Deck 9: Reporting Foreign Operations
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/44
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 9: Reporting Foreign Operations
1
A Canadian company has three subsidiaries that operate autonomously in Asia. What is the most appropriate alternative for handling translation gains and losses?
A)Immediate recognition
B)Limited recognition
C)Deferred recognition
D)Immediate recognition for losses and deferred recognition for gains
A)Immediate recognition
B)Limited recognition
C)Deferred recognition
D)Immediate recognition for losses and deferred recognition for gains
C
2
Which of the following is an indication that a parent company and a foreign subsidiary are integrated?
A)Control of the subsidiary by the parent
B)Financing of subsidiary operations provided by the parent
C)A high volume of intercompany transactions
D)Sales prices of the subsidiary's goods are set by local market conditions
A)Control of the subsidiary by the parent
B)Financing of subsidiary operations provided by the parent
C)A high volume of intercompany transactions
D)Sales prices of the subsidiary's goods are set by local market conditions
C
3
IQ has a wholly owned subsidiary in China. This subsidiary is dependent on IQ for financing and sales. How should foreign exchange gains on translation of the subsidiary's statements to Canadian dollars be reported on IQ's consolidated financial statements?
A)Gains should be credited directly to shareholders' equity.
B)Gains should be reported on the balance sheet as deferred credits and amortized in a systematic and rational manner.
C)Gains from current monetary assets should be credited to income, and any gains from long-term nonmonetary assets should be deferred and amortized.
D)Gains from current monetary assets and any gains from long-term monetary assets should be credited to income.
A)Gains should be credited directly to shareholders' equity.
B)Gains should be reported on the balance sheet as deferred credits and amortized in a systematic and rational manner.
C)Gains from current monetary assets should be credited to income, and any gains from long-term nonmonetary assets should be deferred and amortized.
D)Gains from current monetary assets and any gains from long-term monetary assets should be credited to income.
D
4
What gives rise to accounting exposure to changes in the foreign exchange rate?
A)Holding common shares in a foreign entity
B)Holding preferred shares in a foreign entity
C)The accounting method used to translate the foreign entity's financial statements
D)The impact of exchange rate fluctuations on the present value of future cash flows
A)Holding common shares in a foreign entity
B)Holding preferred shares in a foreign entity
C)The accounting method used to translate the foreign entity's financial statements
D)The impact of exchange rate fluctuations on the present value of future cash flows

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
What is the impact of currency realignment on the earnings ability of a foreign operation known as?
A)Economic exposure
B)Accounting exposure
C)Exchange rate exposure
D)International exposure
A)Economic exposure
B)Accounting exposure
C)Exchange rate exposure
D)International exposure

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Which of the following factors is a primary indicator used to choose a functional currency?
A)Autonomy of the subsidiary
B)Proportion of intercompany transactions
C)Sources of competitive forces and regulations
D)Ability of subsidiary to generate cash flows to service its debts
A)Autonomy of the subsidiary
B)Proportion of intercompany transactions
C)Sources of competitive forces and regulations
D)Ability of subsidiary to generate cash flows to service its debts

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements about the temporal method is true?
A)The accounting exposure is always a net asset balance.
B)The accounting exposure is always a net liability balance.
C)The proportionate amounts of various assets and liabilities change after the statement of financial position is translated.
D)The temporal method and the current rate method both yield the same exchange gain or loss.
A)The accounting exposure is always a net asset balance.
B)The accounting exposure is always a net liability balance.
C)The proportionate amounts of various assets and liabilities change after the statement of financial position is translated.
D)The temporal method and the current rate method both yield the same exchange gain or loss.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
All of the following statements are stated in Brazil reals (R$). Bralta Ltd.
Statement of Financial Position
Iune Additional information:
Selected exchange rates:
Dividends were declared on June 30, 20X5
Opening inventory = R$130,000
Inventory purchases for the year = R$1,570,000
Machinery, land, and buildings were purchased on June 30, 20X4
Bralta is the Brazilian subsidiary of Altapro Co., a Canadian company.
-Under the current-rate method, what is the translation gain or loss?
A)$(85,610)
B)$(35,375)
C)$35,375
D)$85,619
Statement of Financial Position
Iune Additional information:
Selected exchange rates:
Dividends were declared on June 30, 20X5
Opening inventory = R$130,000
Inventory purchases for the year = R$1,570,000
Machinery, land, and buildings were purchased on June 30, 20X4
Bralta is the Brazilian subsidiary of Altapro Co., a Canadian company.
-Under the current-rate method, what is the translation gain or loss?
A)$(85,610)
B)$(35,375)
C)$35,375
D)$85,619

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Which of the following accounts would be translated to the reporting currency at the current rate of exchange for an integrated subsidiary?
A)Sales occurring evenly throughout the year
B)Deposits received from customers for services to be rendered
C)Capital assets
D)Inventory carried at market under the lower-of-cost-or-market principle
A)Sales occurring evenly throughout the year
B)Deposits received from customers for services to be rendered
C)Capital assets
D)Inventory carried at market under the lower-of-cost-or-market principle

