Deck 9: The Aggregate Demand - Aggregate Supply Model
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/124
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 9: The Aggregate Demand - Aggregate Supply Model
1
Money is
A) the same as income.
B) all financial assets.
C) any asset used to make purchases and to settle debts.
D) the sum of assets minus liabilities.
E) the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a year.
A) the same as income.
B) all financial assets.
C) any asset used to make purchases and to settle debts.
D) the sum of assets minus liabilities.
E) the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a year.
any asset used to make purchases and to settle debts.
2
M1 differs from M2 in that
A) M1 includes currency and balances held in chequing accounts,which are not included in M2.
B) M2 includes personal deposits and non-personal demand and notice deposits,which are not included in M1.
C) M2 includes small savings accounts,and money market mutual funds,which are not included in M1.
D) M1 is a broader measure of the money supply than M2.
E) the assets in M2 are more liquid than the assets in M1.
A) M1 includes currency and balances held in chequing accounts,which are not included in M2.
B) M2 includes personal deposits and non-personal demand and notice deposits,which are not included in M1.
C) M2 includes small savings accounts,and money market mutual funds,which are not included in M1.
D) M1 is a broader measure of the money supply than M2.
E) the assets in M2 are more liquid than the assets in M1.
M2 includes personal deposits and non-personal demand and notice deposits,which are not included in M1.
3
When money is used to purchase goods and services,it serves as a
A) financial intermediary.
B) double coincidence of wants.
C) store of value.
D) medium of exchange.
E) unit of account.
A) financial intermediary.
B) double coincidence of wants.
C) store of value.
D) medium of exchange.
E) unit of account.
medium of exchange.
4
Use the information in the table below to calculate the value of the M2 measure of the money supply. 
A) $135 billion.
B) $521 billion.
C) $681 billion.
D) $726 billion.
E) $916 billion.

A) $135 billion.
B) $521 billion.
C) $681 billion.
D) $726 billion.
E) $916 billion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
When money is used as a means to hold wealth,it serves as a
A) financial intermediary.
B) double coincidence of wants.
C) store of value.
D) medium of exchange.
E) unit of account.
A) financial intermediary.
B) double coincidence of wants.
C) store of value.
D) medium of exchange.
E) unit of account.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Use the information in the table below to calculate the value of the M1 measure of the money supply. 
A) $135 billion.
B) $521 billion.
C) $681 billion.
D) $726 billion.
E) $916 billion.

A) $135 billion.
B) $521 billion.
C) $681 billion.
D) $726 billion.
E) $916 billion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The direct trade of goods and services for other goods and services is called
A) financial intermediation.
B) diversification.
C) barter.
D) using a medium of exchange.
E) the efficient allocation of resources.
A) financial intermediation.
B) diversification.
C) barter.
D) using a medium of exchange.
E) the efficient allocation of resources.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Money serves as a store of value when
A) it is used to purchase goods and services.
B) there is direct trade of goods and services.
C) it is a basic measure of economic value.
D) it is a means of holding wealth.
E) there is a double coincidence of wants.
A) it is used to purchase goods and services.
B) there is direct trade of goods and services.
C) it is a basic measure of economic value.
D) it is a means of holding wealth.
E) there is a double coincidence of wants.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Using money as a ________ avoids the problem of the double coincidence of wants.
A) medium of exchange
B) measure of value
C) standard of deferred payment
D) store of value
E) tool of monetary policy
A) medium of exchange
B) measure of value
C) standard of deferred payment
D) store of value
E) tool of monetary policy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Holding money as a store of wealth has the advantage of being useful as a medium of exchange.The disadvantages of holding your wealth in the form of money are that it
A) may be stolen or lost,and people may think you're a smuggler or drug dealer.
B) is difficult to trace,and may be lost or stolen.
C) may be lost or stolen,and usually pays no interest.
D) pays no interest,and it is difficult to trace.
E) pays no interest,and people may think you're a smuggler or drug dealer.
A) may be stolen or lost,and people may think you're a smuggler or drug dealer.
B) is difficult to trace,and may be lost or stolen.
C) may be lost or stolen,and usually pays no interest.
D) pays no interest,and it is difficult to trace.
E) pays no interest,and people may think you're a smuggler or drug dealer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Money serves as a unit of account when
A) it is used to purchase goods and services.
