Deck 9: Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/170
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 9: Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy
1
For a particular process that is carried out at constant pressure,q = 200 kJ and w = -85 kJ.Therefore,
A)ΔE = 115 kJ and ΔH = 200 kJ.
B)ΔE = 200 kJ and ΔH = 115 kJ.
C)ΔE = 200 kJ and ΔH = 285 kJ.
D)ΔE = 285 kJ and ΔH = 200 kJ.
A)ΔE = 115 kJ and ΔH = 200 kJ.
B)ΔE = 200 kJ and ΔH = 115 kJ.
C)ΔE = 200 kJ and ΔH = 285 kJ.
D)ΔE = 285 kJ and ΔH = 200 kJ.
ΔE = 115 kJ and ΔH = 200 kJ.
2
An ideal gas expands into a vacuum (external pressure = 0)without gaining or losing heat.For this expansion
A)ΔE increases.
B)ΔE does not change.
C)ΔE decreases.
D)ΔE = TΔS.
A)ΔE increases.
B)ΔE does not change.
C)ΔE decreases.
D)ΔE = TΔS.
ΔE does not change.
3
A process is carried out at constant pressure.Given that ΔE is positive and ΔH is negative,
A)the system absorbs heat and expands during the process.
B)the system absorbs heat and contracts during the process.
C)the system loses heat and expands during the process.
D)the system loses heat and contracts during the process.
A)the system absorbs heat and expands during the process.
B)the system absorbs heat and contracts during the process.
C)the system loses heat and expands during the process.
D)the system loses heat and contracts during the process.
the system loses heat and contracts during the process.
4
For most chemical reactions
A)ΔH is much larger than ΔE.
B)ΔE is much larger than ΔH.
C)ΔH is equal to ΔE.
D)the difference between ΔH and ΔE is very small.
A)ΔH is much larger than ΔE.
B)ΔE is much larger than ΔH.
C)ΔH is equal to ΔE.
D)the difference between ΔH and ΔE is very small.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
In which case is the work done on the system always positive?
A)ΔE > 0
B)ΔV > 0
C)ΔV = 0
D)ΔV < 0
A)ΔE > 0
B)ΔV > 0
C)ΔV = 0
D)ΔV < 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
For an explosion in an open vessel,one would expect
A)ΔH to be positive and ΔE to be less than ΔH.
B)ΔH to be positive and ΔE to be greater than ΔH.
C)ΔH to be negative and ΔE to be less than ΔH.
D)ΔH to be negative and ΔE to be greater than ΔH.
A)ΔH to be positive and ΔE to be less than ΔH.
B)ΔH to be positive and ΔE to be greater than ΔH.
C)ΔH to be negative and ΔE to be less than ΔH.
D)ΔH to be negative and ΔE to be greater than ΔH.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which of the following states the first law of thermodynamics (conservation of energy)?
A)w = -PΔV
B)ΔEsystem = -ΔEsurroundings
C)ΔH = ΔE + PΔV
D)q = smΔT
A)w = -PΔV
B)ΔEsystem = -ΔEsurroundings
C)ΔH = ΔE + PΔV
D)q = smΔT

