Deck 19: Government in the Market Economy
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 19: Government in the Market Economy
1
When government-run enterprise is sold to the private sector, this process is known as:
A) privatization.
B) liquidation.
C) nationalization.
D) deregulation.
A) privatization.
B) liquidation.
C) nationalization.
D) deregulation.
A
2
The stabilization function of government refers to attempts to control the problems of:
A) unemployment and inflation.
B) negative and positive externalities.
C) externalities and public goods.
D) business failures and unemployment.
A) unemployment and inflation.
B) negative and positive externalities.
C) externalities and public goods.
D) business failures and unemployment.
A
3
Social marginal cost is the cost borne by:
A) all individuals in the economy.
B) individuals with no direct role in a given transaction.
C) all firms in the economy.
D) the government.
A) all individuals in the economy.
B) individuals with no direct role in a given transaction.
C) all firms in the economy.
D) the government.
A
4
One important difference between private and public institutions is:
A) that private sector institutions involve exploitation.
B) the existence of discrimination in the private sector.
C) the power of compulsion or coercion.
D) the importance of self-interest in the private sector.
A) that private sector institutions involve exploitation.
B) the existence of discrimination in the private sector.
C) the power of compulsion or coercion.
D) the importance of self-interest in the private sector.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
It is not generally considered to be an appropriate function of government to:
A) produce public goods.
B) alter individual preferences.
C) eliminate externalities.
D) stabilize the economy.
A) produce public goods.
B) alter individual preferences.
C) eliminate externalities.
D) stabilize the economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
One of the characteristics of a public good is that the:
A) costs are imposed on individual producers.
B) benefits accrue to individuals.
C) payers can be excluded.
D) nonpayers cannot be excluded.
A) costs are imposed on individual producers.
B) benefits accrue to individuals.
C) payers can be excluded.
D) nonpayers cannot be excluded.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The notion that individuals know what is in their own best interest is:
A) consumer sovereignty.
B) paternalism.
C) rational ignorance.
D) the invisible hand.
A) consumer sovereignty.
B) paternalism.
C) rational ignorance.
D) the invisible hand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Expenses that are not directly borne by producers or their customers are called:
A) marginal external costs.
B) marginal social costs.
C) marginal private costs.
D) opportunity costs.
A) marginal external costs.
B) marginal social costs.
C) marginal private costs.
D) opportunity costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Social costs refer to costs borne by:
A) the government.
B) third-party individuals
C) foreign consumers.
D) public sector producers.
A) the government.
B) third-party individuals
C) foreign consumers.
D) public sector producers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
If investment in a public project makes at least one individual better off and no one worse off, the result is called:
A) Pareto satisfactory.
B) Pareto optimal.
C) a potential Pareto improvement.
D) none of these.
A) Pareto satisfactory.
B) Pareto optimal.
C) a potential Pareto improvement.
D) none of these.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
When an anticipated program or project involves positive net benefits it is:
A) Pareto satisfactory.
B) Pareto optimal.
C) a potential Pareto improvement.
D) of benefit to at least one individual, and hurts no one.
A) Pareto satisfactory.
B) Pareto optimal.
C) a potential Pareto improvement.
D) of benefit to at least one individual, and hurts no one.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of the following is the best example of a public good?
A) a pizza.
B) a radio broadcast.
C) a bottle of soda.
D) a video cassette.
A) a pizza.
B) a radio broadcast.
C) a bottle of soda.
D) a video cassette.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Market failure refers to a situation where:
A) nothing useful is produced.
B) markets fail to bring about an equality between losses and gains.
C) economic efficiency is not achieved.
D) scarcity is not eliminated.
A) nothing useful is produced.
B) markets fail to bring about an equality between losses and gains.
C) economic efficiency is not achieved.
D) scarcity is not eliminated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
At the socially efficient price-output level:
A) external costs equal zero.
B) marginal social benefit equals marginal private benefit.