B) there is direct trade of goods and services.
C) it is a basic measure of economic value.
D) it is a means of holding wealth.
E) there is a double coincidence of wants.
A) it is used to purchase goods and services.
B) there is direct trade of goods and services.
C) it is a basic measure of economic value.
D) it is a means of holding wealth.
E) there is a double coincidence of wants.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Money serves as a measure of economic value (i.e. ,a unit of account),allowing
A) people to hold their wealth in a liquid form.
B) governments to restrict the issuance of private monies.
C) easy comparison of the relative prices of goods and services.
D) goods and services to be exchanged with a double coincidence of wants.
E) private money to be issued for local usE.
A) people to hold their wealth in a liquid form.
B) governments to restrict the issuance of private monies.
C) easy comparison of the relative prices of goods and services.
D) goods and services to be exchanged with a double coincidence of wants.
E) private money to be issued for local usE.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
When money is the basic measure of economic value,it serves as a
A) financial intermediary.
B) double coincidence of wants.
C) store of value.
D) medium of exchange.
E) unit of account.
A) financial intermediary.
B) double coincidence of wants.
C) store of value.
D) medium of exchange.
E) unit of account.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
What function is money serving when you buy a ticket to a movie?
A) A store of value.
B) A unit of account.
C) A transaction demand.
D) A medium of exchange.
E) Legal tender.
A) A store of value.
B) A unit of account.
C) A transaction demand.
D) A medium of exchange.
E) Legal tender.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Finding two parties to a trade,each of whom has something for which the other wishes to trade,is called a
A) unit of account.
B) store of value.
C) medium of exchange.
D) double coincidence of wants.
E) diversification of interests.
A) unit of account.
B) store of value.
C) medium of exchange.
D) double coincidence of wants.
E) diversification of interests.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Barter is
A) the direct trade of goods and services for other goods and services.
B) an asset used in purchasing goods and services.
C) the extension of credit to borrowers using funds raised from savers.
D) an equity claim to ownership.
E) a means of channelling funds from savers to borrowers with productive investment opportunities.
A) the direct trade of goods and services for other goods and services.
B) an asset used in purchasing goods and services.
C) the extension of credit to borrowers using funds raised from savers.
D) an equity claim to ownership.
E) a means of channelling funds from savers to borrowers with productive investment opportunities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The specialization in production made possible by the use of money to avoid barter is an illustration of the
A) scarcity principle.
B) principle of comparative advantage.
C) principle of increasing opportunity cost.
D) benefits of diversification.
E) cost-benefit principlE.
A) scarcity principle.
B) principle of comparative advantage.
C) principle of increasing opportunity cost.
D) benefits of diversification.
E) cost-benefit principlE.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Any asset used to make purchases is
A) a bond.
B) a stock.
C) a deposit.
D) money.
E) incomE.
A) a bond.
B) a stock.
C) a deposit.
D) money.
E) incomE.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Money serves as a medium of exchange when
A) it is used to purchase goods and services.
B) there is direct trade of goods and services.
C) it is a basic measure of economic value.
D) it is a means of holding wealth.
E) there is a double coincidence of wants.
A) it is used to purchase goods and services.
B) there is direct trade of goods and services.
C) it is a basic measure of economic value.
D) it is a means of holding wealth.
E) there is a double coincidence of wants.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The M2 measure of money consists of the sum of
A) chequing deposits,saving deposits at banks,and foreign currency deposits.
B) currency,non-personal demand and notice deposits,and personal deposits.
C) currency and non-personal demand and notice deposits.
D) deposits at non-bank financial institutions,and money market mutual funds.
E) non-personal term deposits,and foreign currency deposits at banks.
A) chequing deposits,saving deposits at banks,and foreign currency deposits.
B) currency,non-personal demand and notice deposits,and personal deposits.
C) currency and non-personal demand and notice deposits.
D) deposits at non-bank financial institutions,and money market mutual funds.
E) non-personal term deposits,and foreign currency deposits at banks.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Based on the following information,compute the value of the M2 measure of the money supply. 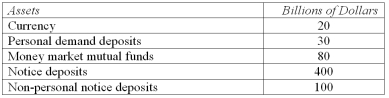
A) $20 billion.
B) $50 billion.
C) $130 billion.
D) $550 billion.
E) $630 billion.

