Deck 12: Improving Air Quality: Controlling Stationary Sources
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/47
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 12: Improving Air Quality: Controlling Stationary Sources
1
The Acid Rain Program (ARP) was defined in Title II of the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990.
False
2
Relative to mobile sources, stationary sources are bigger emitters of sulfur oxides.
True
3
Under a bubble policy, a facility is allowed to measure its emissions as an average of all releases from that facility.
True
4
Major sources of SO2 emissions are automobiles and other mobile sources.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
NOX contributes both to acid rain and to the formation of ground-level ozone.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Of the two major pollutants responsible for acid rain, sulfur dioxide (SO2) is the more significant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
RECLAIM is a California trading program that used trading credits in a regional market for sulfur oxide and nitrogen oxide.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Stationary source emissions are controlled primarily through the use of technology-based standards.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
China's acid rain problem is relatively minor because it is among the lowest consumers of coal in the world.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Acidic compounds are formed from a chemical reaction in the earth's atmosphere, involving sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, water vapor, and oxidants.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
According to the Clean Air Act, the newly GHG emissions standards on mobile sources triggered regulatory requirements for stationary sources.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The Clean Air Interstate Rule (CAIR) included an annual SO2 trading program.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Because NOX readily moves across state borders, a series of interstate collaborations formed over time to address the problem, but none established a trading program.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Emissions limits applicable to new and modified stationary sources are known as New Source Performance Standards (NSPS).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Two new NOX cap-and-trade programs were launched under the Clean Air Interstate Rule (CAIR).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Technology-based standards used to control new sources are more lenient than those used to control existing stationary sources.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Emissions limits used for nonattainment areas are more stringent than those used for PSD areas.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Under the Acid Rain Program (ARP) as initially outlined in the CAAA of 1990, a cap-and-trade allowance program was established for both SO2 and NOX.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Acid rain is a local pollution problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Under the cap-and-trade program established under Title IV of the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990, a permanent annual cap for SO2 was set and tradeable SO2 allowances were issued to stationary sources.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
New Source Performance Standards (NSPS)
A) were revoked by the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990
B) are applicable to new and modified stationary sources
C) are performance-based standards defined by the EPA
D) are more lenient than emissions limits for existing sources
E) none of the above
A) were revoked by the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990
B) are applicable to new and modified stationary sources
C) are performance-based standards defined by the EPA
D) are more lenient than emissions limits for existing sources
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
RECLAIM refers to
A) one of the first state-level trading programs, which was developed in California
B) a federal program for stationary sources to earn credits for reducing pollution
C) a national program to refurbish older, polluting refineries
D) the claiming of SO2 allowances that have been banked in a prior period
A) one of the first state-level trading programs, which was developed in California
B) a federal program for stationary sources to earn credits for reducing pollution
C) a national program to refurbish older, polluting refineries
D) the claiming of SO2 allowances that have been banked in a prior period

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Primary sources of SO2 emissions are
A) fossil-fuel burning power plants and refineries
B) heavy-duty trucks and buses
C) light-duty trucks and automobiles
D) commercial aircraft
A) fossil-fuel burning power plants and refineries
B) heavy-duty trucks and buses
C) light-duty trucks and automobiles
D) commercial aircraft

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which of the following is INCORRECT?
A) Emissions limits in PSD areas are more stringent than those in nonattainment areas
B) New Source Performance Standards are technology-based and defined by the EPA
C) Emissions limits for existing sources are more lenient than for new sources
D) Technology-based standards used to control stationary sources are applied uniformly
A) Emissions limits in PSD areas are more stringent than those in nonattainment areas
B) New Source Performance Standards are technology-based and defined by the EPA
C) Emissions limits for existing sources are more lenient than for new sources
D) Technology-based standards used to control stationary sources are applied uniformly

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
The uniformity of technology-based standards is the characteristic that allows them to achieve cost-effectiveness.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
PSD areas
A) were defined recently by an Executive Order issued by President Obama
B) are those areas defined as 'polluting source designated'
C) face more lenient emissions standards than nonattainment regions
D) are no longer recognized in U.S. policy
E) none of the above
A) were defined recently by an Executive Order issued by President Obama
B) are those areas defined as 'polluting source designated'
C) face more lenient emissions standards than nonattainment regions
D) are no longer recognized in U.S. policy
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Acidic deposition arises when
A) VOCs mix with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and fall to earth as rain or snow
B) carbon monoxide and sulfur dioxide combine to form acidic deposits
C) sulfur and nitrogen oxides mix with other particles and fall to earth as rain, snow, or fog
D) carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides combine and reach the earth in precipitation
A) VOCs mix with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and fall to earth as rain or snow
B) carbon monoxide and sulfur dioxide combine to form acidic deposits
C) sulfur and nitrogen oxides mix with other particles and fall to earth as rain, snow, or fog
D) carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides combine and reach the earth in precipitation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Stationary source emissions currently are controlled primarily by
A) performance-based limits
B) technology-based standards
C) the bubble policy
D) the OTC NOX Budget Program
A) performance-based limits
B) technology-based standards
C) the bubble policy
D) the OTC NOX Budget Program

