in A$461 538; gain of $26 756
A) cost in A$434 782; loss of $134 782
B) cost in A$434 782; loss of $26 756
C) cost in A$461 538; gain of $161 538
D) cost in A$461 538; gain of $26 756

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which of the following are examples of derivative financial instruments?
A) deferred tax and future income tax benefits
B) mortgage loans
C) participating, redeemable preference shares
D) share options
A) deferred tax and future income tax benefits
B) mortgage loans
C) participating, redeemable preference shares
D) share options

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
What is hedging?
A) It is a method of leveraging returns when a company has foreign currency receivables or payables or has outstanding commitments that will be affected by changes in market prices.
B) It is a system for investing in financial instruments such that the entity is guaranteed increased returns and lower risks.
C) It is any activity, entered into by the entity, designed to increase returns and reduce risk.
D) It is an action taken with the object of avoiding or minimising possible adverse effects of movements in things such as exchange rates or market prices.
A) It is a method of leveraging returns when a company has foreign currency receivables or payables or has outstanding commitments that will be affected by changes in market prices.
B) It is a system for investing in financial instruments such that the entity is guaranteed increased returns and lower risks.
C) It is any activity, entered into by the entity, designed to increase returns and reduce risk.
D) It is an action taken with the object of avoiding or minimising possible adverse effects of movements in things such as exchange rates or market prices.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
A compound financial instrument is one that:
A) transfers the risks of a primary instrument to another entity.
B) effectively contains a financial liability and equity instrument.
C) ultimately requires the exchange of a financial asset for an equity instrument.
D) offers interest terms such that interest is paid on interest.
A) transfers the risks of a primary instrument to another entity.
B) effectively contains a financial liability and equity instrument.
C) ultimately requires the exchange of a financial asset for an equity instrument.
D) offers interest terms such that interest is paid on interest.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Partridge Ltd holds a well-diversified portfolio of shares with a current market value on 1 April 2014 of $1 million.On this date Partridge Ltd decides to hedge the portfolio by taking a sell position in 15 SPI futures units.The All Ordinaries SPI is 3130 on 1 April 2014.A unit contract in SPI futures is priced based on All Ordinaries SPI and a price of $25.The futures broker requires a deposit of $80 000.On 30 June the All Ordinaries SPI has fallen to 2980 and the value of the company's share portfolio has fallen to $950 000.What are the appropriate journal entries to record these events?
A)
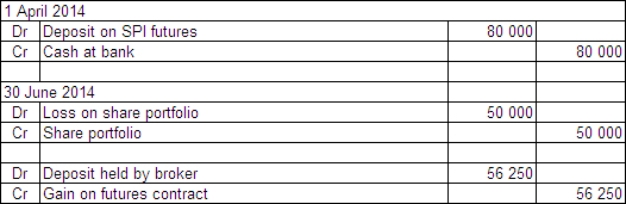
B)
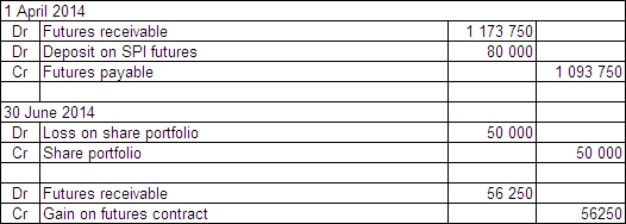
C)
D)
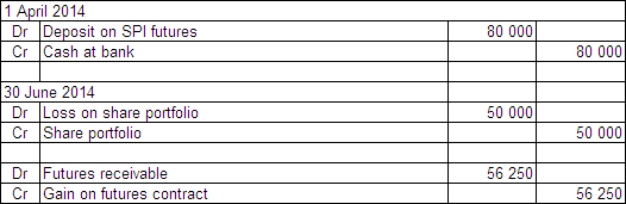
A)

B)

C)
D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
In differentiating between a financial liability and equity,the report preparer must consider:
A) the existence of a contractual obligation to deliver cash or another financial asset.
B) the consequences of recording a financial liability and the associated impacts on profit.
C) the substance of the agreement over its form.
D) the existence of a contractual obligation to deliver cash or another financial asset and the substance of the agreement over its form.
A) the existence of a contractual obligation to deliver cash or another financial asset.
B) the consequences of recording a financial liability and the associated impacts on profit.
C) the substance of the agreement over its form.
D) the existence of a contractual obligation to deliver cash or another financial asset and the substance of the agreement over its form.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The structure of futures contracts as they are traded in Australia is best described in which of the following?
A) All parties that trade in futures make a (relatively small) specific deposit before they enter into the contract. The contract is marked to market on a daily basis and gains on the contract are added to the deposit and losses are deducted. When the deposit reaches a minimum level a margin call will be made to require the trader to reinstate the original deposit.
B) The purchaser of the futures contract is given a set price at which they can exercise the futures contract at or up to a specified date. If during that time or up to that date the buyer of the futures contract decides to exercise it, the buyer pays the exercise price and the seller of the contract agrees to deliver the item within a specified period of the exercise date. In the case of financial futures, they are often closed out before delivery is required.
C) All buyers of futures contracts make a specific deposit that is held in trust by the other party to the contract. As the buyer makes gains, these are deducted from the amount of deposit held by the seller. As the seller makes gains on the contract, the buyer is required to increase the deposit to maintain the same percentage value of deposit. At the delivery date on the contract the deposit has already accumulated the gains and losses and all that is required is for the seller to deliver on the contract. In the case of financial futures, they are often closed out before delivery is required.
D) A futures contract contains an agreement to buy and sell a specified item or financial asset or index at a future date and at an agreed price. The parties to the contract are not required to make any financial commitment at the beginning of the contract, hence futures contracts are considered highly levered and risky for speculation purposes. The buyer pays the agreed sum on delivery by the seller or the contract is closed out before the delivery date.
A) All parties that trade in futures make a (relatively small) specific deposit before they enter into the contract. The contract is marked to market on a daily basis and gains on the contract are added to the deposit and losses are deducted. When the deposit reaches a minimum level a margin call will be made to require the trader to reinstate the original deposit.
B) The purchaser of the futures contract is given a set price at which they can exercise the futures contract at or up to a specified date. If during that time or up to that date the buyer of the futures contract decides to exercise it, the buyer pays the exercise price and the seller of the contract agrees to deliver the item within a specified period of the exercise date. In the case of financial futures, they are often closed out before delivery is required.
C) All buyers of futures contracts make a specific deposit that is held in trust by the other party to the contract. As the buyer makes gains, these are deducted from the amount of deposit held by the seller. As the seller makes gains on the contract, the buyer is required to increase the deposit to maintain the same percentage value of deposit. At the delivery date on the contract the deposit has already accumulated the gains and losses and all that is required is for the seller to deliver on the contract. In the case of financial futures, they are often closed out before delivery is required.