A) $20 billion.
B) $50 billion.
C) $130 billion.
D) $550 billion.
E) $630 billion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Bank reserves divided by bank deposits are called
A) fractional-reserve banking.
B) 100%-reserve banking.
C) the desired reserve-deposit ratio.
D) the asset-liability ratio.
E) the banking system unit of account.
A) fractional-reserve banking.
B) 100%-reserve banking.
C) the desired reserve-deposit ratio.
D) the asset-liability ratio.
E) the banking system unit of account.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Banks hold reserves
A) to earn interest.
B) to increase profits.
C) to escape the double coincidence of wants.
D) to meet depositor withdrawals and payments.
E) only because the government requires them to hold reserves.
A) to earn interest.
B) to increase profits.
C) to escape the double coincidence of wants.
D) to meet depositor withdrawals and payments.
E) only because the government requires them to hold reserves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
In a fractional-reserve banking system,the reserve-deposit ratio is
A) equal to the currency in bank vaults.
B) equal to the currency held by the public divided by deposits.
C) equal to 100%.
D) less than 100%.
E) more than 100%.
A) equal to the currency in bank vaults.
B) equal to the currency held by the public divided by deposits.
C) equal to 100%.
D) less than 100%.
E) more than 100%.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Based on the following information,calculate the value of the M1 measure of the money supply. 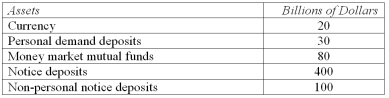
A) $20 billion.
B) $50 billion.
C) $150 billion.
D) $450 billion.
E) $630 billion.

A) $20 billion.
B) $50 billion.
C) $150 billion.
D) $450 billion.
E) $630 billion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
In Macroland,there is $10,000,000 in currency.The public holds half of the currency and banks hold the rest as reserves.If the banks' desired reserve-deposit ratio is 10%,deposits in Macroland equal ________ and the money supply equals ________.
A) $50,000,000;$60,000,000
B) $55,000,000;$55,000,000
C) $50,000,000;$55,000,000
D) $100,000,000;$100,000,000
E) $100,000,000;$110,000,000
A) $50,000,000;$60,000,000
B) $55,000,000;$55,000,000
C) $50,000,000;$55,000,000
D) $100,000,000;$100,000,000
E) $100,000,000;$110,000,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
If the reserve-deposit ratio is less than 100%,then the banking system engages in
A) capital investment.
B) credit allocation.
C) the double coincidence of wants.
D) 100%-reserve banking.
E) fractional-reserve banking.
A) capital investment.
B) credit allocation.
C) the double coincidence of wants.
D) 100%-reserve banking.
E) fractional-reserve banking.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Bank reserves are
A) currency and customer chequing deposits.
B) currency and customer chequing and savings deposits.
C) any asset used to purchase goods and services.
D) financial assets obtained from savers and lent to borrowers.
E) cash and similar assets held to meet depositor withdrawals or payments.
A) currency and customer chequing deposits.
B) currency and customer chequing and savings deposits.
C) any asset used to purchase goods and services.
D) financial assets obtained from savers and lent to borrowers.
E) cash and similar assets held to meet depositor withdrawals or payments.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
When bank reserves exactly equal bank deposits,the bank is said to engage in
A) fractional reserve banking.
B) diversification.
C) 100%-reserve banking.
D) credit allocation.
E) open-market operations.
A) fractional reserve banking.
B) diversification.
C) 100%-reserve banking.
D) credit allocation.
E) open-market operations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The M1 measure of money consists of the sum of
A) currency and demand deposits.
B) currency and travellers' cheques.
C) currency,demand deposits,and savings deposits.
D) demand deposits and travellers' cheques.
E) demand and savings deposits.
A) currency and demand deposits.
B) currency and travellers' cheques.
C) currency,demand deposits,and savings deposits.
D) demand deposits and travellers' cheques.
E) demand and savings deposits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Commodity money refers to
A) gold.
B) silver.
C) fiat money.
D) bank reserves.
E) any asset of intrinsic value that is generally accepted as a means of payment.
A) gold.
B) silver.
C) fiat money.
D) bank reserves.
E) any asset of intrinsic value that is generally accepted as a means of payment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
In Macroland,there is $2,000,000 in currency.The public holds half of the currency and banks hold the rest as reserves.If the banks' desired reserve-deposit ratio is 5%,deposits in Macroland equal ________ and the money supply equals _______.