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
All of the following statements are stated in Brazil reals (R$). Bralta Ltd.
Statement of Financial Position
Iune Additional information:
Selected exchange rates:
Dividends were declared on June 30, 20X5
Opening inventory = R$130,000
Inventory purchases for the year = R$1,570,000
Machinery, land, and buildings were purchased on June 30, 20X4
Bralta is the Brazilian subsidiary of Altapro Co., a Canadian company.
-
Machinery, land, and buildings were purchased on June 30, 20X4
Bralta is the Brazilian subsidiary of Altapro Co., a Canadian company. Under the temporal method, what is the total of the non-monetary assets?
A)$1,565,090
B)$1,735,730
C)$2,151,832
D)$2,185,770
Statement of Financial Position
Iune Additional information:
Selected exchange rates:
Dividends were declared on June 30, 20X5
Opening inventory = R$130,000
Inventory purchases for the year = R$1,570,000
Machinery, land, and buildings were purchased on June 30, 20X4
Bralta is the Brazilian subsidiary of Altapro Co., a Canadian company.
-
Machinery, land, and buildings were purchased on June 30, 20X4
Bralta is the Brazilian subsidiary of Altapro Co., a Canadian company. Under the temporal method, what is the total of the non-monetary assets?
A)$1,565,090
B)$1,735,730
C)$2,151,832
D)$2,185,770

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
ISP has a wholly owned subsidiary in China. This subsidiary is self-sufficient and does not rely on ISP for financing and sales. How should foreign exchange gains on translation of the subsidiary's statements to Canadian dollars be reported on ISP's consolidated financial statements?
A)Gains should be reported under shareholders' equity.
B)Gains should be reported on the statement of financial position as deferred credits and amortized in a systematic and rational manner.
C)Gains from current net assets should be credited to income, and any gains from long-term nonmonetary assets should be deferred and amortized.
D)Gains from current monetary assets should be credited to income and any gains from long-term monetary assets should be deferred and amortized.
A)Gains should be reported under shareholders' equity.
B)Gains should be reported on the statement of financial position as deferred credits and amortized in a systematic and rational manner.
C)Gains from current net assets should be credited to income, and any gains from long-term nonmonetary assets should be deferred and amortized.
D)Gains from current monetary assets should be credited to income and any gains from long-term monetary assets should be deferred and amortized.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
All of the following statements are stated in Brazil reals (R$). Bralta Ltd.
Statement of Financial Position
Iune Additional information:
Selected exchange rates:
Dividends were declared on June 30, 20X5
Opening inventory = R$130,000
Inventory purchases for the year = R$1,570,000
Machinery, land, and buildings were purchased on June 30, 20X4
Bralta is the Brazilian subsidiary of Altapro Co., a Canadian company.
-
Machinery, land, and buildings were purchased on June 30, 20X4
Bralta is the Brazilian subsidiary of Altapro Co., a Canadian company. Under the current-rate method, what is the balance of the total assets?
A)$2,108,625
B)$2,154,000
C)$2,161,688
D)$2,183,620
Statement of Financial Position
Iune Additional information:
Selected exchange rates:
Dividends were declared on June 30, 20X5
Opening inventory = R$130,000
Inventory purchases for the year = R$1,570,000
Machinery, land, and buildings were purchased on June 30, 20X4
Bralta is the Brazilian subsidiary of Altapro Co., a Canadian company.
-
Machinery, land, and buildings were purchased on June 30, 20X4
Bralta is the Brazilian subsidiary of Altapro Co., a Canadian company. Under the current-rate method, what is the balance of the total assets?
A)$2,108,625
B)$2,154,000
C)$2,161,688
D)$2,183,620

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Under the temporal method, which of the following items would be translated using the historical rate?
A)Inventory
B)Accounts receivable
C)Accounts payable
D)Long-term debentures
A)Inventory
B)Accounts receivable
C)Accounts payable
D)Long-term debentures

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements about non-monetary assets is true?
A)Under the temporal method, non-monetary assets are translated at the closing rate.
B)Under the temporal method, non-monetary assets are translated at the average rate.
C)Under the current-rate method, non-monetary assets are translated at the historical rate.
D)Under the current-rate method, non-monetary assets are translated at the closing rate.
A)Under the temporal method, non-monetary assets are translated at the closing rate.
B)Under the temporal method, non-monetary assets are translated at the average rate.
C)Under the current-rate method, non-monetary assets are translated at the historical rate.
D)Under the current-rate method, non-monetary assets are translated at the closing rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Which of the following factors is a secondary indicator used to choose a functional currency?
A)Currency in which the cost of goods sold is denominated
B)Currency in which the selling prices are denominated
C)Sources of competition and regulations
D)Ability of subsidiary to generate cash flows to service its debts
A)Currency in which the cost of goods sold is denominated
B)Currency in which the selling prices are denominated
C)Sources of competition and regulations
D)Ability of subsidiary to generate cash flows to service its debts