D) A futures contract contains an agreement to buy and sell a specified item or financial asset or index at a future date and at an agreed price. The parties to the contract are not required to make any financial commitment at the beginning of the contract, hence futures contracts are considered highly levered and risky for speculation purposes. The buyer pays the agreed sum on delivery by the seller or the contract is closed out before the delivery date.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
When financial instruments are issued that are to appear in the statement of financial position the issuer is required to determine whether the item should be disclosed as a liability or as equity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The characteristics of a call option are best described as follows:
A) It allows the holder to sell the shares of the specified company at a prespecified (strike or exercise) price. The exercise price remains fixed, but the option can be traded in a market and its value will depend on the value of the underlying share such that an increase in the price of the share will lead to a decrease in the value of the option (and vice versa). The holder usually does not have to exercise the option and would choose not to if the share price were above the exercise price.
B) It allows the holder to buy the shares of the specified company at a prespecified (strike or exercise) price. The exercise price will depend on the value of the underlying share such that an increase in the price of the share will lead to an increase in the exercise price (and vice versa). The holder is committed to exercise the option or close out the contract by taking a put option position in the market.
C) It allows the holder to buy the shares of the specified company at a prespecified (strike or exercise) price. The exercise price remains fixed, but the option can be traded in a market and its value will depend on the value of the underlying share such that an increase in the price of the share will lead to an increase in the value of the option (and vice versa). The holder usually does not have to exercise the option and would choose not to if the share price fell below the exercise price.
D) It allows the holder to sell the shares of the specified company at a prespecified (strike or exercise) price. The exercise price remains fixed, but the option can be traded in a market and its value will depend on the value of the underlying share such that an increase in the price of the share will lead to an increase in the value of the option (and vice versa). While the holder of a put option usually does not have to exercise the option and would choose not to if the share price fell below the exercise price, the holder of a call option must either complete the contract or close it out by taking out a put option for the same number of shares in the market.
A) It allows the holder to sell the shares of the specified company at a prespecified (strike or exercise) price. The exercise price remains fixed, but the option can be traded in a market and its value will depend on the value of the underlying share such that an increase in the price of the share will lead to a decrease in the value of the option (and vice versa). The holder usually does not have to exercise the option and would choose not to if the share price were above the exercise price.
B) It allows the holder to buy the shares of the specified company at a prespecified (strike or exercise) price. The exercise price will depend on the value of the underlying share such that an increase in the price of the share will lead to an increase in the exercise price (and vice versa). The holder is committed to exercise the option or close out the contract by taking a put option position in the market.
C) It allows the holder to buy the shares of the specified company at a prespecified (strike or exercise) price. The exercise price remains fixed, but the option can be traded in a market and its value will depend on the value of the underlying share such that an increase in the price of the share will lead to an increase in the value of the option (and vice versa). The holder usually does not have to exercise the option and would choose not to if the share price fell below the exercise price.
D) It allows the holder to sell the shares of the specified company at a prespecified (strike or exercise) price. The exercise price remains fixed, but the option can be traded in a market and its value will depend on the value of the underlying share such that an increase in the price of the share will lead to an increase in the value of the option (and vice versa). While the holder of a put option usually does not have to exercise the option and would choose not to if the share price fell below the exercise price, the holder of a call option must either complete the contract or close it out by taking out a put option for the same number of shares in the market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
When offsetting financial assets and liabilities an entity must settle on a net basis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Pigeon Ltd holds a well-diversified portfolio of shares with a current market value on 1 May 2014 of $900 000.On this date Pigeon Ltd decides to hedge the portfolio by taking a sell position in ten SPI futures units.The All Ordinaries SPI is 2980 on 1 May 2014.A unit contract in SPI futures is priced based on All Ordinaries SPI and a price of $25.The futures broker requires a deposit of $1500.On 30 June the All Ordinaries SPI has fallen to 2570 and the value of the company's share portfolio has fallen to $790 000.What is the gain or loss on the futures contract and the net gain or loss after hedging?
A) loss on futures contract $102 500; net gain after hedging $6000
B) gain on futures contract $10 250; net loss after hedging $99 750
C) gain on futures contract $102 500; net loss after hedging $7500
D) gain on futures contract $164; net loss after hedging $109 836
A) loss on futures contract $102 500; net gain after hedging $6000
B) gain on futures contract $10 250; net loss after hedging $99 750
C) gain on futures contract $102 500; net loss after hedging $7500
D) gain on futures contract $164; net loss after hedging $109 836

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A potential downturn in the share market can be overcome by:
A) taking a buy position on a contract for SPI futures and then closing out the contract if the market begins to rise.
B) taking out a contract SPI futures and agreeing to a sell position. The contract should be closed out if the market begins to rise.
C) entering into a forward exchange rate contract and specifying a specific date to purchase currency at a set rate.
D) hedging by agreeing to deliver goods at a specific date in the future at a predetermined price.
A) taking a buy position on a contract for SPI futures and then closing out the contract if the market begins to rise.
B) taking out a contract SPI futures and agreeing to a sell position. The contract should be closed out if the market begins to rise.
C) entering into a forward exchange rate contract and specifying a specific date to purchase currency at a set rate.
D) hedging by agreeing to deliver goods at a specific date in the future at a predetermined price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Jackson Ltd has a US$50 000 receivable due at the end of March 2014 for the sale of a specialised piece of hydraulic equipment.The sale was made on 1 February 2014 and the equipment cost Jackson Ltd $560 000 to manufacture.In order to hedge the receivable,Jackson Ltd enters into a futures contract on that date to sell five US dollar futures contracts.Each contract is for an amount of US$100 000 and the market rate for each futures contract is A$1 = US$0.6778 on 1 February.Jackson pays a deposit of $25 000 on the contracts.The futures contracts are settled on 31 March 2014,when the debtor pays off the receivable.The spot exchange rates during the period were: The market rate for the futures contracts is A$1 = US$0.7150 on 31 March 2014.What are the entries to record the sale,futures contracts,receipt of payment and the settling of the futures contracts (rounded to the nearest dollar)?
