Deck 4: Appendix A: Wholly Owned Subsidiaries: Reporting Subsequent Acquisitions
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/4
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 4: Appendix A: Wholly Owned Subsidiaries: Reporting Subsequent Acquisitions
1
On December 31, 20X5, Russel Co. purchased 100% of the outstanding common shares of Minsee Ltd. for $1,300,000 in shares and $200,000 in cash. The statements of financial position of Russel and Minsee immediately before the acquisition and issuance of the notes payable were as follows (in 000s): 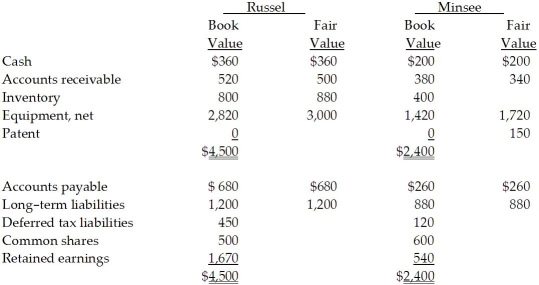 The tax value for each asset and liability is the same as its carrying value except for the equipment, which has a tax value of $950,000, and the patent, which has a tax value of nil. The equipment has a remaining useful life of 15 years from the date of acquisition. The patent has a useful life estimated to be five years from the date of acquisition.
The tax value for each asset and liability is the same as its carrying value except for the equipment, which has a tax value of $950,000, and the patent, which has a tax value of nil. The equipment has a remaining useful life of 15 years from the date of acquisition. The patent has a useful life estimated to be five years from the date of acquisition.
During 20X6, the year following the acquisition, the following occurred:
1. Minsee borrowed $350,000 from Russel on June 1, 20X6, and was charged interest at 10% per annum, which it paid on a monthly basis. There were no repayments of principal made during the remaining of the year.
2. Throughout the year, Minsee purchased merchandise of $800,000 from Russel. Russel's gross margin is 30% of selling price. At December 31, 20X6, Minsee still owed Russel $250,000 on this merchandise; 75% of this merchandise was resold by Minsee prior to December 31, 20X6.
3. Minsee paid dividends of $275,000 at the end of 20X6 and Russel paid dividends of $200,000.
4. Minsee and Russel both have an income tax rate of 30%.
During 20X7, the following occurred:
1. Minsee paid $150,000 on the loan payable to Russel on May 30, 20X7.
2. Throughout the year, Minsee purchased merchandise of $1,000,000 from Russel. Russel's gross margin is 30% of selling price. At December 31, 20X6, Minsee still owed Russel $150,000 on this merchandise; 85% of this merchandise was resold by Minsee prior to December 31, 20X7.
3. Minsee paid dividends of $275,000 at the end of 20X7 and Russel paid dividends of $200,000.
4. Minsee and Russel both have an income tax rate of 30%.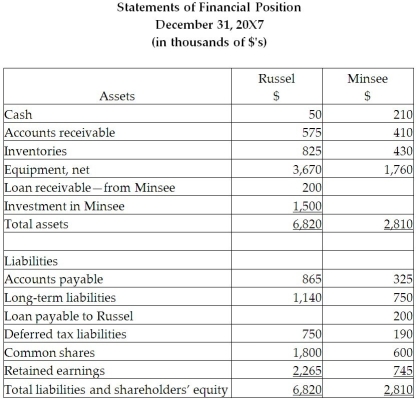
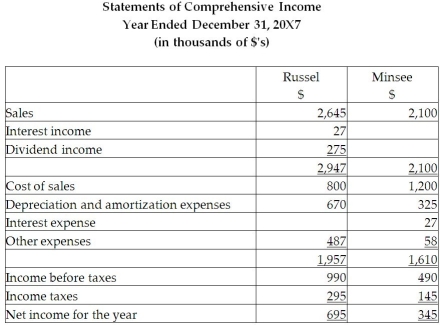 Required:
Required:
Calculate the consolidated retained earnings as at December 31, 20X7, and as at December 31, 20X6.
Prepare the consolidated statement of comprehensive income and the consolidated statement of financial position for the year ended December 31, 20X7, for Russel. Include all relevant income tax calculations.