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
What is the risk of an apparent gain or loss arising from the restatement of financial statements prepared in one currency to another currency called?
A)Transaction exposure
B)Accounting exposure
C)Economic exposure
D)Restatement exposure
A)Transaction exposure
B)Accounting exposure
C)Economic exposure
D)Restatement exposure

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Under the temporal method, which of the following items would be translated using the year-end spot rate?
A)Inventory
B)Land
C)Long-term debentures
D)Building
A)Inventory
B)Land
C)Long-term debentures
D)Building

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Under the current-rate method, which of the following items would be translated using the historical rate?
A)Land
B)Inventory
C)Long-term debentures
D)Share capital
A)Land
B)Inventory
C)Long-term debentures
D)Share capital

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Cho Co., a public Canadian corporation, has a subsidiary in South Africa. It has been determined that the functional currency of the foreign operations is the South African rand. Which of the following statements is true?
A)Cho Co.'s financial statements will have to be translated into South African rand.
B)The presentation currency is the Canadian dollar.
C)Cho's transactions with the subsidiary will need to be re-measured.
D)Cho will not be required to consolidate.
A)Cho Co.'s financial statements will have to be translated into South African rand.
B)The presentation currency is the Canadian dollar.
C)Cho's transactions with the subsidiary will need to be re-measured.
D)Cho will not be required to consolidate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
When it is not clear what the functional currency is, an accountant must use professional judgment to choose the functional currency. What is the main criterion upon which the choice should be based?
A)Whether it faithfully represents the accounting effects of the transactions and events
B)Whether it faithfully represents the economic effects of the transactions and events
C)Whether it faithfully represents the translation effects of the transactions and events
D)Degree to which it minimizes accounting exposure
A)Whether it faithfully represents the accounting effects of the transactions and events
B)Whether it faithfully represents the economic effects of the transactions and events
C)Whether it faithfully represents the translation effects of the transactions and events
D)Degree to which it minimizes accounting exposure

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Water Bottling Inc. (WBI)is a 100% wholly owned subsidiary with operations in France. WBI was purchased by a Canadian parent on January 1, 20X5, and the FVA was €375,000, all allocated to goodwill. The financial records of WBI are maintained in euros and provide the following information with respect to equipment and goodwill.
Equipment: Purchased on January 1, 20X5, for €250,000, and depreciated over five years on a straight-line basis.
Equipment: Purchased on January 1, 20X6, for €175,000, and depreciated over five years on a straight-line basis.
Goodwill had a balance of €375,000.
Foreign exchange rates were as follows:
- Required:
Assume that WBC's functional currency is the euro. Calculate the translated Canadian dollar balances for the following accounts for December 31, 20X7.
a. Equipment
b. Accumulated depreciation-equipment
c. Depreciation expense
d. Goodwill
Equipment: Purchased on January 1, 20X5, for €250,000, and depreciated over five years on a straight-line basis.
Equipment: Purchased on January 1, 20X6, for €175,000, and depreciated over five years on a straight-line basis.
Goodwill had a balance of €375,000.
Foreign exchange rates were as follows:
- Required:
Assume that WBC's functional currency is the euro. Calculate the translated Canadian dollar balances for the following accounts for December 31, 20X7.
a. Equipment
b. Accumulated depreciation-equipment
c. Depreciation expense
d. Goodwill

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
All of the following statements are stated in Brazil reals (R$). 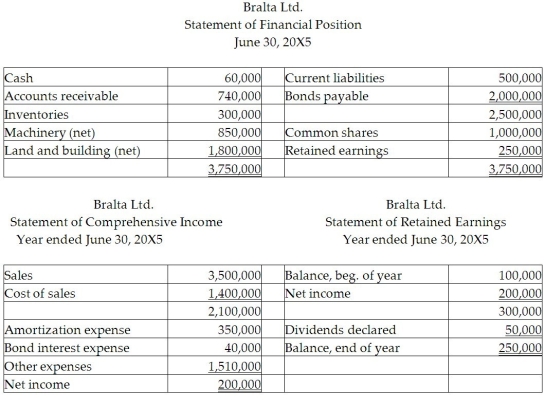 Additional information:
Additional information:
Selected exchange rates:
Date of purchase of inventory on hand at year-end Dividends were declared on June 30, 20X5 Opening inventory = R$130,000
Inventory purchases for the year = R$1,570,000
Machinery, land, and buildings were purchased on June 30, 20X4
-
Bralta is the Brazilian subsidiary of Altapro Co., a Canadian company. Bralta had net assets at June 30, 20X4, of R$1,100,000. What is the cost of sales under the temporal method?
A)$801,406
B)$804,160
C)$807,946
D)$809,896
 Additional information:
Additional information:Selected exchange rates:
Date of purchase of inventory on hand at year-end Dividends were declared on June 30, 20X5 Opening inventory = R$130,000
Inventory purchases for the year = R$1,570,000
Machinery, land, and buildings were purchased on June 30, 20X4
-
Bralta is the Brazilian subsidiary of Altapro Co., a Canadian company. Bralta had net assets at June 30, 20X4, of R$1,100,000. What is the cost of sales under the temporal method?
A)$801,406
B)$804,160
C)$807,946
D)$809,896