A)
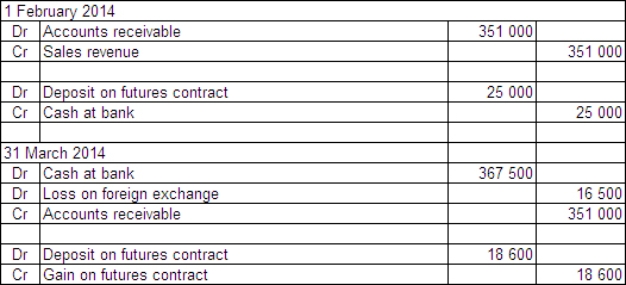
B)
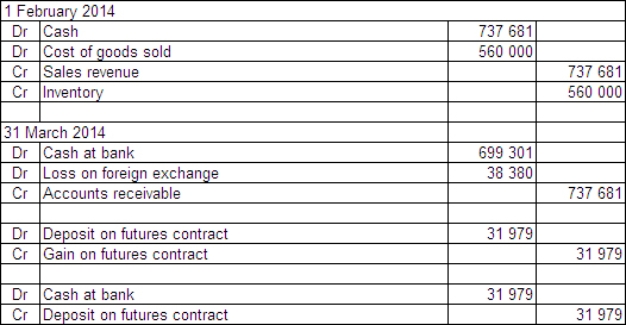
C)
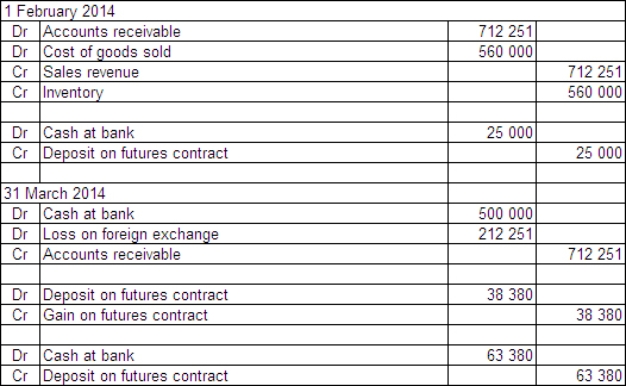
D)
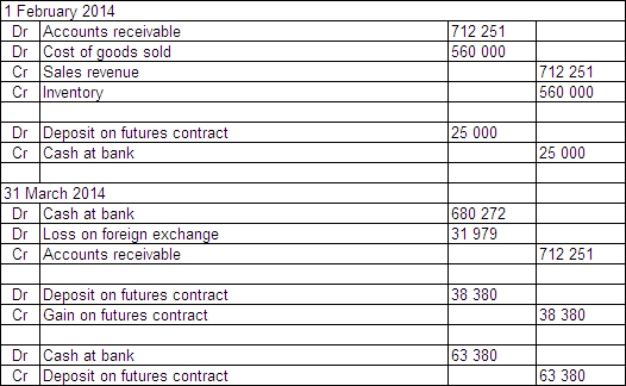
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
A derivative financial instrument is one which:
A) creates a contractual link between two entities such that the financial asset or equity item of one entity becomes the financial liability of the other entity and there is a transfer of risks and returns.
B) creates rights and obligations that have the effect of transferring one or more of the financial risks inherent in an underlying primary financial instrument, and the value of the contract normally reflects changes in the value of the underlying financial instrument.
C) creates a contractual link between a secondary financial instrument and a primary financial instrument such that there is an ultimate transfer of a financial asset between the contracting parties.
D) creates rights and obligations that have the effect of transferring the financial returns inherent in an underlying primary financial instrument, and the value of the contract normally reflects changes in the value of the underlying financial instrument.
A) creates a contractual link between two entities such that the financial asset or equity item of one entity becomes the financial liability of the other entity and there is a transfer of risks and returns.
B) creates rights and obligations that have the effect of transferring one or more of the financial risks inherent in an underlying primary financial instrument, and the value of the contract normally reflects changes in the value of the underlying financial instrument.
C) creates a contractual link between a secondary financial instrument and a primary financial instrument such that there is an ultimate transfer of a financial asset between the contracting parties.
D) creates rights and obligations that have the effect of transferring the financial returns inherent in an underlying primary financial instrument, and the value of the contract normally reflects changes in the value of the underlying financial instrument.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
According to AASB 132,which of the following are considered to be financial assets?
A) an equity instrument of another entity
B) a futures contract for the delivery of a product or service
C) a prepayment
D) a futures contract for the delivery of a product or service and a prepayment
A) an equity instrument of another entity
B) a futures contract for the delivery of a product or service
C) a prepayment
D) a futures contract for the delivery of a product or service and a prepayment

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
AASB 132 defines a financial instrument as:
A) any commitment that gives rise to either a financial asset or a financial liability of the reporting entity.
B) any contract that gives rise to both a financial asset of one entity and a financial liability or equity instrument of another entity.
C) any commitment that ultimately gives rise to an equity instrument of the reporting entity.
D) any contract that gives rise to both a financial asset of one entity and a financial liability or equity instrument of the same entity.
A) any commitment that gives rise to either a financial asset or a financial liability of the reporting entity.
B) any contract that gives rise to both a financial asset of one entity and a financial liability or equity instrument of another entity.
C) any commitment that ultimately gives rise to an equity instrument of the reporting entity.
D) any contract that gives rise to both a financial asset of one entity and a financial liability or equity instrument of the same entity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Catchup Company buys a contract in SPI futures,taking a buy position on 1 April 2013 to 'take delivery' on 30 May 2013.A unit contract in SPI futures is priced at the All Ordinaries SPI multiplied by $25.On 1 April the All Ordinaries SPI is 2950.By 1 May the index has dropped to 2600 and Catchup decides to close out the contract.What is Catchup's gain or loss on the futures contract?
A) gain of $22
B) loss of $8750
C) loss of $350
D) gain of $8750
A) gain of $22
B) loss of $8750
C) loss of $350
D) gain of $8750

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Which of the following are examples of primary financial instruments?
A) futures contracts
B) unearned revenue
C) accrued rent
D) unearned revenue and accrued rent
A) futures contracts
B) unearned revenue
C) accrued rent
D) unearned revenue and accrued rent

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Basket Ltd acquired a parcel of 50 000 call options in Snake and Asp Ltd on 1 November 2014.The price of the options was $0.40 each and they may be exercised any time prior to 30 June 2016.The exercise price is $30.On Basket Ltd's balance date - 30 June 2016 - the company is still holding the options.The market price of the options at that time was $0.39 each and the price of Snake and Asp Ltd shares had risen to $28 having previously fallen to $15.What are the entries required to record the purchase of the options and the likely action of Basket Ltd?
A)

B)
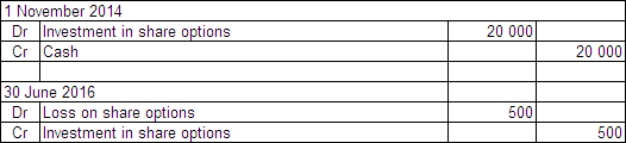
C)
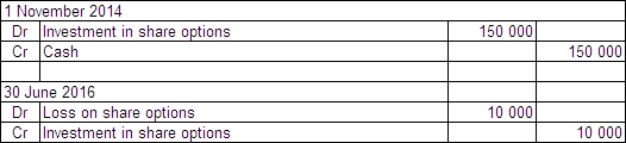
D)
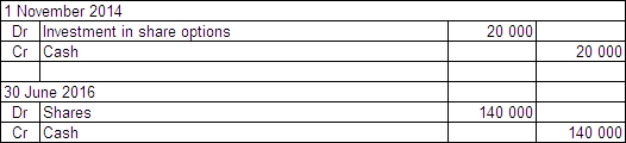
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements is true about a share option:
A) The nature of the holder's right in relation to the option is affected by the likelihood that the option will be exercised.
