Deck 8: Perfect Competition
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/124
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Perfect Competition
1
Part of the ACCC's role is to:
A) improve efficiency in markets by promoting competitive pricing.
B) encourage adherence to fair trading practices.
C) inform the public about the Trade Practices Act.
D) do all the above.
A) improve efficiency in markets by promoting competitive pricing.
B) encourage adherence to fair trading practices.
C) inform the public about the Trade Practices Act.
D) do all the above.
D
2
Assume that the market equilibrium is 100 units at the price of $70. What is the price each firm can charge if each produces 10 units of output?
A) $7
B) $0.7
C) $70
D) $700
A) $7
B) $0.7
C) $70
D) $700
C
3
Marginal analysis is used to determine:
A) the maximum profit by comparing maximum revenue and marginal cost.
B) the profit maximising output.
C) the market price resulting from a one unit change in output.
D) the change in the total cost as the price changes.
A) the maximum profit by comparing maximum revenue and marginal cost.
B) the profit maximising output.
C) the market price resulting from a one unit change in output.
D) the change in the total cost as the price changes.
B
4
Because a competitive firm is a price taker, it:
A) can set its own prices.
B) faces a demand curve that is relatively inelastic.
C) enjoys high barriers to entry.
D) faces a demand curve that is perfectly elastic.
A) can set its own prices.
B) faces a demand curve that is relatively inelastic.
C) enjoys high barriers to entry.
D) faces a demand curve that is perfectly elastic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The body charged with increasing or maintaining competition in the Australian economy is:
A) the ACCC.
B) the Treasury.
C) the Reserve Bank of Australia.
D) the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority.
A) the ACCC.
B) the Treasury.
C) the Reserve Bank of Australia.
D) the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
In a perfectly competitive market, firms:
A) produce a differentiated product.
B) can enter free but exit is costly.
C) extensively advertise to attract more buyers.
D) produce a homogeneous product.
A) produce a differentiated product.
B) can enter free but exit is costly.
C) extensively advertise to attract more buyers.
D) produce a homogeneous product.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Under perfect competition, no matter how much output is produced, the total revenue curve is a:
A) positively sloped line.
B) negatively sloped line.
C) horizontal straight line.
D) U-shaped curve.
A) positively sloped line.
B) negatively sloped line.
C) horizontal straight line.
D) U-shaped curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
A) There is a large number of small firms.
B) Firms sell a homogeneous product.
C) Firms can easily enter or exit the market.
D) Firms are price makers, not price takers.
A) There is a large number of small firms.
B) Firms sell a homogeneous product.
C) Firms can easily enter or exit the market.
D) Firms are price makers, not price takers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
If a perfectly competitive firm sells 50 units of output at a market price of $10 per unit, its marginal revenue is:
A) more than $10.
B) less than $10.
C) $10.
D) $5300.
A) more than $10.
B) less than $10.
C) $10.
D) $5300.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which of the following is not a characteristic of perfect competition?
A) Ease of entry and exit.
B) A few large firms dominate the market.
C) The product is homogeneous.
D) There are many buyers.
A) Ease of entry and exit.
B) A few large firms dominate the market.
C) The product is homogeneous.
D) There are many buyers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Under perfect competition, which of the following are the same (equal) at all levels of output?
A) Market price and marginal cost.
B) Market price and marginal revenue.
C) Marginal cost and marginal revenue.
D) Total cost and total revenue.
A) Market price and marginal cost.
B) Market price and marginal revenue.
C) Marginal cost and marginal revenue.
D) Total cost and total revenue.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
If a firm can easily enter and exit the market it operates in which market?
A) Perfectly competitive.
B) Monopolistically competitive.
C) Monopolistic.
D) Oligopolistic.
A) Perfectly competitive.
B) Monopolistically competitive.
C) Monopolistic.