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Under the temporal method, at what exchange rate is depreciation expense translated?
A)At the average rate for the year
B)At the historical rate when the related assets were acquired
C)At the closing rate
D)At the rate at the beginning of the fiscal period
A)At the average rate for the year
B)At the historical rate when the related assets were acquired
C)At the closing rate
D)At the rate at the beginning of the fiscal period

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
What does a funds-flow statement measure?
A)Exchange gains/losses arising from the income statement
B)Exchange gains/losses arising from monetary assets and liabilities
C)Exchange gains/losses arising from non-monetary assets and liabilities
D)Exchange gains/losses arising from financing instruments
A)Exchange gains/losses arising from the income statement
B)Exchange gains/losses arising from monetary assets and liabilities
C)Exchange gains/losses arising from non-monetary assets and liabilities
D)Exchange gains/losses arising from financing instruments

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Liverpool Company operates retail stores in Canada and an exporting business in London that specializes in buying and selling British tweeds. The London subsidiary, which was acquired on January 1, 1986, provided the following financial statements in pounds sterling to the Canadian parent company.
Statement of Changes in Equity-Partial-Retained Earnings section
Less: Dividends declared and paid,
Liverpool Company was incorporated on January 1, 1984, at which time an amount of property, plant, and equipment with a present (December 31, 20X5)net book value of £3,000,000 was purchased. Additional equipment was purchased December 31, 20X4 (20% of depreciation expense relates to this new equipment). The long-term notes were issued, to replace financing provided by the parent, on January 1, 20X4.
Direct exchange rates for the pound sterling are:
- The January 1, 20X5, retained earnings balance of the London Branch of the Liverpool Company correctly translated to Canadian dollars was $1,783,774. The beginning inventory of £380,000 was acquired during the last quarter of 20X4 and the ending inventory was acquired during the last quarter of 20X5. Sales and purchases were made, and other expenses were incurred, evenly throughout the year.
Required:
Translate the December 31, 20X5, statement of financial position of Liverpool Company into dollars assuming the London branch has a functional currency of C$s and a presentation currency of C$s.
Explain how it might be determined that the London branch had a function currency of Canadian $s.
Statement of Changes in Equity-Partial-Retained Earnings section
Less: Dividends declared and paid,
Liverpool Company was incorporated on January 1, 1984, at which time an amount of property, plant, and equipment with a present (December 31, 20X5)net book value of £3,000,000 was purchased. Additional equipment was purchased December 31, 20X4 (20% of depreciation expense relates to this new equipment). The long-term notes were issued, to replace financing provided by the parent, on January 1, 20X4.
Direct exchange rates for the pound sterling are:
- The January 1, 20X5, retained earnings balance of the London Branch of the Liverpool Company correctly translated to Canadian dollars was $1,783,774. The beginning inventory of £380,000 was acquired during the last quarter of 20X4 and the ending inventory was acquired during the last quarter of 20X5. Sales and purchases were made, and other expenses were incurred, evenly throughout the year.
Required:
Translate the December 31, 20X5, statement of financial position of Liverpool Company into dollars assuming the London branch has a functional currency of C$s and a presentation currency of C$s.
Explain how it might be determined that the London branch had a function currency of Canadian $s.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Under the current-rate method, what is the accounting treatment for exchange gains and losses arising from the current year?
A)Reported as equity
B)Reported in other comprehensive income
C)Reported in consolidated net income
D)Included in opening consolidated retained earnings
A)Reported as equity
B)Reported in other comprehensive income
C)Reported in consolidated net income
D)Included in opening consolidated retained earnings

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
A company has translated its foreign subsidiary's financial statements using the temporal method. What is the accounting treatment for exchange gains and losses arising from previous years?
A)Reported as equity
B)Reported in other comprehensive income
C)Reported in consolidated net income
D)Included in opening consolidated retained earnings
A)Reported as equity
B)Reported in other comprehensive income
C)Reported in consolidated net income
D)Included in opening consolidated retained earnings