B) The nature of the holder's obligations in relation to the option are affected by the likelihood that the option will be exercised.
C) The likelihood of the option being exercised does not affect its classification as a financial liability.
D) The likelihood of the option being exercised does affect its classification as a financial liability.
A) The nature of the holder's right in relation to the option is affected by the likelihood that the option will be exercised.
B) The nature of the holder's obligations in relation to the option are affected by the likelihood that the option will be exercised.
C) The likelihood of the option being exercised does not affect its classification as a financial liability.
D) The likelihood of the option being exercised does affect its classification as a financial liability.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
What is the appropriate accounting treatment for a loan that is the subject of a swap agreement?
A) Since the loan has been swapped with another, the two loans should be set-off in accordance with AASB 132.
B) The original loan should be removed from the statement of financial position and replaced by the other loan in the swap.
C) The original loan should be removed from the statement of financial position and replaced by the other loan in the swap. In the case of a foreign currency swap this treatment is also appropriate but the gain or loss on foreign currency translation should be deferred and amortised over the life of the loan.
D) The original loan, for which the entity has the primary obligation, should be retained in the statement of financial position.
A) Since the loan has been swapped with another, the two loans should be set-off in accordance with AASB 132.
B) The original loan should be removed from the statement of financial position and replaced by the other loan in the swap.
C) The original loan should be removed from the statement of financial position and replaced by the other loan in the swap. In the case of a foreign currency swap this treatment is also appropriate but the gain or loss on foreign currency translation should be deferred and amortised over the life of the loan.
D) The original loan, for which the entity has the primary obligation, should be retained in the statement of financial position.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Under the requirements of the AASB Framework how would convertible notes be classified in the statement of financial position?
A) They have the essential characteristics of debt and, using the principle of prudence, would be classified as a liability.
B) They would be classified in a separate category between liabilities and equity.
C) They would be classified as either liabilities or equity at any balance date based on the probability at that time that the notes would, or would not, be converted.
D) They have the essential characteristics of shares and, using the principle of substance over form, they would be classified as equity.
A) They have the essential characteristics of debt and, using the principle of prudence, would be classified as a liability.
B) They would be classified in a separate category between liabilities and equity.
C) They would be classified as either liabilities or equity at any balance date based on the probability at that time that the notes would, or would not, be converted.
D) They have the essential characteristics of shares and, using the principle of substance over form, they would be classified as equity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Two companies enter into loan agreements on 1 March 2013.On that date they also enter into an agreement to swap the loans.The details for each company and loan are: Exchange rates:
The balance date for both companies is 30 June 2013.What are the accounting entries in the books of Boris Ltd on 1 March and 30 June 2013?
A)
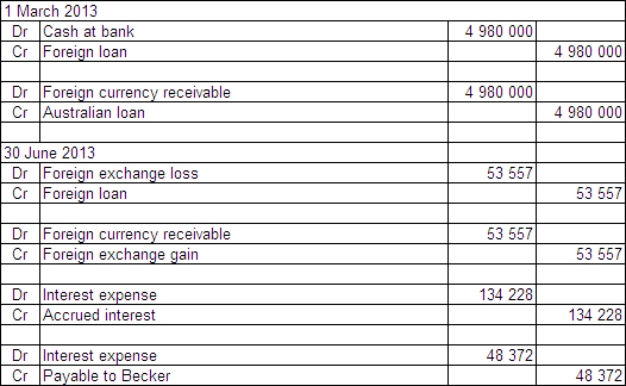
B)
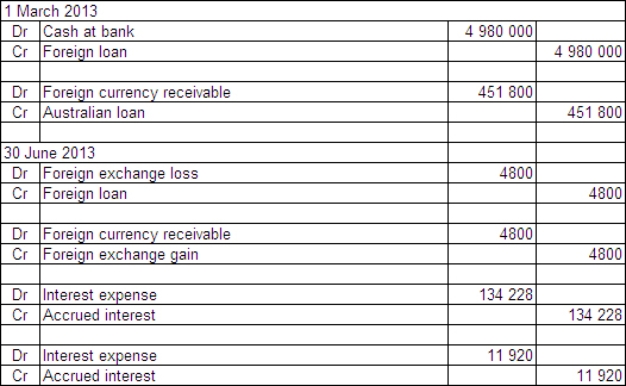
C)
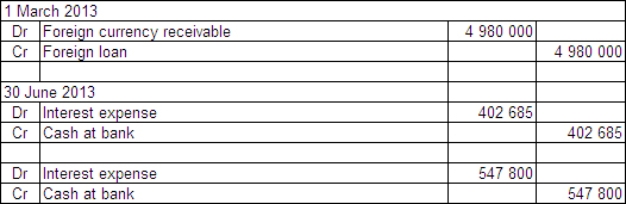
D)
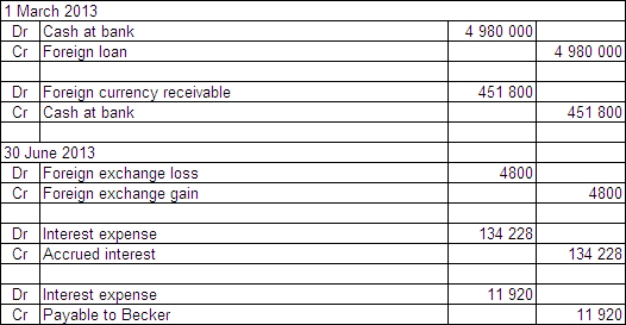
The balance date for both companies is 30 June 2013.What are the accounting entries in the books of Boris Ltd on 1 March and 30 June 2013?
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Layton Enterprises and Hewitt Ltd agree to swap their loans.The terms of the loans are: Under the swap agreement Layton Enterprises will make floating rate payments to Hewitt Ltd at the bank bill rate plus 0.8% and Hewitt will make fixed rate payments to Layton Enterprises at 12%.
Layton Enterprises' alternative to the fixed interest loan was to pay the bank bill rate (a floating rate).Hewitt's alternative was to pay a fixed interest rate of 13.5%.
Is each company better off under the swap agreement than if it had taken up the alternatives offered by the bank?
What is the net difference in the interest rate paid under the swap and the alternative for each company?
A) Layton Enterprises is better off but Hewitt Ltd may not be. Layton pays 2% less but Hewitt Ltd's position will depend on the level of the bank bill rate in each period.
B) Each company is better off. Layton Enterprises pays 1.2% less and Hewitt Ltd pays 1.5% less.
C) Hewitt Ltd is better off but Layton Enterprises may not be. Hewitt Ltd pays 0.2% less and Layton Enterprises' position will depend on the level of the bank bill rate in each period.
D) Each company's position will depend on the level of bank bill rate in each period. In entering the agreement they are anticipating that it will not go over 13.5%.
Layton Enterprises' alternative to the fixed interest loan was to pay the bank bill rate (a floating rate).Hewitt's alternative was to pay a fixed interest rate of 13.5%.