C) marginal social cost equals marginal private cost.
D) social marginal benefit equals social marginal cost.
A) external costs equal zero.
B) marginal social benefit equals marginal private benefit.
C) marginal social cost equals marginal private cost.
D) social marginal benefit equals social marginal cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Market failure refers to:
A) an unequal division between private and public sector uses.
B) a market process that does not yield useful outcomes.
C) an inefficient use of scarce resources.
D) a situation where markets fail to generate profitable market-clearing prices.
A) an unequal division between private and public sector uses.
B) a market process that does not yield useful outcomes.
C) an inefficient use of scarce resources.
D) a situation where markets fail to generate profitable market-clearing prices.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
If use by certain individuals does not reduce availability for others, then a good or service is said to display:
A) the nonrival consumption concept.
B) the nonexclusion concept.
C) positive net social benefits.
D) the private good concept.
A) the nonrival consumption concept.
B) the nonexclusion concept.
C) positive net social benefits.
D) the private good concept.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Water pollution is a familiar type of:
A) private good.
B) positive externality.
C) social benefit.
D) negative externality.
A) private good.
B) positive externality.
C) social benefit.
D) negative externality.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Air and water pollution are examples of:
A) positive externalities.
B) negative externalities.
C) public goods.
D) public bads.
A) positive externalities.
B) negative externalities.
C) public goods.
D) public bads.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Adam Smith's belief that the pursuit of self-interest by individuals leads to social betterment is called the:
A) public good.
B) elimination of externalities.
C) invisible hand.
D) private good.
A) public good.
B) elimination of externalities.
C) invisible hand.
D) private good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
A method used to determine how to best employ resources in a given social program or public-sector investment project is called:
A) social net present value analysis.
B) social benefit-cost ratio analysis.
C) social internal rate of return analysis.
D) cost-effectiveness analysis.
A) social net present value analysis.
B) social benefit-cost ratio analysis.
C) social internal rate of return analysis.
D) cost-effectiveness analysis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
An example of a public good subject to the nonexclusion concept that is provided by the private sector in the United States is:
A) radio broadcasts.
B) cable television services.
C) communicable disease inoculations.
D) college education.
A) radio broadcasts.
B) cable television services.
C) communicable disease inoculations.
D) college education.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
External Social Benefits. Publicly-funded primary and secondary education is common throughout the world. This support is usually justified on the basis that there are significant external social benefits to having an articulate and well-educated populace. Some of the external benefits associated with a more highly educated populace include higher income tax revenues, reduced crime, higher voter participation, and so on.
A. Describe the nonrival consumption concept as it pertains to publicly-funded primary and secondary education.
B. Describe the nonexclusion consumption concept as it pertains to publicly-funded primary and secondary education.
C. In terms of the external social benefits of education argument, is the public support basis for college education as strong as it is for primary and secondary education?
A. Describe the nonrival consumption concept as it pertains to publicly-funded primary and secondary education.
B. Describe the nonexclusion consumption concept as it pertains to publicly-funded primary and secondary education.
C. In terms of the external social benefits of education argument, is the public support basis for college education as strong as it is for primary and secondary education?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Public vs Private Goods. Use the nonrival concept to classify each of the following goods and services as public goods or private goods. Also indicate whether or not the good or service in question can be characterized by the nonexclusion concept. Explain.
A. Lighthouse signals.
B. Small pox vaccinations.
C. Criminal justice system.
D. Local phone service.
E. The Simpsons television program provided on "free" TV.
A. Lighthouse signals.
B. Small pox vaccinations.
C. Criminal justice system.
D. Local phone service.
E. The Simpsons television program provided on "free" TV.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Policies that are designed to reduce barriers to international trade are known as:
A) trade deficit policies.
B) free trade policies.
C) protectionist policies.
D) import quotas.
A) trade deficit policies.
B) free trade policies.
C) protectionist policies.