D) Oligopolistic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Perfectly competitive markets are characterised by:
A) a large number of producers and consumers.
B) very strong barriers to entry and exit.
C) firms selling a quality product.
D) many different products.
A) a large number of producers and consumers.
B) very strong barriers to entry and exit.
C) firms selling a quality product.
D) many different products.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
One of the characteristics of perfect competition is that:
A) some firms can influence price.
B) firms depend on each other in setting the output.
C) firms produce a differentiated product.
D) consumers do not distinguish between the sellers.
A) some firms can influence price.
B) firms depend on each other in setting the output.
C) firms produce a differentiated product.
D) consumers do not distinguish between the sellers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Firms in a perfectly competitive market:
A) compete with each other by undercutting the prices.
B) compete with each other by offering customers a slightly different product.
C) reduce the output so they can increase the price.
D) do not advertise.
A) compete with each other by undercutting the prices.
B) compete with each other by offering customers a slightly different product.
C) reduce the output so they can increase the price.
D) do not advertise.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Under perfect competition, a firm is a price taker because:
A) setting a price higher than the going price results in profits.
B) each firm's product is perceived as different.
C) each firm has a significant market share.
D) setting a price higher than the marginal cost results in zero sales.
A) setting a price higher than the going price results in profits.
B) each firm's product is perceived as different.
C) each firm has a significant market share.
D) setting a price higher than the marginal cost results in zero sales.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
A firm operating in a perfectly competitive market is a price taker because:
A) the firm has a significant market share.
B) every firm sells slightly different product.
C) it can set a price higher than the average market price.
D) it cannot influence the price.
A) the firm has a significant market share.
B) every firm sells slightly different product.
C) it can set a price higher than the average market price.
D) it cannot influence the price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Perfect competition requires that resources be:
A) the highest quality for consumers.
B) fixed over the short run but free over the long run.
C) completely mobile to freely enter or exit the market.
D) completely unmovable and enjoy the economies of scale.
A) the highest quality for consumers.
B) fixed over the short run but free over the long run.
C) completely mobile to freely enter or exit the market.
D) completely unmovable and enjoy the economies of scale.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
One of the characteristics of the perfectly competitive market is:
A) a small number of large firms.
B) firms that sell a heterogeneous product.
C) sellers and buyers both can increase the price on the market.
D) there is a large number of small firms.
A) a small number of large firms.
B) firms that sell a heterogeneous product.
C) sellers and buyers both can increase the price on the market.
D) there is a large number of small firms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Under perfect competition, which of the following determine the market equilibrium?
A) Price and marginal cost.
B) Both demand and supply.
C) Marginal cost and average revenue.
D) Total cost and a number of suppliers.
A) Price and marginal cost.
B) Both demand and supply.
C) Marginal cost and average revenue.
D) Total cost and a number of suppliers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
A perfectly competitive firm has control over:
A) the number of firms in the market.
B) market conditions.
C) the price at which to sell.
D) the quantity of output to produce.
A) the number of firms in the market.
B) market conditions.
C) the price at which to sell.
D) the quantity of output to produce.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.2 Cost per unit curves 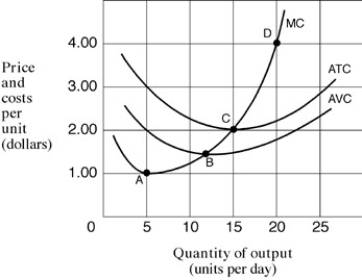
-As shown in Exhibit 7.2, the firm will produce in the short run if the price is at least equal to:
A) $1 per unit.
B) $1.50 per unit.
C) $2 per unit.
D) $3 per unit.

