Deck 15: Chemical Kinetics
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/93
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 15: Chemical Kinetics
1
If the average rate of decomposition of PH3(g)is 3.2 (mol PH3).L-1.min-1 for the reaction 2PH3(g) 2P(g)+ 3H2(g),the unique average reaction rate is
A)3.2 mol.-1.min-1.
B)2.1 mol.-1.min-1
C)1.6 mol.-1.min-1
D)4.8 mol.-1.min-1
E)6.4 mol.-1.min-1
A)3.2 mol.-1.min-1.
B)2.1 mol.-1.min-1
C)1.6 mol.-1.min-1
D)4.8 mol.-1.min-1
E)6.4 mol.-1.min-1
1.6 mol.-1.min-1
2
If the average rate of formation of H2(g)is 3.90 (mol H2).L-1.s-1 for the reaction 2PH3(g) 2P(g)+ 3H2(g),the unique average reaction rate is
A)3.90 mol.L-1.s-1.
B)1.30 mol.L-1.s-1.
C)2.60 mol.L-1.s-1.
D)7.80 mol.L-1.s-1.
E)11.7 mol.L-1.s-1.
A)3.90 mol.L-1.s-1.
B)1.30 mol.L-1.s-1.
C)2.60 mol.L-1.s-1.
D)7.80 mol.L-1.s-1.
E)11.7 mol.L-1.s-1.
1.30 mol.L-1.s-1.
3
If the rate of reaction increases by a factor of 9.6 when the concentration of reactant increases by a factor of 3.1,the order of the reaction with respect to this reactant is
A)1.5
B)3
C)4
D)2
E)1
A)1.5
B)3
C)4
D)2
E)1
2
4
Given: 2NO2(g)+ F2(g) 2NO2F(g)
Rate = - [F2]/ t
The rate of the reaction can also be expressed as
A)-2 [NO2]/ t.
B) [NO2F]/ t.
C)
D)- [NO2]/ t.
E)
Rate = - [F2]/ t
The rate of the reaction can also be expressed as
A)-2 [NO2]/ t.
B) [NO2F]/ t.
C)
D)- [NO2]/ t.
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The concentration-time dependence for a first-order reaction is: 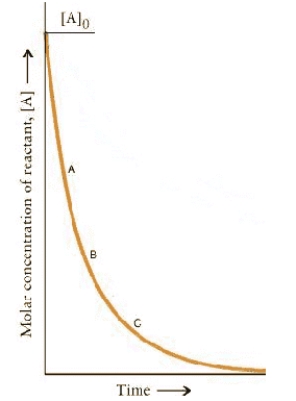
At which point on the curve is the reaction fastest?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)A + t½
E)The rates are the same at all points.

At which point on the curve is the reaction fastest?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)A + t½
E)The rates are the same at all points.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
If the rate of a reaction increases by a factor of 64 when the concentration of reactant increases by a factor of 4,the order of the reaction with respect to this reactant is
A)16.
B)2.
C)4.
D)1.
E)3.
A)16.
B)2.
C)4.
D)1.
E)3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
For the reaction S2O82-(aq)+ 3I-(aq) 2SO42-(aq)+ I3-(aq),rate = k[S2O82-][I-].When the reaction is followed under pseudo-first-order conditions with [S2O82-] = 200 m M and [I-] = 1.5 m M,the rate constant was 1.82 s-1.The second order rate constant,k,for the reaction is
A)1.21 * 103 M-1.s-1.
B)6.07 * 103 M-1.s-1.
C)9.10 M-1.s-1.
D)1.37 * 10-2 M-1.s-1.
E)1.82 M-1.s-1.
A)1.21 * 103 M-1.s-1.
B)6.07 * 103 M-1.s-1.
C)9.10 M-1.s-1.
D)1.37 * 10-2 M-1.s-1.
E)1.82 M-1.s-1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The reaction 2NO(g)+ 2H2(g) N2(g)+ 2H2O(g)
Is first order in H2 and second order in NO.Starting with equal concentrations of H2 and NO,the rate after 25% of the H2 has reacted is what percent of the initial rate?
A)75.0%
B)42.2%
C)6.25%
D)56.3%
E)1.56%
Is first order in H2 and second order in NO.Starting with equal concentrations of H2 and NO,the rate after 25% of the H2 has reacted is what percent of the initial rate?
A)75.0%
B)42.2%
C)6.25%
D)56.3%
E)1.56%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The concentration-time dependence for two first order reactions is: 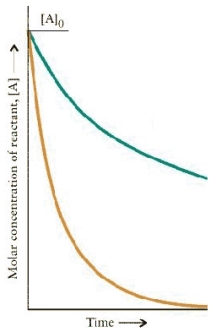
Which reaction has the greater t½?