D) import quotas.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Social Rate of Discount. Assume that the rate of return on long-term government bonds is 5%, a typical after-tax return on investment in the private sector is 7%, the marginal corporate and individual tax rate is 50%, and consumption averages 95% of total income.
A. Based on the information provided, calculate an economically appropriate social rate of discount.
B. Would a decrease in the private-sector savings rate due to new tax benefits for individual retirement accounts increase, decrease, or have no effect on the appropriate social rate of discount?
A. Based on the information provided, calculate an economically appropriate social rate of discount.
B. Would a decrease in the private-sector savings rate due to new tax benefits for individual retirement accounts increase, decrease, or have no effect on the appropriate social rate of discount?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
All of the following influence exports except:
A) prices of foreign goods.
B) prices of domestic goods.
C) incomes in foreign countries.
D) the marginal propensity to import.
A) prices of foreign goods.
B) prices of domestic goods.
C) incomes in foreign countries.
D) the marginal propensity to import.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
An example of a public good subject to nonrival consumption is given by:
A) national defense.
B) local trash pickup.
C) a municipal swimming pool.
D) a municipal softball diamond.
A) national defense.
B) local trash pickup.
C) a municipal swimming pool.
D) a municipal softball diamond.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Nonexclusion Concept. Many public goods display the attribute of being nonexclusionary in consumption.
A. Explain the nonexclusion concept.
B. Do educational TV broadcasts display both the nonrival and nonexclusion attributes?
C. With the emergence and popularity of cable TV, is an optimal amount of educational TV likely to be provided by the private sector?
A. Explain the nonexclusion concept.
B. Do educational TV broadcasts display both the nonrival and nonexclusion attributes?
C. With the emergence and popularity of cable TV, is an optimal amount of educational TV likely to be provided by the private sector?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Demand Estimation for Public Goods. Assume that students and nonstudents have revealed their group demands for secondary education, a public good, in the local school district as follows:



فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Nonexclusion Concept. Many public goods display the attribute of being nonexclusionary in consumption.
A. Explain the nonexclusion concept, and how it differs from the nonrival consumption concept.
B. Does national defense display both the nonrival and nonexclusion attributes?
C. Is an optimal amount of national defense likely to be provided by the private sector?
A. Explain the nonexclusion concept, and how it differs from the nonrival consumption concept.
B. Does national defense display both the nonrival and nonexclusion attributes?
C. Is an optimal amount of national defense likely to be provided by the private sector?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Nonrival Consumption Concept. The essential distinguishing characteristic of public goods is the concept of nonrival consumption.
A. Explain the nonrival consumption concept.
B. Cite some examples of goods that display the nonrival consumption attribute.
A. Explain the nonrival consumption concept.
B. Cite some examples of goods that display the nonrival consumption attribute.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
External Social Benefits. During recent years, professional sports have enjoyed an unprecedented boom all across the United States and Canada. Team revenues have skyrocketed with growing fan interest and attendance, thriving broadcast revenues, and flourishing corporate sponsorship support. At the same time, major and minor league teams in baseball, football, basketball, and hockey have come to increasingly rely upon public funding to cover construction costs and maintenance expenses for sport facilities.
A. Describe the nonrival consumption concept as it applies to publicly-funded sport facilities.
B. Describe the nonexclusion consumption concept as it applies to publicly-funded sport facilities.
C. In terms of the external social benefits concept, is the equity argument in favor of public support for sport facilities as strong as it is for industrial development in general?
A. Describe the nonrival consumption concept as it applies to publicly-funded sport facilities.
B. Describe the nonexclusion consumption concept as it applies to publicly-funded sport facilities.
C. In terms of the external social benefits concept, is the equity argument in favor of public support for sport facilities as strong as it is for industrial development in general?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Social Rate of Discount. Assume that the rate of return on long-term government bonds is 7%, a typical after-tax return on investment in the private sector is 9%, the marginal corporate and individual tax rate is 40%, and consumption averages 94% of total income.