 The tax value for each asset and liability is the same as its carrying value except for the equipment, which has a tax value of $950,000, and the patent, which has a tax value of nil. The equipment has a remaining useful life of 15 years from the date of acquisition. The patent has a useful life estimated to be five years from the date of acquisition.
The tax value for each asset and liability is the same as its carrying value except for the equipment, which has a tax value of $950,000, and the patent, which has a tax value of nil. The equipment has a remaining useful life of 15 years from the date of acquisition. The patent has a useful life estimated to be five years from the date of acquisition.During 20X6, the year following the acquisition, the following occurred:
1. Minsee borrowed $350,000 from Russel on June 1, 20X6, and was charged interest at 10% per annum, which it paid on a monthly basis. There were no repayments of principal made during the remaining of the year.
2. Throughout the year, Minsee purchased merchandise of $800,000 from Russel. Russel's gross margin is 30% of selling price. At December 31, 20X6, Minsee still owed Russel $250,000 on this merchandise; 75% of this merchandise was resold by Minsee prior to December 31, 20X6.
3. Minsee paid dividends of $275,000 at the end of 20X6 and Russel paid dividends of $200,000.
4. Minsee and Russel both have an income tax rate of 30%.
During 20X7, the following occurred:
1. Minsee paid $150,000 on the loan payable to Russel on May 30, 20X7.
2. Throughout the year, Minsee purchased merchandise of $1,000,000 from Russel. Russel's gross margin is 30% of selling price. At December 31, 20X6, Minsee still owed Russel $150,000 on this merchandise; 85% of this merchandise was resold by Minsee prior to December 31, 20X7.
3. Minsee paid dividends of $275,000 at the end of 20X7 and Russel paid dividends of $200,000.
4. Minsee and Russel both have an income tax rate of 30%.

 Required:
Required:Calculate the consolidated retained earnings as at December 31, 20X7, and as at December 31, 20X6.
Prepare the consolidated statement of comprehensive income and the consolidated statement of financial position for the year ended December 31, 20X7, for Russel. Include all relevant income tax calculations.
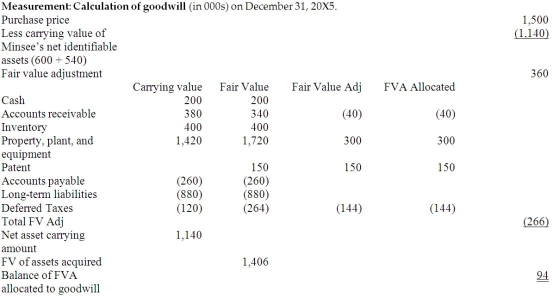
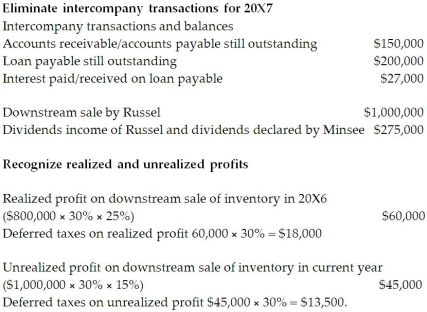
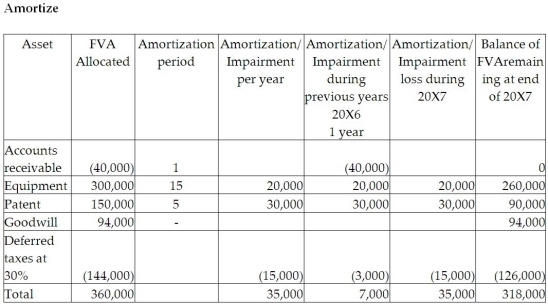
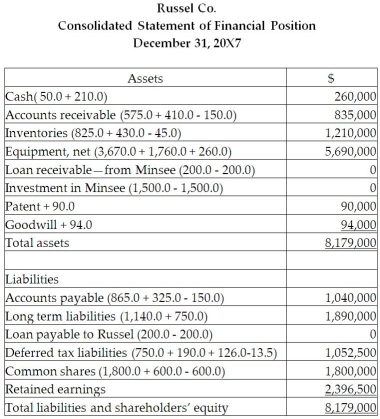 Calculation of the balance in the consolidated retained earnings as at December :
Calculation of the balance in the consolidated retained earnings as at December :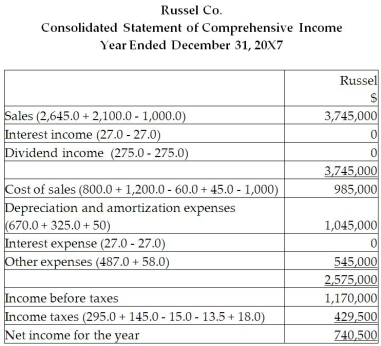
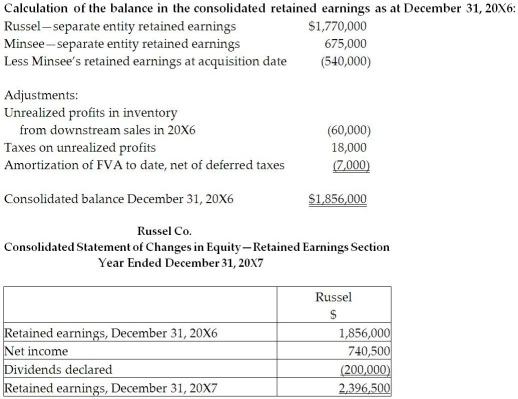
2
Morin Co. acquired all the shares of Lightfoot Ltd. Lightfoot has a number of amortizable capital assets and has properly recorded the related deferred income taxes on its books.
- What deferred income tax adjustment must Morin make for its consolidated financial statements?
A)Adjustment for any changes in temporary differences due to the difference between carrying values and tax bases of Lightfoot's depreciable capital assets
B)Adjustment for any changes in temporary differences due to the amortization of fair value increments