-As shown in Exhibit 7.2, the firm will produce in the short run if the price is at least equal to:
A) $1 per unit.
B) $1.50 per unit.
C) $2 per unit.
D) $3 per unit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.1 Total revenue and total cost graph 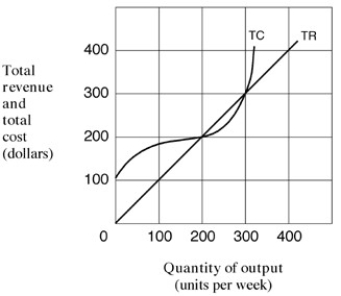
-In Exhibit 7.1, economic profit for the firm is at a maximum when output per week equals:
A) 0 units.
B) 100 units.
C) 200 units.
D) 250 units.

-In Exhibit 7.1, economic profit for the firm is at a maximum when output per week equals:
A) 0 units.
B) 100 units.
C) 200 units.
D) 250 units.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.2 Cost per unit curves 
-In Exhibit 7.2, if the price of the firm's product is $3 per unit, the firm will:
A) suffer a loss.
B) enjoy a profit.
C) be indifferent about whether to produce or not to produce.
D) have to increase the levels of production.

-In Exhibit 7.2, if the price of the firm's product is $3 per unit, the firm will:
A) suffer a loss.
B) enjoy a profit.
C) be indifferent about whether to produce or not to produce.
D) have to increase the levels of production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.3 A firm's cost and marginal revenue curves 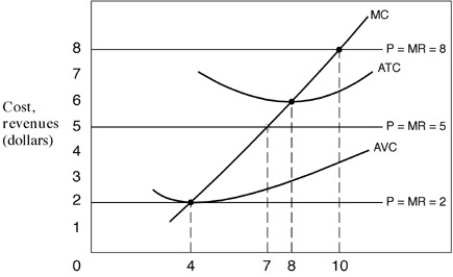
-In Exhibit 7.3, when the price is $2, the profit-maximising (or loss-minimising) firm:
A) should shut down and produce zero.
B) should produce output equal to four.
C) is making an economic profit of $8.
D) should try to produce more output.

-In Exhibit 7.3, when the price is $2, the profit-maximising (or loss-minimising) firm:
A) should shut down and produce zero.
B) should produce output equal to four.
C) is making an economic profit of $8.
D) should try to produce more output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.1 Total revenue and total cost graph 
-In Exhibit 7.1, if output is 200 units per week, economic profit for the firm is:
A) zero.
B) at its minimum.
C) at its maximum.
D) average.

-In Exhibit 7.1, if output is 200 units per week, economic profit for the firm is:
A) zero.
B) at its minimum.
C) at its maximum.
D) average.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
A perfectly competitive firm minimises losses in the short run by producing at the output level at which:
A) total loss is a minimum.
B) total revenue equals marginal cost.
C) total revenue is at a minimum.
D) marginal cost is less than marginal revenue.
A) total loss is a minimum.
B) total revenue equals marginal cost.
C) total revenue is at a minimum.
D) marginal cost is less than marginal revenue.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.2 Cost per unit curves 
-As shown in Exhibit 7.2, the price at which the firm earns zero economic profit in the short run is:
A) $1 per unit.
B) $1.50 per unit.
C) $4 per unit.
D) $2 per unit.

-As shown in Exhibit 7.2, the price at which the firm earns zero economic profit in the short run is:
A) $1 per unit.
B) $1.50 per unit.
C) $4 per unit.
D) $2 per unit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.3 A firm's cost and marginal revenue curves 
-In Exhibit 7.3, when the price is $5, the firm:
A) is making an economic profit of $21.
B) should produce output equal to seven.
C) is breaking even.
D) should shut down.

-In Exhibit 7.3, when the price is $5, the firm:
A) is making an economic profit of $21.
B) should produce output equal to seven.
C) is breaking even.
D) should shut down.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Assume that a firm's marginal revenue just barely exceeds marginal cost. What should the firm do under these conditions?
A) Expand output.
B) Contract output.
C) Maintain output.
D) There is insufficient information to answer the question.
A) Expand output.
B) Contract output.
C) Maintain output.
D) There is insufficient information to answer the question.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
A firm in a perfectly competitive market faces:
A) its own upward-sloping demand curve.
B) its own downward-sloping demand curve.
C) a market demand curve.
D) a perfectly elastic demand curve.
A) its own upward-sloping demand curve.
B) its own downward-sloping demand curve.
C) a market demand curve.
D) a perfectly elastic demand curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.2 Cost per unit curves 
-In Exhibit 7.2, if the price of the firm's product is $2.00 per unit, the firm will produce:
A) five units per day.
B) 10 units per day.
C) 15 units per day.
D) 20 units per day.