A. Based on the information provided, calculate an economically appropriate social rate of discount.
B. Would an increase in the private-sector savings rate due to a reduction in tax benefits for individual retirement accounts increase, decrease, or have no effect on the appropriate social rate of discount?
A. Based on the information provided, calculate an economically appropriate social rate of discount.
B. Would an increase in the private-sector savings rate due to a reduction in tax benefits for individual retirement accounts increase, decrease, or have no effect on the appropriate social rate of discount?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Public Management Theory. A traditional rationale for public sector management of economic resources is that there is a fundamental difference in the economic characteristics of two broad categories of goods and services. These two categories are called public goods and private goods.
A. Describe the essential characteristic of public goods and cite some examples.
B. Describe the essential characteristic of private goods and cite some examples.
A. Describe the essential characteristic of public goods and cite some examples.
B. Describe the essential characteristic of private goods and cite some examples.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
All public goods involve:
A) nonrival consumption.
B)
B) the nonexclusion concept.
C) both A and
D) none of these.
A) nonrival consumption.
B)
B) the nonexclusion concept.
C) both A and
D) none of these.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Social Rate of Discount. Assume that the rate of return on long-term government bonds is 10%, a typical after-tax return on investment in the private sector is 12%, the marginal corporate and individual tax rate is 40%, and consumption averages 95% of total income.
A. Based on the information provided, calculate an economically appropriate social rate of discount.
B. Is a decrease in the marginal corporate tax rate likely to increase, decrease, or have no effect on the appropriate social rate of discount?
A. Based on the information provided, calculate an economically appropriate social rate of discount.
B. Is a decrease in the marginal corporate tax rate likely to increase, decrease, or have no effect on the appropriate social rate of discount?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Social Rate of Discount. Assume that the rate of return on long-term government bonds is 8%, a typical after-tax return on investment in the private sector is 10%, the marginal corporate and individual tax rate is 50%, and consumption averages 94% of total income.
A. Based on the information provided, calculate an economically appropriate social rate of discount.
B. Would an increase in the Federal deficit that led to an increase in the long-term government bond rate affect the appropriate social rate of discount? If so, how? If not, why not?
A. Based on the information provided, calculate an economically appropriate social rate of discount.
B. Would an increase in the Federal deficit that led to an increase in the long-term government bond rate affect the appropriate social rate of discount? If so, how? If not, why not?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Hidden Preferences Problem. Public goods that incorporate both the nonrival consumption and nonexclusive attributes involve a number of difficulties in demand estimation.



فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Public vs Private Goods. Use the nonrival concept to classify each of the following goods and services as public goods or private goods. Also indicate whether or not the good or service in question can be characterized by the nonexclusion concept. Explain.
A. Police protection.
B. Public libraries
C. State and local lotteries.
D. Long-distance phone service.
E. Yellowstone National Park.
A. Police protection.
B. Public libraries
C. State and local lotteries.
D. Long-distance phone service.
E. Yellowstone National Park.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Social Rate of Discount. Assume that the rate of return on long-term government bonds is 9%, a typical after-tax return on investment in the private sector is 10%, the marginal corporate and individual tax rate is 50%, and consumption averages 95% of total income.
A. Based on the information provided, calculate an economically appropriate social rate of discount.
B. Would a reduction in the Federal deficit that led to a decline in the long-term government bond rate affect the appropriate social rate of discount? If so, how? If not, why not?
A. Based on the information provided, calculate an economically appropriate social rate of discount.
B. Would a reduction in the Federal deficit that led to a decline in the long-term government bond rate affect the appropriate social rate of discount? If so, how? If not, why not?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Demand Estimation for Public Goods. The nonrival consumption concept gives rise to fundamental differences between demand estimation for public goods and demand estimation for private goods.