A) $2,000,000;$2,100,000
B) $20,000,000;$21,000,000
C) $20,000,000: $22,000,000
D) $40,000,000;$40,000,000
E) $40,000,000;$42,000,000
A) $2,000,000;$2,100,000
B) $20,000,000;$21,000,000
C) $20,000,000: $22,000,000
D) $40,000,000;$40,000,000
E) $40,000,000;$42,000,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The desired reserve-deposit ratio is equal
A) 10% of bank reserves.
B) 10% of bank deposits.
C) 100% of bank reserves.
D) bank reserves divided by bank deposits.
E) bank deposits divided by bank reserves.
A) 10% of bank reserves.
B) 10% of bank deposits.
C) 100% of bank reserves.
D) bank reserves divided by bank deposits.
E) bank deposits divided by bank reserves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
In Econland,all $5,000,000 in currency is held by banks as reserves.The public does not hold any currency.If the banks' desired reserve-deposit ratio is 10%,the money supply in Econland equals
A) $4,545,545.
B) $5,000,000.
C) $5,500,000.
D) $50,000,000.
E) $55,000,000.
A) $4,545,545.
B) $5,000,000.
C) $5,500,000.
D) $50,000,000.
E) $55,000,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The M2 measure of money consists of all the assets in M1 plus assets that are
A) usable in making payments but at a much lesser cost than currency or chequing accounts
B) usable in making payments but at a much greater cost than currency or chequing accounts
C) only denominated in foreign currency.
D) taxed at different rates as mandated by Canadian banking laws.
E) taxed at identical rates as mandated by Canadian banking laws.
A) usable in making payments but at a much lesser cost than currency or chequing accounts
B) usable in making payments but at a much greater cost than currency or chequing accounts
C) only denominated in foreign currency.
D) taxed at different rates as mandated by Canadian banking laws.
E) taxed at identical rates as mandated by Canadian banking laws.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
In Econland,all $15,000,000 in currency is held by banks as reserves.The public does not hold any currency.If the banks' desired reserve-deposit ratio is 5%,the money supply in Econland equals
A) $14,285,714.
B) $15,000,000.
C) $15,750,000.
D) $300,000,000.
E) $315,000,000.
A) $14,285,714.
B) $15,000,000.
C) $15,750,000.
D) $300,000,000.
E) $315,000,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The M2 measure of money consists of the sum of
A) savings deposits,and money market mutual funds.
B) currency,demand and savings deposits,and small time deposits.
C) currency,demand and savings deposits.
D) M1,personal savings deposits,and non-personal time deposits.
E) M1,savings deposits,and money market mutual funds.
A) savings deposits,and money market mutual funds.
B) currency,demand and savings deposits,and small time deposits.
C) currency,demand and savings deposits.
D) M1,personal savings deposits,and non-personal time deposits.
E) M1,savings deposits,and money market mutual funds.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Cash and similar assets held to meet depositor withdrawals or payments are called
A) deposits.
B) bank reserves.
C) chequing accounts.
D) money.
E) bank liabilities.
A) deposits.
B) bank reserves.
C) chequing accounts.
D) money.
E) bank liabilities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Fiat money refers to
A) a one-dollar coin.
B) coins.
C) currency.
D) bank deposits.
E) an asset of no intrinsic value that is generally accepted as a means of payment.
A) a one-dollar coin.
B) coins.
C) currency.
D) bank deposits.
E) an asset of no intrinsic value that is generally accepted as a means of payment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Money eliminates the need for a double coincidence of wants primarily through its use as a
A) unit of account.
B) medium of exchange.
C) store of value.
D) standard of confidence.
E) legal tender.
A) unit of account.
B) medium of exchange.
C) store of value.
D) standard of confidence.
E) legal tender.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
If banks' desired reserve ratio increases from 10% to 15%,the public still desires to hold the same amount of currency,and the Bank of Canada takes no action,the money supply will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not change.
D) either increase or decrease.
E) equal the quantity of currency that is still in usE.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not change.
D) either increase or decrease.
E) equal the quantity of currency that is still in usE.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Commercial banks create new money
A) by printing currency.
B) by issuing cheques.
C) through multiple rounds of lending and borrowing.
