Deck 28: Quantum Physics
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/86
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 28: Quantum Physics
1
Protons are being accelerated in a particle accelerator. When the speed of the protons is doubled, their de Broglie wavelength will
A) increase by a factor of 4.
B) increase by a factor of 2.
C) decrease by a factor of 2.
D) increase by a factor of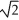 .
.
E) decrease by a factor of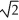 .
.
A) increase by a factor of 4.
B) increase by a factor of 2.
C) decrease by a factor of 2.
D) increase by a factor of
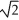 .
.E) decrease by a factor of
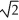 .
.C
2
Monochromatic light falls on a metal surface and electrons are ejected. If the intensity of the light is increased, what will happen to the ejection rate and maximum energy of the electrons?
A) greater rate; same maximum energy.
B) same rate; greater maximum energy.
C) greater rate; greater maximum energy.
D) same rate; same maximum energy.
A) greater rate; same maximum energy.
B) same rate; greater maximum energy.
C) greater rate; greater maximum energy.
D) same rate; same maximum energy.
A
3
When the surface of a metal is exposed to blue light, electrons are emitted. If the intensity of the blue light is increased, which of the following things will also increase?
A) the number of electrons ejected per second
B) the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electrons
C) the time lag between the onset of the absorption of light and the ejection of electrons
D) the work function of the metal
E) all of the above
A) the number of electrons ejected per second
B) the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electrons
C) the time lag between the onset of the absorption of light and the ejection of electrons
D) the work function of the metal
E) all of the above
A
4
If a proton and an electron have the same de Broglie wavelengths, which one is moving faster?
A) the electron
B) the proton
C) They both have the same speed.
A) the electron
B) the proton
C) They both have the same speed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
A blue laser beam is incident on a metallic surface, causing electrons to be ejected from the metal. If the frequency of the laser beam is increased while the intensity of the beam is held fixed,
A) the rate of ejected electrons will decrease and their maximum kinetic energy will increase.
B) the rate of ejected electrons will remain the same but their maximum kinetic energy will increase.
C) the rate of ejected electrons will increase and their maximum kinetic energy will increase.
D) the rate of ejected electrons will remain the same but their maximum kinetic energy will decrease.
A) the rate of ejected electrons will decrease and their maximum kinetic energy will increase.
B) the rate of ejected electrons will remain the same but their maximum kinetic energy will increase.
C) the rate of ejected electrons will increase and their maximum kinetic energy will increase.
D) the rate of ejected electrons will remain the same but their maximum kinetic energy will decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
If a proton and an electron have the same speed, which one has the longer de Broglie wavelength?
A) the electron
B) the proton
C) It is the same for both of them.
A) the electron
B) the proton
C) It is the same for both of them.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which of the following actions will increase the de Broglie wavelength of a speck of dust? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
A) Increase its mass.
B) Increase its speed.
C) Decrease its mass.
D) Decrease its speed.
E) Decrease its momentum.
A) Increase its mass.
B) Increase its speed.
C) Decrease its mass.
D) Decrease its speed.
E) Decrease its momentum.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Two sources emit beams of microwaves. The microwaves from source A have a frequency of 10 GHz, and the ones from source B have a frequency of 20 GHz. This is all we know about the two beams. Which of the following statements about these beams are correct? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
A) Beam B carries twice as many photons per second as beam A.
B) A photon in beam B has twice the energy of a photon in beam A.
C) The intensity of beam B is twice as great as the intensity of beam A.
D) A photon in beam B has the same energy as a photon in beam A.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) Beam B carries twice as many photons per second as beam A.
B) A photon in beam B has twice the energy of a photon in beam A.
C) The intensity of beam B is twice as great as the intensity of beam A.
D) A photon in beam B has the same energy as a photon in beam A.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Protons are being accelerated in a particle accelerator. When the energy of the protons is doubled, their de Broglie wavelength will
A) increase by a factor of 4.
B) increase by a factor of 2.
C) decrease by a factor of 2.
D) increase by a factor of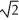 .
.
E) decrease by a factor of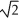 .
.
A) increase by a factor of 4.
B) increase by a factor of 2.
C) decrease by a factor of 2.
D) increase by a factor of
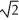 .
.E) decrease by a factor of
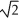 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Light of a given wavelength is used to illuminate the surface of a metal, however, no photoelectrons are emitted. In order to cause electrons to be ejected from the surface of this metal you should
A) use light of a longer wavelength.
B) use light of a shorter wavelength.
C) use light of the same wavelength but increase its intensity.
D) use light of the same wavelength but decrease its intensity.
A) use light of a longer wavelength.
B) use light of a shorter wavelength.
C) use light of the same wavelength but increase its intensity.
D) use light of the same wavelength but decrease its intensity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
If the wavelength of a photon in vacuum is the same as the de Broglie wavelength of an electron, which one is traveling faster through space?
A) The electron because it has more mass.
B) The photon because photons always travel through space faster than electrons.
C) They both have the same speed.
A) The electron because it has more mass.
B) The photon because photons always travel through space faster than electrons.
C) They both have the same speed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
If the maximum possible accuracy in measuring the position of a particle increases, the maximum possible accuracy in measuring its velocity will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not be affected.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not be affected.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Monochromatic light is incident on a metal surface, and the ejected electrons give rise to a current in the circuit shown in the figure. The maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electrons is determined by applying a reverse ('stopping') potential, sufficient to reduce the current in the ammeter to zero. If the intensity of the incident light is increased, how will the required stopping potential change? 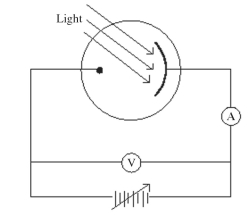
A) It will remain unchanged.
B) It will increase.
C) It will decrease.