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
If a foreign currency is strengthening with respect to the Canadian dollar, which of the following is true?
A)Both the current-rate method and the temporal method would show an exchange gain.
B)Both the current-rate method and the temporal method would show an exchange loss.
C)The current-rate method would show an exchange gain and the temporal method would show an exchange loss.
D)The current-rate method would show an exchange loss and the temporal method would show an exchange gain.
A)Both the current-rate method and the temporal method would show an exchange gain.
B)Both the current-rate method and the temporal method would show an exchange loss.
C)The current-rate method would show an exchange gain and the temporal method would show an exchange loss.
D)The current-rate method would show an exchange loss and the temporal method would show an exchange gain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
For consolidation purposes, what exchange rate is used for converting the retained earnings of a foreign subsidiary into Canadian dollars under the current rate method?
A)Specific historical rate
B)Historical rates of accumulation
C)Current rate
D)Closing rate
A)Specific historical rate
B)Historical rates of accumulation
C)Current rate
D)Closing rate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Under the current-rate method, at what exchange rate is depreciation expense translated?
A)At the average rate for the year
B)At the historical rate when the related assets were acquired
C)At the closing rate
D)At the rate at the beginning of the fiscal period
A)At the average rate for the year
B)At the historical rate when the related assets were acquired
C)At the closing rate
D)At the rate at the beginning of the fiscal period

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Which translation method should be used for the following subsidiaries?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
For publicly accountable companies, with foreign operations in countries with a hyper-inflationary economy, what should be done prior to translation?
A)The subsidiary's financial statements must be adjusted for changes in the price levels of the subsidiary's country.
B)The subsidiary's financial statements must be adjusted for changes in the price level of the parent's country.
C)The subsidiary's financial statements must be adjusted by the average inflation rate of the subsidiary and the parent companies' countries.
D)No adjustment is required unless the changes in price levels of the subsidiary country exceed 1000%.
A)The subsidiary's financial statements must be adjusted for changes in the price levels of the subsidiary's country.
B)The subsidiary's financial statements must be adjusted for changes in the price level of the parent's country.
C)The subsidiary's financial statements must be adjusted by the average inflation rate of the subsidiary and the parent companies' countries.
D)No adjustment is required unless the changes in price levels of the subsidiary country exceed 1000%.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
DNA was incorporated on January 2, 20X0, and commenced active operations immediately. Common shares were issued on the date of incorporation and no new common shares have been issued since then. On December 31, 20X3, INT purchased 70% of the outstanding common shares of DNA for 800,000 Swedish Krona (SEK).
DNA's main operations are located in Switzerland. For the year ending December 31, 20X6, the income statement (in 000s)for DNA was as follows:
The comparative and condensed statements of financial position (in 000s)for DNA were as follows:
OTHER INFORMATION:
• Purchases and sales of merchandise inventory occurred evenly throughout the year.
• The ending inventory was purchased evenly throughout the last month of the year.
• DNA purchased the property, plant, and equipment on hand at the end of 20X6 on March 17, 20X1. There were no purchases or sales of these assets from 20X3 to 20X6.
• Dividends were paid on June 30, 20X6.
Assume that foreign exchange rates were as follows:
- DNA's financial statements need to be translated into Canadian dollars for consolidation with INT's financial statements.
Required:
Translate DNA's statement of financial position at December 31, 20X6, into Canadian dollars under the temporal method.
DNA's main operations are located in Switzerland. For the year ending December 31, 20X6, the income statement (in 000s)for DNA was as follows:
The comparative and condensed statements of financial position (in 000s)for DNA were as follows:
OTHER INFORMATION:
• Purchases and sales of merchandise inventory occurred evenly throughout the year.
• The ending inventory was purchased evenly throughout the last month of the year.
• DNA purchased the property, plant, and equipment on hand at the end of 20X6 on March 17, 20X1. There were no purchases or sales of these assets from 20X3 to 20X6.
• Dividends were paid on June 30, 20X6.
Assume that foreign exchange rates were as follows:
- DNA's financial statements need to be translated into Canadian dollars for consolidation with INT's financial statements.
Required:
Translate DNA's statement of financial position at December 31, 20X6, into Canadian dollars under the temporal method.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
For private enterprises that use the current-rate method, how does reporting under Accounting Standards for Private Enterprises (ASPE)differ from reporting under IFRS?
A)Exchange gains and losses are reported as other comprehensive income.
B)Exchange gains and losses are reported as net income.
C)Exchange gains and losses are reported as a separate component of shareholders' equity.
D)The current-rate method is not permitted under ASPE.
A)Exchange gains and losses are reported as other comprehensive income.
B)Exchange gains and losses are reported as net income.
C)Exchange gains and losses are reported as a separate component of shareholders' equity.
D)The current-rate method is not permitted under ASPE.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Liverpool Company operates retail stores in Canada and an exporting business in London that specializes in buying and selling British tweeds. The London subsidiary provided the following financial statements in pounds sterling to the Canadian parent company.
Less: Dividends declared and paid,
Liverpool Company was incorporated on January 1, 1984, at which time an amount of property, plant, and equipment with a present (December 31, 20X5)net book value of £3,000,000 was purchased. Additional equipment was purchased December 31, 20X4 (20% of depreciation expense relates to this new equipment). The long-term notes were issued, to replace financing provided by the parent, on January 1, 20X4.
Direct exchange rates for the pound sterling are:
The January 1, 20X5, retained earnings balance of the London Branch of the Liverpool Company correctly translated to Canadian dollars was $1,783,774. The beginning inventory of £380,000 was acquired during the last quarter of 20X4 and the ending inventory was acquired during the last quarter of 20X5. Sales and purchases were made, and other expenses were incurred, evenly throughout the year.
Required:
Compute the gain or loss on holding net monetary items for the Liverpool Company for the year ending December 31, 20X5.
Less: Dividends declared and paid,
Liverpool Company was incorporated on January 1, 1984, at which time an amount of property, plant, and equipment with a present (December 31, 20X5)net book value of £3,000,000 was purchased. Additional equipment was purchased December 31, 20X4 (20% of depreciation expense relates to this new equipment). The long-term notes were issued, to replace financing provided by the parent, on January 1, 20X4.
Direct exchange rates for the pound sterling are:
The January 1, 20X5, retained earnings balance of the London Branch of the Liverpool Company correctly translated to Canadian dollars was $1,783,774. The beginning inventory of £380,000 was acquired during the last quarter of 20X4 and the ending inventory was acquired during the last quarter of 20X5. Sales and purchases were made, and other expenses were incurred, evenly throughout the year.
Required:
Compute the gain or loss on holding net monetary items for the Liverpool Company for the year ending December 31, 20X5.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
All of the following statements are stated in Brazil reals (R$).  Additional information:
Additional information:
Selected exchange rates:
Date of purchase of inventory on hand at year-end Dividends were declared on June 30, 20X5 Opening inventory = R$130,000
Inventory purchases for the year = R$1,570,000
Machinery, land, and buildings were purchased on June 30, 20X4
-
Bralta is the Brazilian subsidiary of Altapro Co., a Canadian company. What is the balance of total assets under the temporal method?
A)$2,108,625
B)$2,154,000
C)$2,183,620
D)$2,185,570
 Additional information:
Additional information:Selected exchange rates:
Date of purchase of inventory on hand at year-end Dividends were declared on June 30, 20X5 Opening inventory = R$130,000
Inventory purchases for the year = R$1,570,000
Machinery, land, and buildings were purchased on June 30, 20X4
-
Bralta is the Brazilian subsidiary of Altapro Co., a Canadian company. What is the balance of total assets under the temporal method?
A)$2,108,625
B)$2,154,000
C)$2,183,620
D)$2,185,570