D) when they buy government bonds from the Bank of Canada.
E) when they increase their desired reserve-deposit ratio.
A) by printing currency.
B) by issuing cheques.
C) through multiple rounds of lending and borrowing.
D) when they buy government bonds from the Bank of Canada.
E) when they increase their desired reserve-deposit ratio.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
When the actual reserve-deposit ratio is less than the desired reserve-deposit ratio,banks will
A) do nothing because this is a profitable situation.
B) stop making loans.
C) send the extra reserves to the central bank.
D) request that customers withdraw deposits from the bank.
E) make more loans in order to earn interest.
A) do nothing because this is a profitable situation.
B) stop making loans.
C) send the extra reserves to the central bank.
D) request that customers withdraw deposits from the bank.
E) make more loans in order to earn interest.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
There is $5,000,000 of currency in Econland,all held by banks as reserves.The public does not hold any currency.If the banks' desired reserve-deposit ratio is 25%,then the money supply equals
A) $5,000,000.
B) $6,250,000.
C) $10,000,000.
D) $20,000,000.
E) $25,000,000.
A) $5,000,000.
B) $6,250,000.
C) $10,000,000.
D) $20,000,000.
E) $25,000,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
The money supply in Econland is 1,500,and currency held by the public is equal to bank reserves.The desired reserve-deposit ratio is 0.20.Bank reserves equal
A) 200.
B) 250.
C) 300.
D) 500.
E) 1,500.
A) 200.
B) 250.
C) 300.
D) 500.
E) 1,500.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
In Macroland,there is $1,000,000 in currency that can either be held by the public or used by banks as reserves.The banks' desired reserve-deposit ratio is 10%.If the public of Macroland decides to hold less currency,decreasing the proportion they hold from 50% to 25%,the money supply in Macroland will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) may either increase or decrease.
E) will increase initially,but then return to the original level.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) may either increase or decrease.
E) will increase initially,but then return to the original level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
In Macroland,there is $1,000,000 in currency that can either be held by the public or used by banks as reserves.The banks' desired reserve-deposit ratio is 10%.If the public of Macroland decides to hold more currency,increasing the proportion they hold from 50% to 75%,the money supply in Macroland will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) may either increase or decrease.
E) will increase initially,but then return to the original level.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) may either increase or decrease.
E) will increase initially,but then return to the original level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
If the public switches from doing most of its shopping with currency to using cheques instead,and the Bank of Canada takes no action,the money supply will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not change.
D) either increase or decrease.
E) equal the quantity of currency that is still in usE.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not change.
D) either increase or decrease.
E) equal the quantity of currency that is still in usE.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
There is $5,000,000 of currency in Econland,all held by banks as reserves.The public does not hold any currency.If the banks' desired reserve-deposit ratio is 20%,then the money supply equals
A) $5,000,000.
B) $6,000,000.
C) $10,000,000.
D) $20,000,000.
E) $25,000,000.
A) $5,000,000.
B) $6,000,000.
C) $10,000,000.
D) $20,000,000.
E) $25,000,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
If bank reserves are 200,the public holds 400 in currency,and the desired reserve-deposit ratio is 25%,deposits are ________ and the money supply is ________.
A) 200;600
B) 400;800
C) 600;1,000
D) 800;1,200
E) 2,400;2,800
A) 200;600
B) 400;800
C) 600;1,000
D) 800;1,200
E) 2,400;2,800

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
The money supply is 2000,of which 500 is currency held by the public.Bank reserves are 150.The desired reserve-deposit ratio equals
A) 5%.
B) 10%.
C) 15%.
D) 20%.
E) 25%.
A) 5%.
B) 10%.
C) 15%.
D) 20%.
E) 25%.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The money supply in Econland is 1,000,and currency held by the public is equal to bank reserves.The desired reserve-deposit ratio is 25%.Bank reserves equal
A) 200.
B) 250.
C) 400.
D) 800.
E) 1,000.
A) 200.
B) 250.
C) 400.
D) 800.
E) 1,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The amount of money in Canada is determined by
A) the Bank of Canada.
B) the commercial banks.
C) the public.
D) the combined behaviour of the commercial banks and the public.
E) the combined behaviour of the commercial banks and the public,and the actions of the Bank of Canada.
A) the Bank of Canada.
B) the commercial banks.