A) It will remain unchanged.
B) It will increase.
C) It will decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A beam of light falling on a metal surface is causing electrons to be ejected from the surface. If we now double the frequency of the light, which of the following statements are correct? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
A) The kinetic energy of the ejected electrons doubles.
B) The speed of the ejected electrons doubles.
C) The number of electrons ejected per second doubles.
D) Twice as many photons hit the metal surface as before.
E) None of the above things occur.
A) The kinetic energy of the ejected electrons doubles.
B) The speed of the ejected electrons doubles.
C) The number of electrons ejected per second doubles.
D) Twice as many photons hit the metal surface as before.
E) None of the above things occur.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
A proton and an electron are both accelerated to the same final kinetic energy. If λp is the de Broglie wavelength of the proton and λe is the de Broglie wavelength of the electron, then
A) λp > λe.
B) λp = λe.
C) λp < λe.
A) λp > λe.
B) λp = λe.
C) λp < λe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Certain planes of a crystal of halite have a spacing of 0.399 nm. The crystal is irradiated by a beam of x-rays. First order constructive interference occurs when the beam makes an angle of 20° with the planes of the crystal surface. What is the wavelength of the x-rays?
A) 0.14 nm
B) 0.17 nm
C) 0.21 nm
D) 0.24 nm
E) 0.27 nm
A) 0.14 nm
B) 0.17 nm
C) 0.21 nm
D) 0.24 nm
E) 0.27 nm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
A researcher is using x-rays to investigating a cubic crystal. He is looking at Bragg reflection from the planes parallel to the cube faces. He finds that when using x-rays with a wavelength of 0.165 nm, a strong first maximum occurs when the beam makes an angle of 23.5° with the planes. What is the spacing of adjacent atoms in this crystal?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
If the maximum possible accuracy in measuring the velocity of a particle increases, the maximum possible accuracy in measuring its position will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not be affected.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not be affected.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
A proton and an electron are both accelerated to the same final speed. If λp is the de Broglie wavelength of the proton and λe is the de Broglie wavelength of the electron, then
A) λp > λe.
B) λp = λe.
C) λp < λe.
A) λp > λe.
B) λp = λe.
C) λp < λe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Two sources emit beams of light of wavelength 550 nm. The light from source A has an intensity of 10 µW/m2, and the light from source B has an intensity of 20 µW/m2. This is all we know about the two beams. Which of the following statements about these beams are correct? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
A) Beam B carries twice as many photons per second as beam A.
B) A photon in beam B has twice the energy of a photon in beam A.
C) The frequency of the light in beam B is twice as great as the frequency of the light in beam A.
D) A photon in beam B has the same energy as a photon in beam A.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) Beam B carries twice as many photons per second as beam A.
B) A photon in beam B has twice the energy of a photon in beam A.
C) The frequency of the light in beam B is twice as great as the frequency of the light in beam A.
D) A photon in beam B has the same energy as a photon in beam A.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The work function of a particular metal is 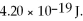 What is the photoelectric cutoff (threshold) wavelength for this metal? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
What is the photoelectric cutoff (threshold) wavelength for this metal? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 473 nm
B) 308 nm
C) 393 nm
D) 554 nm
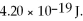 What is the photoelectric cutoff (threshold) wavelength for this metal? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
What is the photoelectric cutoff (threshold) wavelength for this metal? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)A) 473 nm
B) 308 nm
C) 393 nm
D) 554 nm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
An 84-kW AM radio station broadcasts at 1000 kHz. How many photons are emitted each second by the transmitting antenna? (h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 1.3 ×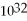
B) 2.9 ×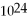
C) 6.3 ×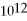
D) 1.4 ×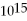
A) 1.3 ×
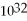
B) 2.9 ×
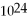
C) 6.3 ×
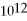
D) 1.4 ×
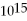