-In Exhibit 7.2, if the price of the firm's product is $2.00 per unit, the firm will produce:
A) five units per day.
B) 10 units per day.
C) 15 units per day.
D) 20 units per day.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.1 Total revenue and total cost graph 
-In Exhibit 7.1, the firm will produce at which level of output:
A) zero.
B)150.
C)350.
D) 250.

-In Exhibit 7.1, the firm will produce at which level of output:
A) zero.
B)150.
C)350.
D) 250.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
In the short run, if a perfectly competitive firm is producing at a price above average total cost, its economic profit must be:
A) positive.
B) zero.
C) negative.
D) normal.
A) positive.
B) zero.
C) negative.
D) normal.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.1 Total revenue and total cost graph 
-In Exhibit 7.1, if output is between 100 and 200 units per week, economic profit for the firm is:
A) zero.
B) negative or zero.
C) at its maximum.
D) positive or zero.

-In Exhibit 7.1, if output is between 100 and 200 units per week, economic profit for the firm is:
A) zero.
B) negative or zero.
C) at its maximum.
D) positive or zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
A perfectly competitive firm in the short run maximises its profit by producing the output where:
A) average cost equals price.
B) marginal product equals marginal revenue.
C) total profit is at maximum.
D) total profit is at minimum.
A) average cost equals price.
B) marginal product equals marginal revenue.
C) total profit is at maximum.
D) total profit is at minimum.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Total revenue is computed as:
A) the product price times the quantity.
B) the product cost times the quantity.
C) the product price minus the product cost.
D) the product marginal cost times the price.
A) the product price times the quantity.
B) the product cost times the quantity.
C) the product price minus the product cost.
D) the product marginal cost times the price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Assume the market equilibrium price is $100. In a perfectly competitive market, some firms can sell a good at the price of $120 and:
A) undercut their competitors.
B) therefore they can influence the price.
C) force their competitors to reduce output.
D) risk selling zero output.
A) undercut their competitors.
B) therefore they can influence the price.
C) force their competitors to reduce output.
D) risk selling zero output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
A perfectly competitive firm always set the price:
A) equal to market cost of production.
B) below the equilibrium market price.
C) above the equilibrium market price.
D) equal to the equilibrium market price.
A) equal to market cost of production.
B) below the equilibrium market price.
C) above the equilibrium market price.
D) equal to the equilibrium market price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
A sandwich shop owner has the following information: P = $4, ATC = $2, AVC = $1, MC = 4 and Q = 500. From this, she can determine:
A) her profits are not being maximised.
B) she has earned zero economic profits.
C) she has earned economic profits of $1000.
D) she has earned economic profits of $1500.
A) her profits are not being maximised.
B) she has earned zero economic profits.
C) she has earned economic profits of $1000.
D) she has earned economic profits of $1500.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.3 A firm's cost and marginal revenue curves 
-In Exhibit 7.3, when the output is eight units, the firm:
A) has a profit.
B) should not operate.
C) should ask for a higher price.
D) should produce more.
E) is operating at the minimum ATC.

-In Exhibit 7.3, when the output is eight units, the firm:
A) has a profit.
B) should not operate.
C) should ask for a higher price.
D) should produce more.
E) is operating at the minimum ATC.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Consider a firm with the following cost and revenue information: ATC = $8, AVC = $6, MR = $6 and MC = $6. If the firm produces Q = 60 units in the short run, it:
A) is minimising losses.
B) makes a total loss of $60.
C) should produce more output.
D) is indifferent concerning whether to keep operating or shut down.
A) is minimising losses.
B) makes a total loss of $60.
C) should produce more output.
D) is indifferent concerning whether to keep operating or shut down.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
If the price of a product falls below average total cost in the short run, the firm:
A) has an economic profit.
B) cannot cover total fixed costs.
C) experiences a loss.
D) must always shut down.
A) has an economic profit.
B) cannot cover total fixed costs.
C) experiences a loss.
D) must always shut down.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.4 Marginal revenue and cost per unit curves 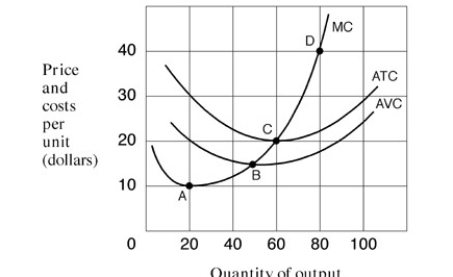
-As shown in Exhibit 7.4, the short-run supply curve for the firm corresponds to which segment of its marginal cost curve?
A) C and all points above.
B) B and all points above.
C) A and all points above.
D) A to C only.

