Deck 8: Waves and Water Dynamics
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/47
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Waves and Water Dynamics
1
A curling wave formed over an air pocket is called a plunging breaker.
True
2
A storm surge might form in association with a seafloor avalanche.
False
3
A wave will break when wave steepness is equal to 1/20.
False
4
Swells are examples of free waves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Refer to the figure below detailing wave characteristics.Use the information on the figure to answer questions
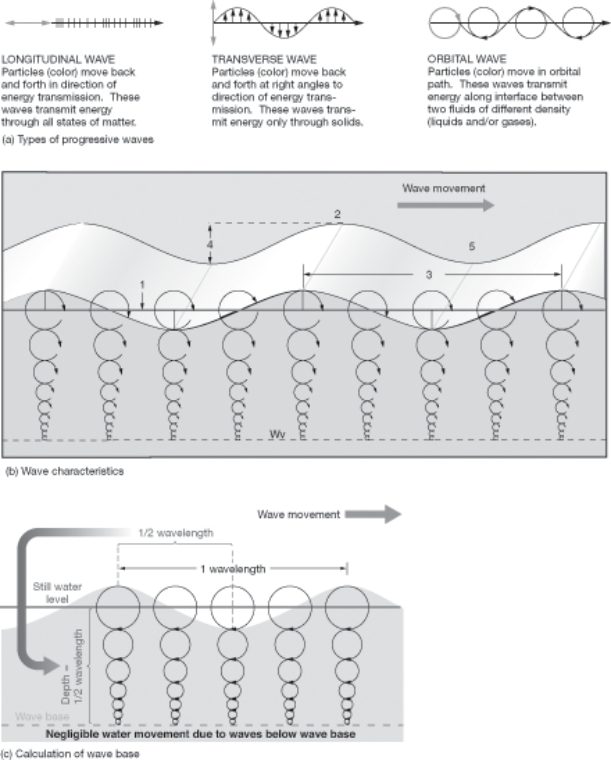
The portion of the wave that is also known as the zero energy level is indicated by the number:
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)4.
E)5.

The portion of the wave that is also known as the zero energy level is indicated by the number:
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)4.
E)5.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A shallow water wave must form in water depth less than 100 meters.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Refer to the figure below detailing wave characteristics.Use the information on the figure to answer questions

The wavelength is labeled with the number:
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)4.
E)5.

The wavelength is labeled with the number:
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)4.
E)5.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A standing wave is caused by wave reflection.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Refer to the figure below detailing wave characteristics.Use the information on the figure to answer questions

The crest is the portion of the wave corresponding to the number:
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)4.
E)5.

The crest is the portion of the wave corresponding to the number:
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)4.
E)5.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Internal waves have never been directly observed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The orbital motion of water molecules in a wave goes down to a depth equal to the wavelength divided by two.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Refer to the figure below detailing wave characteristics.Use the information on the figure to answer questions

The lowest part of the wave corresponds to the number:
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)4.
E)5.