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
A crystal is irradiated with x-rays with a wavelength of 0.120 nm. The atomic planes in the crystal are separated by 0.21 nm. At what angles of incidence with respect to the normal will the x-rays reflect from the crystal?
A) 73°, 55°, 31°
B) only 55°
C) only 73° and 31°
D) only 73°
A) 73°, 55°, 31°
B) only 55°
C) only 73° and 31°
D) only 73°

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
What is the cutoff (threshold) frequency for a metal surface that has a work function of 5.42 eV? (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 1.31 ×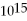 Hz
Hz
B) 2.01 ×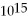 Hz
Hz
C) 3.01 ×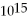 Hz
Hz
D) 5.02 ×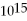 Hz
Hz
E) 6.04 ×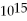 Hz
Hz
A) 1.31 ×
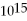 Hz
HzB) 2.01 ×
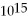 Hz
HzC) 3.01 ×
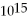 Hz
HzD) 5.02 ×
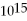 Hz
HzE) 6.04 ×
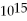 Hz
Hz
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
What is the wavelength of a 6.32-eV photon? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J)
A) 197 nm
B) 167 nm
C) 216 nm
D) 234 nm
A) 197 nm
B) 167 nm
C) 216 nm
D) 234 nm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The work function of a certain metal is 1.90 eV. What is the longest wavelength of light that can cause photoelectron emission from this metal? (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 231 nm
B) 14.0 nm
C) 62.4 nm
D) 344 nm
E) 654 nm
A) 231 nm
B) 14.0 nm
C) 62.4 nm
D) 344 nm
E) 654 nm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
A photoelectric surface has a work function of 2.10 eV. Calculate the maximum kinetic energy, in eV, of electrons ejected from this surface by electromagnetic radiation of wavelength 356 nm. (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A laser emits a pulse of light that lasts 10 ns. The light has a wavelength of 690 nm, and each pulse has an energy of 480 mJ. How many photons are emitted in each pulse? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 1.7 × 1018
B) 2.1 ×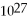
C) 2.6 ×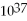
D) 3.1 ×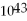
A) 1.7 × 1018
B) 2.1 ×
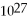
C) 2.6 ×
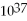
D) 3.1 ×
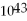