A. Explain the graphical difference between aggregating individual demand for public goods versus private goods.
B. Can the aggregate value of a given public good ever be less than the maximum value placed upon it by a single individual?
A. Explain the graphical difference between aggregating individual demand for public goods versus private goods.
B. Can the aggregate value of a given public good ever be less than the maximum value placed upon it by a single individual?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Size of Government. Both unregulated private markets and government-administered resources have their strengths and weaknesses.
A. Discuss a primary weakness of the unregulated private-sector allocation of economic resources.
B. Discuss a primary weakness of government-administered social programs or public-sector investment projects.
A. Discuss a primary weakness of the unregulated private-sector allocation of economic resources.
B. Discuss a primary weakness of government-administered social programs or public-sector investment projects.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Costs of Regulation. The Montana Coal Company sells coal to electric utilities in the Pacific Northwest. Unfortunately, Montana's coal has high particulate content and, therefore, the company is adversely affected by state and local regulations governing smoke and dust emissions at its customer's electricity-generating plants. Montana's total cost and marginal cost relations are:
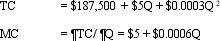 where Q is tons of coal produced per month and TC includes a normal rate of return on investment.
where Q is tons of coal produced per month and TC includes a normal rate of return on investment.

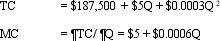 where Q is tons of coal produced per month and TC includes a normal rate of return on investment.
where Q is tons of coal produced per month and TC includes a normal rate of return on investment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Demand Estimation for Public Goods. Assume that park visitors and nonvisitors have revealed their group demands for national park service, a public good, as follows:



فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Benefit-cost Analysis. The economic valuation of human life has consequences for a broad range of management decisions in both the private and public sectors. Because resources are limited for individual companies and for society as a whole, rational decision makers cannot argue that any individual company or society should spend "whatever it takes" to save a human life.
A. Explain how public sector managers might obtain reliable life value estimates based upon actual economic behavior.
B. Describe some of the limitations of such life value estimates based upon actual economic behavior.
A. Explain how public sector managers might obtain reliable life value estimates based upon actual economic behavior.
B. Describe some of the limitations of such life value estimates based upon actual economic behavior.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Theory of Regulation. The Badger Power & Light Company generates electricity, and in the process emits sulfur dioxide into the local atmosphere. As a concerned citizen, you are appalled at the aesthetic and environmental implications of the company's policies, as well as the potential health hazard to the local population.
A. Pollution is a negative production externality and an example of market failure. What might you cite as reasons why markets fail?
B. In analyzing remedies to the current situation, consider two general types of controls to limit pollution:
Regulations--licenses, permits, compulsory standards, and so on.
Charges--excise taxes on polluting fuels (coal, oil, and so forth), pollution discharge taxes, and others.
Review each of these methods of pollution control.
1. Determine the incentive structure for the polluter under each form of control.
2. Decide who pays for a clean environment under each form of control. (Note that each form of control has definite implications about who owns the property rights to the environment.)
3. Defend a particular form of control on the basis of your analysis, including both efficiency and equity considerations.
A. Pollution is a negative production externality and an example of market failure. What might you cite as reasons why markets fail?
B. In analyzing remedies to the current situation, consider two general types of controls to limit pollution:
Regulations--licenses, permits, compulsory standards, and so on.
Charges--excise taxes on polluting fuels (coal, oil, and so forth), pollution discharge taxes, and others.
Review each of these methods of pollution control.
1. Determine the incentive structure for the polluter under each form of control.
2. Decide who pays for a clean environment under each form of control. (Note that each form of control has definite implications about who owns the property rights to the environment.)
3. Defend a particular form of control on the basis of your analysis, including both efficiency and equity considerations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Privatization. With airline regulation, high prices were eaten away by ever-rising costs for new airplane equipment, fancy meals, and redundant employees. In the post-deregulation period, passenger fares have plummeted as consumers made known their preference for safe and reliable service with cheap airfares. Critics of public sector management of the U.S. Post Office contend that experience with airline deregulation suggests that privatization of the U.S. Post office would lead to dramatic cost reductions and service improvements.