Which reaction has the greater t½?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Given: 4Fe2+(aq)+ O2(aq)+ 2H2O(l) 4Fe3+(aq)+ 4OH-(aq)
Rate = k[Fe2+][OH-]2[O2]
The overall order of the reaction and the order with respect to O2 are
A)4 and 1.
B)5 and 1.
C)3 and 1.
D)4 and 2.
E)7 and 1.
Rate = k[Fe2+][OH-]2[O2]
The overall order of the reaction and the order with respect to O2 are
A)4 and 1.
B)5 and 1.
C)3 and 1.
D)4 and 2.
E)7 and 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Given: 2O3(g) 3O2(g)
Rate = k[O3]2[O2]-1
The overall order of the reaction and the order with respect to [O3] are
A)-1 and 3.
B)1 and 2.
C)0 and 1.
D)2 and 2.
E)3 and 2.
Rate = k[O3]2[O2]-1
The overall order of the reaction and the order with respect to [O3] are
A)-1 and 3.
B)1 and 2.
C)0 and 1.
D)2 and 2.
E)3 and 2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The concentration-time curves for two sets of reactions,A/B and C/D,are: 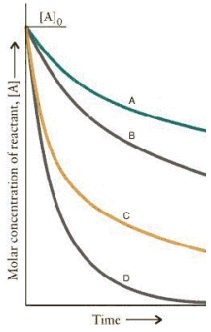
Which set of reactions has the largest rate constant?

Which set of reactions has the largest rate constant?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
For the reaction
2NO(g)+ 2H2(g) N2(g)+ 2H2O(g)
the following data were collected.
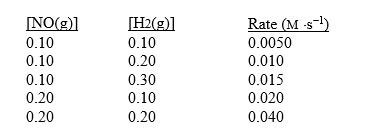
What is the rate law for this reaction?
2NO(g)+ 2H2(g) N2(g)+ 2H2O(g)
the following data were collected.

What is the rate law for this reaction?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The rate of formation of oxygen in the reaction 2N2O5(g) 4NO2(g)+ O2(g)
Is 2.28 (mol O2).L-1.s-1.What is the rate of formation of NO2?
A)0.57 (mol NO2).L-1.s-1
B)9.12 (mol NO2).L-1.s-1
C)2.28 (mol NO2).L-1.s-1
D)1.14 (mol NO2).L-1.s-1
E)4.56 (mol NO2).L-1.s-1
Is 2.28 (mol O2).L-1.s-1.What is the rate of formation of NO2?
A)0.57 (mol NO2).L-1.s-1
B)9.12 (mol NO2).L-1.s-1
C)2.28 (mol NO2).L-1.s-1
D)1.14 (mol NO2).L-1.s-1
E)4.56 (mol NO2).L-1.s-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The reaction 2NO(g)+ 2H2(g) N2(g)+ 2H2O(g)
Is first order in H2 and second order in NO.Starting with equal concentrations of H2 and NO,the rate after 50% of the H2 has reacted is what percent of the initial rate?
A)18.8%
B)37.5%
C)25.0%
D)50.0%
E)12.5%
Is first order in H2 and second order in NO.Starting with equal concentrations of H2 and NO,the rate after 50% of the H2 has reacted is what percent of the initial rate?
A)18.8%
B)37.5%
C)25.0%
D)50.0%
E)12.5%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Given: 2A(g)+ B(g) C(g)+ D(g)
When [A] = [B] = 0.10 M,the rate is 2.0 M.s-1; for [A] = [B] = 0.20,the rate is 8.0 M.s-1; and for [A] = 0.10 M,[B] = 0.20 M,the rate is 2.0 M.s-1.The rate law is
A)rate = k[A].
B)rate = k[B]2.
C)rate = k[A][B]0.
D)rate = k[A][B].
E)rate = k[A]2.
When [A] = [B] = 0.10 M,the rate is 2.0 M.s-1; for [A] = [B] = 0.20,the rate is 8.0 M.s-1; and for [A] = 0.10 M,[B] = 0.20 M,the rate is 2.0 M.s-1.The rate law is
A)rate = k[A].
B)rate = k[B]2.
C)rate = k[A][B]0.
D)rate = k[A][B].
E)rate = k[A]2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
It is important to distinguish between the reaction rate and the rate constant.The units of reaction rate are M∙s-1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
If the rate of reaction increases by a factor of 2.3 when the concentration of reactant increases by a factor of 1.5,the order of the reaction with respect to this reactant is
A)2.
B)1.
C)1.5.
D)4.
E)3.
A)2.
B)1.
C)1.5.
D)4.
E)3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
For the reaction 2A + B products
Determine the rate law for the reaction given the following data:
![<strong>For the reaction 2A + B \rightarrow products Determine the rate law for the reaction given the following data: </strong> A)rate = k[B]<sup>2 </sup> B)rate = k[A][B]<sup>0 </sup> C)rate = k[A]<sup>2 </sup> D)rate = k[A][B] E)rate = k[A]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1441/11ec8970_aab7_b027_b0d8_3f59ed553079_TB1441_00.jpg)
A)rate = k[B]2
B)rate = k[A][B]0
C)rate = k[A]2
D)rate = k[A][B]
E)rate = k[A]
Determine the rate law for the reaction given the following data:
![<strong>For the reaction 2A + B \rightarrow products Determine the rate law for the reaction given the following data: </strong> A)rate = k[B]<sup>2 </sup> B)rate = k[A][B]<sup>0 </sup> C)rate = k[A]<sup>2 </sup> D)rate = k[A][B] E)rate = k[A]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1441/11ec8970_aab7_b027_b0d8_3f59ed553079_TB1441_00.jpg)
A)rate = k[B]2
B)rate = k[A][B]0
C)rate = k[A]2
D)rate = k[A][B]
E)rate = k[A]

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The concentration-time dependence is shown below for two first-order reactions is: 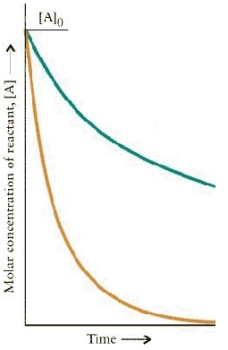
Which reaction has the larger rate constant?