-As shown in Exhibit 7.4, the short-run supply curve for the firm corresponds to which segment of its marginal cost curve?
A) C and all points above.
B) B and all points above.
C) A and all points above.
D) A to C only.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
If there is no level of output at which the firm earns a profit, the firm should:
A) shut down.
B) perform an analysis regarding whether to operate or not.
C) diversify.
D) try to push the price up.
A) shut down.
B) perform an analysis regarding whether to operate or not.
C) diversify.
D) try to push the price up.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Assume that the market price is $10 and the minimum AVC is $15. The firm should:
A) increase production.
B) continue to operate at the same level.
C) decrease production.
D) shut down.
A) increase production.
B) continue to operate at the same level.
C) decrease production.
D) shut down.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
If a competitive firm suffers loss, it should:
A) always shut down.
B) shut down if its losses are greater than total fixed costs.
C) shut down if its total fixed costs are greater than losses.
D) raise its price.
A) always shut down.
B) shut down if its losses are greater than total fixed costs.
C) shut down if its total fixed costs are greater than losses.
D) raise its price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
If ATC = $20, AVC = $12, MR = $15 and MC = $15, then the result for the perfectly competitive firm would be:
A) making a short-run loss.
B) making a short-run profit.
C) breaking even.
D) shutting down.
A) making a short-run loss.
B) making a short-run profit.
C) breaking even.
D) shutting down.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
If the market price is equal to the average variable cost, the firm should:
A) keep operating or shut down.
B) increase the output.
C) change fixed inputs.
D) increase the price.
A) keep operating or shut down.
B) increase the output.
C) change fixed inputs.
D) increase the price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
At an output level of 100 units, TC = $1000, TVC = $500, MC = $3 and MR = $3, the short-run result/s for the perfectly competitive firm will be:
A) making a short-run loss of $500.
B) breaking even, as MC = MR.
C) shutting down and incurring a loss of $1000.
D) making a loss of $1000 but continuing to operate.
A) making a short-run loss of $500.
B) breaking even, as MC = MR.
C) shutting down and incurring a loss of $1000.
D) making a loss of $1000 but continuing to operate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
If ATC = $20, AVC = $15, AFC = $5, MC = $15 and MR = $15, then a perfectly competitive firm should:
A) decrease output because MR> AFC.
B) increase output because ATC > MR.
C) shut down if the price will be below AVC.
D) maximize its profit because MR = MC.
A) decrease output because MR> AFC.
B) increase output because ATC > MR.
C) shut down if the price will be below AVC.
D) maximize its profit because MR = MC.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
If ATC = $10, AVC = $8, market price = $25 and MC = $25, then the result for a perfectly competitive firm will:
A) be making a short-run loss.
B) be making a short-run profit.
C) be breaking even.
D) be shutting down.
A) be making a short-run loss.
B) be making a short-run profit.
C) be breaking even.
D) be shutting down.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The firm in a perfectly competitive market will:
A) set the price lower than the variable cost of producing the product or service to gain a market share.
B) set the price higher than the fixed cost of producing the product or service but lower than the variable cost to prevent competition.
C) set the price as low as possible to prevent competition.
D) set the price higher than the variable cost of producing the product or service.
A) set the price lower than the variable cost of producing the product or service to gain a market share.
B) set the price higher than the fixed cost of producing the product or service but lower than the variable cost to prevent competition.
C) set the price as low as possible to prevent competition.
D) set the price higher than the variable cost of producing the product or service.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.4 Marginal revenue and cost per unit curves 
-As shown in Exhibit 7.4, the firm will produce in the short run if the price per unit is at least equal to:
A) $10.
B) $15.
C) $20.
D) $30.