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
In an allowance market, buyers will purchase allowances as long as the price is higher than their MAC, which results in a cost-effective solution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
According to the cost-effectiveness criterion, trading of SO2 allowances under the CAA should continue as long as MSBabatement > MSCabatement.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Under the national Acid Rain Program (ARP)
A) two phases were defined that began in 1980
B) a cap-and-trade program was defined only for SO2
C) a cap-and-trade program was defined for both SO2 and NOX
D) the EPA issued emission allowances that could be used or banked, but not traded
A) two phases were defined that began in 1980
B) a cap-and-trade program was defined only for SO2
C) a cap-and-trade program was defined for both SO2 and NOX
D) the EPA issued emission allowances that could be used or banked, but not traded

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The GHG permitting requirements
A) are applicable to both mobile and stationary sources
B) will not be in force until 2016
C) are part of the New Source Review requirements
D) all of the above
A) are applicable to both mobile and stationary sources
B) will not be in force until 2016
C) are part of the New Source Review requirements
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The dual-control approach refers to
A) dual trading programs, one for sulfur dioxide and one for nitrogen oxides
B) different standards used in PSD areas versus nonattainment areas
C) the netting program and the offset program
D) state control of existing sources and federal control of new or modified sources
A) dual trading programs, one for sulfur dioxide and one for nitrogen oxides
B) different standards used in PSD areas versus nonattainment areas
C) the netting program and the offset program
D) state control of existing sources and federal control of new or modified sources

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
According to the dual-control approach, states set abatement levels for existing stationary sources below the EPA-administered standard for new sources. The "new source bias" associated with this approach is that
A) firms have an incentive to shut down their businesses
B) states have an economic motive to set very stringent standards for existing sources
C) firms have an incentive not to start new construction and instead remain in older, existing facilities
D) the EPA has an incentive to set lenient standards for new sources
A) firms have an incentive to shut down their businesses
B) states have an economic motive to set very stringent standards for existing sources
C) firms have an incentive not to start new construction and instead remain in older, existing facilities
D) the EPA has an incentive to set lenient standards for new sources

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Consider the following two statements to answer this question: (1) The bubble policy allows a facility to measure its emissions as an average of all emission points from that facility.
(2) Netting was developed as a trading program to control emissions in PSD areas.
A) (1) is true and (2) is false
B) both (1) and (2) are false
C) (1) is false and (2) is true
D) both (1) and (2) are true
(2) Netting was developed as a trading program to control emissions in PSD areas.
A) (1) is true and (2) is false
B) both (1) and (2) are false
C) (1) is false and (2) is true
D) both (1) and (2) are true

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The Clean Air Interstate Rule (CAIR)
A) established three trading programs, one for SO2 and two for NOX
B) was enacted under the Obama Administration
C) set emissions limits without any accompanying trading program
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) established three trading programs, one for SO2 and two for NOX
B) was enacted under the Obama Administration
C) set emissions limits without any accompanying trading program
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Because of the dual-control approach, emissions limits tend to be more stringent for newer facilities, creating a bias against building newer, and hence cleaner, facilities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
According to the newly established GHG regulations, new or modified stationary sources of GHGs
A) would immediately face stringent emissions limits, regardless of their contribution to GHG emissions
B) would be subject to the New Source Review requirements
C) are required to eliminate all GHG emissions
D) none of the above
A) would immediately face stringent emissions limits, regardless of their contribution to GHG emissions
B) would be subject to the New Source Review requirements
C) are required to eliminate all GHG emissions
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Which of the following are among the effects of exposure to SO2 and NOX?
A) visibility impairment
B) acidification of surface waters
C) forest damage
D) all of the above
A) visibility impairment
B) acidification of surface waters
C) forest damage
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Overall, empirical studies fail to support the claim that command-and-control policy is more costly to implement than more flexible approaches.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Based on available information about the annual auctions for SO2 allowances
A) only the largest electric utilities are allowed to bid
B) allowance prices have been much higher than predicted
C) allowance prices are unrelated to energy prices
D) prices of SO2 allowances are lower than originally anticipated
A) only the largest electric utilities are allowed to bid
B) allowance prices have been much higher than predicted
C) allowance prices are unrelated to energy prices
D) prices of SO2 allowances are lower than originally anticipated