Is each company better off under the swap agreement than if it had taken up the alternatives offered by the bank?
What is the net difference in the interest rate paid under the swap and the alternative for each company?
A) Layton Enterprises is better off but Hewitt Ltd may not be. Layton pays 2% less but Hewitt Ltd's position will depend on the level of the bank bill rate in each period.
B) Each company is better off. Layton Enterprises pays 1.2% less and Hewitt Ltd pays 1.5% less.
C) Hewitt Ltd is better off but Layton Enterprises may not be. Hewitt Ltd pays 0.2% less and Layton Enterprises' position will depend on the level of the bank bill rate in each period.
D) Each company's position will depend on the level of bank bill rate in each period. In entering the agreement they are anticipating that it will not go over 13.5%.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
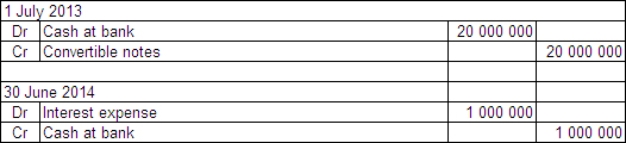
Sampras Ltd issued $20 million of convertible notes on 1 July 2013.The notes have a life of 6 years and a face value of $20 each.Annual interest of 5% is payable at the end of each year.The notes were issued at their face value and can be converted at any time over their lives.Organisations with a similar risk profile to Sampras Ltd have issued debt with similar terms but without the option to convert at the rate of 7%.What are the appropriate accounting entries to record the issue of the convertible notes and the first payment of interest in accordance with guidance provided in AASB 132?
A)
B)
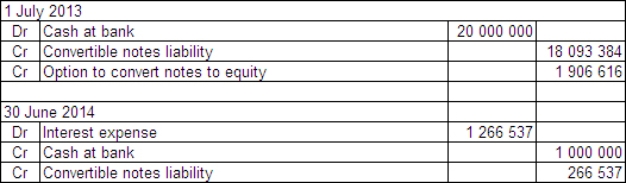
C)
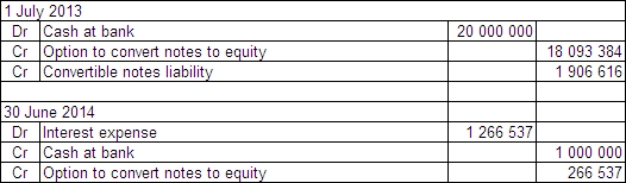
D)
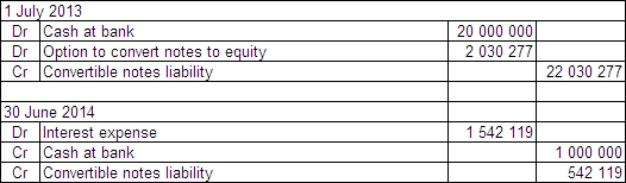
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The characteristics of a swap agreement may be best described as:
A) an agreement in which companies agree to exchange their shares as part of a merger or company acquisition arrangement. The swap provides certainty for the shareholders in both companies as to the timing and relative weighting of the shares in the swap. Swaps must be registered with the stock exchange.
B) an agreement in which lenders exchange portfolios of loan receivables in order to better balance their risks. This is an especially important facility for small banks that may face higher risk exposures as a result of concentrating their loan receivables in a small or niche market.
C) an agreement in which borrowers exchange aspects of their respective loan obligations. Two types of swaps that are commonly used are interest rate swaps and foreign currency swaps. Swap agreements are derivative financial instruments.
D) an agreement in which investors agree to swap entitlements to dividends but retain ownership of the underlying share. This allows traders in the market to make contracts that result in high cash dividends as well as high capital returns on shares.
A) an agreement in which companies agree to exchange their shares as part of a merger or company acquisition arrangement. The swap provides certainty for the shareholders in both companies as to the timing and relative weighting of the shares in the swap. Swaps must be registered with the stock exchange.
B) an agreement in which lenders exchange portfolios of loan receivables in order to better balance their risks. This is an especially important facility for small banks that may face higher risk exposures as a result of concentrating their loan receivables in a small or niche market.
C) an agreement in which borrowers exchange aspects of their respective loan obligations. Two types of swaps that are commonly used are interest rate swaps and foreign currency swaps. Swap agreements are derivative financial instruments.
D) an agreement in which investors agree to swap entitlements to dividends but retain ownership of the underlying share. This allows traders in the market to make contracts that result in high cash dividends as well as high capital returns on shares.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
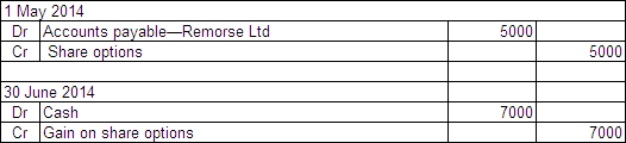
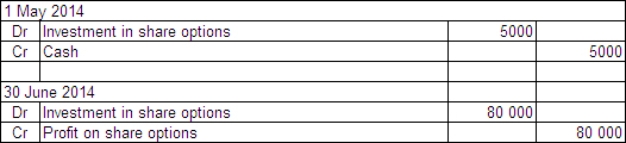
Penitent Ltd acquired a parcel of 10 000 call options in Remorse Company Ltd on 1 May 2014.The price of the options was $0.50 each and they may be exercised any time over the next 3 years.The exercise price is $11.On Penitent Ltd's balance date - 30 June 2014 - the company is still holding the options.The market price of the options at that time was $1.20 each and the price of Remorse Company's shares had risen to $19.What are the entries required to record the purchase of the options and the adjusting entry to mark the options to market in Penitent's books?
A)
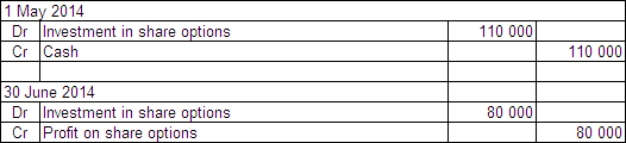
B)
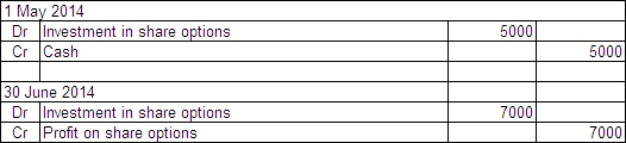
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Which of the following statements about a swap instrument is correct?
A) A company may seek to swap a short-term loan for a long-term loan (or vice versa). Another type of swap is where a company swaps a loan denominated in local currency for a foreign currency loan. After the swap agreement has been made, the primary borrower no longer has a commitment to the primary lender.
B) A company may seek to swap a fixed interest loan for a variable rate interest loan (or vice versa). Another type of swap is where a company swaps a loan denominated in local currency for a foreign currency loan. After the swap agreement has been made, the primary borrower still has a commitment to the primary lender should the other party to the swap default on the arrangement.