-As shown in Exhibit 7.4, the firm will produce in the short run if the price per unit is at least equal to:
A) $10.
B) $15.
C) $20.
D) $30.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
If a firm is operating at a loss in the short run and finds that its price is greater than average variable cost, then in the short run:
A) it should produce where MR = MC.
B) it should produce zero output.
C) it should go out of business.
D) total revenue is less than total variable costs.
A) it should produce where MR = MC.
B) it should produce zero output.
C) it should go out of business.
D) total revenue is less than total variable costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
If a firm's MR currently equals MC and product price = $24, AVC = $22 and ATC = $26, then in the long run this firm:
A) will continue to operate at a loss.
B) will earn a positive profit.
C) will go out of business.
D) should increase output.
A) will continue to operate at a loss.
B) will earn a positive profit.
C) will go out of business.
D) should increase output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Suppose the market demand for second-hand books has decreased to the level less than the average total cost. The firm will:
A) reduce its losses to zero.
B) produce at the output level where ATC = MC.
C) produce at the level of output that keeps its losses to a minimum.
D) increase its output to make up for losses.
A) reduce its losses to zero.
B) produce at the output level where ATC = MC.
C) produce at the level of output that keeps its losses to a minimum.
D) increase its output to make up for losses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
At an output level of 500 units, ATC = $10, AVC = $5, MR = $3 and MC = $3, the result for the perfectly competitive firm will be:
A) making a loss of ($5 - $3) 500 = $1000.
B) a decrease in output, so MC > MR.
C) making a short-run loss of $2500.
D) an increased output, so MR > MC.
A) making a loss of ($5 - $3) 500 = $1000.
B) a decrease in output, so MC > MR.
C) making a short-run loss of $2500.
D) an increased output, so MR > MC.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
If ATC = $25, AVC = $20, TFC = $600, MR = $15 and MC = $15, then the result for the perfectly competitive firm will be:
A) a loss of $10 per unit.
B) a loss of $600.
C) continuing to operate because it covers its variable costs.
D) breaking even because MR = MC.
A) a loss of $10 per unit.
B) a loss of $600.
C) continuing to operate because it covers its variable costs.
D) breaking even because MR = MC.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The firm in a perfectly competitive market will:
A) set the price as high as possible to make maximum profit.
B) use different rules for loss minimisation and for profit maximisation.
C) use non-price competition techniques like advertising to sell more.
D) try to keep the average total cost below the market price.
A) set the price as high as possible to make maximum profit.
B) use different rules for loss minimisation and for profit maximisation.
C) use non-price competition techniques like advertising to sell more.
D) try to keep the average total cost below the market price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.8 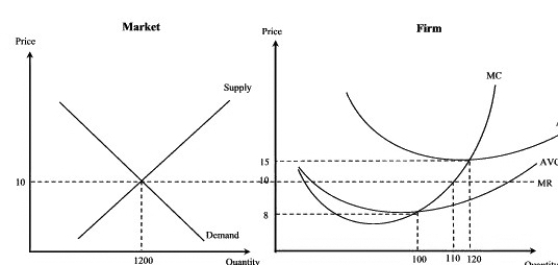
-According to Exhibit 7.8, the output level of the short-run equilibrium for this firm is:
A)1200.
B)100.
C)110.
D) 120.

-According to Exhibit 7.8, the output level of the short-run equilibrium for this firm is:
A)1200.
B)100.
C)110.
D) 120.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
As the marginal revenue curve moves upward the perfectly competitive firm will:
A) change the selection of products it offers to the customers.
B) change its output and will be able to charge a higher price.
C) change its output but will not be able to change the price.
D) change its price and will not change its output.
A) change the selection of products it offers to the customers.
B) change its output and will be able to charge a higher price.
C) change its output but will not be able to change the price.
D) change its price and will not change its output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
A perfectly competitive firm's short-run supply curve is the:
A) average total cost curve.
B) demand curve above the marginal revenue curve.
C) same as the market supply curve.
D) marginal cost curve above the average variable cost curve.
A) average total cost curve.
B) demand curve above the marginal revenue curve.
C) same as the market supply curve.
D) marginal cost curve above the average variable cost curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.7 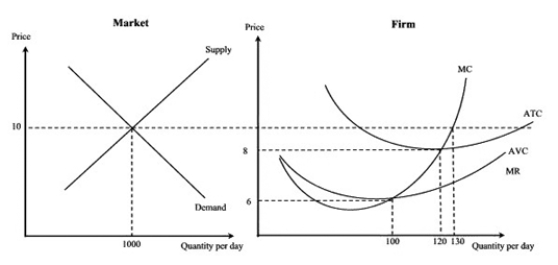
-According to Exhibit 7.7, the short-run equilibrium output level for this perfectly competitive firm is:
A)1000.
B)100.
C)120.
D) 130.