C) the public.
D) the combined behaviour of the commercial banks and the public.
E) the combined behaviour of the commercial banks and the public,and the actions of the Bank of Canada.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
If bank reserves are 200,the public holds 400 in currency,and the desired reserve-deposit ratio is 20%,deposits are ________ and the money supply is ________.
A) 200;600
B) 400;800
C) 600;1,000
D) 1,000;1,400
E) 2,400;2,800
A) 200;600
B) 400;800
C) 600;1,000
D) 1,000;1,400
E) 2,400;2,800

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
In Macroland,there is $1,000,000 in currency that can either be held by the public or used by banks as reserves.If the banks' desired reserve-deposit ratio decreases from 10% to 5% and the public continues to hold the same amount of currency,the money supply in Macroland will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) either increase or decrease.
E) increase initially,but then return to the original level.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) either increase or decrease.
E) increase initially,but then return to the original level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
When the actual reserve-deposit ratio exceeds the desired reserve-deposit ratio,banks will
A) do nothing because this is a profitable situation.
B) stop making loans.
C) send the extra reserves to the central bank.
D) request that customers withdraw deposits from the bank.
E) make more loans in order to earn interest.
A) do nothing because this is a profitable situation.
B) stop making loans.
C) send the extra reserves to the central bank.
D) request that customers withdraw deposits from the bank.
E) make more loans in order to earn interest.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
In Macroland,there is $1,000,000 in currency that can either be held by the public or used by banks as reserves.If the banks' desired reserve-deposit ratio increases from 10% to 15% and the public continues to hold the same amount of currency,the money supply in Macroland will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) either increase or decrease.
E) increase initially,but then return to the original level.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) either increase or decrease.
E) increase initially,but then return to the original level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
If the actual reserve-deposit ratio equals 8% for a bank,but the desired reserve-deposit ratio for this bank is 10%,the bank should
A) do nothing because this is a profitable situation.
B) stop making loans.
C) send the extra reserves to the central bank.
D) request that customers withdraw deposits from the bank.
E) make more loans in order to earn interest.
A) do nothing because this is a profitable situation.
B) stop making loans.
C) send the extra reserves to the central bank.
D) request that customers withdraw deposits from the bank.
E) make more loans in order to earn interest.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The money supply is 1,500,of which 500 is currency held by the public.Bank reserves are 200.The desired reserve-deposit ratio equals
A) 5%.
B) 10%.
C) 15%.
D) 20%.
E) 25%.
A) 5%.
B) 10%.
C) 15%.
D) 20%.
E) 25%.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
If the actual reserve-deposit ratio equals 15% for a bank,but the desired reserve-deposit ratio for this bank is 10%,the bank should
A) do nothing because this is a profitable situation.
B) stop making loans.
C) send the extra reserves to the central bank.
D) request that customers withdraw deposits from the bank.
E) make more loans in order to earn interest.
A) do nothing because this is a profitable situation.
B) stop making loans.
C) send the extra reserves to the central bank.
D) request that customers withdraw deposits from the bank.
E) make more loans in order to earn interest.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Banks could not create money if
A) the required reserve ratio was zero.
B) the Bank of Canada stopped selling bonds.
C) people held no money as cash.
D) people held all their money as cash.
E) people stopped using bank machines.
A) the required reserve ratio was zero.
B) the Bank of Canada stopped selling bonds.
C) people held no money as cash.
D) people held all their money as cash.
E) people stopped using bank machines.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
If a bank's desired reserve-deposit ratio is 33% and it has deposit liabilities of $100 million and reserves of $50 million,it
A) has too few reserves and will reduce its lending.
B) has excess reserves and will increase its lending.
C) has the correct amount of reserves and outstanding loans.
D) should increase the amount of its reserves.
E) should decrease the amount of its reserves.
A) has too few reserves and will reduce its lending.
B) has excess reserves and will increase its lending.
C) has the correct amount of reserves and outstanding loans.
D) should increase the amount of its reserves.
E) should decrease the amount of its reserves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
The banking system can increase chequing deposits by more than a single bank,because
A) the banking system must keep reserves equal to 100% of its chequing deposits.
B) the central bank follows policies that prevent reserves from falling below the level required by law.
C) excess reserves loaned out by any particular bank will be deposited in some other bank.