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Most chemical reactions are carried out in one of two ways: I.in an open vessel at constant atmospheric pressure
II.in a closed vessel
Which is true?
A)ΔH = q for condition I and ΔE = q for condition II.
B)ΔE = q for condition I and ΔH = q for condition II.
C)ΔH = w for condition I and ΔE = w for condition II.
D)ΔE = w for condition I and ΔH = w for condition II.
II.in a closed vessel
Which is true?
A)ΔH = q for condition I and ΔE = q for condition II.
B)ΔE = q for condition I and ΔH = q for condition II.
C)ΔH = w for condition I and ΔE = w for condition II.
D)ΔE = w for condition I and ΔH = w for condition II.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
What is expected when the reaction shown below takes place in a thermally-insulated container outfitted with a movable piston at a constant atmospheric pressure of 1 atm? 2 C2H6(g)+ 7 O2(g)→ 4 CO2(g)+ 6 H2O(g)
A)Volume will decrease and work will be done by the system.
B)Volume will decrease and work will be done on the system.
C)Volume will increase and work will be done by the system.
D)Volume will increase and work will be done on the system.
A)Volume will decrease and work will be done by the system.
B)Volume will decrease and work will be done on the system.
C)Volume will increase and work will be done by the system.
D)Volume will increase and work will be done on the system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
At constant pressure for the reaction shown below,what can be said about PΔV and ΔE? N2(g)+ 3 H2(g)→ 2 NH3(g)ΔH° = - 92.2 kJ
A)PΔV > 0 and ΔE > -92.2 kJ
B)PΔV > 0 and ΔE < -92.2 kJ
C)PΔV < 0 and ΔE > -92.2 kJ
D)PΔV < 0 and ΔE < -92.2 kJ
A)PΔV > 0 and ΔE > -92.2 kJ
B)PΔV > 0 and ΔE < -92.2 kJ
C)PΔV < 0 and ΔE > -92.2 kJ
D)PΔV < 0 and ΔE < -92.2 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Under thermodynamic standard state conditions the element oxygen occurs as
A)O(g)
B)O2(g)
C)O2(l)
D)O3(g)
A)O(g)
B)O2(g)
C)O2(l)
D)O3(g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
For a process at constant volume,
A)q = 0,w = 0,and ΔE = 0.
B)w = 0 and ΔE = q.
C)w = 0 and ΔH = q.
D)w = 0 and ΔE = ΔH.
A)q = 0,w = 0,and ΔE = 0.
B)w = 0 and ΔE = q.
C)w = 0 and ΔH = q.
D)w = 0 and ΔE = ΔH.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A process is carried out at constant pressure.Given that 0 > ΔH > ΔE,
A)the system absorbs heat and expands during the process.
B)the system absorbs heat and contracts during the process.
C)the system loses heat and expands during the process.
D)the system loses heat and contracts during the process.
A)the system absorbs heat and expands during the process.
B)the system absorbs heat and contracts during the process.
C)the system loses heat and expands during the process.
D)the system loses heat and contracts during the process.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
For a process at constant pressure,
A)ΔE = w and q = 0.
B)ΔE = q and w = 0.
C)ΔE = ΔH.
D)ΔH = q.
A)ΔE = w and q = 0.
B)ΔE = q and w = 0.
C)ΔE = ΔH.
D)ΔH = q.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Find ΔE° for the reaction below if the process is carried out at a constant pressure of 1.00 atm and ΔV (the volume change)= -24.5 L.(1 L ∙ atm = 101 J) 2 CO(g)+ O2 (g)→ 2 CO2(g)ΔH° = -566.kJ
A)+2.47 kJ
B)-2.47 kJ
C)-564 kJ
D)-568 kJ
A)+2.47 kJ
B)-2.47 kJ
C)-564 kJ
D)-568 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Calculate the work energy,w,gained or lost by the system when a gas expands from 20 L to 35 L against a constant external pressure of 2.0 atm.[1 L ∙ atm = 101 J]
A)-5.3 kJ
B)-3.0 kJ
C)+3.0 kJ
D)+5.3 kJ
A)-5.3 kJ
B)-3.0 kJ
C)+3.0 kJ
D)+5.3 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
When 10.0 mol of benzene is vaporized at a constant pressure of 1.00 atm and at its normal boiling point of 80.1°C,339 kJ are absorbed and PΔV for the vaporization process is equal to 29.0 kJ,then
A)ΔE = 310.kJ and ΔH = 339.kJ.
B)ΔE = 368.kJ and ΔH = 339.kJ.
C)ΔE = 339.kJ and ΔH = 310.kJ.
D)ΔE = 339.kJ and ΔH = 368.kJ.
A)ΔE = 310.kJ and ΔH = 339.kJ.
B)ΔE = 368.kJ and ΔH = 339.kJ.
C)ΔE = 339.kJ and ΔH = 310.kJ.
D)ΔE = 339.kJ and ΔH = 368.kJ.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which is a measure of the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of each particle in the system?
A)E,the internal energy
B)G,the Gibbs free energy
C)H,the enthalpy
D)T,the temperature
A)E,the internal energy
B)G,the Gibbs free energy
C)H,the enthalpy
D)T,the temperature

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which depends only on the initial and final state?
A)q
B)w
C)q + w
D)q - w
A)q
B)w
C)q + w
D)q - w