-According to Exhibit 7.7, the short-run equilibrium output level for this perfectly competitive firm is:
A)1000.
B)100.
C)120.
D) 130.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
The perfectly competitive industry's short-run market supply curve is the sum of:
A) the outputs that each of the firms will supply at the highest price.
B) the outputs that each of the firms will supply at the lowest price.
C) the outputs that each of the firms will supply at the price below average variable cost.
D) the outputs that each of the firms will supply at each possible price.
A) the outputs that each of the firms will supply at the highest price.
B) the outputs that each of the firms will supply at the lowest price.
C) the outputs that each of the firms will supply at the price below average variable cost.
D) the outputs that each of the firms will supply at each possible price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.5 Short-run profit and loss 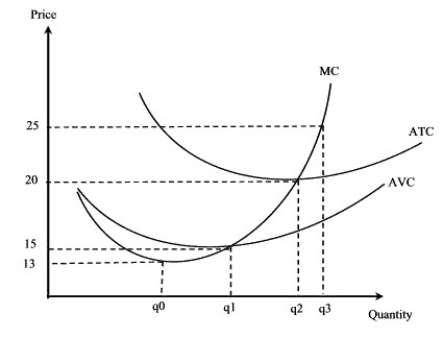
-According to Exhibit 7.5, this firm will be making a short-run loss, but will continue to produce when the price is:
A) between $15 and $20.
B) between $25 and $13.
C) between $20 and $25.
D) between $15 and $13.

-According to Exhibit 7.5, this firm will be making a short-run loss, but will continue to produce when the price is:
A) between $15 and $20.
B) between $25 and $13.
C) between $20 and $25.
D) between $15 and $13.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
For a perfectly competitive firm, short-run equilibrium is determined by:
A) the point where P = MC.
B) the point where P = ATC.
C) the point where P = AVC.
D) the point where MC = ATC.
A) the point where P = MC.
B) the point where P = ATC.
C) the point where P = AVC.
D) the point where MC = ATC.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
How long will the state of short-run equilibrium remain unchanged?
A) Forever.
B) Until some factors change.
C) Six months.
D) One year.
A) Forever.
B) Until some factors change.
C) Six months.
D) One year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.5 Short-run profit and loss 
-According to Exhibit 7.5, a perfectly competitive firm will be making a short-run loss but still keep operating if price drops below:
A) $20.
B) $15.
C) $13.
D) $25.

-According to Exhibit 7.5, a perfectly competitive firm will be making a short-run loss but still keep operating if price drops below:
A) $20.
B) $15.
C) $13.
D) $25.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.6 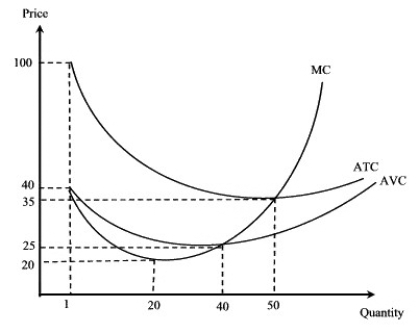
-According to Exhibit 7.6, if MR = $20, the result for a perfectly competitive firm will be:
A) making a short-run profit.
B) making a short-run loss of $10 per unit.
C) making a short-run loss.
D) making a short-run loss of $5

-According to Exhibit 7.6, if MR = $20, the result for a perfectly competitive firm will be:
A) making a short-run profit.
B) making a short-run loss of $10 per unit.
C) making a short-run loss.
D) making a short-run loss of $5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Above the shutdown point, a competitive firm's supply curve coincides with its:
A) marginal revenue curve.
B) marginal cost curve.
C) average variable cost curve.
D) average total cost curve.
A) marginal revenue curve.
B) marginal cost curve.
C) average variable cost curve.
D) average total cost curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.7 
-Refer to Exhibit 7.7. The short-run results for this firm are:
A) a positive economic profit.
B) a normal profit.
C) a quasi-loss.
D) such a large loss it should shut down.