C) A company may seek to swap a compound interest loan for a simple interest rate loan (or vice versa). Another type of swap is where a company swaps a fixed interest rate loan for a variable interest rate loan (or vice versa). The swap agreement is enforceable by both parties and the risk of default by either party is minimal.
D) A company may seek to swap a short-term loan for a long-term loan (or vice versa). Another type of swap is where a company swaps a portion of its shares for the shares in another company. After the swap agreement has been made, the relationship between the two companies is stronger and can form the basis of an ongoing strategic alliance.
A) A company may seek to swap a short-term loan for a long-term loan (or vice versa). Another type of swap is where a company swaps a loan denominated in local currency for a foreign currency loan. After the swap agreement has been made, the primary borrower no longer has a commitment to the primary lender.
B) A company may seek to swap a fixed interest loan for a variable rate interest loan (or vice versa). Another type of swap is where a company swaps a loan denominated in local currency for a foreign currency loan. After the swap agreement has been made, the primary borrower still has a commitment to the primary lender should the other party to the swap default on the arrangement.
C) A company may seek to swap a compound interest loan for a simple interest rate loan (or vice versa). Another type of swap is where a company swaps a fixed interest rate loan for a variable interest rate loan (or vice versa). The swap agreement is enforceable by both parties and the risk of default by either party is minimal.
D) A company may seek to swap a short-term loan for a long-term loan (or vice versa). Another type of swap is where a company swaps a portion of its shares for the shares in another company. After the swap agreement has been made, the relationship between the two companies is stronger and can form the basis of an ongoing strategic alliance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Racquet Ltd issued $20 million of convertible notes on 1 July 2013.The notes have a life of 6 years and a face value of $20 each.Annual interest of 5% is payable at the end of each year.The notes were issued at their face value and can be converted at any time over their lives.Organisations with a similar risk profile to Racquet Ltd have issued debt with similar terms but without the option to convert at the rate of 7%.What are the appropriate accounting entries to record the conversion of the notes to equity on 1 July 2014 (after interest has been paid and recorded)?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Prepayments are:
A) not financial instruments because they typically provide a right to future goods or services.
B) financial instruments because they typically provide a right to future goods or services.
C) not financial instruments because they typically provide a right to cash or another financial instrument.
D) financial instruments because they typically provide a right to future goods or services
A) not financial instruments because they typically provide a right to future goods or services.
B) financial instruments because they typically provide a right to future goods or services.
C) not financial instruments because they typically provide a right to cash or another financial instrument.
D) financial instruments because they typically provide a right to future goods or services

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
AASB 139 stipulates how financial instruments are to be recognised and measured.Specifically these instruments could be:
A) recorded at their fair value with any changes included in the period's profit or loss unless the instrument was acquired as a hedge.
B) recorded at fair value with any changes recorded directly to equity and only transferred to profit when the asset is derecognised.
C) measured and amortised at cost using the effective interest method.
D) all of the given answers.
A) recorded at their fair value with any changes included in the period's profit or loss unless the instrument was acquired as a hedge.
B) recorded at fair value with any changes recorded directly to equity and only transferred to profit when the asset is derecognised.
C) measured and amortised at cost using the effective interest method.
D) all of the given answers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
An attribute of an equity instrument is that:
A) the holder is entitled to a fixed-rate return.
B) the holder is not entitled to a fixed-rate return.
C) it always confers voting rights upon the holder.
D) it is always issued at par value.
A) the holder is entitled to a fixed-rate return.
B) the holder is not entitled to a fixed-rate return.
C) it always confers voting rights upon the holder.
D) it is always issued at par value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
A convertible note may be accurately described as:
A) a derivative financial instrument that affords the holder a stream of cash flows and benefits associated with being a shareholder but transfers the risk to the holders of the convertible options.
B) a secondary financial instrument that from the perspective of the issuer contains a contractual obligation to deliver cash and a put option.
C) a simple financial instrument that affords the holder access to a stream of cash flows in the form of either dividends or interest payments.
D) a compound financial instrument that from the perspective of the issuer contains a contractual obligation to deliver cash and a call option.
A) a derivative financial instrument that affords the holder a stream of cash flows and benefits associated with being a shareholder but transfers the risk to the holders of the convertible options.
B) a secondary financial instrument that from the perspective of the issuer contains a contractual obligation to deliver cash and a put option.
C) a simple financial instrument that affords the holder access to a stream of cash flows in the form of either dividends or interest payments.
D) a compound financial instrument that from the perspective of the issuer contains a contractual obligation to deliver cash and a call option.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
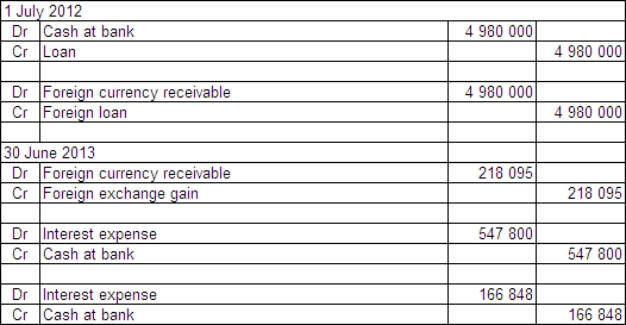
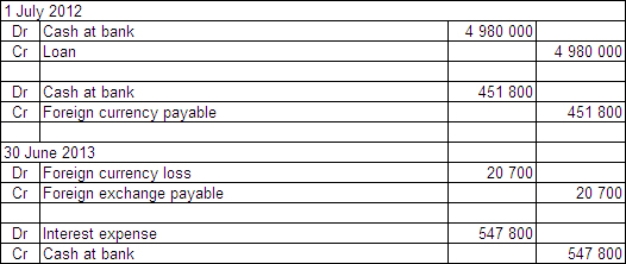
Two companies enter into loan agreements on 1 July 2012.On that date they also enter into an agreement to swap the loans.The details for each company and loan are: Exchange rates:
The balance date for both companies is 30 June 2013.What are the accounting entries in the books of Agassi Ltd on 1 July 2002 and 30 June 2013?
A)
B)
C)
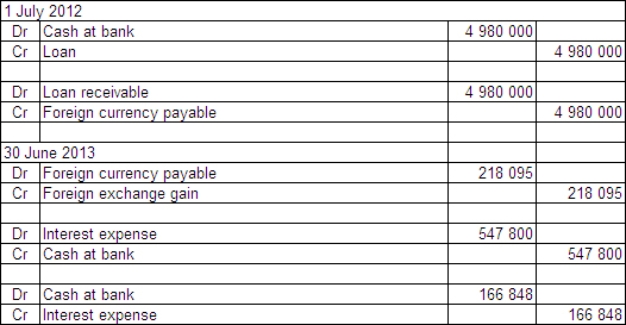
D)
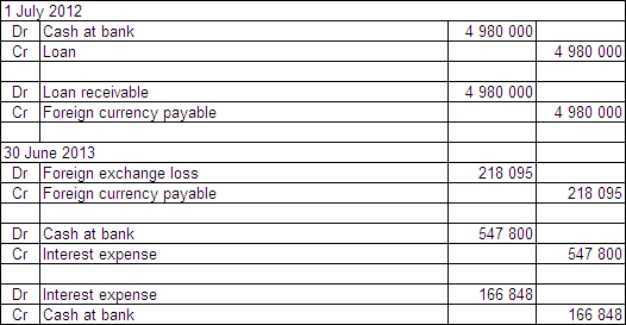
The balance date for both companies is 30 June 2013.What are the accounting entries in the books of Agassi Ltd on 1 July 2002 and 30 June 2013?