Which reaction has the larger rate constant?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Consider the reaction 2N2O5(g) 4NO2(g)+ O2(g)
Rate = k[N2O5]
If the initial concentration of N2O5 is 0.80 M,the concentration after 5 half-lives is
A)0.11 M.
B)0.025 M.
C)0.032 M.
D)0.16 M.
E)0.050 M.
Rate = k[N2O5]
If the initial concentration of N2O5 is 0.80 M,the concentration after 5 half-lives is
A)0.11 M.
B)0.025 M.
C)0.032 M.
D)0.16 M.
E)0.050 M.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The concentration-time curves for two sets of reactions,A/B and C/D,are: 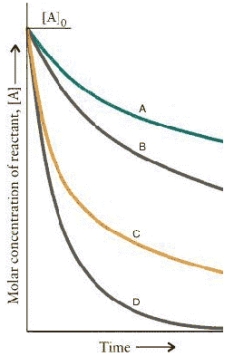
Which of the reactions are first order?
A)B and D
B)A and B
C)C and D
D)A and C

Which of the reactions are first order?
A)B and D
B)A and B
C)C and D
D)A and C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
For the reaction A products,the following data were collected. 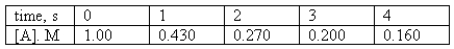
Determine the order of the reaction and calculate the rate constant.

Determine the order of the reaction and calculate the rate constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
For the reaction cyclopropane propene
A plot of ln[cyclopropane] vs time in seconds gives a straight line with slope -4.1 * 10-3 s-1 at 550 C.What is the rate constant for this reaction?
A)3.9 * 10-2 s-1
B)8.2 * 10-3 s-1
C)4.1 * 10-3 s-1
D)1.8 * 10-3 s-1
E)2.1 * 10-3 s-1
A plot of ln[cyclopropane] vs time in seconds gives a straight line with slope -4.1 * 10-3 s-1 at 550 C.What is the rate constant for this reaction?
A)3.9 * 10-2 s-1
B)8.2 * 10-3 s-1
C)4.1 * 10-3 s-1
D)1.8 * 10-3 s-1
E)2.1 * 10-3 s-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
For a given first-order reaction,after 2.00 min,20% of the reactants remain.Calculate the rate constant for the reaction.
A)0.0134 s-1
B)0.000808 s-1
C)74.6 s-1
D)0.00582 s-1
E)0.00186 s-1
A)0.0134 s-1
B)0.000808 s-1
C)74.6 s-1
D)0.00582 s-1
E)0.00186 s-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
For a second-order reaction,a straight line is obtained from a plot of
A)1/[A] vs t.
B)ln(1/t)vs [A].
C)[A] vs t.
D)ln[A] vs t.
E)ln(t)vs [A].
A)1/[A] vs t.
B)ln(1/t)vs [A].
C)[A] vs t.
D)ln[A] vs t.
E)ln(t)vs [A].

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The reaction
2ClO2(g)+ F2(g) 2FClO2(g)
Is first order in both ClO2 and F2.When the initial concentrations of ClO2 and F2 are equal,the rate after 25% of the F2 has reacted is what percent of the initial rate?
A)75.0%
B)18.8%
C)37.5%
D)28.1%
E)12.5%
2ClO2(g)+ F2(g) 2FClO2(g)
Is first order in both ClO2 and F2.When the initial concentrations of ClO2 and F2 are equal,the rate after 25% of the F2 has reacted is what percent of the initial rate?
A)75.0%
B)18.8%
C)37.5%
D)28.1%
E)12.5%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Consider the reaction 2N2O(g) 2N2(g)+ O2(g)
Rate = k[N2O]
For an initial concentration of N2O of 0.50 M,what is the concentration of N2O remaining after 2.0 min if k = 3.4 * 10-3 s-1?
A)0.50 M
B)0.55 M
C)0.66 M
D)0.33 M
E)0.17 M
Rate = k[N2O]
For an initial concentration of N2O of 0.50 M,what is the concentration of N2O remaining after 2.0 min if k = 3.4 * 10-3 s-1?
A)0.50 M
B)0.55 M
C)0.66 M
D)0.33 M
E)0.17 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Technetium-99m,used to image the heart and brain,has a half-life of 6.00 h.What fraction of technetium-99m remains in the body after 1 day?
A)0.0625
B)0.250
C)0.0313
D)0.125
A)0.0625
B)0.250
C)0.0313
D)0.125

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
A given compound decomposes with a half-life of 8.0 s and the half-life is independent of the concentration.How long does it take for the concentration to decrease to one-ninth of its initial value?
A)32 s
B)25 s
C)72 s
D)64 s
E)3.6 s
A)32 s
B)25 s
C)72 s
D)64 s
E)3.6 s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Consider the reaction 2N2O5(g) 4NO2(g)+ O2(g)
Rate = k[N2O5]
Calculate the time for the concentration of N2O5 to fall to one-fourth its initial value if the half-life is 133 s.
A)133 s
B)33.3 s
C)266 s
D)66.6 s
E)533 s
Rate = k[N2O5]
Calculate the time for the concentration of N2O5 to fall to one-fourth its initial value if the half-life is 133 s.
A)133 s
B)33.3 s
C)266 s
D)66.6 s
E)533 s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug is metabolized with a first-order rate constant of 3.25 day-1.What fraction of the drug remains in the body after 13.0 hr?
A)0.172
B)0.0174
C)0.828
D)0.873
E)0.127
A)0.172
B)0.0174
C)0.828
D)0.873
E)0.127