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Suppose Michigan's NOX abatement standard for existing (E) sources is 4 units and the EPA's standard for new (N) sources is 10 units and that MACE = 1.8AE and MACN = 1.2AN. To meet the same combined abatement level of 14 but in a cost-effective manner, the standards for each should be
A) AE = 7; AN = 7
B) AE = 4.8; AN = 7.2
C) AE = 5.6; AN = 8.4
D) none of the above
A) AE = 7; AN = 7
B) AE = 4.8; AN = 7.2
C) AE = 5.6; AN = 8.4
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Suppose the Clean Air Act calls for a rise in NO2 abatement (A) from 50 to 60 percent and that the MSC (in millions) is MSC = 12 + 0.8A, where A is measured in percent. Then, the incremental cost of this policy change is
A) $8 million
B) $40 million
C) $560 million
D) $500 million
A) $8 million
B) $40 million
C) $560 million
D) $500 million

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Suppose that there are only two stationary sources in a given air quality region. The first source has been in existence for several years, while the second source is new. The following functions represent marginal abatement costs (MAC) for each polluting source:
MACEX = 10.0 + 0.7A EX, MACN = 9.2 + 0.5A N,
where AEX is the percentage abatement level for the existing source, and AN is the percentage abatement level for the new source.
Assume that the aggregate abatement standard (i.e., for the region as a whole) is set at 40 percent and that the two firms' current abatement levels are AEX = 10 and AN = 30.
Explain why the current abatement levels for the two sources do not achieve cost effectiveness.
MACEX = 10.0 + 0.7A EX, MACN = 9.2 + 0.5A N,
where AEX is the percentage abatement level for the existing source, and AN is the percentage abatement level for the new source.
Assume that the aggregate abatement standard (i.e., for the region as a whole) is set at 40 percent and that the two firms' current abatement levels are AEX = 10 and AN = 30.
Explain why the current abatement levels for the two sources do not achieve cost effectiveness.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
The cost-effective solution is:
A) Ax = 15; Ay = 15
B) Ax = 9; Ay = 4.5
C) Ax = 10; Ay = 20
D) none of the above
A) Ax = 15; Ay = 15
B) Ax = 9; Ay = 4.5
C) Ax = 10; Ay = 20
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Using the labels on the graph below, the total cost for both firms at the cost-effective solution is ________, and the excess cost from using the uniform standard is___________
A) ABCGH; CGH
B) ACH; CGH
C) ACDEH; CDE
D) ACH; CDE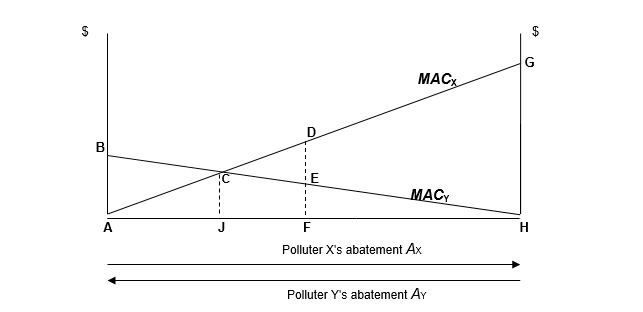
A) ABCGH; CGH
B) ACH; CGH
C) ACDEH; CDE
D) ACH; CDE


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Suppose that there are only two stationary sources in a given air quality region. The first source has been in existence for several years, while the second source is new. The following functions represent marginal abatement costs (MAC) for each polluting source:
MACEX = 10.0 + 0.7A EX, MACN = 9.2 + 0.5A N,
where AEX is the percentage abatement level for the existing source, and AN is the percentage abatement level for the new source.
Assume that the aggregate abatement standard (i.e., for the region as a whole) is set at 40 percent and that the two firms' current abatement levels are AEX = 10 and AN = 30.
-Find the cost effective allocation of abatement across the two sources that also satisfies the 40 percent aggregate abatement level. Support with calculations.
MACEX = 10.0 + 0.7A EX, MACN = 9.2 + 0.5A N,
where AEX is the percentage abatement level for the existing source, and AN is the percentage abatement level for the new source.
Assume that the aggregate abatement standard (i.e., for the region as a whole) is set at 40 percent and that the two firms' current abatement levels are AEX = 10 and AN = 30.
-Find the cost effective allocation of abatement across the two sources that also satisfies the 40 percent aggregate abatement level. Support with calculations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