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
When 20.00 moles of H2(g)reacts with 10.00 mol of O2(g)to form 20.00 mol of H2O(l)at 25°C and a constant pressure of 1.00 atm.If 1366 kJ of heat are released during this reaction,and PΔV is equal to -74.00 kJ,then
A)ΔH° = +1366 kJ and ΔE° = +1440 kJ.
B)ΔH° = +1366 kJ and ΔE° = +1292 kJ.
C)ΔH° = -1366 kJ and ΔE° = -1292 kJ.
D)ΔH° = -1366 kJ and ΔE° = -1440 kJ.
A)ΔH° = +1366 kJ and ΔE° = +1440 kJ.
B)ΔH° = +1366 kJ and ΔE° = +1292 kJ.
C)ΔH° = -1366 kJ and ΔE° = -1292 kJ.
D)ΔH° = -1366 kJ and ΔE° = -1440 kJ.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
At constant pressure,the combustion of 30.00 g of C2H6(g)releases 1560 kJ of heat.What is ΔH for the reaction given below? 2 C2H6(g)+ 7 O2(g)→ 4 CO2(g)+ 6 H2O(l)
A)-43.2 kJ
B)-779 kJ
C)-1560 kJ
D)-3120 kJ
A)-43.2 kJ
B)-779 kJ
C)-1560 kJ
D)-3120 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
At 25°C the heat of fusion of aluminum is 10.6 kJ/mol and the heat of sublimation is 326.4 kJ/mol.What is the heat of vaporization of aluminum at 25°C?
A)158.2 kJ/mol
B)168.5 kJ/mol
C)315.8 kJ/mol
D)337.0 kJ/mol
A)158.2 kJ/mol
B)168.5 kJ/mol
C)315.8 kJ/mol
D)337.0 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
When 0.700 g of anthracene,C14H10,is combusted in a bomb calorimeter that has a water jacket containing 500.g of water,the temperature of the water increases by 13.27°C.Assuming that the specific heat of water is 4.18 J/(g ∙ °C),and that the heat absorption by the calorimeter is negligible,estimate the enthalpy of combustion per mole of anthracene.
A)+39.7 kJ/mol
B)-39.7 kJ/mol
C)-7060 kJ/mol
D)-8120 kJ/mol
A)+39.7 kJ/mol
B)-39.7 kJ/mol
C)-7060 kJ/mol
D)-8120 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
When 2.500 mol of CH4(g)reacts with excess Cl2(g)at constant pressure according to the chemical equation shown below,1770.kJ of heat are released.Calculate the value of ΔH for this reaction,as written. 2 CH4(g)+ 3 Cl2(g)→ 2 CHCl3(l)+ 3 H2(g)ΔH = ?
A)-1416 kJ
B)-708.0 kJ
C)+708.0 kJ
D)+1416 kJ
A)-1416 kJ
B)-708.0 kJ
C)+708.0 kJ
D)+1416 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which is the most exothermic reaction?
A)CH4(g)+ 2 O2(g)→ CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(g)
B)CH4(g)+ 2 O2(g)→ CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(l)
C)CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(l)→CH4(g)+ 2 O2(g)
D)CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(g)→CH4(g)+ 2 O2(g)
A)CH4(g)+ 2 O2(g)→ CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(g)
B)CH4(g)+ 2 O2(g)→ CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(l)
C)CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(l)→CH4(g)+ 2 O2(g)
D)CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(g)→CH4(g)+ 2 O2(g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The enthalpy of fusion,or heat of fusion (ΔHfusion),of water is positive and corresponds to which physical change?
A)H2O(g)→ H2O(s)
B)H2O(l)→ H2O(s)
C)H2O(s)→ H2O(l)
D)H2O(s)→ H2O(g)
A)H2O(g)→ H2O(s)
B)H2O(l)→ H2O(s)
C)H2O(s)→ H2O(l)
D)H2O(s)→ H2O(g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Sodium metal reacts with water to produce hydrogen gas and sodium hydroxide according to the chemical equation shown below.When 0.0500 mol of Na is added to 100.00 g of water,the temperature of the resulting solution rises from 25.00°C to 46.23°C.If the specific heat of the solution is 4.18 J/(g ∙ °C),calculate ΔH for the reaction,as written. 2 Na(s)+ 2 H2O(l)→ 2 NaOH(aq)+ H2(g)ΔH = ?
A)-5.41 kJ
B)-90.0 kJ
C)-180 kJ
D)-362 kJ
A)-5.41 kJ
B)-90.0 kJ
C)-180 kJ
D)-362 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Water has an unusually high
A)electrical conductivity.
B)heat of combustion.
C)heat of formation.
D)specific heat.
A)electrical conductivity.
B)heat of combustion.
C)heat of formation.
D)specific heat.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
In the lab,you mix two solutions (each originally at the same temperature)and the temperature of the resulting solution decreases.Which of the following is true?
A)The chemical reaction is releasing energy.
B)The energy released is equal to s × m × ΔT.
C)The chemical reaction is absorbing energy.
D)The chemical reaction is exothermic.
A)The chemical reaction is releasing energy.
B)The energy released is equal to s × m × ΔT.
C)The chemical reaction is absorbing energy.
D)The chemical reaction is exothermic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
When 50.0 mL of 0.400 M Ca(NO3)2 is added to 50.0 mL of 0.800 M NaF,CaF2 precipitates,as shown in the net ionic equation below.The initial temperature of both solutions is 30.00°C.Assuming that the reaction goes to completion,and that the resulting solution has a mass of 100.00 g and a specific heat of 4.18 J/(g ∙ °C),calculate the final temperature of the solution. Ca2+(aq)+ 2 F-(aq)→ CaF2(s)ΔH° = -11.5 kJ
A)29.45°C
B)30.55°C
C)31.10°C
D)31.65°C
A)29.45°C
B)30.55°C
C)31.10°C
D)31.65°C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Calculate the total quantity of heat required to convert 50.0 g of liquid CCl4(l)from 25.0°C to gaseous CCl4 at 76.8°C (the normal boiling point for CCl4)? The specific heat of CCl4(l)is 0.857 J/(g ∙ °C),its heat of fusion is 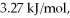 and its heat of vaporization is
and its heat of vaporization is 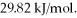
A)2.22 kJ
B)3.28 kJ
C)11.91 kJ
D)12.98 kJ
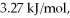 and its heat of vaporization is
and its heat of vaporization is 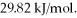
A)2.22 kJ
B)3.28 kJ
C)11.91 kJ
D)12.98 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
At 1 atm pressure the heat of sublimation of gallium is 277 kJ/mol and the heat of vaporization is 271 kJ/mol.How much heat is required to melt 0.500 mol of gallium at 1.00 atm pressure?
A)6.00 kJ
B)3.00 kJ
C)268 kJ
D)271 kJ
A)6.00 kJ
B)3.00 kJ
C)268 kJ
D)271 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
When 8.00 g of Ba(s)is added to 100.00 g of water in a container open to the atmosphere,the reaction shown below occurs and the temperature of the resulting solution rises from 22.00°C to 77.62°C.If the specific heat of the solution is 4.18 J/(g ∙ °C),calculate ΔH for the reaction,as written. Ba(s)+ 2 H2O(l)→ Ba(OH)2(aq)+ H2(g)ΔH = ?
A)-431 kJ
B)-3.14 kJ
C)3.14 kJ
D)431 kJ
A)-431 kJ
B)-3.14 kJ
C)3.14 kJ
D)431 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
It takes 15.5 kJ of energy to raise the temperature of 200 g of benzene from 25.0°C to 70.0°C.What is the specific heat of benzene?
A)1.10 J/(g ∙ °C)
B)1.72 J/(g ∙ °C)
C)3.48 J/(g ∙ °C)
D)5.41 J/(g ∙ °C)
A)1.10 J/(g ∙ °C)
B)1.72 J/(g ∙ °C)
C)3.48 J/(g ∙ °C)
D)5.41 J/(g ∙ °C)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
How much heat is absorbed/released when 10.00 g of NH3(g)reacts in the presence of excess O2(g)to produce NO(g)and H2O(l)according to the following chemical equation? 4 NH3(g)+ 5 O2(g)→ 4 NO(g)+ 6 H2O(l)ΔH° = +1168 kJ
A)171.5 kJ of heat are absorbed.
B)171.5 kJ of heat are released.
C)686.0 kJ of heat are absorbed.
D)686.0 kJ of heat are released.
A)171.5 kJ of heat are absorbed.
B)171.5 kJ of heat are released.
C)686.0 kJ of heat are absorbed.
D)686.0 kJ of heat are released.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
How much heat is absorbed when 20.00 g of C(s)reacts in the presence of excess SO2(g)to produce CS2(l)and CO(g)according to the following chemical equation? 5 C(s)+ 2 SO2(g)→ CS2(l)+ 4 CO(g)ΔH° = +239.9 kJ
A)79.97 kJ
B)159.9 kJ
C)399.5 kJ
D)959.3 kJ
A)79.97 kJ
B)159.9 kJ
C)399.5 kJ
D)959.3 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The specific heat of copper is 0.385 J/(g ∙ °C).If 34.2 g of copper,initially at 25°C,absorbs 7.880 kJ,what will be the final temperature of the copper?
A)25.4°C
B)27.8°C
C)598°C
D)623°C
A)25.4°C
B)27.8°C
C)598°C
D)623°C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
For the reaction I2(g)→ I2(s),ΔH° = -62.4 kJ at 25°C.Based on these data,at 25°C
A)ΔH°vap = -62.4 kJ/mol.
B)ΔH°vap = 62.4 kJ/mol.
C)ΔH°sub = -62.4 kJ/mol.
D)ΔH°sub = 62.4 kJ/mol.
A)ΔH°vap = -62.4 kJ/mol.
B)ΔH°vap = 62.4 kJ/mol.
C)ΔH°sub = -62.4 kJ/mol.
D)ΔH°sub = 62.4 kJ/mol.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
The heat of vaporization of water at 100°C is 40.66 kJ/mol.Calculate the quantity of heat that is absorbed/released when 20.00 g of steam condenses to liquid water at 100°C.
A)45.2 kJ of heat are absorbed.
B)45.2 kJ of heat are released.
C)813.2 kJ of heat are absorbed.
D)813.2 kJ of heat are released.
A)45.2 kJ of heat are absorbed.
B)45.2 kJ of heat are released.
C)813.2 kJ of heat are absorbed.
D)813.2 kJ of heat are released.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Which of the following scenarios involves a transfer of heat from system to surroundings?
A)evaporating rubbing alcohol from your skin
B)solidifying molten gold into a gold bar
C)melting solid gallium metal with heat from your hand
D)none of these
A)evaporating rubbing alcohol from your skin
B)solidifying molten gold into a gold bar
C)melting solid gallium metal with heat from your hand
D)none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The values of ΔH°f for the three states of benzene are approximately -22 kcal/mol,-11 kcal/mol,and 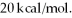 Which is the value for solid benzene?
Which is the value for solid benzene?
A)-22 kcal/mol
B)-11 kcal/mol
C)20 kcal/mol
D)cannot be determined without additional information
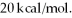 Which is the value for solid benzene?
Which is the value for solid benzene?A)-22 kcal/mol
B)-11 kcal/mol
C)20 kcal/mol
D)cannot be determined without additional information