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Olin Ltd. is a foreign subsidiary of Rainier Ltd., a Canadian corporation. Rainier translated Olin's financial statements to Canadian dollars using the temporal method, which resulted in a cumulative translation gain of $15,500. How should the $15,500 be treated on Rainier's consolidated financial statements?
A)The $15,500 should be disclosed in the opening consolidated retained earnings.
B)The $15,500 should be reported on the consolidated SCI.
C)The part of the $15,500 that relates to the prior years should be included in the opening consolidated retained earnings and the balance should be reported on the consolidated SCI.
D)The $15,500 should only be disclosed in the notes to the consolidated financial statements.
A)The $15,500 should be disclosed in the opening consolidated retained earnings.
B)The $15,500 should be reported on the consolidated SCI.
C)The part of the $15,500 that relates to the prior years should be included in the opening consolidated retained earnings and the balance should be reported on the consolidated SCI.
D)The $15,500 should only be disclosed in the notes to the consolidated financial statements.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
DNA was incorporated on January 2, 20X0, and commenced active operations immediately. Common shares were issued on the date of incorporation and no new common shares have been issued since then. On December 31, 20X3, INT purchased 70% of the outstanding common shares of DNA for 800,000 Swedish Krona (SEK).
DNA's main operations are located in Switzerland. For the year ending December 31, 20X6, the income statement (in 000s)for DNA was as follows:
The comparative and condensed statements of financial position (in 000s)for DNA were as follows:
OTHER INFORMATION:
• Purchases and sales of merchandise inventory occurred evenly throughout the year.
• The ending inventory was purchased evenly throughout the last month of the year.
• DNA purchased the property, plant, and equipment on hand at the end of 20X6 on March 17, 20X1. There were no purchases or sales of these assets from 20X3 to 20X6.
• Dividends were paid on June 30, 20X6.
Assume that foreign exchange rates were as follows:
- DNA's financial statements need to be translated into Canadian dollars for consolidation with INT's financial statements.
Required:
Calculate the exchange gain/loss on current monetary items for 20X6 under the temporal method.
DNA's main operations are located in Switzerland. For the year ending December 31, 20X6, the income statement (in 000s)for DNA was as follows:
The comparative and condensed statements of financial position (in 000s)for DNA were as follows:
OTHER INFORMATION:
• Purchases and sales of merchandise inventory occurred evenly throughout the year.
• The ending inventory was purchased evenly throughout the last month of the year.
• DNA purchased the property, plant, and equipment on hand at the end of 20X6 on March 17, 20X1. There were no purchases or sales of these assets from 20X3 to 20X6.
• Dividends were paid on June 30, 20X6.
Assume that foreign exchange rates were as follows:
- DNA's financial statements need to be translated into Canadian dollars for consolidation with INT's financial statements.
Required:
Calculate the exchange gain/loss on current monetary items for 20X6 under the temporal method.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
LaSalle Ltd., a Canadian company, has a subsidiary in Brazil that produces a component used in LaSalle's manufacturing. All of the components that the subsidiary produces are sold to LaSalle. The subsidiary also purchases most of the raw materials used in its production from LaSalle. Both companies use the Canadian dollar as their functional currency. Which of the following statements is true?
A)The current rate method of translation should be used.
B)Nothing needs to be done with the subsidiary's financial statements prior to consolidation.
C)The subsidiary's financial statements need to be re-measured in the functional currency prior to consolidation.
D)The subsidiary is considered to be an extension of the parent company and consolidation is not required.
A)The current rate method of translation should be used.
B)Nothing needs to be done with the subsidiary's financial statements prior to consolidation.
C)The subsidiary's financial statements need to be re-measured in the functional currency prior to consolidation.
D)The subsidiary is considered to be an extension of the parent company and consolidation is not required.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Liverpool Company operates retail stores in Canada and an exporting business in London that specializes in buying and selling British tweeds. The London subsidiary, which was acquired on January 1, 1986, provided the following financial statements in pounds sterling to the Canadian parent company.
Statement of Changes in Equity-Partial-Retained Earnings section
Less: Dividends declared and paid,
Liverpool Company was incorporated on January 1, 1984, at which time an amount of property, plant, and equipment with a present (December 31, 20X5)net book value of £3,000,000 was purchased. Additional equipment was purchased December 31, 20X4 (20% of depreciation expense relates to this new equipment). The long-term notes were issued, to replace financing provided by the parent, on January 1, 20X4.