The lowest part of the wave corresponds to the number:
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)4.
E)5.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The speed of a shallow water wave is a function of wave period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A wave train is caused by wave energy moving more slowly than individual waves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The vertical distance between the wave trough and the wave crest is the wavelength.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The largest wind-generated waves tend to be associated with the:
A)doldrums.
B)horse latitudes.
C)polar regions.
D)trade winds.
E)westerlies.
A)doldrums.
B)horse latitudes.
C)polar regions.
D)trade winds.
E)westerlies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Wave energy is focused on headlands due to wave refraction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The horizontal distance between two successive troughs is called the wave height.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The circular motion of water molecules extends to a depth that is equal to:
A)wave height/wavelength.
B)wave height/wave period.
C)wavelength/wave height.
D)wavelength/2.
E)wavelength/20.
A)wave height/wavelength.
B)wave height/wave period.
C)wavelength/wave height.
D)wavelength/2.
E)wavelength/20.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The speed of a deep-water wave is proportional to:
A)water depth.
B)wave frequency.
C)wave height.
D)wave period.
E)wavelength.
A)water depth.
B)wave frequency.
C)wave height.
D)wave period.
E)wavelength.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Waves that are breaking along the shore and are forming a curling crest over an air pocket are called:
A)gravity waves.
B)plunging breakers.
C)spilling breakers.
D)surf.
E)swells.
A)gravity waves.
B)plunging breakers.
C)spilling breakers.
D)surf.
E)swells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Constructive interference results in larger waves while destructive interference produces:
A)capillary waves.
B)rouge waves.
C)smaller waves.
D)swells.
E)tsunamis.
A)capillary waves.
B)rouge waves.
C)smaller waves.
D)swells.
E)tsunamis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The ratio of wave height to wavelength is called the:
A)frequency.
B)period.
C)wave height.
D)wavelength.
E)wave steepness.
A)frequency.
B)period.
C)wave height.
D)wavelength.
E)wave steepness.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
As a wave begins to feel bottom near a shoreline,its wave height:
A)decreases and steepness decreases.
B)decreases and wavelength increases.
C)increases and frequency decreases.
D)increases and wavelength decreases
E)increases and wavelength remains the same.
A)decreases and steepness decreases.
B)decreases and wavelength increases.
C)increases and frequency decreases.
D)increases and wavelength decreases
E)increases and wavelength remains the same.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A deep-water wave occurs when the water depth is equal to:
A)the fetch.
B)wave height.
C)wavelength.
D)½ of wavelength.
E)1/20 of wavelength.
A)the fetch.
B)wave height.
C)wavelength.
D)½ of wavelength.
E)1/20 of wavelength.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Waves that are moving faster than local wind and are sorted out be wavelength are called:
A)capillary waves.
B)constructive waves.
C)surf.
D)swell.
E)wind waves.
A)capillary waves.
B)constructive waves.
C)surf.
D)swell.
E)wind waves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
An internal wave might form:
A)at a density boundary within the ocean.
B)at the boundary between the atmosphere and the ocean.
C)at the boundary between the ocean and the seafloor.
D)close to shore as it moves into shallow water.
E)only as a result of tidal activity.
A)at a density boundary within the ocean.
B)at the boundary between the atmosphere and the ocean.
C)at the boundary between the ocean and the seafloor.
D)close to shore as it moves into shallow water.
E)only as a result of tidal activity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The fetch refers to:
A)a method of shoreline erosion control.
B)a type of wave-cut platform.
C)the circular pattern made by water particles when a wave passes.
D)the distance between the trough of a wave and the still water level.
E)the distance over which wind blows without interruption.
A)a method of shoreline erosion control.
B)a type of wave-cut platform.
C)the circular pattern made by water particles when a wave passes.
D)the distance between the trough of a wave and the still water level.
E)the distance over which wind blows without interruption.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Storm surges are generated by intense:
A)earthquakes.
B)high-pressure systems.
C)landslides.
D)low-pressure systems.
E)thunderstorms
A)earthquakes.
B)high-pressure systems.
C)landslides.
D)low-pressure systems.
E)thunderstorms