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
What is the longest wavelength of light that can cause photoelectron emission from a metal that has a work function of 2.20 eV? (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 417 nm
B) 257 nm
C) 344 nm
D) 565 nm
E) 610 nm
A) 417 nm
B) 257 nm
C) 344 nm
D) 565 nm
E) 610 nm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
If the longest wavelength of light that is able to dislodge electrons from a metal is 373 nm, what is the work function of that metal, in electron-volts? (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
A metal surface has a work function of 2.50 eV. What is the longest wavelength of light that will eject electrons from the surface of this metal? (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
For what wavelength does a 100-mW laser beam deliver 1.6 × 1017 photons in one second? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 320 nm
B) 330 nm
C) 340 nm
D) 350 nm
A) 320 nm
B) 330 nm
C) 340 nm
D) 350 nm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
A helium-neon laser emits light at 632.8 nm. If the laser emits 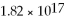 photons/second, what is its power output in mW? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
photons/second, what is its power output in mW? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 57.2 mW
B) 28.6 mW
C) 37.2 mW
D) 45.7 mW
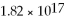 photons/second, what is its power output in mW? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
photons/second, what is its power output in mW? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)A) 57.2 mW
B) 28.6 mW
C) 37.2 mW
D) 45.7 mW

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A laser pulse of duration 25 ms has a total energy of 1.4 J. If the wavelength of this radiation is 567 nm, how many photons are emitted in one pulse? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 4.0 × 1018
B) 9.9 × 1019
C) 4.8 × 1019
D) 1.6 × 1017
E) 3.2 × 1017
A) 4.0 × 1018
B) 9.9 × 1019
C) 4.8 × 1019
D) 1.6 × 1017
E) 3.2 × 1017

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Certain planes of a crystal of halite have a spacing of 0.399 nm. The crystal is irradiated by a beam of x-rays. First order constructive interference occurs when the beam makes an angle of 20° with the planes of the crystal surface. What angle does the beam make with the crystal planes for second order constructive?
A) 37°
B) 40°
C) 43°
D) 46°
E) 49°
A) 37°
B) 40°
C) 43°
D) 46°
E) 49°

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The lattice spacing of the principal Bragg planes in sodium chloride is 0.282 nm. For what wavelength of x-rays will the first order reflected beam diffract at 55° with respect to the normal to the crystal planes?
A) 0.323 nm
B) 0.530 nm
C) 0.662 nm
D) 0.150 nm
E) 0.462 nm
A) 0.323 nm
B) 0.530 nm
C) 0.662 nm
D) 0.150 nm
E) 0.462 nm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Gamma rays are photons with very high energy. What is the wavelength of a gamma-ray photon with energy 7.7 × 10-13 J? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 2.6 × 10-13 m
B) 3.9 × 10-13 m
C) 3.1 × 10-13 m
D) 3.5 × 10-13 m
A) 2.6 × 10-13 m
B) 3.9 × 10-13 m
C) 3.1 × 10-13 m
D) 3.5 × 10-13 m

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A metal has a work function of 4.50 eV. Find the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons if light of wavelength 250 nm shines on the metal. (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 0.00 eV
B) 0.37 eV
C) 0.47 eV
D) 0.53 eV
A) 0.00 eV
B) 0.37 eV
C) 0.47 eV
D) 0.53 eV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
A metallic surface is illuminated with light of wavelength 400 nm. If the work function for this metal is 2.40 eV, what is the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electrons, in electron-volts? (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Gamma rays are photons with very high energy. How many visible-light photons with a wavelength of 500 nm would you need to equal the energy of a gamma-ray photon with energy 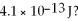
A) 1.0 × 106
B) 1.4 × 108
C) 6.2 × 109
D) 3.9 × 103
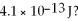
A) 1.0 × 106
B) 1.4 × 108
C) 6.2 × 109
D) 3.9 × 103