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
For the reaction cyclopropane(g) propene(g)at 500 C,a plot of ln[cyclopropane] vs t gives a straight line with a slope of -0.00067 s-1.What is the order of this reaction and what is the rate constant?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A given first-order reaction has a rate constant of 0.00300 s-1.The time required for 85% reaction is
A)632 s.
B)23.5 s.
C)275 s.
D)316 s.
E)54.2 s.
A)632 s.
B)23.5 s.
C)275 s.
D)316 s.
E)54.2 s.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Given: A P rate = k[A] If 20% of A reacts in 5.12 min,calculate the time required for 90% of A to react.
A)52.8 min
B)1.05 min
C)2.42 min
D)3170 min
E)22.9 min
A)52.8 min
B)1.05 min
C)2.42 min
D)3170 min
E)22.9 min

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
For a given first-order reaction,after 230 s,33% of the reactants remain.Calculate the rate constant for the reaction.
A)207 s-1
B)0.00174 s-1
C)0.00209 s-1
D)0.000756 s-1
E)0.00482 s-1
A)207 s-1
B)0.00174 s-1
C)0.00209 s-1
D)0.000756 s-1
E)0.00482 s-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The rates of first-order and second-order reactions do not change with elapsed time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A first-order reaction has a half-life of 1.10 s.If the initial concentration of reactant is 0.384 M,how long will it take for the reactant concentration to reach 0.00100 M?
A)9.45 s
B)0.106 s
C)4.10 s
D)1.52 s
E)0.244 s
A)9.45 s
B)0.106 s
C)4.10 s
D)1.52 s
E)0.244 s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
A first-order reaction has a rate constant of 0.00300 s-1.The time required for 60% reaction is
A)153 s.
B)73.9 s.
C)170 s.
D)133 s.
E)305 s.
A)153 s.
B)73.9 s.
C)170 s.
D)133 s.
E)305 s.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Consider the reaction 2N2O(g) 2N2(g)+ O2(g)
Rate = k[N2O]
Calculate the time required for the concentration of N2O(g)to decrease from 0.75 M to 0.33 M.The rate constant for the reaction is k = 6.8 * 10-3 s-1.
A)2.7 min
B)1.7 min
C)0.87 min
D)0.92 min
E)2.0 min
Rate = k[N2O]
Calculate the time required for the concentration of N2O(g)to decrease from 0.75 M to 0.33 M.The rate constant for the reaction is k = 6.8 * 10-3 s-1.
A)2.7 min
B)1.7 min
C)0.87 min
D)0.92 min
E)2.0 min