Direct exchange rates for the pound sterling are:
- The January 1, 20X5 retained earnings balance of the London Branch of the Liverpool Company correctly translated to Canadian dollars was $1,783,774. The beginning inventory of £380,000 was acquired during the last quarter of 20X4 and the ending inventory was acquired during the last quarter of 20X5. Sales and purchases were made, and other expenses were incurred, evenly throughout the year.
Required:
Translate the statement of comprehensive income and statement of changes in equity-partial-retained earnings section of Liverpool Company for the year ending December 31, 20X5, into dollars, assuming that the temporal method is appropriate.
Statement of Changes in Equity-Partial-Retained Earnings section
Less: Dividends declared and paid,
Liverpool Company was incorporated on January 1, 1984, at which time an amount of property, plant, and equipment with a present (December 31, 20X5)net book value of £3,000,000 was purchased. Additional equipment was purchased December 31, 20X4 (20% of depreciation expense relates to this new equipment). The long-term notes were issued, to replace financing provided by the parent, on January 1, 20X4.
Direct exchange rates for the pound sterling are:
- The January 1, 20X5 retained earnings balance of the London Branch of the Liverpool Company correctly translated to Canadian dollars was $1,783,774. The beginning inventory of £380,000 was acquired during the last quarter of 20X4 and the ending inventory was acquired during the last quarter of 20X5. Sales and purchases were made, and other expenses were incurred, evenly throughout the year.
Required:
Translate the statement of comprehensive income and statement of changes in equity-partial-retained earnings section of Liverpool Company for the year ending December 31, 20X5, into dollars, assuming that the temporal method is appropriate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
On January 1, 20X6, Clock Inc. of Vancouver purchased 75% of the outstanding shares of Time Limited in London, England. Time Limited's statements of financial position and statements of comprehensive income and changes in equity-retained earnings section for the year ended December 31, 20X7, are below.
Additional information:
1. Time was incorporated on January 1, 20X3, when it acquired all its equipment for £4,005,000 and issued its 10-year bonds payable.
2. Time's purchases and sales occurred evenly over the year. Inventories on hand at December 31, 20X6, and December 20X7 were purchased evenly over the last quarter of 20X6 and 20X7, respectively. Inventories as at December 31, 20X7, were £650,000.
3. Dividends were paid on March 31, 20X7.
4. Foreign exchange rates are as follows:
Required:
Translate Time's statement of comprehensive income for the year ended December 31, 20X7 into Canadian dollars assuming its functional currency is Canadian dollars. Calculate the translation gain or loss arising in 20X7.
Additional information:
1. Time was incorporated on January 1, 20X3, when it acquired all its equipment for £4,005,000 and issued its 10-year bonds payable.
2. Time's purchases and sales occurred evenly over the year. Inventories on hand at December 31, 20X6, and December 20X7 were purchased evenly over the last quarter of 20X6 and 20X7, respectively. Inventories as at December 31, 20X7, were £650,000.
3. Dividends were paid on March 31, 20X7.
4. Foreign exchange rates are as follows:
Required:
Translate Time's statement of comprehensive income for the year ended December 31, 20X7 into Canadian dollars assuming its functional currency is Canadian dollars. Calculate the translation gain or loss arising in 20X7.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Water Bottling Inc. (WBI)is a 100% wholly owned subsidiary with operations in France. WBI was purchased by a Canadian parent on January 1, 20X5, and the FVA was €375,000, all allocated to goodwill. The financial records of WBI are maintained in euros and provide the following information with respect to equipment and goodwill.
Equipment: Purchased on January 1, 20X5, for €250,000, and depreciated over five years on a straight-line basis.
Equipment: Purchased on January 1, 20X6, for €175,000, and depreciated over five years on a straight-line basis.
Goodwill had a balance of €375,000.
Foreign exchange rates were as follows:
- Required:
Assume that WBC's functional currency is the Canadian dollar. Calculate the translated Canadian dollar balances for the following accounts for December 31, 20X7:
a. Equipment
b. Accumulated depreciation-equipment
c. Depreciation expense
d. Investment property
e. Goodwill
Equipment: Purchased on January 1, 20X5, for €250,000, and depreciated over five years on a straight-line basis.
Equipment: Purchased on January 1, 20X6, for €175,000, and depreciated over five years on a straight-line basis.
Goodwill had a balance of €375,000.
Foreign exchange rates were as follows:
- Required:
Assume that WBC's functional currency is the Canadian dollar. Calculate the translated Canadian dollar balances for the following accounts for December 31, 20X7:
a. Equipment
b. Accumulated depreciation-equipment
c. Depreciation expense
d. Investment property
e. Goodwill