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
What is the longest wavelength of electromagnetic radiation that will eject photoelectrons from sodium metal for which the work function is 2.28 eV? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J)
A) 580 nm
B) 499 nm
C) 633 nm
D) 668 nm
E) 545 nm
A) 580 nm
B) 499 nm
C) 633 nm
D) 668 nm
E) 545 nm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
In her physics laboratory, Mathilda shines electromagnetic radiation on a material and collects photoelectric data to determine Planck's constant. She measures a stopping potential of 5.82 V for radiation of wavelength 100 nm, and 17.99 V for radiation of wavelength 50.0 nm. (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s)
(a) Using Mathilda's data, what value does she determine for Planck's constant?
(b) What is the work function of the material Mathilda is using, in electron-volts?
(a) Using Mathilda's data, what value does she determine for Planck's constant?
(b) What is the work function of the material Mathilda is using, in electron-volts?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
A photocathode that has a work function of 2.4 eV is illuminated with monochromatic light having photon energy 3.5 eV. What is the wavelength of this light? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J)
A) 350 nm
B) 330 nm
C) 300 nm
D) 380 nm
E) 410 nm
A) 350 nm
B) 330 nm
C) 300 nm
D) 380 nm
E) 410 nm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
When it is struck by 240-nm photons, a metal ejects electrons with a maximum kinetic energy of 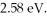 What is the work function of this material? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 16.0 × 10-19 J)
What is the work function of this material? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 16.0 × 10-19 J)
A) 2.60 eV
B) 2.18 eV
C) 3.02 eV
D) 3.43 eV
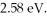 What is the work function of this material? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 16.0 × 10-19 J)
What is the work function of this material? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 16.0 × 10-19 J)A) 2.60 eV
B) 2.18 eV
C) 3.02 eV
D) 3.43 eV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
When light of wavelength 350 nm is incident on a metal surface, the stopping potential of the photoelectrons is 0.500 V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of these electrons? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J)
A) 0.500 eV
B) 3.04 eV
C) 3.54 eV
D) 4.12 eV
A) 0.500 eV
B) 3.04 eV
C) 3.54 eV
D) 4.12 eV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
When light of wavelength 350 nm is incident on a metal surface, the stopping potential of the photoelectrons is measured to be 0.500 V. What is the work function of this metal? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J)
A) 0.500 eV
B) 3.05 eV
C) 3.54 eV
D) 4.12 eV
A) 0.500 eV
B) 3.05 eV
C) 3.54 eV
D) 4.12 eV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
When a photoelectric surface is illuminated with light of wavelength 437 nm, the stopping potential is measured to be 1.67 V. (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, e = 1.60 × 10-19 C, melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
(a) What is the work function of the metal, in eV?
(b) What is the maximum speed of the ejected electrons?
(a) What is the work function of the metal, in eV?
(b) What is the maximum speed of the ejected electrons?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
A photocathode whose work function is 2.9 eV is illuminated with white light that has a continuous wavelength band from 400 nm to 700 nm. What is the range of the wavelength band in this white light illumination for which photoelectrons are not produced?(c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J)
A) 430 nm to 700 nm
B) 400 nm to 480 nm
C) 430 nm to 480 nm
D) 400 nm to 430 nm
E) 480 nm to 700 nm
A) 430 nm to 700 nm
B) 400 nm to 480 nm
C) 430 nm to 480 nm
D) 400 nm to 430 nm
E) 480 nm to 700 nm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
A photocathode having a work function of 2.8 eV is illuminated with monochromatic electromagnetic radiation whose photon energy is 4.0 eV. What is the threshold (cutoff) frequency for photoelectron production? (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 6.8 × 1014 Hz
B) 2.9 × 1014 Hz
C) 7.7 × 1014 Hz
D) 8.6 × 1014 Hz
E) 9.7 × 1014 Hz
A) 6.8 × 1014 Hz
B) 2.9 × 1014 Hz
C) 7.7 × 1014 Hz
D) 8.6 × 1014 Hz
E) 9.7 × 1014 Hz

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
When light of wavelength 350 nm is incident on a metal surface, the stopping potential of the photoelectrons is 0.500 V. What is the threshold (cutoff) frequency of this metal? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J)
A) 3.47 × 1014 Hz
B) 3.74 × 1014 Hz
C) 4.73 × 1014 Hz
D) 7.36 × 1014 Hz
A) 3.47 × 1014 Hz
B) 3.74 × 1014 Hz
C) 4.73 × 1014 Hz
D) 7.36 × 1014 Hz