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
A second-order reaction has a rate constant of 1.25 M-1.s-1.If the initial reactant concentration is 1.0 M,calculate the time required for 90% reaction.
A)1.3 s
B)7.2 s
C)0.13 s
D)17 s
E)0.89 s
A)1.3 s
B)7.2 s
C)0.13 s
D)17 s
E)0.89 s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Consider the reaction for the dimerization of butadiene(g)at a certain temperature.
2C4H6(g) C8H12(g)rate = k[C4H6]2.
When the initial concentration of butadiene is 0.500 M,the time required for 80% dimerization is measured at 11.4 s.What is the rate constant for the dimerization?
2C4H6(g) C8H12(g)rate = k[C4H6]2.
When the initial concentration of butadiene is 0.500 M,the time required for 80% dimerization is measured at 11.4 s.What is the rate constant for the dimerization?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
What is the half-life of a second order reaction?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
A reaction has k = 8.39 M-1.s-1.How long does it take for the reactant concentration to drop from 0.0840 M to 0.0220 M?
A)5.42 s
B)2.00 s
C)1.42 s
D)8.39 s
E)4.00 s
A)5.42 s
B)2.00 s
C)1.42 s
D)8.39 s
E)4.00 s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Given:
CH4(g)+ Cl2(g) CH3Cl(g)+ HCl(g)
The rate law for this elementary process is
A)rate = k[Cl2].
B)k[CH3Cl][HCl].
C)rate = k[CH4][Cl2].
D)rate = k[CH4].
E)rate = k[CH4]2.
CH4(g)+ Cl2(g) CH3Cl(g)+ HCl(g)
The rate law for this elementary process is
A)rate = k[Cl2].
B)k[CH3Cl][HCl].
C)rate = k[CH4][Cl2].
D)rate = k[CH4].
E)rate = k[CH4]2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
What is the rate constant for a first-order reaction with a half-life of 9.0 ms?
A)13 s-1
B)77 s-1
C)9.0 s-1
D)6.2 s-1
E)0.11 s-1
A)13 s-1
B)77 s-1
C)9.0 s-1
D)6.2 s-1
E)0.11 s-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
A certain reaction has a rate constant of 8.8 s-1 at 298 K and 140 s-1 at 323 K.What is the activation energy for this reaction?
A)38 kJ.mol-1
B)89 kJ.mol-1
C)120 kJ.mol-1
D)23 kJ.mol-1
E)1.2 kJ.mol-1
A)38 kJ.mol-1
B)89 kJ.mol-1
C)120 kJ.mol-1
D)23 kJ.mol-1
E)1.2 kJ.mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
For the reaction cyclobutane(g) 2ethylene(g)at 800 K,the half-life is 0.43 s.Calculate the time needed for the concentration of cyclobutane to fall to 1/64 of its initial value.
A)2.2 s
B)2.6 s
C)16 ms
D)0.38 s
E)0.43 s
A)2.2 s
B)2.6 s
C)16 ms
D)0.38 s
E)0.43 s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
A reaction that has a very low activation energy
A)has a rate that is very sensitive to temperature.
B)has a rate that does not change much with temperature.
C)must be second order.
D)gives a curved Arrhenius plot.
E)must be first order.
A)has a rate that is very sensitive to temperature.
B)has a rate that does not change much with temperature.
C)must be second order.
D)gives a curved Arrhenius plot.
E)must be first order.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The reaction [(CN)5CoOH2]2-(aq)+ SCN-(aq) [(CN)5CoSCN]3- + H2O(l)has the rate law,rate = k[(CN)5CoOH22-].Postulate a mechanism for this reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Consider the reaction
NOBr(g) NO(g)+ ½Br2(g)
A plot of [NOBr]-1 vs t gives a straight line with a slope of 2.00 M-1.s-1.The order of the reaction and the rate constant,respectively,are
A)second-order and 0.500 M-1.s-1
B)first-order and 2.00 s-1
C)second-order and 2.00 M-1.s-1
D)first-order and 0.241 s-1.
E)second-order and 16.6 M-1.s-1
NOBr(g) NO(g)+ ½Br2(g)
A plot of [NOBr]-1 vs t gives a straight line with a slope of 2.00 M-1.s-1.The order of the reaction and the rate constant,respectively,are
A)second-order and 0.500 M-1.s-1
B)first-order and 2.00 s-1
C)second-order and 2.00 M-1.s-1
D)first-order and 0.241 s-1.
E)second-order and 16.6 M-1.s-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
An elementary process has an activation energy of 92 kJ/mol.If the enthalpy change for the reaction is -62 kJ/mol,what is the activation energy for the reverse reaction?
A)154 kJ/mol
B)62 kJ/mol
C)92 kJ/mol
D)30 kJ/mol
A)154 kJ/mol
B)62 kJ/mol
C)92 kJ/mol
D)30 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The reaction profile for the reaction
[(CN)5CoOH2]2-(aq)+ SCN-(aq) [(CN)5CoSCN]3- + H2O(l)