-Refer to Exhibit 7.7. The short-run results for this firm are:
A) a positive economic profit.
B) a normal profit.
C) a quasi-loss.
D) such a large loss it should shut down.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.6 
-Refer to Exhibit 7.6. If market price is $22, the firm should:
A) increase the price.
B) increase the output.
C) decrease the output.
D) shut down.
E) continue to operate.

-Refer to Exhibit 7.6. If market price is $22, the firm should:
A) increase the price.
B) increase the output.
C) decrease the output.
D) shut down.
E) continue to operate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.7 
-According to Exhibit 7.7, the firm's short-run economic profit will be:
A) zero.
B) $260.
C) $520.
D) indeterminate from the information given.

-According to Exhibit 7.7, the firm's short-run economic profit will be:
A) zero.
B) $260.
C) $520.
D) indeterminate from the information given.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
The market curve derived for the perfectly competitive market is based on the following assumptions:
A) input prices remain unchanged as output expands.
B) output prices remain unchanged as output expands.
C) input prices reduce as output expands.
D) input prices increase as output expands.
A) input prices remain unchanged as output expands.
B) output prices remain unchanged as output expands.
C) input prices reduce as output expands.
D) input prices increase as output expands.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
A perfectly competitive industry's short-run market supply curve is derived from:
A) horizontal summation of the short-run supply curves of major firms in the industry.
B) horizontal summation of the long-run supply curves of all firms in the industry.
C) vertical summation of the short-run supply curves of all firms in the industry.
D) horizontal summation of the short-run supply curves of all firms in the industry.
A) horizontal summation of the short-run supply curves of major firms in the industry.
B) horizontal summation of the long-run supply curves of all firms in the industry.
C) vertical summation of the short-run supply curves of all firms in the industry.
D) horizontal summation of the short-run supply curves of all firms in the industry.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
A perfectly competitive firm's supply curve follows the upward-sloping segment of its marginal cost curve above the:
A) average total cost curve.
B) average variable cost curve.
C) average fixed curve.
D) average price curve.
A) average total cost curve.
B) average variable cost curve.
C) average fixed curve.
D) average price curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
A perfectly competitive firm's short-run supply curve is the part of its marginal cost curve that is:
A) upward-sloping.
B) above its average variable cost.
C) above the average fixed cost.
D) below the average fixed cost.
A) upward-sloping.
B) above its average variable cost.
C) above the average fixed cost.
D) below the average fixed cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.5 Short-run profit and loss 
-According to Exhibit 7.5, if the price of the good is $17, then the result for the perfectly competitive firm will be:
A) making a long-run profit.
B) making a long-run loss and so it will shut down.
C) making a short-run loss but it will continue to produce.
D) making a normal profit.
E) indeterminate.

-According to Exhibit 7.5, if the price of the good is $17, then the result for the perfectly competitive firm will be:
A) making a long-run profit.
B) making a long-run loss and so it will shut down.
C) making a short-run loss but it will continue to produce.
D) making a normal profit.
E) indeterminate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Narrbegin Exhibit 7.7 
-According to Exhibit 7.7, given the short-run equilibrium of this firm, we would expect in the long run:
A) the market supply curve to shift to the left.
B) the price to increase.
C) firms to exit the industry.
D) new firms to enter the industry.

-According to Exhibit 7.7, given the short-run equilibrium of this firm, we would expect in the long run:
A) the market supply curve to shift to the left.
B) the price to increase.
C) firms to exit the industry.
D) new firms to enter the industry.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 124 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