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
When a metal is illuminated by light, photoelectrons are observed provided that the wavelength of the light is less than 520 nm. What is the metal's work function? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J)
A) 2.4 eV
B) 2.6 eV
C) 2.8 eV
D) 3.0 eV
A) 2.4 eV
B) 2.6 eV
C) 2.8 eV
D) 3.0 eV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
For a certain metal, light of frequency 7.24 × 10-14 Hz is just barely able to dislodge photoelectrons from the metal. (h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, e = 1.60 × 10-19C)
(a) What will be the stopping potential if light of frequency 8.75 × 10-14 Hz is shone on the metal?
(b) What is the work function (in electron-volts) of this metal?
(a) What will be the stopping potential if light of frequency 8.75 × 10-14 Hz is shone on the metal?
(b) What is the work function (in electron-volts) of this metal?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
A monochromatic light beam is incident on the surface of a metal having a work function of 2.50 eV. If a 1.0-V stopping potential is required to make the electron current zero, what is the wavelength of light? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J)
A) 355 nm
B) 423 nm
C) 497 nm
D) 744 nm
A) 355 nm
B) 423 nm
C) 497 nm
D) 744 nm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Light with a frequency of 8.70 × 1014 Hz is incident on a metal that has a work function of 2.80 eV. What is the maximum kinetic energy that a photoelectron ejected in this process can have? (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 8.7 × 10-19 J
B) 3.1 × 10-19 J
C) 1.3 × 10-19 J
D) 2.4 × 10-19 J
E) 4.5 × 10-19 J
A) 8.7 × 10-19 J
B) 3.1 × 10-19 J
C) 1.3 × 10-19 J
D) 2.4 × 10-19 J
E) 4.5 × 10-19 J

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
A beam of light with a frequency range from 3.01 × 1014 Hz to 6.10 × 1014 Hz is incident on a metal surface. If the work function of the metal surface is 2.20 eV, what is the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons ejected from this surface? (h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J)
A) 0.33 eV
B) 0.21 eV
C) 0.42 eV
D) 0.16 eV
E) 0.48 eV
A) 0.33 eV
B) 0.21 eV
C) 0.42 eV
D) 0.16 eV
E) 0.48 eV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
When it is struck by 240-nm photons, a material having a work function of 2.60 eV emits electrons. What is the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J)
A) 2.58 eV
B) 5.18 eV
C) 2.00 eV
D) 4.21 eV
A) 2.58 eV
B) 5.18 eV
C) 2.00 eV
D) 4.21 eV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
A photocathode having a work function of 2.4 eV is illuminated with monochromatic light whose photon energy is 3.4 eV. What is maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons produced?(c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J)
A) 1.6 × 10-19 J
B) 3.8 × 10-19 J
C) 4.4 × 10-19 J
D) 4.9 × 10-19 J
E) 5.4 × 10-19 J
A) 1.6 × 10-19 J
B) 3.8 × 10-19 J
C) 4.4 × 10-19 J
D) 4.9 × 10-19 J
E) 5.4 × 10-19 J

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
If the work function of a metal surface is 2.20 eV, what frequency of incident light would give a maximum kinetic energy of 0.25 eV to the photoelectrons ejected from this surface? (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 2.05 × 1014 Hz
B) 1.02 × 1014 Hz
C) 2.50 × 1014 Hz
D) 3.53 × 1014 Hz
E) 5.92 × 1014 Hz
A) 2.05 × 1014 Hz
B) 1.02 × 1014 Hz
C) 2.50 × 1014 Hz
D) 3.53 × 1014 Hz
E) 5.92 × 1014 Hz