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Financial assets do not include:
A) cash.
B) notes receivable.
C) an equity instrument of another entity.
D) inventories.
A) cash.
B) notes receivable.
C) an equity instrument of another entity.
D) inventories.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
The market price of an option is a function of:
A) market expectations regarding the medium term dividend stream expected on the shares underlying the option. Where the exercise price is expected to be greater than the sum of 2 to 3 years' dividends the option will sell at a discount. Where the exercise price is less than 1 year's expected dividend it will sell at a premium.
B) the difference between the market price of the share and the exercise price on the option. The market price of the option will, however, be greater than this difference where the option does not expire for some time. All other things being equal, the greater the time until the option is to be exercised the greater the difference will be between the price of the option and the difference between the exercise price and the share price.
C) the liquidity of the shares underlying the options. Investors in the market are more interested in options over shares that are subsequently easily traded. A measure of the liquidity of a share is the average volume of shares turned over during a period. The higher this measure, the higher the market price of the option.
D) the market price as being closely linked to the exercise price and where it does not vary significantly from that. The only situation in which this ceases to be true is when significant impacts on the whole market shift the prices of many shares down at once (for example, in the case of a major impact to a whole economy such as was experienced in the September 2001 attack on the World Trade Center in New York).
A) market expectations regarding the medium term dividend stream expected on the shares underlying the option. Where the exercise price is expected to be greater than the sum of 2 to 3 years' dividends the option will sell at a discount. Where the exercise price is less than 1 year's expected dividend it will sell at a premium.
B) the difference between the market price of the share and the exercise price on the option. The market price of the option will, however, be greater than this difference where the option does not expire for some time. All other things being equal, the greater the time until the option is to be exercised the greater the difference will be between the price of the option and the difference between the exercise price and the share price.
C) the liquidity of the shares underlying the options. Investors in the market are more interested in options over shares that are subsequently easily traded. A measure of the liquidity of a share is the average volume of shares turned over during a period. The higher this measure, the higher the market price of the option.
D) the market price as being closely linked to the exercise price and where it does not vary significantly from that. The only situation in which this ceases to be true is when significant impacts on the whole market shift the prices of many shares down at once (for example, in the case of a major impact to a whole economy such as was experienced in the September 2001 attack on the World Trade Center in New York).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
For a financial instrument to be classified as an equity instrument,the instrument must include:
A) no contractual obligations whatsoever
B) a certification of public approval from ASIC.
C) a contractual obligation to exchange financial assets or financial liabilities with another entity under conditions that are unfavourable to the issuer.
D) no contractual obligation for the issuer to deliver a variable number of shares of its own equity if settled with such an issue.
A) no contractual obligations whatsoever
B) a certification of public approval from ASIC.
C) a contractual obligation to exchange financial assets or financial liabilities with another entity under conditions that are unfavourable to the issuer.
D) no contractual obligation for the issuer to deliver a variable number of shares of its own equity if settled with such an issue.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
A preference share is a financial liability:
A) if it provides for mandatory redemption by the issuer for a fixed or determinable amount at a fixed or determinable future date.
B) if it gives the holder the right to require the issuer to redeem the instrument at or after a particular date for a fixed or determinable amount.
C) if it gives the issuer the sole discretion to redeem the instrument at a date of their choice for a fixed or determinable amount.
D) if it provides for mandatory redemption by the issuer for a fixed or determinable amount at a fixed or determinable future date and if it gives the holder the right to require the issuer to redeem the instrument at or after a particular date for a fixed or determinable amount.
A) if it provides for mandatory redemption by the issuer for a fixed or determinable amount at a fixed or determinable future date.
B) if it gives the holder the right to require the issuer to redeem the instrument at or after a particular date for a fixed or determinable amount.
C) if it gives the issuer the sole discretion to redeem the instrument at a date of their choice for a fixed or determinable amount.
D) if it provides for mandatory redemption by the issuer for a fixed or determinable amount at a fixed or determinable future date and if it gives the holder the right to require the issuer to redeem the instrument at or after a particular date for a fixed or determinable amount.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
In disclosing information about how a financial asset or financial liability meets the conditions to be classified as 'at fair value through profit and loss',an entity must have a narrative description of how this designation is consistent with:
A) industry practice.
B) its own documented investment strategy.
C) ASIC's requirements.
D) the law.
A) industry practice.
B) its own documented investment strategy.
C) ASIC's requirements.
D) the law.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Documentation that constitutes a financial instrument as a hedging instrument must include:
A) how the entity will assess the effectiveness of the hedging instrument.
B) the nature of the risk being hedged.
C) the risk management objective and strategy.
D) all of the given answers.
A) how the entity will assess the effectiveness of the hedging instrument.
B) the nature of the risk being hedged.
C) the risk management objective and strategy.
D) all of the given answers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Which of the following statements are true?
I)The initial measurement of financial assets is to be at fair value.
II)The initial measurement of financial liabilities is to be at present value.
III)The initial measurement of financial liabilities is to be at fair value.
IV)The subsequent measurement of financial assets and financial liabilities will be at fair value.
V)The subsequent measurement of financial assets and financial liabilities will be dependent upon the category to which the financial instrument belongs.
A) I, II and V
B) I, II and IV
C) I, III and IV
D) I, III and V
I)The initial measurement of financial assets is to be at fair value.
II)The initial measurement of financial liabilities is to be at present value.
III)The initial measurement of financial liabilities is to be at fair value.
IV)The subsequent measurement of financial assets and financial liabilities will be at fair value.
V)The subsequent measurement of financial assets and financial liabilities will be dependent upon the category to which the financial instrument belongs.
A) I, II and V
B) I, II and IV
C) I, III and IV
D) I, III and V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Which of the following items is not a financial instrument?
A) cash
B) derivative instrument that is unfavourable to the entity
C) goodwill
D) trade accounts receivable
A) cash
B) derivative instrument that is unfavourable to the entity
C) goodwill
D) trade accounts receivable

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
David Ltd acquired a parcel of 50 000 call options in Goliath Ltd on 1 November 2012.The price of the options was $1.50 each and they may be exercised any time prior to 30 June 2015 at exercise price of $30.On the same date the market price for Goliath Ltd shares is $25.On David Ltd's balance date - 30 June 2013 - the company is still holding the options.The market price of the options at that time was $1.80 each and the share price is $27. What is the financial effect of the above transactions on David Ltd's statement of comprehensive income for the year ending 30 June 2013?