is![The reaction profile for the reaction [(CN)<sub>5</sub>CoOH<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ SCN<sup>-</sup>(aq) \rightarrow [(CN)<sub>5</sub>CoSCN]<sup>3</sup><sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O(l) is Identify the structure of B.What do A and C represent?](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1441/11ea856c_40f4_3681_a343_131ed3782045_TB1441_00.jpg)
Identify the structure of B.What do A and C represent?
[(CN)5CoOH2]2-(aq)+ SCN-(aq) [(CN)5CoSCN]3- + H2O(l)
is
![The reaction profile for the reaction [(CN)<sub>5</sub>CoOH<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ SCN<sup>-</sup>(aq) \rightarrow [(CN)<sub>5</sub>CoSCN]<sup>3</sup><sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O(l) is Identify the structure of B.What do A and C represent?](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1441/11ea856c_40f4_3681_a343_131ed3782045_TB1441_00.jpg)
Identify the structure of B.What do A and C represent?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The activation energy of a reaction is given by
A)+(slope of a plot of lnk vs 1/T) R.
B)-(slope of a plot of lnk vs 1/T) R.
C)-R (slope of a plot of lnk vs 1/T).
D)+(slope of a plot of lnk vs 1/T)* R.
E)-(slope of a plot of lnk vs 1/T)* R.
A)+(slope of a plot of lnk vs 1/T) R.
B)-(slope of a plot of lnk vs 1/T) R.
C)-R (slope of a plot of lnk vs 1/T).
D)+(slope of a plot of lnk vs 1/T)* R.
E)-(slope of a plot of lnk vs 1/T)* R.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
For the reaction
HO(g)+ H2(g) H2O(g)+ H(g)
A plot of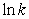 versus 1/T gives a straight line with a slope equal to -5.1 * 103 K.What is the activation energy for the reaction?
versus 1/T gives a straight line with a slope equal to -5.1 * 103 K.What is the activation energy for the reaction?
A)42 kJ.mol-1
B)98 kJ.mol-1
C)0.61 kJ.mol-1
D)5.1 kJ.mol-1
E)12 kJ.mol-1
HO(g)+ H2(g) H2O(g)+ H(g)
A plot of
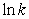 versus 1/T gives a straight line with a slope equal to -5.1 * 103 K.What is the activation energy for the reaction?
versus 1/T gives a straight line with a slope equal to -5.1 * 103 K.What is the activation energy for the reaction?A)42 kJ.mol-1
B)98 kJ.mol-1
C)0.61 kJ.mol-1
D)5.1 kJ.mol-1
E)12 kJ.mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
A catalyst facilitates a reaction by
A)increasing the activation energy for the reverse reaction.
B)lowering the activation energy of the reaction.
C)shifting the position of the equilibrium of the reaction.
D)decreasing the temperature at which the reaction will proceed spontaneously.
E)making the reaction more exothermic.
A)increasing the activation energy for the reverse reaction.
B)lowering the activation energy of the reaction.
C)shifting the position of the equilibrium of the reaction.
D)decreasing the temperature at which the reaction will proceed spontaneously.
E)making the reaction more exothermic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
The reaction 2NO(g)+ O2(g) 2NO2(g)has Hr = -114 kJ.mol-1.A possible mechanism for this reaction is
2NO(g)b N2O2(g)
rapid equilibrium,K
N2O2(g)+ O2(g) 2NO2(g)
slow,k
Draw the reaction profile diagram (plot of energy vs reaction coordinate)for this reaction and label any intermediates and activated complexes.
2NO(g)b N2O2(g)
rapid equilibrium,K
N2O2(g)+ O2(g) 2NO2(g)
slow,k
Draw the reaction profile diagram (plot of energy vs reaction coordinate)for this reaction and label any intermediates and activated complexes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
For the reaction cyclobutane(g) 2ethylene(g)at 800 K,a plot of ln[cyclobutane] vs t gives a straight line with a slope of -1.6 s-1.Calculate the time needed for the concentration of cyclobutane to fall to 1/16 of its initial value.
A)2.3 s
B)1.7 s
C)1.3 s
D)0.63 s
E)1.6 s
A)2.3 s
B)1.7 s
C)1.3 s
D)0.63 s
E)1.6 s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
What is the half-life of a reaction that has a rate constant of 280 s-1?
A)194 s
B)3.6 ms
C)404 ms
D)Because the concentration of reactant is not given,the calculation cannot be performed.
E)2.5 ms
A)194 s
B)3.6 ms
C)404 ms
D)Because the concentration of reactant is not given,the calculation cannot be performed.
E)2.5 ms