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Calculate the kinetic energy, in electron-volts, of a neutron that has a de Broglie wavelength of 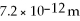 (mneutron = 1.675 × 10-27 kg, 1 eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
(mneutron = 1.675 × 10-27 kg, 1 eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
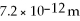 (mneutron = 1.675 × 10-27 kg, 1 eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
(mneutron = 1.675 × 10-27 kg, 1 eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Light with a wavelength of 310 nm is incident on a metal that has a work function of 3.80 eV. What is the maximum kinetic energy that a photoelectron ejected in this process can have? (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 0.62 × 10-19 J
B) 0.21 × 10-19 J
C) 0.36 × 10-19 J
D) 0.48 × 10-19 J
E) 0.33 × 10-19 J
A) 0.62 × 10-19 J
B) 0.21 × 10-19 J
C) 0.36 × 10-19 J
D) 0.48 × 10-19 J
E) 0.33 × 10-19 J

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
If the momentum of an electron is 1.95 × 10-27 kg ∙ m/s, what is its de Broglie wavelength? (h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 340 nm
B) 210 nm
C) 170 nm
D) 420 nm
E) 520 nm
A) 340 nm
B) 210 nm
C) 170 nm
D) 420 nm
E) 520 nm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Atoms in crystals are typically separated by distances of 0.10 nm. What kinetic energy must a nonrelativistic electron have, in electron-volts, in order to have a wavelength of 0.10 nm? (melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
An electron has the same de Broglie wavelength as the wavelength of a 1.8 eV photon. What is the speed of the electron? (melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J)
A) 1100 m/s
B) 980 m/s
C) 910 m/s
D) 840 m/s
E) 770 m/s
A) 1100 m/s
B) 980 m/s
C) 910 m/s
D) 840 m/s
E) 770 m/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The electrons in a beam are moving at 18 m/s. (melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
(a) What is its de Broglie wavelength these electrons?
(b) If the electron beam falls normally on a diffraction grating, what would have to be the spacing between slits in the grating to give a first-order maximum at an angle of 30° with the normal to the grating?
(a) What is its de Broglie wavelength these electrons?
(b) If the electron beam falls normally on a diffraction grating, what would have to be the spacing between slits in the grating to give a first-order maximum at an angle of 30° with the normal to the grating?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
If the de Broglie wavelength of an electron is 380 nm, what is the speed of this electron? (melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 2.0 km/s
B) 3.8 km/s
C) 1.9 km/s
D) 4.1 km/s
E) 5.2 km/s
A) 2.0 km/s
B) 3.8 km/s
C) 1.9 km/s
D) 4.1 km/s
E) 5.2 km/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
What is the de Broglie wavelength of a ball of mass 200 g moving at 30 m/s? (h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 1.1 × 10-34 m
B) 2.2 × 10-34 m
C) 4.5 × 10-28 m
D) 6.7 × 10-27 m
A) 1.1 × 10-34 m
B) 2.2 × 10-34 m
C) 4.5 × 10-28 m
D) 6.7 × 10-27 m

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
How "slow" must a 200-g ball move to have a de Broglie wavelength of 1.0 mm? (h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
If an electron has the same de Broglie wavelength as the wavelength of a 390-nm photon in vacuum, what is the speed of the electron? (melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, c = 3.0 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 1900 m/s
B) 2100 m/s
C) 1700m/s
D) 1500 m/s
E) 540 m/s
A) 1900 m/s
B) 2100 m/s
C) 1700m/s
D) 1500 m/s
E) 540 m/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Find the de Broglie wavelength of a 1.30-kg missile moving at 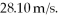 (h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
(h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 1.81 × 10-35 m
B) 2.05 × 10-35 m
C) 2.28 × 10-35 m
D) 2.57 × 10-35 m
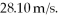 (h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
(h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)A) 1.81 × 10-35 m
B) 2.05 × 10-35 m
C) 2.28 × 10-35 m
D) 2.57 × 10-35 m