D) borrowers often retain a portion of a loan in cash.
E) excess reserves loaned out by any particular bank will be taken out of circulation.
A) the banking system must keep reserves equal to 100% of its chequing deposits.
B) the central bank follows policies that prevent reserves from falling below the level required by law.
C) excess reserves loaned out by any particular bank will be deposited in some other bank.
D) borrowers often retain a portion of a loan in cash.
E) excess reserves loaned out by any particular bank will be taken out of circulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
An episode when depositors,spurred by news or rumours of the imminent bankruptcy of a particular bank,rush to withdraw their deposits from that bank is called a(n)
A) open-market withdrawal.
B) open-market sale.
C) banking panic.
D) bank run.
E) reserve requirement crisis.
A) open-market withdrawal.
B) open-market sale.
C) banking panic.
D) bank run.
E) reserve requirement crisis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
A banking panic is an episode in which
A) depositors,spurred by news or rumours of the possible bankruptcy of multiple banks,rush to withdraw deposits from the banking system.
B) commercial banks,fearing Bank of Canada sanctions,unwillingly participate in open-market operations.
C) commercial banks,concerned about high interest rates,rush to borrow from the overnight market.
D) depositors,afraid of increasing interest rates,attempt to engage in borrowing from the Bank of Canada.
E) the Bank of Canada,concerned about unusually rapid increases in the money supply,refuses to make loans to commercial banks.
A) depositors,spurred by news or rumours of the possible bankruptcy of multiple banks,rush to withdraw deposits from the banking system.
B) commercial banks,fearing Bank of Canada sanctions,unwillingly participate in open-market operations.
C) commercial banks,concerned about high interest rates,rush to borrow from the overnight market.
D) depositors,afraid of increasing interest rates,attempt to engage in borrowing from the Bank of Canada.
E) the Bank of Canada,concerned about unusually rapid increases in the money supply,refuses to make loans to commercial banks.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
A bank run is an episode in which
A) depositors,spurred by news or rumours of the possible bankruptcy of multiple banks,rush to withdraw deposits from the banking system.
B) depositors,spurred by news or rumours of the possible bankruptcy of a particular bank,rush to withdraw deposits from that bank.
C) commercial banks,concerned about high interest rates,rush to borrow from the overnight market.
D) depositors,afraid of increasing interest rates,attempt to engage in borrowing from the Bank of Canada.
E) the Bank of Canada,concerned about unusually rapid increases in the money supply,refuses to make loans to commercial banks.
A) depositors,spurred by news or rumours of the possible bankruptcy of multiple banks,rush to withdraw deposits from the banking system.
B) depositors,spurred by news or rumours of the possible bankruptcy of a particular bank,rush to withdraw deposits from that bank.
C) commercial banks,concerned about high interest rates,rush to borrow from the overnight market.
D) depositors,afraid of increasing interest rates,attempt to engage in borrowing from the Bank of Canada.
E) the Bank of Canada,concerned about unusually rapid increases in the money supply,refuses to make loans to commercial banks.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
If the reserve-deposit ratio is 10% and the banking system receives an additional $10 million in reserves,bank deposits will increase by
A) $4 million.
B) $10 million.
C) $40 million.
D) $100 million.
E) $250 million.
A) $4 million.
B) $10 million.
C) $40 million.
D) $100 million.
E) $250 million.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
The Bank of Canada first began operation in
A) 1867.
B) 1914.
C) 1935.
D) 1946.
E) 1967.
A) 1867.
B) 1914.
C) 1935.
D) 1946.
E) 1967.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Given a required reserve-deposit ratio of 5% for all banks and assuming individuals hold no cash,total bank reserves of $400 billion can support deposits of
A) $400 billion.
B) $800 billion.
C) $4,000 billion.
D) $8,000 billion.
E) $9,000 billion.
A) $400 billion.
B) $800 billion.
C) $4,000 billion.
D) $8,000 billion.
E) $9,000 billion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Suppose the banking system has $100,000 in outstanding deposits and actual reserves of $35,000.If the required reserve ratio is 10% and individuals hold no cash,the maximum amount the banking system can now add to the money supply is
A) $25,000.
B) $35,000.
C) $250,000.
D) $1,000,000.
E) $1,500,000.
A) $25,000.
B) $35,000.
C) $250,000.
D) $1,000,000.