A. Explain how breaking the U.S. Post Office monopoly could help reduce the cost and improve the quality of first-class mail delivery.
B. Explain why privatizing the U.S. Post Office might not lead to such advantages.
A. Explain how breaking the U.S. Post Office monopoly could help reduce the cost and improve the quality of first-class mail delivery.
B. Explain why privatizing the U.S. Post Office might not lead to such advantages.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Theory of Regulation. The New England Power & Light Company generates electricity, and in the process emits sulfur dioxide into the local atmosphere. As a concerned citizen, you are appalled at the aesthetic and environmental implications of the company's policies, as well as the potential health hazard to the local population.
A. Pollution is a negative production externality and an example of market failure. What might you cite as reasons why markets fail?
B. In analyzing remedies to the current situation, consider two general types of controls to limit pollution:
Regulations--licenses, permits, compulsory standards, and so on.
Payments--various types of government aid to help companies install pollution-control equipment. Aid can take the form of forgiven local property taxes, income tax credits, special accelerated depreciation allowances for pollution-control equipment, low-cost government loans, and so on.
Review each of these methods of pollution control and:
1. Determine the incentive structure for the polluter under each form of control.
2. Decide who pays for a clean environment under each form of control. (Note that each form of control has definite implications about who owns the property rights to the environment.)
3. Defend a particular form of control on the basis of your analysis, including both efficiency and equity considerations.
A. Pollution is a negative production externality and an example of market failure. What might you cite as reasons why markets fail?
B. In analyzing remedies to the current situation, consider two general types of controls to limit pollution:
Regulations--licenses, permits, compulsory standards, and so on.
Payments--various types of government aid to help companies install pollution-control equipment. Aid can take the form of forgiven local property taxes, income tax credits, special accelerated depreciation allowances for pollution-control equipment, low-cost government loans, and so on.
Review each of these methods of pollution control and:
1. Determine the incentive structure for the polluter under each form of control.
2. Decide who pays for a clean environment under each form of control. (Note that each form of control has definite implications about who owns the property rights to the environment.)
3. Defend a particular form of control on the basis of your analysis, including both efficiency and equity considerations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Demand Estimation for Public Goods. Assume that patients and nonpatients have revealed their group demands for hospital emergency room service, a public good, as follows:



فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Economics of Health Care. Technological progress in the form of new medical knowledge, medicines, treatments, and medical devices has allowed Americans and people worldwide to live longer, healthier lives. As new treatment options become available, it is not surprising that the United States and other major industrialized countries continue to shift more resources to health care. Research suggests that between 50 and 75 percent of the growth rate in health expenditures in the United States is attributable to technological progress in health care goods and services. However, the increase in resources devoted to health care has led to concern about its affordability, both for families and for the Nation as a whole. The United States expends a higher fraction of GDP on health care than does any other industrialized country. According to an international comparison released in 2003, the United States spent 13.9 percent of GDP on health care in 2001, while the average among industrialized countries was 8.4 percent of GDP. Measures of health outcomes such as longevity and infant mortality, however, are not markedly different in the United States than in other advanced economies that spend substantially less on health care.
A. Use a normal good (demand-side) argument to explain why the U. S. consumer, among the richest in the world, spends a higher percentage of income on health care than do consumers in most poorer countries.
B. Use a supply-side argument to explain why the costs of providing health care services appear higher for Americans than for other world-wide beneficiaries of health care innovation.
A. Use a normal good (demand-side) argument to explain why the U. S. consumer, among the richest in the world, spends a higher percentage of income on health care than do consumers in most poorer countries.
B. Use a supply-side argument to explain why the costs of providing health care services appear higher for Americans than for other world-wide beneficiaries of health care innovation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