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Wave speed is equal to
A)wave height divided by frequency.
B)wave height divided by period.
C)wavelength divided by fetch.
D)wavelength divided by frequency.
E)wavelength divided by period.
A)wave height divided by frequency.
B)wave height divided by period.
C)wavelength divided by fetch.
D)wavelength divided by frequency.
E)wavelength divided by period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The speed of a shallow-water wave is proportional to:
A)water depth.
B)wave frequency.
C)wave height.
D)wave period.
E)wavelength.
A)water depth.
B)wave frequency.
C)wave height.
D)wave period.
E)wavelength.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
All of the following are shallow-water waves except:
A)near shore wind-generated waves.
B)surf.
C)tides.
D)tsunamis.
E)All of the above are examples of shallow-water waves.
A)near shore wind-generated waves.
B)surf.
C)tides.
D)tsunamis.
E)All of the above are examples of shallow-water waves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The time between two successive waves is called the:
A)crest.
B)frequency.
C)height.
D)period.
E)trough.
A)crest.
B)frequency.
C)height.
D)period.
E)trough.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A wave will break when:
A)distance from shore < wavelength.
B)steepness = 1:7.
C)water depth = wave height.
D)water depth = wavelength/20.
E)wavelength < wave height.
A)distance from shore < wavelength.
B)steepness = 1:7.
C)water depth = wave height.
D)water depth = wavelength/20.
E)wavelength < wave height.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Capillary and gravity waves are named for the:
A)dominant restoring force.
B)force that creates them.
C)rate at which they travel.
D)wave dispersion.
E)wave refraction pattern they create.
A)dominant restoring force.
B)force that creates them.
C)rate at which they travel.
D)wave dispersion.
E)wave refraction pattern they create.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Water waves are:
A)capillary waves.
B)longitudinal waves.
C)refracted waves.
D)orbital waves.
E)transverse waves.
A)capillary waves.
B)longitudinal waves.
C)refracted waves.
D)orbital waves.
E)transverse waves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The diameter of a wave orbital at the surface is equal to:
A)wave height.
B)wave height/wavelength.
C)wavelength.
D)wavelength/wave period.
E)wave period.
A)wave height.
B)wave height/wavelength.
C)wavelength.
D)wavelength/wave period.
E)wave period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The height of a wave depends upon
A)fetch.
B)fetch and wind speed.
C)fetch,wind duration,and wind speed.
D)wind duration.
E)wind duration and wind speed.
A)fetch.
B)fetch and wind speed.
C)fetch,wind duration,and wind speed.
D)wind duration.
E)wind duration and wind speed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
A tsunami is considered to be a:
A)capillary wave.
B)deep-water wave.
C)reflected wave.
D)refracted wave
E)shallow water wave.
A)capillary wave.
B)deep-water wave.
C)reflected wave.
D)refracted wave
E)shallow water wave.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Waves converge on headlands due to:
A)constructive interference.
B)destructive interference.
C)wave diffraction.
D)wave reflection.
E)wave refraction.
A)constructive interference.
B)destructive interference.
C)wave diffraction.
D)wave reflection.
E)wave refraction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Standing waves may be caused by:
A)constructive interference.
B)destructive interference.
C)wave diffraction.
D)wave reflection.
E)wave refraction
A)constructive interference.
B)destructive interference.
C)wave diffraction.
D)wave reflection.
E)wave refraction

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
If a surfer wishes to have a really long ride,what type of wave should he or she look for?
A)gravity waves
B)plunging breakers
C)spilling breakers
D)surf
E)swells
A)gravity waves
B)plunging breakers
C)spilling breakers
D)surf
E)swells

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Which of the following from earliest to latest represents the typical wave formation?
A)sea,surf,swell
B)sea,swell,surf
C)surf,swell,sea
D)surf,sea,swell
E)swell,sea,surf
A)sea,surf,swell
B)sea,swell,surf
C)surf,swell,sea
D)surf,sea,swell
E)swell,sea,surf

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
A tsunami may result from:
A)a large deep-water wave.
B)a storm surge.
C)an intense storm.
D)constructive wave interference.
E)tectonic activity on the seafloor.
A)a large deep-water wave.
B)a storm surge.
C)an intense storm.
D)constructive wave interference.
E)tectonic activity on the seafloor.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Rogue waves tend to occur:
A)in areas where wind belts converge.
B)In coastal areas where the ocean depth rapidly decreases.
C)in upwelling zones.
D)only in the southern ocean below 60ºS latitude.
E)where storm waves move against strong surface currents.
A)in areas where wind belts converge.
B)In coastal areas where the ocean depth rapidly decreases.
C)in upwelling zones.
D)only in the southern ocean below 60ºS latitude.
E)where storm waves move against strong surface currents.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