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Heat of formation for CO is -110.5 KJ/mol and the heat of formation for MgO is -602 KJ/mol.Which of the following statements is true?
A)The bond in CO is stronger than the bond in MgO.
B)The bond in MgO is stronger than the bond in CO.
C)The bonds in MgO and CO are equally strong.
D)Impossible to determine to given data.
A)The bond in CO is stronger than the bond in MgO.
B)The bond in MgO is stronger than the bond in CO.
C)The bonds in MgO and CO are equally strong.
D)Impossible to determine to given data.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Two metals of equal mass with different heat capacities are subjected to the same amount of heat.Which undergoes the smallest change in temperature?
A)The metal with the highest heat capacity.
B)The metal with the lowest heat capacity.
C)Both undergo the same change in temperature.
D)You need to know the initial temperatures of both metals.
A)The metal with the highest heat capacity.
B)The metal with the lowest heat capacity.
C)Both undergo the same change in temperature.
D)You need to know the initial temperatures of both metals.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Given that ΔH°= -311 kJ for the hydrogenation of acetylene,C2H2: H-C  C-H(g)+ 2 H2(g)→ CH3-CH3(g)
C-H(g)+ 2 H2(g)→ CH3-CH3(g)
And the following bond dissociation energies,estimate a value for the C-to-C triple bond dissociation energy.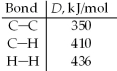
A)1050 kJ/mol
B)833 kJ/mol
C)807 kJ/mol
D)397 kJ/mol
 C-H(g)+ 2 H2(g)→ CH3-CH3(g)
C-H(g)+ 2 H2(g)→ CH3-CH3(g)And the following bond dissociation energies,estimate a value for the C-to-C triple bond dissociation energy.