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
What is the wavelength of the matter wave associated with an electron moving with a speed of 2.5 × 107 m/s? (melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 29 pm
B) 35 pm
C) 47 pm
D) 53 pm
A) 29 pm
B) 35 pm
C) 47 pm
D) 53 pm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
A proton has a speed of 7.2 x 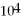 m/s. What is the energy of a photon that has the same wavelength as the de Broglie wavelength of this proton? (melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
m/s. What is the energy of a photon that has the same wavelength as the de Broglie wavelength of this proton? (melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 230 keV
B) 150 keV
C) 300 keV
D) 370 keV
E) 440 keV
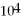 m/s. What is the energy of a photon that has the same wavelength as the de Broglie wavelength of this proton? (melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
m/s. What is the energy of a photon that has the same wavelength as the de Broglie wavelength of this proton? (melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)A) 230 keV
B) 150 keV
C) 300 keV
D) 370 keV
E) 440 keV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
What would be the de Broglie wavelength for 1-g object moving at the earth's escape speed 25,000 mph (about 11 km/s)? (h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
After an electron has been accelerated through a potential difference of 0.15 kV, what is its de Broglie wavelength? (e = 1.60 × 10-19 C, melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 0.10 nm
B) 1.0 nm
C) 1.0 mm
D) 1.0 cm
A) 0.10 nm
B) 1.0 nm
C) 1.0 mm
D) 1.0 cm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
An electron is moving with the speed of 1780 m/s. What is its de Broglie wavelength? (melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 409 nm
B) 302 nm
C) 205 nm
D) 420 nm
E) 502 nm
A) 409 nm
B) 302 nm
C) 205 nm
D) 420 nm
E) 502 nm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
What is the wavelength of the matter wave associated with a 0.50-kg ball moving at 25 m/s? (h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 3.5 × 10-35 m
B) 5.3 × 10-35 m
C) 3.5 × 10-33 m
D) 5.3 × 10-33 m
A) 3.5 × 10-35 m
B) 5.3 × 10-35 m
C) 3.5 × 10-33 m
D) 5.3 × 10-33 m

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
A crystal diffracts a beam of electrons, like a diffraction grating, as they hit it perpendicular to its surface. The crystal spacing is 0.18 nm, and the first maximum scattering occurs at 80° relative to the normal to the surface. (e = 1.60 × 10-19 C, melectron = 9.11 × 10-13 kg, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
(a) What is the wavelength of the electrons?
(b) What potential difference accelerated the electrons if they started from rest?
(a) What is the wavelength of the electrons?
(b) What potential difference accelerated the electrons if they started from rest?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
If an electron has a wavelength of 0.123 nm, what is its kinetic energy, in electron-volts? This energy is not in the relativistic region. (melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 19.8 eV
B) 60.2 eV
C) 80.4 eV
D) 99.5 eV
E) 124 eV
A) 19.8 eV
B) 60.2 eV
C) 80.4 eV
D) 99.5 eV
E) 124 eV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
A proton that is moving freely has a wavelength of 0.600 pm. (mproton = 1.67 × 10-27 kg, e = 1.60 × 10-19 C, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
(a) What is its momentum?
(b) What is its speed?
(c) What potential difference would it have been accelerated through, starting from rest, to reach this speed?
(a) What is its momentum?
(b) What is its speed?
(c) What potential difference would it have been accelerated through, starting from rest, to reach this speed?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
If the de Broglie wavelength of an electron is 2.4 μm, what is the speed of the electron? 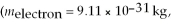
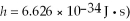
A) 3.0 × 102 m/s
B) 2.5 × 105 m/s
C) 1.7 × 103 m/s
D) 8.3 × 106 m/s
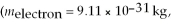
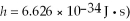
A) 3.0 × 102 m/s
B) 2.5 × 105 m/s
C) 1.7 × 103 m/s
D) 8.3 × 106 m/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
A person of mass 50 kg has a de Broglie wavelength of 4.4 × 10-36 m while jogging. How fast is she running? (h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ∙ s)
A) 2.0 m/s
B) 3.0 m/s
C) 4.0 m/s
D) 5.0 m/s
A) 2.0 m/s
B) 3.0 m/s
C) 4.0 m/s
D) 5.0 m/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 86 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