A) Increase by $15 000
B) Decrease by $15 000
C) Increase by $100 000
D) Decrease by $100 000
A) Increase by $15 000
B) Decrease by $15 000
C) Increase by $100 000
D) Decrease by $100 000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
On 31 October 2012 Gordon Investment Ltd has a well diversified portfolio of shares that it is intending to sell in 3 months time.To hedge against the adverse movements in the price of these shares,the manager obtained four 'sell' contracts with DSI Futures.A deposit of $20 000 was required by the broker.A standard futures contract is $25 per basis point.On 31 January 2013,Gordon Investment Ltd closed out all four contracts.The following information is provided. What is the fair value of the futures contract on 31 December 2012 and the cash received from DSI Futures on 31 January 2013 respectively?
A) ($5000); $370 000
B) ($5000; $40 000
C) $10 000; $370 000
D) $10 000; $40 000
A) ($5000); $370 000
B) ($5000; $40 000
C) $10 000; $370 000
D) $10 000; $40 000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
The classification of a preference share as an equity instrument or financial liability is:
A) affected by a history of making distributions.
B) affected by an intention to make distributions in the future.
C) not affected by a history of making distributions.
D) not affected by the other rights that attach to them if they are non-redeemable.
A) affected by a history of making distributions.
B) affected by an intention to make distributions in the future.
C) not affected by a history of making distributions.
D) not affected by the other rights that attach to them if they are non-redeemable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
If an entity issued a convertible note at a price of $40.00 and it was determined that a debt instrument of similar risk and rate of interest of 10%-but without the option to convert to equity-could be sold for $32.00,what would be the liability component of the convertible note?
A) $40.00
B) $32.00
C) $44.00
D) $36.00
A) $40.00
B) $32.00
C) $44.00
D) $36.00

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Identify which of the following financial instruments are required under AASB 139 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement to be measured at amortised cost:
A) I, II and III
B) I, II and IV
C) II, III and IV
D) II, IV and V
A) I, II and III
B) I, II and IV
C) II, III and IV
D) II, IV and V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
The risks arising from financial instruments are typically:
A) credit risk, fair value risk and market risk.
B) credit risk, liquidity risk and financial risk.
C) inherent risk, liquidity risk and market risk.
D) credit risk, liquidity risk and market risk.
A) credit risk, fair value risk and market risk.
B) credit risk, liquidity risk and financial risk.
C) inherent risk, liquidity risk and market risk.
D) credit risk, liquidity risk and market risk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
The following journal entry pertains to convertible notes with a face value of $10 million: Which of the following statements are correct?
A) The instrument was over-valued when it was initially recognised.
B) The convertible note has been converted.
C) The value of the option to convert has increased over the period from initial recognition to conversion, by $477 238.
D) The instrument was over-valued when it was initially recognised and the value of the option to convert has increased over the period from initial recognition to conversion, by $477 238.
A) The instrument was over-valued when it was initially recognised.
B) The convertible note has been converted.
C) The value of the option to convert has increased over the period from initial recognition to conversion, by $477 238.
D) The instrument was over-valued when it was initially recognised and the value of the option to convert has increased over the period from initial recognition to conversion, by $477 238.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
The amortised cost of a financial asset or financial liability is the amount at which the asset or liability is measured at initial recognition:
A) minus principal repayments.
B) plus or minus the cumulative amortisation using the effective interest method of any difference between that initial amount and the maturity amount.
C) minus any reduction for impairment.
D) All of the given answers are correct.
A) minus principal repayments.
B) plus or minus the cumulative amortisation using the effective interest method of any difference between that initial amount and the maturity amount.
C) minus any reduction for impairment.
D) All of the given answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Under AASB 123,interest incurred on a financial instrument,is able to be capitalised as part of a qualifying asset.When this is done:
A) interest is never expensed.
B) interest will be expensed as part of cost of goods sold when the asset is sold.
C) interest will be expensed as part of the accounts payable balance.
D) interest is recognised immediately.
A) interest is never expensed.
B) interest will be expensed as part of cost of goods sold when the asset is sold.
C) interest will be expensed as part of the accounts payable balance.
D) interest is recognised immediately.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
On 31 October 2012 DGC Investment Ltd purchased a well-diversified portfolio of shares that it is intending to sell in 3 months time.To hedge against the adverse movements in price of these shares,on the same date,the manager obtained four 'sell' contracts with DSI Futures.A deposit of $20 000 was required by the broker for the futures contract.A standard futures contract is $25 per basis point.On 31 January 2013,DGC Investment Ltd sold the portfolio and closed out all four contracts.The following information is provided. What is the financial effect of the above transactions on the statement of comprehensive income of DGC Investment Ltd for the reporting period ending 31 December 2012?
A) decrease by $5000
B) decrease by $15 000
C) increase by $5000
D) increase by $10 000
A) decrease by $5000
B) decrease by $15 000
C) increase by $5000
D) increase by $10 000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
The exercise price of an option:
A) varies with changes in the market price of an underlying share
B) remains fixed for the duration of the option.
C) is always at a price below market price when issued.
D) All of the given answers are correct.
A) varies with changes in the market price of an underlying share
B) remains fixed for the duration of the option.
C) is always at a price below market price when issued.
D) All of the given answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Which of the following ratios are used as an indicator of the inherent risk in investing in an entity?
A) quick
B) current
C) leverage
D) gross profit
A) quick
B) current
C) leverage
D) gross profit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
The carrying amount of a financial 'held-to-maturity' asset,subject to an impairment loss:
A) can be reduced through an allowance account.
B) can be reduced through a provision account.
C) must be reduced through an allowance account.
D) must be reduced directly.
A) can be reduced through an allowance account.
B) can be reduced through a provision account.
C) must be reduced through an allowance account.
D) must be reduced directly.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Which of the following financial instruments can underlie an option contract?
A) interest bearing instruments
B) financial assets
C) shares in other entities
D) all of the given answers
A) interest bearing instruments
B) financial assets
C) shares in other entities
D) all of the given answers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Identify which of the following financial instruments are required under AASB 139 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement to be measured at fair value through profit and loss:
A) I, II and III
B) I, II and IV
C) II, III and IV
D) II, IV and V
A) I, II and III
B) I, II and IV
C) II, III and IV
D) II, IV and V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
If an entity issued a convertible note at a price of $40.00 and it was determined that a debt instrument of similar risk and rate of interest of 10%-but without the option to convert to equity-could be sold for $32.00,what would be the equity component of the convertible note?
A) $40.00
B) $32.00
C) $8.00
D) $12.00
A) $40.00
B) $32.00
C) $8.00
D) $12.00

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