A)1050 kJ/mol
B)833 kJ/mol
C)807 kJ/mol
D)397 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
For the reaction 2CH4 (g)+ 3 Cl2 (g)→ 2 CHCl3 (l)+ 3 H2 (g),ΔH° = -118.6 kJ. ΔH°f = -134.1 kJ/mol for CHCl3 (l).Find ΔH°f for CH4 (g).
A)-193.4 kJ/mol
B)-74.8 kJ/mol
C)74.8 kJ/mol
D)193.4 kJ/mol
A)-193.4 kJ/mol
B)-74.8 kJ/mol
C)74.8 kJ/mol
D)193.4 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Ethyl alcohol is produced by the fermentation of glucose,C6H12O6. C6H12O6(s)→ 2 C2H5OH(l)+ 2 CO2(g)ΔH° = -69.1 kJ
Given that the enthalpy of formation is -277.7 kJ/mol for C2H5OH(l)and -393.5 kJ/mol for CO2(g),find the enthalpy of formation for C6H12O6.
A)-1411.5 kJ/mol
B)-1273.3 kJ/mol
C)-740.3 kJ/mol
D)-602.1 kJ/mol
Given that the enthalpy of formation is -277.7 kJ/mol for C2H5OH(l)and -393.5 kJ/mol for CO2(g),find the enthalpy of formation for C6H12O6.
A)-1411.5 kJ/mol
B)-1273.3 kJ/mol
C)-740.3 kJ/mol
D)-602.1 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Determine the sign of ΔS° for each of the following: I.C6H6(s)→ C6H6(l)
II.2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)→ 2 SO3(g)
A)ΔS° should be negative for I and negative for II.
B)ΔS° should be negative for I and positive for II.
C)ΔS° should be positive for I and negative for II.
D)ΔS° should be positive for I and positive for II.
II.2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)→ 2 SO3(g)
A)ΔS° should be negative for I and negative for II.
B)ΔS° should be negative for I and positive for II.
C)ΔS° should be positive for I and negative for II.
D)ΔS° should be positive for I and positive for II.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Use the given average bond dissociation energies,D,to estimate ΔH for the reaction of methane,CH4(g),with fluorine according to the equation: CH4(g)+ 2 F2(g)→ CF4(g)+ 2 H2(g) 
A)-716 kJ
B)-318 kJ
C)+318 kJ
D)+716 kJ

A)-716 kJ
B)-318 kJ
C)+318 kJ
D)+716 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The heat of combustion per mole for acetylene,C2H2(g),is -1299.5 kJ/mol.Assuming that the combustion products are CO2(g)and H2O(l),and given that the enthalpy of formation is -393.5 kJ/mol for CO2(g)and -285.8 kJ/mol for H2O(l),find the enthalpy of formation of C2H2(g).
A)-846.1 kJ/mol
B)-620.2 kJ/mol
C)-226.7 kJ/mol
D)+226.7 kJ/mol
A)-846.1 kJ/mol
B)-620.2 kJ/mol
C)-226.7 kJ/mol
D)+226.7 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Which of the following can be interpreted as a measure of randomness?
A)enthalpy
B)entropy
C)free energy
D)temperature
A)enthalpy
B)entropy
C)free energy
D)temperature

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Coal gasification can be represented by the equation: 2 C(s)+ 2 H2O(g)→ CH4(g)+ CO2(g)ΔH = ?
Use the following information to find ΔH for the reaction above.
CO(g)+ H2(g)→ C(s)+ H2O(g)ΔH = -131 kJ
CO(g)+ H2O(g)→ CO2(g)+ H2(g)ΔH = -41 kJ
CO(g)+ 3 H2(g)→ CH4(g)+ H2O(g)ΔH = -206 kJ
A)15 kJ
B)116 kJ
C)-116 kJ
D)-372 kJ
Use the following information to find ΔH for the reaction above.
CO(g)+ H2(g)→ C(s)+ H2O(g)ΔH = -131 kJ
CO(g)+ H2O(g)→ CO2(g)+ H2(g)ΔH = -41 kJ
CO(g)+ 3 H2(g)→ CH4(g)+ H2O(g)ΔH = -206 kJ
A)15 kJ
B)116 kJ
C)-116 kJ
D)-372 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Find ΔH° for the reaction C3H8(g)+ 5 O2(g)→ 3 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(l). ΔH° = -2046 kJ for the reaction: C3H8(g)+ 5 O2(g)→ 3 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(g)
The heat of vaporization of water is 44.0 kJ/mol.Note that H2O is a liquid in the first reaction and a gas in the second.
A)-2222 kJ
B)-2090 kJ
C)-2002 kJ
D)-1870 kJ
The heat of vaporization of water is 44.0 kJ/mol.Note that H2O is a liquid in the first reaction and a gas in the second.
A)-2222 kJ
B)-2090 kJ
C)-2002 kJ
D)-1870 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Which of CH4(g),C2H2(g),and CH3OH(l)provides the most energy per gram upon combustion and which provides the least? CH4(g)+ 2 O2(g)→ CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(l)ΔH° = -890 kJ
2 C2H2(g)+ 5 O2(g)→ 4 CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(l)ΔH° = -2599 kJ
2 CH3OH(l)+ 3 O2(g)→ 2 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(l)ΔH° = -1453 kJ
A)C2H2 provides the most energy per gram and CH4 the least.
B)C2H2 provides the most energy per gram and CH3OH the least.
C)CH4 provides the most energy per gram and CH3OH the least.
D)CH4 provides the most energy per gram and C2H2 the least.
2 C2H2(g)+ 5 O2(g)→ 4 CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(l)ΔH° = -2599 kJ
2 CH3OH(l)+ 3 O2(g)→ 2 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(l)ΔH° = -1453 kJ
A)C2H2 provides the most energy per gram and CH4 the least.
B)C2H2 provides the most energy per gram and CH3OH the least.
C)CH4 provides the most energy per gram and CH3OH the least.
D)CH4 provides the most energy per gram and C2H2 the least.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Which thermodynamic function is most related to disorder and probability?
A)enthalpy
B)internal energy
C)entropy
D)heat capacity
A)enthalpy
B)internal energy
C)entropy
D)heat capacity