C)Adjustment for any changes in temporary differences due to the amortization of goodwill
D)No adjustment is necessary.
- What deferred income tax adjustment must Morin make for its consolidated financial statements?
A)Adjustment for any changes in temporary differences due to the difference between carrying values and tax bases of Lightfoot's depreciable capital assets
B)Adjustment for any changes in temporary differences due to the amortization of fair value increments
C)Adjustment for any changes in temporary differences due to the amortization of goodwill
D)No adjustment is necessary.
Adjustment for any changes in temporary differences due to the amortization of fair value increments
3
Morin Co. acquired all the shares of Lightfoot Ltd. Lightfoot has a number of amortizable capital assets and has properly recorded the related deferred income taxes on its books.
- At the time of acquisition, the fair values of these assets were higher than their carrying values and their tax bases. In Morin's consolidation each year, it must adjust for the deferred taxes that resulted from these temporary differences. Which of the following statements is true?
A)The consolidation adjustment will always result in an increase in the deferred tax liability.
B)The consolidation adjustment will always result in a decrease in the deferred tax liability.
C)The consolidation adjustment can result in either an increase or a decrease in the deferred tax liability.
D)The consolidation adjustment is required only if the tax basis changes.
- At the time of acquisition, the fair values of these assets were higher than their carrying values and their tax bases. In Morin's consolidation each year, it must adjust for the deferred taxes that resulted from these temporary differences. Which of the following statements is true?
A)The consolidation adjustment will always result in an increase in the deferred tax liability.
B)The consolidation adjustment will always result in a decrease in the deferred tax liability.
C)The consolidation adjustment can result in either an increase or a decrease in the deferred tax liability.
D)The consolidation adjustment is required only if the tax basis changes.
The consolidation adjustment will always result in a decrease in the deferred tax liability.
4
Which of the following statements is true with respect to adjusting the deferred tax account on consolidation?
A)Deferred taxes only need to be adjusted for unrealized profits in inventory at the end of the year.
B)Deferred taxes only need to be adjusted for unrealized profits in inventory at the beginning of the year.
C)Deferred taxes need to be adjusted for unrealized profits in inventory at both the beginning and the end of the year.
D)Deferred taxes do not need to be adjusted for unrealized profits.
A)Deferred taxes only need to be adjusted for unrealized profits in inventory at the end of the year.
B)Deferred taxes only need to be adjusted for unrealized profits in inventory at the beginning of the year.
C)Deferred taxes need to be adjusted for unrealized profits in inventory at both the beginning and the end of the year.
D)Deferred taxes do not need to be adjusted for unrealized profits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 4 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