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Consider the dimerization reaction below:
2A A2
Rate = k[A]2
When the initial concentration of A is 2.0 M,it requires 30 min for 60% of A to react.Calculate the rate constant.
A)1.1 * 10-3 M-1.s-1
B)3.2 * 10-4 M-1.s-1
C)5.0 * 10-4 M-1.s-1
D)1.9* 10-4 M-1.s-1
E)4.2 * 10-4 M-1.s-1
2A A2
Rate = k[A]2
When the initial concentration of A is 2.0 M,it requires 30 min for 60% of A to react.Calculate the rate constant.
A)1.1 * 10-3 M-1.s-1
B)3.2 * 10-4 M-1.s-1
C)5.0 * 10-4 M-1.s-1
D)1.9* 10-4 M-1.s-1
E)4.2 * 10-4 M-1.s-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Consider the reaction
A + B C + D rate = k[A]2
The time it takes for [A] to decrease from 1.0 to 0.50 M is the same as the time it takes for [A] to decrease from0.50 to 0.25 M.
A + B C + D rate = k[A]2
The time it takes for [A] to decrease from 1.0 to 0.50 M is the same as the time it takes for [A] to decrease from0.50 to 0.25 M.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
The reaction between nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide is thought to occur by the mechanism 2NO2(g) NO3(g)+ NO(g)
K1,slow
NO3(g)+ CO(g) NO2(g)+ CO2(g)
K2,fast
The rate law for this mechanism is
A)rate = k1k2[NO2]2[CO].
B)rate = (k1/k2)[NO2]2[CO].
C)rate = k1[NO3][NO].
D)rate = k2[NO3][CO].
E)rate = k1[NO2]2.
K1,slow
NO3(g)+ CO(g) NO2(g)+ CO2(g)
K2,fast
The rate law for this mechanism is
A)rate = k1k2[NO2]2[CO].
B)rate = (k1/k2)[NO2]2[CO].
C)rate = k1[NO3][NO].
D)rate = k2[NO3][CO].
E)rate = k1[NO2]2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
The rate law for the following mechanism is Cl2(g) → 2Cl(g)
K1,fast
Cl(g)+ CO(g)![<strong>The rate law for the following mechanism is Cl<sub>2</sub>(g) → 2Cl(g) K<sub>1</sub>,fast Cl(g)+ CO(g) COCl(g) K<sub>2</sub>,fast COCl(g)+ Cl<sub>2</sub>(g) \rightarrow COCl<sub>2</sub>(g)+ Cl(g) K<sub>3</sub>,slow</strong> A)rate = k<sub>3</sub>K<sub>1</sub>0.5K<sub>2</sub>[CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1.5</sup>.<sup> </sup> B)rate = k<sub>3</sub>K<sub>1</sub>0.5K<sub>2</sub>[CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>0.5</sup>.<sup> </sup> C)rate = k<sub>3</sub>K<sub>1</sub>K<sub>2</sub>[CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]. D)rate = k<sub>3</sub>[COCl][Cl<sub>2</sub>]. E)rate = k<sub>3</sub>[COCl][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1.5</sup>.<sup> </sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1441/11ea856c_40f5_9614_a343_99f65f93dcbe_TB1441_11.jpg) COCl(g)
COCl(g)
K2,fast
COCl(g)+ Cl2(g) COCl2(g)+ Cl(g)
K3,slow
A)rate = k3K10.5K2[CO][Cl2]1.5.
B)rate = k3K10.5K2[CO][Cl2]0.5.
C)rate = k3K1K2[CO][Cl2].
D)rate = k3[COCl][Cl2].
E)rate = k3[COCl][Cl2]1.5.
K1,fast
Cl(g)+ CO(g)
![<strong>The rate law for the following mechanism is Cl<sub>2</sub>(g) → 2Cl(g) K<sub>1</sub>,fast Cl(g)+ CO(g) COCl(g) K<sub>2</sub>,fast COCl(g)+ Cl<sub>2</sub>(g) \rightarrow COCl<sub>2</sub>(g)+ Cl(g) K<sub>3</sub>,slow</strong> A)rate = k<sub>3</sub>K<sub>1</sub>0.5K<sub>2</sub>[CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1.5</sup>.<sup> </sup> B)rate = k<sub>3</sub>K<sub>1</sub>0.5K<sub>2</sub>[CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>0.5</sup>.<sup> </sup> C)rate = k<sub>3</sub>K<sub>1</sub>K<sub>2</sub>[CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]. D)rate = k<sub>3</sub>[COCl][Cl<sub>2</sub>]. E)rate = k<sub>3</sub>[COCl][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1.5</sup>.<sup> </sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1441/11ea856c_40f5_9614_a343_99f65f93dcbe_TB1441_11.jpg) COCl(g)
COCl(g)K2,fast
COCl(g)+ Cl2(g) COCl2(g)+ Cl(g)
K3,slow
A)rate = k3K10.5K2[CO][Cl2]1.5.
B)rate = k3K10.5K2[CO][Cl2]0.5.
C)rate = k3K1K2[CO][Cl2].
D)rate = k3[COCl][Cl2].
E)rate = k3[COCl][Cl2]1.5.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
In the Michaelis-Menten mechanism of enzyme reaction,the Michaelis constant,KM,is
A)KM = k1/k2.
B)KM = k1'/k2.
C)KM = (k1' + k2)/k1.
D)KM = k1' + k2.
E)KM = k1/k1'.
A)KM = k1/k2.
B)KM = k1'/k2.
C)KM = (k1' + k2)/k1.
D)KM = k1' + k2.
E)KM = k1/k1'.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
A possible mechanism for the reaction
2NO(g)+ O2(g) 2NO2(g)is: 2NO(g) →N2O2(g)
K1,k1',fast
N2O2(g)+ O2(g) 2NO2(g)
K2,slow
Application of the steady-state approximation gives
A)[N2O2] = 0.
B)k1[NO]2 -k2[N2O2][O2] = 0.
C)[N2O2] = (k1/k2)[NO]2.
D)k1[NO]2 -k1'[N2O2] - k2[N2O2][O2] = 0.
E)[N2O2] = (k1/k1')[NO]2.
2NO(g)+ O2(g) 2NO2(g)is: 2NO(g) →N2O2(g)
K1,k1',fast
N2O2(g)+ O2(g) 2NO2(g)
K2,slow
Application of the steady-state approximation gives
A)[N2O2] = 0.
B)k1[NO]2 -k2[N2O2][O2] = 0.
C)[N2O2] = (k1/k2)[NO]2.
D)k1[NO]2 -k1'[N2O2] - k2[N2O2][O2] = 0.
E)[N2O2] = (k1/k1')[NO]2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
The rate law for the following mechanism is NO2(g)+ F2(g) NO2F(g)+ F(g)
K1,slow
F(g)+ NO2(g) NO2F(g)
K2,fast
A)rate = k2[NO2]2.
B)rate = k2[NO2][F].
C)rate = k1[NO2][F2].
D)rate = k1k2[NO2]2.
E)rate = k1[NO2F][F].
K1,slow
F(g)+ NO2(g) NO2F(g)
K2,fast
A)rate = k2[NO2]2.
B)rate = k2[NO2][F].
C)rate = k1[NO2][F2].
D)rate = k1k2[NO2]2.
E)rate = k1[NO2F][F].