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
For the reaction,C2H2(g)→ 2 C(g)+ 2 H(g),one would expect
A)ΔH° to be negative and ΔS° to be negative.
B)ΔH° to be negative and ΔS° to be positive.
C)ΔH° to be positive and ΔS° to be negative.
D)ΔH° to be positive and ΔS° to be positive.
A)ΔH° to be negative and ΔS° to be negative.
B)ΔH° to be negative and ΔS° to be positive.
C)ΔH° to be positive and ΔS° to be negative.
D)ΔH° to be positive and ΔS° to be positive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Given: S (s)+ O2 (g)→ SO2 (g)ΔH° = -296.1 kJ 2 SO3 (g)→ 2 SO2 (g)+ O2 (g)ΔH° = 198.2 kJ
Find ΔH° for : 2 S(s)+ 3 O2(g)→ 2 SO3(g)
A)-790.4 kJ
B)-394.0 kJ
C)-97.9 kJ
D)+97.9 kJ
Find ΔH° for : 2 S(s)+ 3 O2(g)→ 2 SO3(g)
A)-790.4 kJ
B)-394.0 kJ
C)-97.9 kJ
D)+97.9 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
One method for making ethanol,C2H5OH,involves the gas-phase hydration of ethylene,C2H4: Estimate ΔH for this reaction from the given average bond dissociation energies,D. 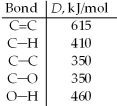
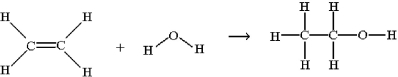
A)-580 kJ
B)-35 kJ
C)+35 kJ
D)580 kJ


A)-580 kJ
B)-35 kJ
C)+35 kJ
D)580 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Which equation represents the reaction whose ΔH,represents the standard enthalpy of formation of CHCl3(l)at 25°C? (i.e. ,for which is ΔH = ΔH°f of CHCl3)
A)CHCl3(l)→ C(s)+ H(g)+ 3 Cl(g)
B)C(s)+ H(g)+ 3 Cl(g)→ CHCl3(l)
C)C(s)+ 1/2 H2(g)+ 3/2 Cl2(g)→ CHCl3(l)
D)2 C(s)+ H2(g)+ 3 Cl2(g)→ 2 CHCl3(l)
A)CHCl3(l)→ C(s)+ H(g)+ 3 Cl(g)
B)C(s)+ H(g)+ 3 Cl(g)→ CHCl3(l)
C)C(s)+ 1/2 H2(g)+ 3/2 Cl2(g)→ CHCl3(l)
D)2 C(s)+ H2(g)+ 3 Cl2(g)→ 2 CHCl3(l)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Use the given standard enthalpies of formation to calculate ΔH° for the following reaction 3 Fe2O3(s)+ CO(g)→ 2 Fe3O4(s)+ CO2(g). 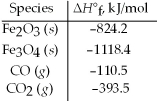
A)-5213.4 kJ
B)-577.2 kJ
C)-47.2 kJ
D)+47.2 kJ

A)-5213.4 kJ
B)-577.2 kJ
C)-47.2 kJ
D)+47.2 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Calculate the enthalpy of combustion per mole for C6H12O6.Assume that the combustion products are CO2(g)and H2O(l). 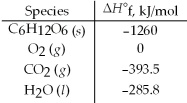
A)-5336 kJ/mol
B)-2816 kJ/mol
C)-1939 kJ/mol
D)580.7 kJ/mol

A)-5336 kJ/mol
B)-2816 kJ/mol
C)-1939 kJ/mol
D)580.7 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Reactant R reacts with reactant S in two steps to yield product Z. 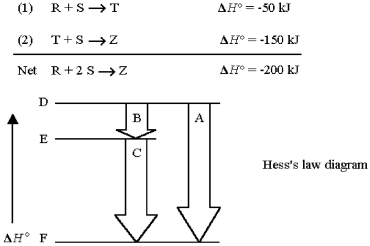
Step (1)in the reaction is represented by
A)arrow A.
B)arrow B.
C)arrow C.
D)line E.