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
On January 1, 20X6, Clock Inc. of Vancouver purchased 75% of the outstanding shares of Time Limited in London, England. Time Limited's statements of financial position and statements of comprehensive income and changes in equity-retained earnings section for the year ended December 31, 20X7, are below.
Additional information:
1. Time was incorporated on January 1, 20X3, when it acquired all its equipment for £4,005,000 and issued its 10-year bonds payable.
2. Time's purchases and sales occurred evenly over the year. Inventories on hand at December 31, 20X6, and December 20X7 were purchased evenly over the last quarter of 20X6 and 20X7, respectively. Inventories as at December 31, 20X7, were £650,000.
3. Dividends were paid on March 31, 20X7.
4. Foreign exchange rates are as follows:
Required:
Translate Time's statement of financial position at December 31, 20X7, into Canadian dollars, assuming its functional currency is Canadian dollars. Calculate the translation gain or loss arising in 20X7.
Additional information:
1. Time was incorporated on January 1, 20X3, when it acquired all its equipment for £4,005,000 and issued its 10-year bonds payable.
2. Time's purchases and sales occurred evenly over the year. Inventories on hand at December 31, 20X6, and December 20X7 were purchased evenly over the last quarter of 20X6 and 20X7, respectively. Inventories as at December 31, 20X7, were £650,000.
3. Dividends were paid on March 31, 20X7.
4. Foreign exchange rates are as follows:
Required:
Translate Time's statement of financial position at December 31, 20X7, into Canadian dollars, assuming its functional currency is Canadian dollars. Calculate the translation gain or loss arising in 20X7.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
On January 1, 20X7, Clock Inc. of Vancouver purchased 75% of the outstanding shares of Time Limited in London, England. Time Limited's statements of financial position and statements of comprehensive income and changes in equity-retained earnings section for the year ended December 31, 20X7, are below.
Additional information:
1. Time was incorporated on January 1, 20X3, when it acquired all its equipment for £4,005,000 and issued its 10-year bonds payable.
2. Time's purchases and sales occurred evenly over the year. Inventories on hand at December 31, 20X6, and December 20X7 were purchased evenly over the last quarter of 20X6 and 20X7, respectively. Inventories as at December 31, 20X7, were £650,000.
3. Dividends were paid on March 31, 20X7. There were no changes in share capital over the year.
4. Foreign exchange rates are as follows:
Required:
Translate Time's statement of financial position at December 31, 20X7, into Canadian dollars, assuming its functional currency is British pound sterling. Include a calculation to prove the amount of the cumulative foreign exchange translation gains and losses.
Additional information:
1. Time was incorporated on January 1, 20X3, when it acquired all its equipment for £4,005,000 and issued its 10-year bonds payable.
2. Time's purchases and sales occurred evenly over the year. Inventories on hand at December 31, 20X6, and December 20X7 were purchased evenly over the last quarter of 20X6 and 20X7, respectively. Inventories as at December 31, 20X7, were £650,000.
3. Dividends were paid on March 31, 20X7. There were no changes in share capital over the year.
4. Foreign exchange rates are as follows:
Required:
Translate Time's statement of financial position at December 31, 20X7, into Canadian dollars, assuming its functional currency is British pound sterling. Include a calculation to prove the amount of the cumulative foreign exchange translation gains and losses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