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
For the elementary reaction A + 2B products,rate = k[A][B].

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
For the reaction A products,the following data were collected. 
The half-life for this reaction is
A)0.521 s
B)0.752 s
C)0.922 s
D)1.08 s

The half-life for this reaction is
A)0.521 s
B)0.752 s
C)0.922 s
D)1.08 s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
For a zero-order reaction,the rate constant has the same units as the rate of reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
The reaction 2NO2(g) 2NO(g)+ O2(g)
Is postulated to occur via the mechanism
NO2(g)+ NO2(g) NO(g)+ NO3(g)
Slow
NO3(g) NO(g)+ O2(g)
Fast
An intermediate in this reaction is
A)NO2(g).
B)ON-NO3(g).
C)O2(g).
D)NO(g).
E)NO3(g).
Is postulated to occur via the mechanism
NO2(g)+ NO2(g) NO(g)+ NO3(g)
Slow
NO3(g) NO(g)+ O2(g)
Fast
An intermediate in this reaction is
A)NO2(g).
B)ON-NO3(g).
C)O2(g).
D)NO(g).
E)NO3(g).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
The reaction profile for the mechanism
NO2(g)+ F2(g) NO2F(g)+ F(g)slow
F(g)+ NO2(g) NO2F(g)fast
Shows
A)two maxima,the first maximum being the higher.
B)two maxima,the second maximum being the higher.
C)one maximum for the second step.
D)two maxima,both the same height.
NO2(g)+ F2(g) NO2F(g)+ F(g)slow
F(g)+ NO2(g) NO2F(g)fast
Shows
A)two maxima,the first maximum being the higher.
B)two maxima,the second maximum being the higher.
C)one maximum for the second step.
D)two maxima,both the same height.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
The reduction of M3+ by Cr2+ was studied with [Cr2+] 100 times the concentration of Cr2+.When [Cr2+] = 0.0050 M,the rate was 2.5 s-1.The rate constant for this reaction is
A)1.3 M-1·s-1
B)0.013 M-1·s-1
C)5.0 M-1·s-1
D)500 M-1·s-1
A)1.3 M-1·s-1
B)0.013 M-1·s-1
C)5.0 M-1·s-1
D)500 M-1·s-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
The HBr synthesis is thought to involve the following reactions:
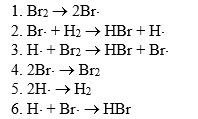
The chain propagation reactions in this mechanism are reactions
A)6.
B)1,2,3,and 6.
C)2 and 3.
D)1,2,and 3.
E)2,3,and 6.
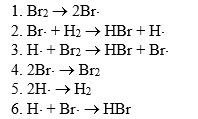
The chain propagation reactions in this mechanism are reactions
A)6.
B)1,2,3,and 6.
C)2 and 3.
D)1,2,and 3.
E)2,3,and 6.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
A possible mechanism for the reaction A + B + D E + F is
A + B → C
k1,k-1,fast
C + D E + F
k2
where C is a reactive intermediate present in very low concentrations.Calculate the steady state concentration of C in terms of the rate constants for the individual steps and the concentrations of the reactants.
A + B → C
k1,k-1,fast
C + D E + F
k2
where C is a reactive intermediate present in very low concentrations.Calculate the steady state concentration of C in terms of the rate constants for the individual steps and the concentrations of the reactants.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
The reaction 2NO(g)+ O2(g) 2NO2(g)has Hr = -114 kJ.mol-1.A possible mechanism for this reaction is 2NO(g) →N2O2(g)
Rapid equilibrium,K
N2O2(g)+ O2(g) 2NO2(g)
Slow,k
If the activation energy for the reverse reaction is 225 kJ.mol-1,what is the activation energy for the forward reaction?
A)Because an intermediate is involved,the forward activation energy cannot be calculated with the given information.
B)111 kJ.mol-1
C)339 kJ.mol-1
D)114 kJ.mol-1
E)55.5 kJ.mol-1
Rapid equilibrium,K
N2O2(g)+ O2(g) 2NO2(g)
Slow,k
If the activation energy for the reverse reaction is 225 kJ.mol-1,what is the activation energy for the forward reaction?
A)Because an intermediate is involved,the forward activation energy cannot be calculated with the given information.
B)111 kJ.mol-1
C)339 kJ.mol-1
D)114 kJ.mol-1
E)55.5 kJ.mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Given: A + B P rate = k[A][B] Which of the following is true?
A)k = ln 2/t1/2
B)ln [A]t = +kt + ln [A]o
C)[A]t = [A]o/(1 + kt[A]o)
D)1/[A]t = 1/kt
A)k = ln 2/t1/2
B)ln [A]t = +kt + ln [A]o
C)[A]t = [A]o/(1 + kt[A]o)
D)1/[A]t = 1/kt

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
The reaction 2A + B D + E has the rate law,rate = a[A]2[B]/(b + c[A])where a,b,and c are constants.The following mechanism has been proposed for this reaction.
A + B →
k1,k-1
I + A D + E
k2
I is an unstable intermediate present in minute concentrations.Show that this mechanism leads to the observed rate law and evaluate the constants a,b,and c in terms of the rate constants k1,k-1,and k2.
A + B →
k1,k-1
I + A D + E
k2
I is an unstable intermediate present in minute concentrations.Show that this mechanism leads to the observed rate law and evaluate the constants a,b,and c in terms of the rate constants k1,k-1,and k2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
The rate law for a reaction can be determined from the coefficients in the overall reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
The HBr synthesis is thought to involve the following reactions:
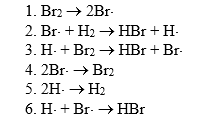
The chain termination reactions in this mechanism are reactions
A)3,4,and 5.
B)4 and 5.
C)4,5,and 6.
D)6.
E)3 and 4.
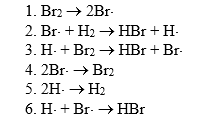
The chain termination reactions in this mechanism are reactions
A)3,4,and 5.
B)4 and 5.
C)4,5,and 6.
D)6.
E)3 and 4.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
The rate law for the following mechanism is ClO-(aq)+ H2O(l) →HOCl(aq)+ OH-(aq)
K,fast
I-(aq)+ HOCl(aq) HOI(aq)+ Cl-(aq)
K1,slow
HOI(aq)+ OH-(aq) OI-(aq)+ H2O(l)
K2,fast
A)rate = k1[I-][HOCl].
B)rate = k1K[ClO-][I-][OH-].
C)rate = k1K[ClO-][I-][OH-]-1.
D)rate = k1k2K[ClO-][I-].
E)rate = k1K[ClO-][I-].
K,fast
I-(aq)+ HOCl(aq) HOI(aq)+ Cl-(aq)
K1,slow
HOI(aq)+ OH-(aq) OI-(aq)+ H2O(l)
K2,fast
A)rate = k1[I-][HOCl].
B)rate = k1K[ClO-][I-][OH-].
C)rate = k1K[ClO-][I-][OH-]-1.
D)rate = k1k2K[ClO-][I-].
E)rate = k1K[ClO-][I-].

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 93 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