Step (1)in the reaction is represented by
A)arrow A.
B)arrow B.
C)arrow C.
D)line E.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Consider the conversion of white tin to gray tin: Sn(white)→ Sn(gray)ΔH° = -2.09 kJ ΔS° = -7.41 J/K
Based on these data,
A)white tin is stable below 9°C and gray tin is stable above 9°C.
B)gray tin is stable below 9°C and white tin is stable above 9°C.
C)white tin is stable below 15°C and gray tin is stable above 15°C.
D)gray tin is stable below 15°C and white tin is stable above 15°C.
Based on these data,
A)white tin is stable below 9°C and gray tin is stable above 9°C.
B)gray tin is stable below 9°C and white tin is stable above 9°C.
C)white tin is stable below 15°C and gray tin is stable above 15°C.
D)gray tin is stable below 15°C and white tin is stable above 15°C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
For the of freezing liquid butane at a given temperature and pressure,
A)ΔH is negative and ΔS is negative.
B)ΔH is negative and ΔS is positive.
C)ΔH is positive and ΔS is negative.
D)ΔH is positive and ΔS is positive.
A)ΔH is negative and ΔS is negative.
B)ΔH is negative and ΔS is positive.
C)ΔH is positive and ΔS is negative.
D)ΔH is positive and ΔS is positive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Which of the following is not true?
A)A spontaneous reaction need not occur immediately.
B)A spontaneous reaction must be exothermic and must have an increase in entropy.
C)The reverse of a nonspontaneous reaction is always spontaneous.
D)A spontaneous reaction is one that can proceed on its own.
A)A spontaneous reaction need not occur immediately.
B)A spontaneous reaction must be exothermic and must have an increase in entropy.
C)The reverse of a nonspontaneous reaction is always spontaneous.
D)A spontaneous reaction is one that can proceed on its own.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
The enthalpy of fusion of naphthalene,C10H8,is 19.1 kJ/mol at 78.2°C,its melting point.Calculate the entropy of fusion at the melting point.
A)ΔS°fus = 244 J/(K ∙ mol)
B)ΔS°fus = 54.4 J/(K ∙ mol)
C)ΔS°fus = 1.49 J/(K ∙ mol)
D)ΔS°fus = -1.49 J/(K ∙ mol)
A)ΔS°fus = 244 J/(K ∙ mol)
B)ΔS°fus = 54.4 J/(K ∙ mol)
C)ΔS°fus = 1.49 J/(K ∙ mol)
D)ΔS°fus = -1.49 J/(K ∙ mol)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
For the conversion of water to ice at 25°C and 1 atm,
A)ΔG is negative and ΔH is negative.
B)ΔG is negative and ΔH is positive.
C)ΔG is positive and ΔH is negative.
D)ΔG is positive and ΔH is positive.
A)ΔG is negative and ΔH is negative.
B)ΔG is negative and ΔH is positive.
C)ΔG is positive and ΔH is negative.
D)ΔG is positive and ΔH is positive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Imagine a reaction that results in a change in both volume and temperature,as shown in the diagram below.What is the sign of the work being done and the sign of the enthalpy change involved in this reaction? 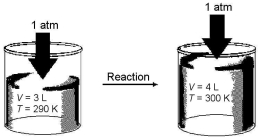
A)w = + and ΔH = +
B)w = + and ΔH = -
C)w = - and ΔH = +
D)w = - and ΔH = -

A)w = + and ΔH = +
B)w = + and ΔH = -
C)w = - and ΔH = +
D)w = - and ΔH = -

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Methanol can be produced from carbon monoxide and hydrogen with suitable catalysts: CO(g)+ 2 H2(g)→ CH3OH(l)at 25°C ΔH° = -128.1 kJ and ΔS° = -332 J/K
Find ΔG° at 25°C.
A)-157.2 kJ
B)-29.1 kJ
C)98.9 kJ
D)157.2 kJ
Find ΔG° at 25°C.
A)-157.2 kJ
B)-29.1 kJ
C)98.9 kJ
D)157.2 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
If an endothermic reaction is spontaneous at constant temperature and pressure,
A)ΔG is negative and ΔS may be positive or negative.
B)ΔG is negative and ΔS is positive.
C)ΔG is positive and ΔS is negative.
D)ΔG is positive and ΔS may be positive or negative.
A)ΔG is negative and ΔS may be positive or negative.
B)ΔG is negative and ΔS is positive.
C)ΔG is positive and ΔS is negative.
D)ΔG is positive and ΔS may be positive or negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
The reaction 4 Ag(s)+ O2(g)→ 2 Ag2O(s)favors Ag2O at low temperature,but it favors Ag and O2 at high temperatures.How can this be explained in terms of ΔH and ΔS?
A)ΔH is negative and ΔS is negative.
B)ΔH is negative and ΔS is positive.
C)ΔH is positive and ΔS is negative.
D)ΔH is positive and ΔS is positive.
A)ΔH is negative and ΔS is negative.
B)ΔH is negative and ΔS is positive.
C)ΔH is positive and ΔS is negative.
D)ΔH is positive and ΔS is positive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
For the expansion of an ideal gas into a vacuum at constant temperature,ΔH = 0.What can be said about ΔE and ΔS?
A)ΔE is negative and ΔS is positive.
B)ΔE is zero and ΔS is positive.
C)ΔE is negative and ΔS is zero.
D)ΔE is positive and ΔS is negative.
A)ΔE is negative and ΔS is positive.
B)ΔE is zero and ΔS is positive.
C)ΔE is negative and ΔS is zero.
D)ΔE is positive and ΔS is negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Imagine a reaction that results in a change in both volume and temperature,as shown in the diagram below.What is the sign of the work being done,and what is the sign of the enthalpy change involved in this reaction? 
A)w = + and ΔH = +
B)w = + and ΔH = -
C)w = - and ΔH = +
D)w = - and ΔH = -