E) $1,500,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71

The table above represents a bank's T-account.Suppose it is the only bank in town and individuals in town hold no cash.Assuming the reserve ratio is 10%,what will be the bank's loans at the end of the money creation process?
A) $180,000.
B) $200,000.
C) $1,800,000.
D) $2,000,000.
E) $2,200,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
If the reserve-deposit ratio is 25% and the banking system receives an additional $10 million in reserves,bank deposits will increase by
A) $10 million.
B) $250 million.
C) $400 million.
D) $4 million.
E) $40 million.
A) $10 million.
B) $250 million.
C) $400 million.
D) $4 million.
E) $40 million.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
When an individual deposits currency into a chequing account,
A) bank reserves increase,which increases the amount banks can lend,thereby increasing the money supply.
B) bank reserves decrease,which reduces the amount banks can lend,thereby reducing the money supply.
C) bank reserves are unchanged.
D) bank reserves decrease,which increases the amount banks can lend,thereby increasing the money supply.
E) bank reserves increase,which reduces the amount banks can lend,thereby reducing the money supply.
A) bank reserves increase,which increases the amount banks can lend,thereby increasing the money supply.
B) bank reserves decrease,which reduces the amount banks can lend,thereby reducing the money supply.
C) bank reserves are unchanged.
D) bank reserves decrease,which increases the amount banks can lend,thereby increasing the money supply.
E) bank reserves increase,which reduces the amount banks can lend,thereby reducing the money supply.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
If the reserve-deposit ratio is 5% and the banking system receives an additional $10 million in reserves,bank deposits will increase by
A) $4 million.
B) $10 million.
C) $40 million.
D) $200 million.
E) $400 million.
A) $4 million.
B) $10 million.
C) $40 million.
D) $200 million.
E) $400 million.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75

The table above represents a bank's T-account.Suppose it is the only bank in town and individuals in town hold no cash.Assuming the reserve ratio is 10%,what will be the bank's deposits and reserves at the end of the money creation process?
A) Deposits will equal $200,000 and reserves will equal $20,000.
B) Both deposits and reserves will equal $200,000.
C) Deposits will equal $2,000,000 and reserves will equal $200,000.
D) Both deposits and reserves will equal $2,000,000.
E) Both deposits and reserves will equal $2,200,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Suppose r is the desired reserve-deposit ratio (R/D)and the money supply (M)consists of currency (C)and bank deposits (D).Then,the money supply (M)will equal
A) C + R/r.
B) D + R/r.
C) R + C/r.
D) C - R/r.
E) C x R/r.
A) C + R/r.
B) D + R/r.
C) R + C/r.
D) C - R/r.
E) C x R/r.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
When a bank makes a loan by crediting the borrower's chequing account balance with an amount equal to the loan,
A) money is created.
B) the bank gains new reserves.
C) the bank immediately loses reserves.
D) money is destroyed.
E) the Bank of Canada has made an open-market purchasE.
A) money is created.
B) the bank gains new reserves.
C) the bank immediately loses reserves.
D) money is destroyed.
E) the Bank of Canada has made an open-market purchasE.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
If the reserve-deposit ratio falls,then
A) the ability of commercial banks to create money is greater.
B) the ability of commercial banks to create money is lower.
C) the money multiplier is smaller.
D) the level of required reserves is greater.
E) the ability of commercial banks to create money is unaffected.
A) the ability of commercial banks to create money is greater.
B) the ability of commercial banks to create money is lower.
C) the money multiplier is smaller.
D) the level of required reserves is greater.
E) the ability of commercial banks to create money is unaffected.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
If the reserve-deposit ratio is 20% and the banking system receives an additional $10 million in reserves,bank deposits will increase by
A) $4 million.
B) $10 million.
C) $50 million.
D) $250 million.
E) $400 million.
A) $4 million.
B) $10 million.
C) $50 million.
D) $250 million.
E) $400 million.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
An episode when depositors,spurred by news or rumours of the imminent bankruptcy of one or more banks,rush to withdraw their deposits from the banking system is called a(n)
A) open-market withdrawal.
B) open-market sale.
C) banking panic.
D) bank run.
E) reserve requirement crisis.
A) open-market withdrawal.
B) open-market sale.
C) banking panic.
D) bank run.
E) reserve requirement crisis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