A)w = + and ΔH = +
B)w = + and ΔH = -
C)w = - and ΔH = +
D)w = - and ΔH = -

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Determine the sign of ΔS° for each of the following: I.The mixing of two gases at a given temperature and pressure
II.C(s)+ 2 H2O(g)→ CO2(g)+ 2 H2(g)
A)ΔS° is negative for I and negative for II.
B)ΔS° is negative for I and positive for II.
C)ΔS° is positive for I and negative for II.
D)ΔS° is positive for I and positive for II.
II.C(s)+ 2 H2O(g)→ CO2(g)+ 2 H2(g)
A)ΔS° is negative for I and negative for II.
B)ΔS° is negative for I and positive for II.
C)ΔS° is positive for I and negative for II.
D)ΔS° is positive for I and positive for II.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Imagine a reaction that results in a change in both volume and temperature,as shown in the diagram below.What is the sign of the work being done,and what is the sign of the enthalpy change involved in this reaction? 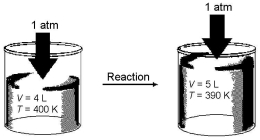
A)w = + and ΔH = +
B)w = + and ΔH = -
C)w = - and ΔH = +
D)w = - and ΔH = -

A)w = + and ΔH = +
B)w = + and ΔH = -
C)w = - and ΔH = +
D)w = - and ΔH = -

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
If a reaction with a negative value of ΔS is nonspontaneous at constant temperature and pressure,
A)ΔG is negative and ΔH may be positive or negative.
B)ΔG is negative and ΔH is positive.
C)ΔG is positive and ΔH may be positive or negative.
D)ΔG is positive and ΔH is positive.
A)ΔG is negative and ΔH may be positive or negative.
B)ΔG is negative and ΔH is positive.
C)ΔG is positive and ΔH may be positive or negative.
D)ΔG is positive and ΔH is positive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Calculate ΔG° for the reaction below and tell whether it is spontaneous or nonspontaneous under standard conditions at 25°C. 2 S (s)+ 3 O2 (g)+ 2 H2O (l)→ 2 H2SO4 (l)ΔH° = -1056 kJ/mol
ΔS° = -505 J/mol
A)ΔG° = -1207 kJ and the process is spontaneous.
B)ΔG° = -1207 kJ and the process is nonspontaneous.
C)ΔG° = -906 kJ and the process is spontaneous.
D)ΔG° = -906 kJ and the process is nonspontaneous.
ΔS° = -505 J/mol
A)ΔG° = -1207 kJ and the process is spontaneous.
B)ΔG° = -1207 kJ and the process is nonspontaneous.
C)ΔG° = -906 kJ and the process is spontaneous.
D)ΔG° = -906 kJ and the process is nonspontaneous.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Which combination always results in a reaction being spontaneous?
A)ΔH is negative and ΔS is negative.
B)ΔH is negative and ΔS is positive.
C)ΔH is positive and ΔS is negative.
D)ΔH is positive and ΔS is positive.
A)ΔH is negative and ΔS is negative.
B)ΔH is negative and ΔS is positive.
C)ΔH is positive and ΔS is negative.
D)ΔH is positive and ΔS is positive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
When heated,mercury(II)oxide decomposes into elemental mercury and oxygen: 2 HgO(s)→ 2 Hg(l)+ O2(g)ΔH° = 181.6 kJ ΔS° = 216.4 J/K
Estimate the temperature at which HgO should begin to decompose if the partial pressure of O2(g)is constant at 1.00 atm.
A)-34.8°C
B)34.8°C
C)566°C
D)840°C
Estimate the temperature at which HgO should begin to decompose if the partial pressure of O2(g)is constant at 1.00 atm.
A)-34.8°C
B)34.8°C
C)566°C
D)840°C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
What is the thermodynamic criterion for equilibrium for a reaction at constant temperature and pressure (PV work only)?
A)ΔS = 0
B)ΔG = 0
C)ΔS > 0
D)ΔG < 0
A)ΔS = 0
B)ΔG = 0
C)ΔS > 0
D)ΔG < 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Imagine a reaction that results in a change in both volume and temperature,as shown in the diagram below.What is the sign of the work being done and the sign of the enthalpy change involved in this reaction? 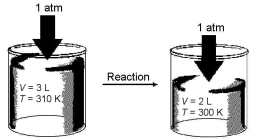
A)w = + and ΔH = +
B)w = + and ΔH = -
C)w = - and ΔH = +
D)w = - and ΔH = -

A)w = + and ΔH = +
B)w = + and ΔH = -
C)w = - and ΔH = +
D)w = - and ΔH = -

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 170 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








